Professional Documents
Culture Documents
L9 Thermal Stress
Uploaded by
Angelica Shane A. SaludoOriginal Description:
Original Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
L9 Thermal Stress
Uploaded by
Angelica Shane A. SaludoCopyright:
Available Formats
L9-Thermal Stress
Wednesday, 25 January 2023 2:54 pm
Temperature changes cause the body to expand o contract. The amount St, is given by
where a is the, coefficient of thermal expansion in m/m°C, L is the length in meter, T i, and Tf is the initial and final
temperatures, respectively in °C. For steel, α = 11.25 × 10-6 /°C.
If temperature deformation is permitted to occur freely, no load or stress will be induced in the structure. In some cases wh ere
temperature deformation is not permitted, an internal stress is created. The internal stress created is termed as thermal stress.
For homogeneous rod mounted between unyielding supports as shown, the thermal stress is computed as:
deformation due to temperature changes;
Deformation due to equivalent axial stress
where is the thermal stress in Mpa, E is the modulus of elasticity of the rod in MPa.
If the wall yields a distance of r as shown, the following calculations will be made:
where represents the thermal stress.
Take note that as the temperature rises above the normal, the rod will be in compression, and if the temperature drops below the
normal, the rod is it tension.
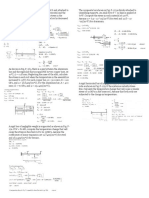
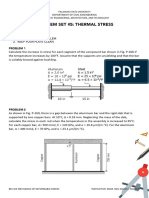
Problem 9.1 A steel rod with a cross-sectional area of 0.25 in 2 is stretched between two fixed points. The tensile load at final
temperature of 70°F is 1200 Ib. (a) What will be the stress (in ksi) if the initial temperature is 0°F? (b) At what temperatu re
(in °F) will the stress be zero if the initial temperature is 70°F? Assume α = 6.5 × 10-6 in/ (in-°F) and E = 29 × 106 psi.
Given:
70°F
α 6.5 × 10-6 in/ (in-°F)
Required: (a)
Solution:
(a)
(b)
Midterm- Simple Strain Page 1
α
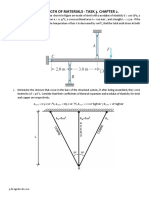
Problem 9.2 Calculate the increase in stress for each segment of the compound bar shown in figure below if the temperature increases
by 100°F. Assume that the supports are unyielding and that the bar is suitably braced against buckling.
Given:
α =12.8 × 10-6/°F
α=6.5 × 10-6/°F
°F
Required: (a)
Solution:
α α
α α
But
α α
α α
α α
α α
α α
Problem 9.3 A rigid bar of negligible weight is supported as shown in Fig. P-271. If W = 80 kN, compute the
temperature change (in °C) that will cause the stress in the steel rod to be 55 MPa. Assume the coefficients of
linear expansion are 11.7 µm/(m-°C) for steel and 18.9. µm/(m-°C) for bronze.
Midterm- Simple Strain Page 2
temperature change (in °C) that will cause the stress in the steel rod to be 55 MPa. Assume the coefficients of
linear expansion are 11.7 µm/(m-°C) for steel and 18.9. µm/(m-°C) for bronze.
Given:
α =11.7 µm/(m-°C)
α =18.9 µm/(m-°C)
=55 MPa
Required:
Solution:
By ratio and proportion:
α α
α α
α α
α α
Midterm- Simple Strain Page 3
You might also like
- Thermal Stress RumusDocument16 pagesThermal Stress RumusVakin Agung PermanaNo ratings yet
- 1-Thermal ADocument5 pages1-Thermal ABOITIZON, Julius C.No ratings yet
- Mechanics of Solids-I: Thermal StressesDocument16 pagesMechanics of Solids-I: Thermal StressesHammad AhmadNo ratings yet
- Sample Problems: Thermal StressDocument2 pagesSample Problems: Thermal StressPaul PatropezNo ratings yet
- الاجهاد الحراريDocument3 pagesالاجهاد الحراريAmjed AL-KAHTEEBNo ratings yet
- Note Chapt IIDocument27 pagesNote Chapt IIRitesh KishoreNo ratings yet
- 5 MEC32-1 THERMAL STRESS (Robles)Document7 pages5 MEC32-1 THERMAL STRESS (Robles)John BurnsideNo ratings yet
- Thermal StressDocument12 pagesThermal StressAel Xander LorescoNo ratings yet
- Thermal Stress or Thermal Deformation Problems and SolutionDocument9 pagesThermal Stress or Thermal Deformation Problems and SolutionMiah EchavesNo ratings yet
- Lec-4 Strength of MaterialsDocument18 pagesLec-4 Strength of MaterialsNathaniel Española Ovivir100% (1)
- Notes/Lect 5 MMTDocument10 pagesNotes/Lect 5 MMTIldjohn CarrilloNo ratings yet
- Strength of Materials - Task 3. Chapter 2.Document4 pagesStrength of Materials - Task 3. Chapter 2.Alen Dejesus Suarez SierraNo ratings yet
- Mats 3 Sol 3Document7 pagesMats 3 Sol 3Devansh GargNo ratings yet
- Assignment Strength of MaterialsDocument11 pagesAssignment Strength of MaterialsVinay Korukonda0% (1)
- ReviewerDocument4 pagesRevieweranonymousoreviewerNo ratings yet
- Known: Comments:: Bending Impact-Effect of Compound SpringsDocument2 pagesKnown: Comments:: Bending Impact-Effect of Compound SpringsGermán EdilbertoNo ratings yet
- Thermal Stress: Mechanics of Deformable BodiesDocument10 pagesThermal Stress: Mechanics of Deformable BodiesPao CastillonNo ratings yet
- BrasdaDocument3 pagesBrasdaJayson Brylle MojaresNo ratings yet
- Assignment 6 SolutionsDocument8 pagesAssignment 6 SolutionsTalitha AdhyaksantiNo ratings yet
- Thermal StressesDocument17 pagesThermal StressesLacasaNo ratings yet
- Part 3Document20 pagesPart 3Loriel MendozaNo ratings yet
- Plate 5 Thermal StressDocument1 pagePlate 5 Thermal Stress202240273No ratings yet
- Shearing DeformationDocument21 pagesShearing DeformationRyan Joseph Rabino100% (1)
- Thermal PropertiesDocument13 pagesThermal Propertiesoreaby05No ratings yet
- Strain ProblemsDocument4 pagesStrain ProblemsBianca GuevarraNo ratings yet
- Module 2 - Simple StrainDocument8 pagesModule 2 - Simple StrainYnah Marie BoragayNo ratings yet
- Quiz No 2 - Set ADocument2 pagesQuiz No 2 - Set AMayoune Nasinopa Galvez100% (1)
- CE397-Lecture Notes (Topic 4)Document11 pagesCE397-Lecture Notes (Topic 4)Justine AligangaNo ratings yet
- Lesson 4 - Thermal Stress - For PresentationDocument13 pagesLesson 4 - Thermal Stress - For PresentationGabriel JavelonaNo ratings yet
- Mechanics of Deformable Bodies: Engr. Ramir C. Del Mundo February 06, 2021Document51 pagesMechanics of Deformable Bodies: Engr. Ramir C. Del Mundo February 06, 2021Joshua DariaNo ratings yet
- Thermal Stress For ReportDocument5 pagesThermal Stress For ReportGeraldineNo ratings yet
- Unit 1 QuestionsDocument10 pagesUnit 1 Questions015-RAJKUMARNo ratings yet
- Unit 1 QuestionsDocument10 pagesUnit 1 Questions015-RAJKUMARNo ratings yet
- SOM Sheet - 3Document4 pagesSOM Sheet - 3Sonali VasisthaNo ratings yet
- Thermal StressDocument13 pagesThermal StressRalph EvidenteNo ratings yet
- Week 5 Lecture 14 To 16Document7 pagesWeek 5 Lecture 14 To 16ChetanNo ratings yet
- Creep QuestionDocument8 pagesCreep QuestionWaris Nawaz KhanNo ratings yet
- Assignment 6 Solutions PDFDocument8 pagesAssignment 6 Solutions PDFKarim TouqanNo ratings yet
- Cven306 502 Hw06 SolutionDocument5 pagesCven306 502 Hw06 SolutiontwinbedtxNo ratings yet
- 02Document16 pages02Vergel Pabunan NogadasNo ratings yet
- Sec Module 03Document22 pagesSec Module 03kenji belanizo100% (1)
- Chapter 4Document21 pagesChapter 4rienalen placaNo ratings yet
- FFT 2Document3 pagesFFT 2Avinash Kumar Jha 4-Year B.Tech. Mechanical EngineeringNo ratings yet
- Tarea 2do ParcialDocument3 pagesTarea 2do ParcialBrayan PopNo ratings yet
- Assignment 2 On-Line Edition PDFDocument11 pagesAssignment 2 On-Line Edition PDFEm CervasNo ratings yet
- 13 ThermoelasticityDocument18 pages13 ThermoelasticityaderancNo ratings yet
- Tutorial 3 - Desgn For Fatigue Strength - MD - IDocument3 pagesTutorial 3 - Desgn For Fatigue Strength - MD - ISR SuryaNo ratings yet
- Ratio and ThermalDocument5 pagesRatio and ThermalTugas00No ratings yet
- Es 13 Module 5 Statically Indeterminate Structures PDFDocument51 pagesEs 13 Module 5 Statically Indeterminate Structures PDFRaymond RabaraNo ratings yet
- Materials Science and Engineering Concept Check Part2 PDFDocument27 pagesMaterials Science and Engineering Concept Check Part2 PDF李宛芸No ratings yet
- Chapter4 Thermal StressDocument5 pagesChapter4 Thermal Stressعبدالله خيريNo ratings yet
- CE234-Plate 03 BDocument1 pageCE234-Plate 03 BNicholas Bonn SingNo ratings yet
- Statically Indeterminate Members & Thermal StressesDocument24 pagesStatically Indeterminate Members & Thermal StressesBuddy SinghNo ratings yet
- Thermal ProblemsDocument2 pagesThermal Problemsحسين علي صبيحNo ratings yet
- 1 T 3Document14 pages1 T 3Kristi GjokaNo ratings yet
- Lecture3 2019 MPDocument12 pagesLecture3 2019 MPpumaNo ratings yet
- HOL - Instance-Conservation of Momentum2Document4 pagesHOL - Instance-Conservation of Momentum2Martin DelgadoNo ratings yet
- Sandler - Chemical and Engineering ThermodynamicsDocument575 pagesSandler - Chemical and Engineering ThermodynamicsDarllan Pinheiro64% (11)
- Moorman 1952Document17 pagesMoorman 1952Olesea NesterencoNo ratings yet
- Drag Characteristics of AirplaneDocument22 pagesDrag Characteristics of AirplaneNouman NadeemNo ratings yet
- Differential Calculus PDFDocument182 pagesDifferential Calculus PDFMarifel Clarisse Opeña100% (1)
- Medidor de Radiações Ionizantes GRAETZDocument1 pageMedidor de Radiações Ionizantes GRAETZJair EduardoNo ratings yet
- Chemistry Practical Salt Analysis and Volumetric Analysis Class 12Document20 pagesChemistry Practical Salt Analysis and Volumetric Analysis Class 12Science RetroNo ratings yet
- Coating Procedure: For Internal Lining of Steel Pipelines Using Epoxy Praimer PaintDocument12 pagesCoating Procedure: For Internal Lining of Steel Pipelines Using Epoxy Praimer Paintlemuel bacsaNo ratings yet
- Vdocuments - MX TMC Cable CatalogDocument71 pagesVdocuments - MX TMC Cable CatalogDaniel Eduardo AguirreNo ratings yet
- Math Task Sheet 15 - MYP 5 Extended - 22.11.21Document4 pagesMath Task Sheet 15 - MYP 5 Extended - 22.11.21GatikNo ratings yet
- Touch Screen With FeelingsDocument27 pagesTouch Screen With FeelingsJYOTHIRMAI MOPARTHINo ratings yet
- Gavin and Igoe - Final PublishedDocument12 pagesGavin and Igoe - Final PublisheddigoeNo ratings yet
- Multi-Component Acoustic Characterization of Porous Media - Karel N. Van DalenDocument182 pagesMulti-Component Acoustic Characterization of Porous Media - Karel N. Van DalenSasaNo ratings yet
- Faq On Earthing Standards 16/08/2018: EDM# 28984244 (Published) EDM# 23131817 (Word)Document12 pagesFaq On Earthing Standards 16/08/2018: EDM# 28984244 (Published) EDM# 23131817 (Word)anji201No ratings yet
- Lab 6 - Consolidation TestDocument9 pagesLab 6 - Consolidation TestHanis RahamanNo ratings yet
- CATALOGO-SOLAR-INGLES Dic WEBDocument29 pagesCATALOGO-SOLAR-INGLES Dic WEBMoshNo ratings yet
- Engr. Yoshiaki C. Mikami, Bsce Msce-Ste RMP: Prepared byDocument27 pagesEngr. Yoshiaki C. Mikami, Bsce Msce-Ste RMP: Prepared byDenzel NgNo ratings yet
- 03 CAN Bus Rev DDocument58 pages03 CAN Bus Rev DJim Vivanco Aylas0% (1)
- Collision TheoryDocument5 pagesCollision TheoryJenmar HemmingsNo ratings yet
- Chemistry: Unit I. Chemistry and Us Factual KnowledgeDocument31 pagesChemistry: Unit I. Chemistry and Us Factual KnowledgeMARICEL MIRANDANo ratings yet
- New Scientist USA - 23 March 2024Document54 pagesNew Scientist USA - 23 March 2024dsfasdfaNo ratings yet
- Bearing Heaters TIH 025Document2 pagesBearing Heaters TIH 025SherifMounirNo ratings yet
- CBR600F Diagrama ElectricoDocument1 pageCBR600F Diagrama ElectricoanxonyNo ratings yet
- Mechanics of Materials (AM 551) : P.R.Shakya 1Document35 pagesMechanics of Materials (AM 551) : P.R.Shakya 1Iris rumiNo ratings yet
- Notable People in The Field of Fluid MechanicsDocument2 pagesNotable People in The Field of Fluid MechanicsGeemaica MacaraigNo ratings yet
- Required Practical - Young's Slit Experiment & Diffraction GratingsDocument31 pagesRequired Practical - Young's Slit Experiment & Diffraction GratingsrizwanNo ratings yet
- Chapter 2 NumericalsDocument36 pagesChapter 2 NumericalsAASHISH KATUWALNo ratings yet
- Physics PracticalDocument43 pagesPhysics PracticalParam BalodiyaNo ratings yet
- Problem Set #2 WPS 760Document15 pagesProblem Set #2 WPS 760weilong9183% (12)