Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Chemical Equilibrium: 2020-2021 Spring Semester
Uploaded by
naverfallOriginal Description:
Original Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Chemical Equilibrium: 2020-2021 Spring Semester
Uploaded by
naverfallCopyright:
Available Formats
Remove Watermark Wondershare
PDFelement
Gazi University
Department of Chemical Engineering
ChE 244 Physical Chemistry
2020-2021 Spring Semester
CHEMICAL EQUILIBRIUM
1) The following reaction reaches equilibrium at 370 oC and 1 atm.
2HCl(g) + ½ O2(g) ↔ Cl2(g) + H2O(g)
Initially, pure HCl and 95 % O2 (5 % N2) are mixed to maintain HCl / O2 = 4 (in mole) and fed to the reactor
at 65 oC and 1 atm. Reaction product flow leaves the reactor at 370 oC and is in equilibrium.
Find the mole fraction of Cl2 in product flow.
DATA:
Component Cp (cal/mole K) ΔH0f (cal/mole) ΔG0f (cal/mole)
O2 7.4 -- --
H2O 8.6 -57798 -54636
Cl2 8.9 -- --
HCl 7.5 -22063 -22769
N2 7.0 -- --
2) When alkanes are heated up, they loose hydrogen and alkenes are produced. For example,
C2H6(g)→ C2H4(g) + H2(g) ; K=0.36 at 1000 K
If this is the only reaction that occurs when ethane is heated upto 1000 K, at what total pressure will ethane be
(a) 10% dissociated and (b) %90 dissociated to ethylene and hydrogen?
3) The first order reversible liquid reaction A ↔ 2B takes place in a batch reactor, C Ao = 10 mol/liter, CBo=2
mol/liter. The equilibrium conversion under the reaction conditions is given as 50 % after 5 minutes, conversion
of A is determined as %10.2. Find the rate constant for this reaction.
4) Derive an expression which will give the equilibrium constant at any temperature for the following reaction:
CO + H2O H2 + CO2
Note: K = K(T) expression will be derived.
Remove Watermark Wondershare
PDFelement
You might also like
- Cutting-Edge Technology for Carbon Capture, Utilization, and StorageFrom EverandCutting-Edge Technology for Carbon Capture, Utilization, and StorageKarine Ballerat-BusserollesNo ratings yet
- Sustainable Energy 1.818J/2.65J/3.564J/10.391J/11.371J/22.811J/ESD166JDocument3 pagesSustainable Energy 1.818J/2.65J/3.564J/10.391J/11.371J/22.811J/ESD166JaaaNo ratings yet
- Problem Set-II - Single and Multiple Units Reacting SystemDocument4 pagesProblem Set-II - Single and Multiple Units Reacting SystemDeepak TholiaNo ratings yet
- c06s02 PDFDocument6 pagesc06s02 PDFDewiRSNo ratings yet
- Metro ViewerDocument5 pagesMetro ViewerSteve WanNo ratings yet
- NF RT N: (Note: Data W Question 1 Will Be Needed For This Question.)Document3 pagesNF RT N: (Note: Data W Question 1 Will Be Needed For This Question.)mh sepahdarNo ratings yet
- Process System Analysis CHEM2002: Simulation of The Methanol ProcessDocument10 pagesProcess System Analysis CHEM2002: Simulation of The Methanol ProcessSaeed AlzeediNo ratings yet
- Che1211 Module 5 PDFDocument5 pagesChe1211 Module 5 PDFMaries San PedroNo ratings yet
- Energy BalancesDocument3 pagesEnergy BalancesDaniel DubeNo ratings yet
- Mass Balance 3Document22 pagesMass Balance 3barbadosiyNo ratings yet
- Dissolved Gas Analysis (DGA) : Basic Theory Sample Collection Extraction of Gases Analysis of Gases ActionDocument45 pagesDissolved Gas Analysis (DGA) : Basic Theory Sample Collection Extraction of Gases Analysis of Gases Actionsantoshnarinoi241100% (1)
- Task 3 and 4Document8 pagesTask 3 and 4tlsandiaaaNo ratings yet
- Energy BalancesDocument3 pagesEnergy BalancesDaniel DubeNo ratings yet
- Gujarat Technological UniversityDocument4 pagesGujarat Technological UniversityMohit PatelNo ratings yet
- Soal Heat BalanceDocument5 pagesSoal Heat BalanceRfc KusyadiNo ratings yet
- Thermophysical PropertiesDocument7 pagesThermophysical PropertiesWei JianNo ratings yet
- Latihan Soal Neraca PanasDocument2 pagesLatihan Soal Neraca PanasFathurRahman100% (2)
- HW MgoDocument5 pagesHW MgotauqeerNo ratings yet
- Final Examination CCB31202 (Separation Processes 2)Document7 pagesFinal Examination CCB31202 (Separation Processes 2)Surendra Louis Dupuis NaikerNo ratings yet
- PC Question Paper Nov 2021Document4 pagesPC Question Paper Nov 2021venkatesan sivaramuNo ratings yet
- CAP 10 Principles of Chemical Engineering Processes Material and Energy Balances Second Edition T.LDocument7 pagesCAP 10 Principles of Chemical Engineering Processes Material and Energy Balances Second Edition T.LAnel Viridiana Alfonso BocarandoNo ratings yet
- CHEM 1 Module 8 PDFDocument2 pagesCHEM 1 Module 8 PDFGwen YosheenNo ratings yet
- 1415 Exam 1 Answers (ICP) (EN)Document8 pages1415 Exam 1 Answers (ICP) (EN)김하은No ratings yet
- CHE 310 Conversion / Degree of Completion: DefinitionDocument30 pagesCHE 310 Conversion / Degree of Completion: DefinitionNelsonNo ratings yet
- End-Semester Examination, 7 July-2021: National Institute of Technology Sikkim, Ravangla CampusDocument2 pagesEnd-Semester Examination, 7 July-2021: National Institute of Technology Sikkim, Ravangla CampusSANGIT PRADHANNo ratings yet
- Rr210803 Material Energy BalanceDocument8 pagesRr210803 Material Energy BalanceSrinivasa Rao G100% (2)
- Chemical Process CalculationsDocument9 pagesChemical Process CalculationsYolandaNo ratings yet
- Solvay Haber-Bosch ProcessesDocument30 pagesSolvay Haber-Bosch ProcessesTiên PhạmNo ratings yet
- Jumadiao, Yra Marielle M. Exercise 9: Heat Balance and Theoretical Flame Temperature GivenDocument4 pagesJumadiao, Yra Marielle M. Exercise 9: Heat Balance and Theoretical Flame Temperature GivenJanelle M. JumadiaoNo ratings yet
- Sulphur Recovery UnitDocument39 pagesSulphur Recovery UnitWoMeiYouNo ratings yet
- 1 s2.0 S1876610211005960 MainDocument8 pages1 s2.0 S1876610211005960 MainRenalyn TorioNo ratings yet
- Midterm Chem4EngDocument2 pagesMidterm Chem4EngNathan Ray Alim50% (2)
- Qu. All - NDocument28 pagesQu. All - NArima KouseiNo ratings yet
- CPC 2018 Make UpDocument3 pagesCPC 2018 Make UpHarshith ShettyNo ratings yet
- Ex: # 01: A Sample of Dry Anthracite Has The Following: 44kg CODocument12 pagesEx: # 01: A Sample of Dry Anthracite Has The Following: 44kg COnicoolNo ratings yet
- Electricity Generation Powered by Natural Gas Via Steam GenerationDocument7 pagesElectricity Generation Powered by Natural Gas Via Steam GenerationJabin Sta. TeresaNo ratings yet
- NSS Chemistry Part 8 Chemical Reactions and Energy PDFDocument17 pagesNSS Chemistry Part 8 Chemical Reactions and Energy PDF6A(24) Marsh WongNo ratings yet
- Design and Production of Hydrogen Gas by Steam Methane Reforming Process - A Theoretical ApproachDocument6 pagesDesign and Production of Hydrogen Gas by Steam Methane Reforming Process - A Theoretical Approach63011373No ratings yet
- Activated Carbon From Agave Bagasse - 2Document13 pagesActivated Carbon From Agave Bagasse - 2Ian GuerreroNo ratings yet
- Pde ReportDocument10 pagesPde ReportChellam Siva Chellam SivaNo ratings yet
- Gas Laws Homework IIIDocument3 pagesGas Laws Homework IIIchpwalkerNo ratings yet
- Hoja Tecnica Monoxido de CarbonoDocument6 pagesHoja Tecnica Monoxido de CarbonoLuna ArboledaNo ratings yet
- Lampiran IIDocument30 pagesLampiran IIyogaNo ratings yet
- 5 MiDocument4 pages5 MiBuat MainNo ratings yet
- Material Stream: Etanol: ConditionsDocument2 pagesMaterial Stream: Etanol: ConditionsNorman TerceroNo ratings yet
- Gene Chem ExamDocument2 pagesGene Chem Examhiru mangoNo ratings yet
- Methanol Synthesis (Safety)Document16 pagesMethanol Synthesis (Safety)furqankausarhaiderNo ratings yet
- Designing of The Calcination Unit: Temperature and Energy ProfileDocument7 pagesDesigning of The Calcination Unit: Temperature and Energy ProfileTJPRC PublicationsNo ratings yet
- 21-Electrospinning Ru Carbon Nanofibers Boost CO2 Reduction in A H2 CO2 Fuel Cell SiDocument15 pages21-Electrospinning Ru Carbon Nanofibers Boost CO2 Reduction in A H2 CO2 Fuel Cell Siee20b044No ratings yet
- Equilibrium Constant Expressions Le ChatDocument2 pagesEquilibrium Constant Expressions Le ChatLyra GurimbaoNo ratings yet
- Exercise Chapter 2Document22 pagesExercise Chapter 2yewhouNo ratings yet
- Kjeldahl Dumas: Which Method Is The Better Choice For The Analytical Scope in My Lab?Document1 pageKjeldahl Dumas: Which Method Is The Better Choice For The Analytical Scope in My Lab?Lượng Nguyễn VănNo ratings yet
- Study Guide Chapter 3 Fall2016Document6 pagesStudy Guide Chapter 3 Fall2016edwardppppNo ratings yet
- Process Notes: Final ProjectDocument8 pagesProcess Notes: Final ProjectCluisantony Jayco DizeNo ratings yet
- Section 07 Split Stream DealkalyzerDocument7 pagesSection 07 Split Stream DealkalyzerSheikh SahabNo ratings yet
- 물리화학 6장 레포트Document4 pages물리화학 6장 레포트vaibhavNo ratings yet
- PC Gatequestion PaperDocument28 pagesPC Gatequestion PaperSofia Maan GuintoNo ratings yet
- Softening 2Document5 pagesSoftening 2Xherine Bico CordialNo ratings yet
- Technological Institute of The Philippines: (Aq) 2 (L) 2 3(s) 3(s)Document17 pagesTechnological Institute of The Philippines: (Aq) 2 (L) 2 3(s) 3(s)VaanNo ratings yet
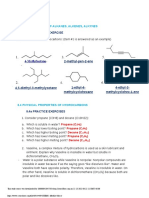
- ENG 203 Connectives Exercises For StudentsDocument2 pagesENG 203 Connectives Exercises For StudentsnaverfallNo ratings yet
- Key To Eng 203 Clauses 2020-21Document9 pagesKey To Eng 203 Clauses 2020-21naverfallNo ratings yet
- 4th and 5th WeeksDocument57 pages4th and 5th WeeksnaverfallNo ratings yet
- Che222 Term ProjectDocument1 pageChe222 Term ProjectnaverfallNo ratings yet
- Imperfectionsin SolidsDocument30 pagesImperfectionsin SolidsnaverfallNo ratings yet
- Me204 March 29 2023Document40 pagesMe204 March 29 2023naverfallNo ratings yet
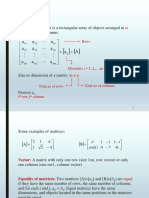
- Matrices: A A A A A ADocument449 pagesMatrices: A A A A A AnaverfallNo ratings yet
- Kinetic Study On The Hydrotreating of Heavy Oil. 1. Effect of Catalyst Pellet Size in Relation To Pore SizeDocument6 pagesKinetic Study On The Hydrotreating of Heavy Oil. 1. Effect of Catalyst Pellet Size in Relation To Pore SizenaverfallNo ratings yet
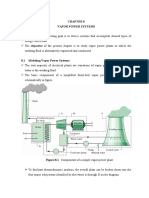
- Chapter 8Document41 pagesChapter 8naverfallNo ratings yet