Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Thermal Problems
Uploaded by
حسين علي صبيحOriginal Description:
Original Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Thermal Problems
Uploaded by
حسين علي صبيحCopyright:
Available Formats
Question 1. A rod is 3 m long at a temperature of 15°C.
Find the expansion of the rod, when the temperature
is raised to 95°C. If this expansion is prevented, find the stress induced in the material of the rod. Take E = 1
× 105 N/mm2 and α = 0.000012 per degree centigrade.
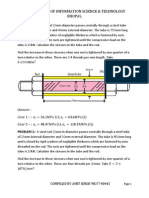
Question 2. A steel rod 5 cm diameter and 6 m long is connected to two grips and the rod is maintained at a
temperature of 100°C. Determine the stress and pull exerted when the temperature falls to 20°C if (i) the ends
do not yield, and (ii) the ends yield by 0.15 cm. Take E = 2 × 105 N/mm2 and α = 12 × 10–6/°C.
Question 3. A steel rod of 20 mm diameter passes centrally through a copper tube of 40 mm external diameter
and 30 mm internal diameter. The tube is closed at each end by rigid plates of negligible thickness. The nuts
are tightened lightly home on the projecting parts of the rod. If the temperature of the assembly is raised by
60°C, calculate the stresses developed in copper and steel. Take E for steel and copper as 200 GN/m2 and 100
GN/m2 and α for steel and copper as 12 × 10–6 per °C and 18 × 10–6 per °C.
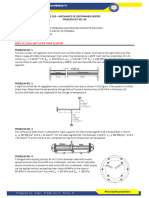
Question 4. The concrete post (Ec = 3.6 x 106 MN/m2 and 𝞪c = 5.5 x 10-6/ ˚C) is
reinforced with six steel bars, each of 15 mm diameter (Es = 29 x 106 MN/m2 and 𝞪s =
6.5 x 10-6/ ˚C). Determine the normal stresses induced in the steel and in the concrete
by a temperature rise of 65 ˚C.
Question 5. The assembly shown consists of an aluminum shell (Ea
= 10.6 x 106 MPa, 𝞪a = 12.9 x 10-6/ °C) fully bonded to a steel core
(Es =29x106 MPa, 𝞪s = 6.5 x 10-6/ °C) and is unstressed. Determine
a) the largest allowable change in temperature if the stress in the
aluminum shell is not to exceed 60 N/mm2, (b) the corresponding
change in length of the assembly.
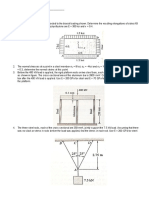
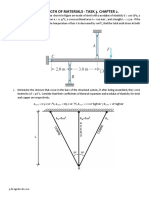
Question 6. A rigid block is supported by rods
symmetrically as shown. Determine the stresses in each
rod after a temperature rise of 40 ˚C, the lower ends of the
rods are assumed to have been the same level before the
block was attached and the temperature changed.
E for steel = 200 kN/mm2, E for bronze = 83 kN/mm2
Area of steel = 500 mm2, Area of bronze = 900 mm2
α for steel = 11.7 * 10 -6 1/ ˚C, α for bronze = 18.9 * 10 -6
1/ ˚C
Question 7. Find the change of temperature in steel bar only if you
know the steel bar is no stress.
E for steel = 200 × 106 MPa,
Area = 200 mm2
Length of steel bar = 2 m
α = 12 × 10 -6 1/ ˚C
Question 8. The rigid bar ABC is hinge by three cable,
two aluminum and one is steel, find the displacement
at C due to increase in temperature 50 ˚C increase.
Question 9. The rigid bars in figure are separated
by a roller at C and hinged at A and D. The steel
rod at B helps to support the load of 60 kN.
Compute the vertical displacement of the roller at
C if the temperature in member EB is raised by 60
˚C.
Question 10. Find ΔT so that a tension stresses in the steel rod equal to 60 MPa.
You might also like
- Simple Stress and StrainDocument3 pagesSimple Stress and StrainManish KumarNo ratings yet
- Thermal Stress RumusDocument16 pagesThermal Stress RumusVakin Agung PermanaNo ratings yet
- Week 5 Lecture 14 To 16Document7 pagesWeek 5 Lecture 14 To 16ChetanNo ratings yet
- Statically Indeterminate MembersDocument7 pagesStatically Indeterminate MembersKhan ToothNo ratings yet
- CE 6306 / Strength of Materials Mechanical Engineering 2016-17Document6 pagesCE 6306 / Strength of Materials Mechanical Engineering 2016-17amdevaNo ratings yet
- MOM Assignment IDocument3 pagesMOM Assignment IAll_regNo ratings yet
- Problem Set 3 - Deformations, Normal and Shear Strains, and Statically Indeterminate Members, Thermal Stress Problem 1Document5 pagesProblem Set 3 - Deformations, Normal and Shear Strains, and Statically Indeterminate Members, Thermal Stress Problem 1JamED ALRubioNo ratings yet
- Tarea 2do ParcialDocument3 pagesTarea 2do ParcialBrayan PopNo ratings yet
- QuestionsDocument5 pagesQuestionsAli KasimNo ratings yet
- Note Chapt IIDocument27 pagesNote Chapt IIRitesh KishoreNo ratings yet
- Set 6Document15 pagesSet 6Tare Er Kshitij60% (5)
- Thermal Stress: Mechanics of Deformable BodiesDocument10 pagesThermal Stress: Mechanics of Deformable BodiesPao CastillonNo ratings yet
- Assignment No 1 MD-1..Document3 pagesAssignment No 1 MD-1..Yadnyesh TaNo ratings yet
- Som Prob SetDocument50 pagesSom Prob SetAnonymous mXicTi8hBNo ratings yet
- Thermal StressesDocument3 pagesThermal StressesYatharth KhicharNo ratings yet
- Es-103 PS4Document1 pageEs-103 PS4Frederick Perez IINo ratings yet
- MOM2Tutorial 10-1Document3 pagesMOM2Tutorial 10-1Ishola mujeebNo ratings yet
- Sample Engineering Analysis ProblemsDocument10 pagesSample Engineering Analysis ProblemsHareesh R IyerNo ratings yet
- CHPT 8 PhsicsDocument7 pagesCHPT 8 PhsicsMayankNo ratings yet
- Ce003 PsDocument4 pagesCe003 PsJaimeNo ratings yet
- Assignment Strength of MaterialsDocument11 pagesAssignment Strength of MaterialsVinay Korukonda0% (1)
- SOM - Fieldwork 02Document1 pageSOM - Fieldwork 02Alexander MugabeNo ratings yet
- Ae2203 Ut 2 QP (Set A)Document2 pagesAe2203 Ut 2 QP (Set A)Aravindan SivanandanNo ratings yet
- Recitation Sheet 3 Solutions PDFDocument10 pagesRecitation Sheet 3 Solutions PDFankushkapoor2003No ratings yet
- Part 3Document20 pagesPart 3Loriel MendozaNo ratings yet
- 18ME404 Assignment 1Document2 pages18ME404 Assignment 1BharanitharanNo ratings yet
- Tutorial 3Document1 pageTutorial 3SARVAYESWARAN L MX-llNo ratings yet
- SOM Assignment No 2Document4 pagesSOM Assignment No 2suhani mittalNo ratings yet
- 9A01401 Strength of Materials - IIDocument4 pages9A01401 Strength of Materials - IIsivabharathamurthyNo ratings yet
- Compilations of Board Exam Problem1 PDFDocument65 pagesCompilations of Board Exam Problem1 PDFJevan Calaque100% (1)
- 12 - Page 58 PDFDocument1 page12 - Page 58 PDFvik03223No ratings yet
- Week 1 TutorialsDocument5 pagesWeek 1 TutorialsViliameNo ratings yet
- MosDocument3 pagesMosrajapratyNo ratings yet
- Strength WorksheetDocument9 pagesStrength WorksheetHabtamu GetaNo ratings yet
- Strength of Materials Question BankDocument2 pagesStrength of Materials Question BankSudarshan SalokheNo ratings yet
- Mechanics of Solids-I: Thermal StressesDocument16 pagesMechanics of Solids-I: Thermal StressesHammad AhmadNo ratings yet
- Strength of Materials - Task 3. Chapter 2.Document4 pagesStrength of Materials - Task 3. Chapter 2.Alen Dejesus Suarez SierraNo ratings yet
- 1 Basic Principles of ElectricityDocument4 pages1 Basic Principles of Electricitydabs_orangejuiceNo ratings yet
- Assignment 1Document2 pagesAssignment 1Sahil GaudeNo ratings yet
- Thermal StressesDocument2 pagesThermal StressesNigel Ceasar SilvaNo ratings yet
- Mse SW2BDocument25 pagesMse SW2BmarkkkkkNo ratings yet
- Mechanics of Materials July 2013Document0 pagesMechanics of Materials July 2013Prasad C MNo ratings yet
- Cat Solid MechanicsDocument1 pageCat Solid MechanicsMoses TheuriNo ratings yet
- CE6302Document14 pagesCE6302Daniel MabengoNo ratings yet
- ME 352 - All Problem Class - 14-18 BatchDocument125 pagesME 352 - All Problem Class - 14-18 BatchEntertainment GamingNo ratings yet
- Board Exam ProblemsDocument120 pagesBoard Exam ProblemsLanz de la Cruz83% (6)
- Mec32 HW3Document4 pagesMec32 HW3Isabelle LunaNo ratings yet
- Worked Solution To Various QuestionsDocument29 pagesWorked Solution To Various QuestionsJohn MutumaNo ratings yet
- Quiz No 2 - Set ADocument2 pagesQuiz No 2 - Set AMayoune Nasinopa Galvez100% (1)
- ME302 Fall 2020 - Homework Assignment 2Document5 pagesME302 Fall 2020 - Homework Assignment 2Daniela GaldoNo ratings yet
- ME302 Fall 2020 - Homework Assignment 2 PDFDocument5 pagesME302 Fall 2020 - Homework Assignment 2 PDFDaniela GaldoNo ratings yet
- Module Taxation 2Document1 pageModule Taxation 2RyanCallejaNo ratings yet
- Theory of Elasticity and PlasticityDocument2 pagesTheory of Elasticity and PlasticityNaren GujjarNo ratings yet
- How Two Boys Made Their Own Electrical Apparatus Containing Complete Directions for Making All Kinds of Simple Apparatus for the Study of Elementary ElectricityFrom EverandHow Two Boys Made Their Own Electrical Apparatus Containing Complete Directions for Making All Kinds of Simple Apparatus for the Study of Elementary ElectricityNo ratings yet
- How to Make Electrical Machines: Containing Full Directions for Making Electrical Machines, Induction Coils, Dynamos, and Many Novel Toys to Be Worked by ElectricityFrom EverandHow to Make Electrical Machines: Containing Full Directions for Making Electrical Machines, Induction Coils, Dynamos, and Many Novel Toys to Be Worked by ElectricityNo ratings yet
- How Two Boys Made Their Own Electrical Apparatus: Containing Complete Directions for Making All Kinds of Simple Apparatus for the Study of Elementary ElectricityFrom EverandHow Two Boys Made Their Own Electrical Apparatus: Containing Complete Directions for Making All Kinds of Simple Apparatus for the Study of Elementary ElectricityNo ratings yet
- The Study of Elementary Electricity and Magnetism by Experiment: Containing Two Hundred Experiments Performed with Simple, Home-made ApparatusFrom EverandThe Study of Elementary Electricity and Magnetism by Experiment: Containing Two Hundred Experiments Performed with Simple, Home-made ApparatusNo ratings yet
- Solutions Manual to accompany Engineering Materials ScienceFrom EverandSolutions Manual to accompany Engineering Materials ScienceRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (1)
- Supplemental Guidance For The Determination of Biochemical Oxygen Demand (BODs) and Carbonaceous BOD (CBODs) in Water and Wastewater (PDFDrive)Document62 pagesSupplemental Guidance For The Determination of Biochemical Oxygen Demand (BODs) and Carbonaceous BOD (CBODs) in Water and Wastewater (PDFDrive)Thoriq RamadhanNo ratings yet
- Chemistry 2Document9 pagesChemistry 2arch360No ratings yet
- Asme Material SpecsDocument4 pagesAsme Material SpecsRajwinder Singh100% (1)
- X-Ray Crystallography FDocument11 pagesX-Ray Crystallography F0921pyNo ratings yet
- En 1 4547 - 1510 Valbruna Nordic EnglishDocument2 pagesEn 1 4547 - 1510 Valbruna Nordic Englishpinky_y2kNo ratings yet
- Carburizing, Nitriding, and Boronizing in Vacuum Furnaces - IpsenDocument9 pagesCarburizing, Nitriding, and Boronizing in Vacuum Furnaces - Ipsenarkan1976No ratings yet
- Flash TanksDocument3 pagesFlash TanksnincitoNo ratings yet
- VWT Water Recycle and Reuse BrochureDocument8 pagesVWT Water Recycle and Reuse BrochureManjunath GangadharNo ratings yet
- 06 Lubrication SystemDocument55 pages06 Lubrication Systemramalingeswarao annamdevulaNo ratings yet
- 09 - SF9 - U02 - T01 Science Focus 9Document11 pages09 - SF9 - U02 - T01 Science Focus 9Nathan Gavenlock100% (1)
- Product Data Sheet: Transpoxy Masterbond 4.68Document2 pagesProduct Data Sheet: Transpoxy Masterbond 4.68rajeshNo ratings yet
- BGAS-MCQ-Exam QuestionsDocument11 pagesBGAS-MCQ-Exam QuestionsShanmuga Navaneethan100% (5)
- KL Jack Fasteners-Technical Data and ChartsDocument32 pagesKL Jack Fasteners-Technical Data and ChartsphuyangNo ratings yet
- CH 23Document61 pagesCH 23Anonymous 9yhXGZVNo ratings yet
- WoodwardDocument21 pagesWoodwardanastasia0% (1)
- Meija 2014 Adición EstándarDocument5 pagesMeija 2014 Adición EstándarDïö ValNo ratings yet
- BASIC EE - Module 1Document4 pagesBASIC EE - Module 1Stephanie BesanaNo ratings yet
- Akinlua Etal 2007 PDFDocument11 pagesAkinlua Etal 2007 PDFJavierNo ratings yet
- Drop Weight CrusherDocument2 pagesDrop Weight CrushermuralidharanNo ratings yet
- Study The Rate of Fermentation of Fruits and Vegetables JuicesDocument9 pagesStudy The Rate of Fermentation of Fruits and Vegetables JuicesYogesh ZopeNo ratings yet
- Virtual Field Trip 1Document1 pageVirtual Field Trip 1nicoNo ratings yet
- MS Chemistry Course OutlineDocument4 pagesMS Chemistry Course OutlinejunaidiqbalsialNo ratings yet
- Materials Studio Paper ImportantDocument11 pagesMaterials Studio Paper ImportantMd.Helal Hossain100% (1)
- ME6404 Thermal EngineeringDocument18 pagesME6404 Thermal EngineeringAnonymous mRBbdopMKfNo ratings yet
- Installation of Fuel Pipe Line Method StatementDocument10 pagesInstallation of Fuel Pipe Line Method StatementWufei Chang100% (2)
- Salt AnalysisDocument3 pagesSalt Analysistanish jainNo ratings yet
- Asme B 31.4Document16 pagesAsme B 31.4Arun Sankar100% (2)
- Catalogo Tosaca 1216Document16 pagesCatalogo Tosaca 1216isa.cuenta.26No ratings yet
- IBO 2008 Theory Part B - CCL PDFDocument81 pagesIBO 2008 Theory Part B - CCL PDFNelson NelNo ratings yet
- Alkane & Alkene MJ 2020Document8 pagesAlkane & Alkene MJ 2020FenNo ratings yet