Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Nuclear Fission
Uploaded by
szyzyp0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
1 views2 pagesNuclear fission is the splitting of a large atomic nucleus into smaller nuclei. When a neutron strikes a nucleus like uranium, it induces fission where the nucleus splits into two or more daughter nuclei. This triggers a chain reaction as the ejected neutrons collide with other nuclei, causing further fission until all material has undergone fission or the reaction is stopped. The enormous energy released during fission comes from the strong repelling force between protons in the nucleus that are barely held together; when the nucleus splits, the total mass of fragments is less than the starting nucleus, and the missing mass is converted to energy according to E=mc2.
Original Description:
Copyright
© © All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
DOCX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentNuclear fission is the splitting of a large atomic nucleus into smaller nuclei. When a neutron strikes a nucleus like uranium, it induces fission where the nucleus splits into two or more daughter nuclei. This triggers a chain reaction as the ejected neutrons collide with other nuclei, causing further fission until all material has undergone fission or the reaction is stopped. The enormous energy released during fission comes from the strong repelling force between protons in the nucleus that are barely held together; when the nucleus splits, the total mass of fragments is less than the starting nucleus, and the missing mass is converted to energy according to E=mc2.
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as DOCX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
1 views2 pagesNuclear Fission
Uploaded by
szyzypNuclear fission is the splitting of a large atomic nucleus into smaller nuclei. When a neutron strikes a nucleus like uranium, it induces fission where the nucleus splits into two or more daughter nuclei. This triggers a chain reaction as the ejected neutrons collide with other nuclei, causing further fission until all material has undergone fission or the reaction is stopped. The enormous energy released during fission comes from the strong repelling force between protons in the nucleus that are barely held together; when the nucleus splits, the total mass of fragments is less than the starting nucleus, and the missing mass is converted to energy according to E=mc2.
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as DOCX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
You are on page 1of 2
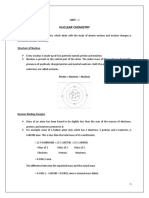
Nuclear Fission
Nuclear fission is defined as the splitting of a large atomic nucleus into a smaller nuclei.
High mass nuclei such as Uranium can undergo fission and release energy
Fission must first be induced by firing neutrons at a nucleus, when the nucleus is struck by a
neutron, it is absorbed and then it splits into two, or more, daughter nuclei.
During fission, neutrons are ejected from the nucleus, which in turn, can collide with other
nuclei which trigger a cascade effect.
This leads to a chain reaction, this last until all of the material has undergone fission, or the
reaction is stopped by a moderator.
Calculating Energy Released in Nuclear Reactions.
E = (Δm)c2
E= binding energy released in jules.
Δm = mass defect
C = speed of light
Where does the energy come from
The enormous energy that is released from the splitting comes from how hard the protons
are repelling each other with the coulomb force, barely held together by the strong force,
each proton is pushing every other proton with about 20N of force, this force is incredibly
large for such a small particle. This force over a small distance leads to a fair amount of
energy being releases which leads to measurable reduction in mass, This means that’s the
total mass of each fission fragment is less than the starting nucleus. This missing mass is
called the mass defect.
You might also like
- 3 Nuclear Reactions, Fission, Fusion - PresentationDocument105 pages3 Nuclear Reactions, Fission, Fusion - PresentationVorizionNo ratings yet
- What's the Difference Between Fission and Fusion? | Children's Physics of EnergyFrom EverandWhat's the Difference Between Fission and Fusion? | Children's Physics of EnergyNo ratings yet
- Nuclear ChemistryDocument27 pagesNuclear ChemistryveluselvamaniNo ratings yet
- Nuclear Reactions:: Fission & FusionDocument21 pagesNuclear Reactions:: Fission & FusionBrasa Y. de AlmiraNo ratings yet
- Nuclear FusionDocument11 pagesNuclear Fusiondo4 humanNo ratings yet
- Nuclear PhysicsDocument28 pagesNuclear PhysicsSatish Kumar100% (1)
- Nuclear Binding EnergyDocument9 pagesNuclear Binding EnergyBastab DeyNo ratings yet
- The Atomic NucleusDocument85 pagesThe Atomic NucleusARUNA RESHMINo ratings yet
- Ib HL Study Guide Organizer-Nuclear PhysicsDocument20 pagesIb HL Study Guide Organizer-Nuclear PhysicsCarlos Andres Vásquez100% (1)
- Fission ReactionDocument5 pagesFission ReactionHemant RathvaNo ratings yet
- Nuclear PhysicsDocument21 pagesNuclear PhysicsAbdur RehmanNo ratings yet
- ++nuclear PhysicsDocument284 pages++nuclear Physicssaid cheradiNo ratings yet
- Nuclei in One Shot - Class Notes - LEC-6 - PPT-6 - Physics - Nuclei - Vijeta Series - Kshitiz Kanik Sir - RAM NIWASDocument61 pagesNuclei in One Shot - Class Notes - LEC-6 - PPT-6 - Physics - Nuclei - Vijeta Series - Kshitiz Kanik Sir - RAM NIWASprajwal jhaNo ratings yet
- Nuclear ReactionDocument15 pagesNuclear ReactionShah Rafidzah KhalidNo ratings yet
- Nuclear Energy 1Document17 pagesNuclear Energy 1sohailnoreen5062No ratings yet
- Part 2Document24 pagesPart 2Rochelle Ann MallariNo ratings yet
- Nuclear PhysicsDocument37 pagesNuclear Physicsvipexe4113No ratings yet
- RevisionDocument13 pagesRevisionrajayush67780No ratings yet
- Nuclear Fission and Fusion: Unit IV: Atomic Physics Welter Class NotesDocument5 pagesNuclear Fission and Fusion: Unit IV: Atomic Physics Welter Class Notesbharathy100% (1)
- Energy Unit 4Document22 pagesEnergy Unit 4Joseph MartinNo ratings yet
- Nuclei IDocument20 pagesNuclei IShoaibNo ratings yet
- Fusion and FissionDocument22 pagesFusion and FissionDeiparineIrisNo ratings yet
- Describe The Fundamental Forces That Operate Within Atomic NucleiDocument4 pagesDescribe The Fundamental Forces That Operate Within Atomic NucleiAnjali yiascmNo ratings yet
- Nuclear Fusion & Nuclear FissionDocument7 pagesNuclear Fusion & Nuclear FissionHari KrishnanNo ratings yet
- Nuclear Binding EnergyDocument17 pagesNuclear Binding EnergyTrajce StojanovNo ratings yet
- CH 17 - Nuclear PhysicsDocument37 pagesCH 17 - Nuclear PhysicsOKAY JAROD PUGNo ratings yet
- Nuclei 2022-23Document3 pagesNuclei 2022-23GayatriNo ratings yet
- 23 Nuclear PhysicsDocument52 pages23 Nuclear Physicsdayana hanis hassanNo ratings yet
- NucleiDocument28 pagesNucleisomarshidubeyNo ratings yet
- Nucleus - 2021Document5 pagesNucleus - 2021Aswin P TNo ratings yet
- Modern Physics-1Document22 pagesModern Physics-1Minato NamikazeNo ratings yet
- 7.2 Nuclear ReactionsDocument2 pages7.2 Nuclear ReactionsEjaz AhmadNo ratings yet
- Radioactivity HSCDocument11 pagesRadioactivity HSCRushita LingiahNo ratings yet
- New Microsoft Word DocumentDocument6 pagesNew Microsoft Word DocumentanimeshtechnosNo ratings yet
- Basic Forces in NatureDocument11 pagesBasic Forces in NatureKarl Rickni GurbuxaniNo ratings yet
- Fisiune Vs Fuziune NuclearaDocument3 pagesFisiune Vs Fuziune NuclearaVladPopoviciNo ratings yet
- Fusion and FissionDocument22 pagesFusion and FissionJoey JonesNo ratings yet
- NEUTRON - The Neutron Is ADocument10 pagesNEUTRON - The Neutron Is AsushreenandaNo ratings yet
- Nuclear FisssionDocument5 pagesNuclear FisssionShozab Ghazi NaqviNo ratings yet
- Atoms and NucleiDocument53 pagesAtoms and NucleiGirish Arora100% (1)
- Chapter: 7 Nuclear Energy and ForcesDocument15 pagesChapter: 7 Nuclear Energy and ForcesHaris ShahidNo ratings yet
- Radioactivity Part 4Document14 pagesRadioactivity Part 4Sharvinder SinghNo ratings yet
- Nuclear Energy Energy ScienceDocument9 pagesNuclear Energy Energy Sciencevipinvishwakarmavns2005No ratings yet
- 40 Nuclear Fission and FusionDocument16 pages40 Nuclear Fission and FusionAdityaNo ratings yet
- Fission and FusionDocument5 pagesFission and FusionT. Christabel VijithaNo ratings yet
- Parent Nuclei: Q: Briefly Describe Fission Reaction? AnswerDocument2 pagesParent Nuclei: Q: Briefly Describe Fission Reaction? AnswerShazaib MirzaNo ratings yet
- Supernova Neutrinos - WikipediaDocument8 pagesSupernova Neutrinos - WikipediaBibhubhusan SwainNo ratings yet
- L2 - Nuclear Physics - 23rd NovDocument45 pagesL2 - Nuclear Physics - 23rd NovAkshat SinghNo ratings yet
- UNIT-5: Nuclear Power Asst. Prof Kunal GadgilDocument134 pagesUNIT-5: Nuclear Power Asst. Prof Kunal GadgilKunal GadgilNo ratings yet
- Strong InteractionDocument6 pagesStrong InteractionAkhilesh MishraNo ratings yet
- Nuclear EnergyDocument12 pagesNuclear EnergyOjashwi SharmaNo ratings yet
- Nuclear DecayDocument16 pagesNuclear DecayKulya RodrigoNo ratings yet
- Chap 13 NucleiDocument2 pagesChap 13 NucleiV MohithNo ratings yet
- EnergyDocument2 pagesEnergyajit jainNo ratings yet
- PhysicsDocument19 pagesPhysicschan benieNo ratings yet
- Nucli Note ADocument5 pagesNucli Note AMani MajhiNo ratings yet
- PC Chapter 46Document93 pagesPC Chapter 46ultimuNo ratings yet
- NeutronDocument2 pagesNeutronapi-9101692100% (2)
- TR 12Document53 pagesTR 12yaksha2024maanNo ratings yet