Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Modes of Reproduction of Animals
Uploaded by
calebprince6Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Modes of Reproduction of Animals
Uploaded by
calebprince6Copyright:
Available Formats
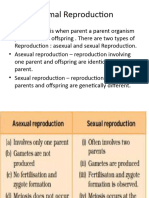
Modes of Reproduction of Animals Asexual Reproduction-
Sexual Reproduction- Does not need one male and one female parent to produce an offspring. A
animals produce a new individual when two parents are present. It takes single parent organism simply makes identical copies of itself.
place when sex cells from two parent animals (one male and one female)
unite to form a new animal. Methods of Asexual Reproduction
Sex cells or gametes- contains information about new organism 1. Binary fission- also called splitting, occurs when a parent animal
divides itself into two. Each half grows into a new individual. Some
Two types of sex Cell or Gametes very small animals and certain marine animals reproduce through
1. Egg cell- for females this method. This allows them to clusters of closely living groups or
2. Sperm Cell- for males colonies. Ex. Sea anemone-splits its polyp or body into halves, then
it grows into two new sea anemones.
Fertilization-takes place when a sperm cell unites with an egg cell
Zygote- fertilized egg that develops into embryo.
Embryo-undergoes continuous development until it eventually grows into a
newborn animal.
*Fertilization in animal may be internal or external
1. Internal Fertilization- happens when the male animal releases sperm
cell into the body of a female animal to fertilize the egg cell. The
embryo can either be develop inside the female body until it is born
alive or develop inside an egg laid by the female. Ex. Insects, birds,
cats and cows
2. Budding- happens when an outgrowth of the parent animal
2. External Fertilization- occurs outside the bodies of the parents. The develops into a new animal. Plants also develop a new plant through
female releases eggs into the water or attaches them to a plant or the process of budding. A bulge appears on the parent’s body, grows
rock. The male then releases sperm cells over the egg to fertilize into a bud, and eventually becomes a miniature copy of the parent.
them. Ex. Frogs, fishes The young continues to grow while still attached to the parent and
eventually detaches when it is mature enough to survive by itself Ex.
Hydra and jellyfish
You might also like
- Camp's Zoology by the Numbers: A comprehensive study guide in outline form for advanced biology courses, including AP, IB, DE, and college courses.From EverandCamp's Zoology by the Numbers: A comprehensive study guide in outline form for advanced biology courses, including AP, IB, DE, and college courses.No ratings yet
- The Animal Mating Game: The Wacky, Weird World of Sex in the Animal KingdomFrom EverandThe Animal Mating Game: The Wacky, Weird World of Sex in the Animal KingdomNo ratings yet
- Hermaphroditism, The Condition of Having Both MaleDocument11 pagesHermaphroditism, The Condition of Having Both Maleaimee mallariNo ratings yet
- Earth and Life Science Reproduction LessonDocument2 pagesEarth and Life Science Reproduction LessonZild Frigg CorbitaNo ratings yet
- EARTH AND LIFE SCIENCE 4th Quarter Module 2 Lesson 3Document8 pagesEARTH AND LIFE SCIENCE 4th Quarter Module 2 Lesson 3christianaries.lapuzNo ratings yet
- W4 ScienceDocument69 pagesW4 ScienceAngie Lea Serra-YlardeNo ratings yet
- How Representative Animals ReproduceDocument29 pagesHow Representative Animals ReproduceIMY PAMEROYANNo ratings yet
- Reproduction in AnimalsDocument3 pagesReproduction in Animalsevelynlinda370No ratings yet
- Animal RepdoductionDocument24 pagesAnimal RepdoductionSichayra GamotiaNo ratings yet
- Earth and Life Sciences SLHTQ2 3Document9 pagesEarth and Life Sciences SLHTQ2 3Melissa GerzonNo ratings yet
- 2.3 Lesson Perpetuation of LifeDocument2 pages2.3 Lesson Perpetuation of LifeHazel Aloha100% (1)
- EALS Group1Document41 pagesEALS Group1keithjustinetabajonda1No ratings yet
- The Reproduction of AnimalsDocument23 pagesThe Reproduction of AnimalsAngel Janel BaluntangNo ratings yet
- Lesson 3 ANIMAL REPRODUCTION Students NotesDocument6 pagesLesson 3 ANIMAL REPRODUCTION Students NotesrasingtanyaroseNo ratings yet
- ReproductionDocument37 pagesReproductionChristian Quiñones100% (1)
- SCIENCE-5-Q2-Module 3Document16 pagesSCIENCE-5-Q2-Module 3Mary Ann Gabion80% (5)
- Perpetuaion of Life - How Animals ReproduceDocument3 pagesPerpetuaion of Life - How Animals ReproduceBenjamin Fernandez Jr.No ratings yet
- EARTHLIFE SCIENCE Q2 Week 3 4aDocument28 pagesEARTHLIFE SCIENCE Q2 Week 3 4aEinjhel Gaverielle ReyesNo ratings yet
- Introduction To ReproductionDocument45 pagesIntroduction To ReproductionCharmaine Fernandez100% (1)
- Class 8 Science: Reproduction in AnimalsDocument21 pagesClass 8 Science: Reproduction in AnimalsJ CNo ratings yet
- Notes Science Modes in ReproductionDocument1 pageNotes Science Modes in Reproductionmary-ann escalaNo ratings yet
- WEEK 3 - Q2 - Earth and LifeDocument22 pagesWEEK 3 - Q2 - Earth and Lifenoreen lubindino100% (1)
- Q4-Module 1 (Reproduction Lesson 1)Document31 pagesQ4-Module 1 (Reproduction Lesson 1)Christian LuzandeNo ratings yet
- Gen Bio 02 Q4Document7 pagesGen Bio 02 Q4Charles EspiloyNo ratings yet
- ELS Q2 M4 How-Representative... 15pDocument15 pagesELS Q2 M4 How-Representative... 15pRachel Ann Canlas100% (1)
- Q2 Lesson 3 Part 1Document81 pagesQ2 Lesson 3 Part 1mrfwbsttr9No ratings yet
- Animal Form and Function Gen Bio IIDocument73 pagesAnimal Form and Function Gen Bio IIPalad , John Carlo BernabeNo ratings yet
- Science DLPDocument7 pagesScience DLPVanessa RamosNo ratings yet
- By: Trisha Mae Besenio Devine Grace Ambayec Kyle RodriguezDocument16 pagesBy: Trisha Mae Besenio Devine Grace Ambayec Kyle RodriguezTyrone RogelNo ratings yet
- Reproduction of Plants and Animals General Biology 2 Quarter 1Document10 pagesReproduction of Plants and Animals General Biology 2 Quarter 1Christian DavidNo ratings yet
- Animal ReproductionDocument10 pagesAnimal Reproductiontalhaabdrahman7No ratings yet
- REVIEWER IN SCIENCE 3rd GDocument3 pagesREVIEWER IN SCIENCE 3rd GGab OlarteNo ratings yet
- Asexual ReproductionDocument30 pagesAsexual Reproductiondgbalogo2019No ratings yet
- Lesson 3.1 Types of Sexual and Asexual Reproduction PDFDocument47 pagesLesson 3.1 Types of Sexual and Asexual Reproduction PDFDarrel Clariño100% (1)
- Animal ReproductionDocument2 pagesAnimal ReproductionNinda SantikaNo ratings yet
- Human Reproduction HSCDocument29 pagesHuman Reproduction HSCpatrixsigmaNo ratings yet
- 4Q - Animal Forms Functions 1 - ReproductionDocument41 pages4Q - Animal Forms Functions 1 - ReproductionMaymayNo ratings yet
- How Living Things ReproduceDocument36 pagesHow Living Things Reproduceailynmirano885No ratings yet
- ReproductionDocument6 pagesReproductioniancyrillvillamer10No ratings yet
- Exp SC 8 - Chapter 09Document16 pagesExp SC 8 - Chapter 09megamind publicationNo ratings yet
- L5 - Teachsci Plant ReproductionDocument11 pagesL5 - Teachsci Plant ReproductionMs.Muriel MorongNo ratings yet
- Introduction To ReproductionDocument10 pagesIntroduction To ReproductionRalph EspejoNo ratings yet
- Module 4 ReproductionDocument15 pagesModule 4 Reproductionapi-18956468950% (2)
- Earth and Life Sciences SLHTQ2 3Document7 pagesEarth and Life Sciences SLHTQ2 3Joy Valerie AricayosNo ratings yet
- Animal Reproduction Week 3Document12 pagesAnimal Reproduction Week 3Ian Miguel LaguitanNo ratings yet
- HeredityDocument17 pagesHeredityKitKatKNo ratings yet
- III.B. The Reproduction of AnimalsDocument22 pagesIII.B. The Reproduction of AnimalsDarwin NoolNo ratings yet
- Grade 7 Lesson: ReproductionDocument4 pagesGrade 7 Lesson: ReproductionJoedelyn Wagas100% (1)
- Complete Year 12 HSC Biology SummaryDocument45 pagesComplete Year 12 HSC Biology SummaryClaudiaNo ratings yet
- General Biology 2 NotesDocument17 pagesGeneral Biology 2 NotesAlyssa Mae BinoNo ratings yet
- Reproduction and Embryonic Development in Plants and AnimalsDocument3 pagesReproduction and Embryonic Development in Plants and AnimalsJoy BoyNo ratings yet
- Modes of ReproductionDocument4 pagesModes of ReproductionSayie GulmaticoNo ratings yet
- Animal Form and FunctionDocument8 pagesAnimal Form and FunctionPalad , John Carlo BernabeNo ratings yet
- Q4 Week 3 - ELSDocument7 pagesQ4 Week 3 - ELSAgatha KimNo ratings yet
- Reproduction in Animals Class 8Document7 pagesReproduction in Animals Class 8jahnavi poddar100% (1)
- Reproduction in AnimalsDocument3 pagesReproduction in Animalsbinu_praveenNo ratings yet
- Week 3 Perpetuation of Life (Autosaved)Document38 pagesWeek 3 Perpetuation of Life (Autosaved)SANTIAGO, David Joshua B.No ratings yet
- Perpetuation of LifeDocument1 pagePerpetuation of LifeSonoko SuzukiNo ratings yet
- Perpetuation of Life Animal ReproductionDocument23 pagesPerpetuation of Life Animal ReproductionKyla Heart ZaragozaNo ratings yet
- Exploding Ants: Amazing Facts About How Animals AdaptFrom EverandExploding Ants: Amazing Facts About How Animals AdaptRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (11)
- Describing FoodDocument4 pagesDescribing FoodJohn SmithNo ratings yet
- Bobcat Classification and EvolutionDocument3 pagesBobcat Classification and EvolutionagnaNo ratings yet
- English GrammarDocument29 pagesEnglish GrammarJohn CarloNo ratings yet
- The Effects of Deforestation On Wildlife Along The Transamazon HighwayDocument8 pagesThe Effects of Deforestation On Wildlife Along The Transamazon HighwayCleber Dos SantosNo ratings yet
- Animal Farm (Novel Units)Document8 pagesAnimal Farm (Novel Units)M M100% (1)
- Ppt. Surgery Wild AnimalsDocument165 pagesPpt. Surgery Wild AnimalsAsha RaniNo ratings yet
- Respiratory HistologyDocument25 pagesRespiratory HistologyUttari DalemNo ratings yet
- Australian Animals ScreenDocument31 pagesAustralian Animals ScreenLTookerNo ratings yet
- Assesment C&G Prepare, Cook and Finish EggsDocument6 pagesAssesment C&G Prepare, Cook and Finish Eggsعلي صالحNo ratings yet
- Inguino Scrotal SwellingDocument3 pagesInguino Scrotal SwellingYurni Dwi AstutiNo ratings yet
- Crusnik WriteupDocument2 pagesCrusnik Writeupxw77No ratings yet
- Advanced Sentence Correction For GMAT SCDocument27 pagesAdvanced Sentence Correction For GMAT SCharshv3No ratings yet
- Arch105 Paper 2Document4 pagesArch105 Paper 2Bambi DragonNo ratings yet
- Foto Polos Abdomen - PPTX William Bunga DatuDocument39 pagesFoto Polos Abdomen - PPTX William Bunga DatuWilliam Bunga DatuNo ratings yet
- The Werewolf in The Crested KimonoDocument17 pagesThe Werewolf in The Crested KimonoEstrimerNo ratings yet
- Science Paper 1Document17 pagesScience Paper 1Hoo Pooi TengNo ratings yet
- Mam Level 2 FlashcardsDocument38 pagesMam Level 2 FlashcardsAhmedSameh100% (1)
- Ã'Tia' Fiakdkdhl Úohd, H - FLD U 07: D.S. Senanayake College - Colombo 07Document12 pagesÃ'Tia' Fiakdkdhl Úohd, H - FLD U 07: D.S. Senanayake College - Colombo 07joker boyNo ratings yet
- Quarter 4 - CompleteDocument115 pagesQuarter 4 - Completemaria luisa mendozaNo ratings yet
- LEC 05 - Growth - Puberty DisordersDocument58 pagesLEC 05 - Growth - Puberty DisordersIoana CozmaNo ratings yet
- Westside Deli MenuDocument6 pagesWestside Deli MenuCharlestonCityPaperNo ratings yet
- California Zephyr Dining MenuDocument2 pagesCalifornia Zephyr Dining MenuekaterinaNo ratings yet
- Pranayama RahasyaDocument128 pagesPranayama RahasyaShiva AgrawalNo ratings yet
- The Summoner V3.0 - The HomebreweryDocument20 pagesThe Summoner V3.0 - The HomebreweryBertran RousseauNo ratings yet
- Suzy and Leah Reading GuideDocument15 pagesSuzy and Leah Reading Guideapi-260353457100% (1)
- Unit 2 The Physiology of FitnessDocument11 pagesUnit 2 The Physiology of FitnessIas UpscNo ratings yet
- Grooming Black Russian TerrierDocument15 pagesGrooming Black Russian TerrierFiorenzo TassottiNo ratings yet
- 030722the Physiology of MicturitionDocument3 pages030722the Physiology of MicturitionAnnizah Paramitha100% (1)
- FoodDocument54 pagesFoodBrihad Maurya0% (1)
- Ineffective Airway ClearanceDocument1 pageIneffective Airway Clearancerozj0750% (2)