Professional Documents
Culture Documents
PADIS Study Guide
Uploaded by
chelsea garzaOriginal Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
PADIS Study Guide
Uploaded by
chelsea garzaCopyright:
Available Formats
Pain Agitation/ Sedation Delirium
Description an unpleasant sensory and emotional Between 70-90% of ICU patients experience as the sudden severe confusion and rapid changes in brain function that
experience associated with actual or agitation occur with physical or mental illness
potential tissue damage
Complications Short-term: impair wound healing, Injury to self or others
increased risk of infection, increased stress
response Dislodged tubes and lines
Long-term: chronic pain, post-traumatic Ventilator dyssynchrony
stress disorder, lower health-related quality
of life PTSD and other long-term cognitive deficits
Interference with patient care
Causes Mechanical ventilation Pain / withdrawal Immobility Restraints
Surgery or procedures Sleep disturbances / delirium Procedures Pain
Lines and tubes Lines and tubes Medications Withdrawal
Oncologic/chronic pain Medications Issues with environment Sleep wake issues
Immobility Hypoxemia
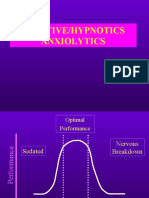
Assessment tools Numeric Rating Scale 0-10 is the gold RASS CAM-ICU
standard - Deep sedation -5 to -4 - Scored as + or –
- Moderate sedation -3
CPOT or BPS - Light sedation -2 to +1 ICDSC
- Scored between 0-8
SAS - 0 -no delirium
- Deep sedation 1-2 - 1-3 “subsyndromal delirium”
- Light sedation 3-4 - ≥ delirium
Frequency of Pain is assessed Q4H or is assessed Q4H or Patients should be screened for delirium once per nursing shift (~every 12
assessment w/ every dose titration w/ every dose titration hours)
Goals of CPOT goal 0-2 Light Sedation Deep Sedation
assessment - RASS -2 to +1 - RASS -4 to -5
BPS goal 0-3 - SAS 3 to 4 - SAS 1 to 2
Medication Opioids Benzos Benzos
options - MOA: μ opioid receptor agonist - MOA: acts on GABAa receptor
- Class SEs - Class SEs Anticholinergic medications
o Sedation o Respiratory depression - Metoclopramide
o Respiratory depression o Hypotension - H2 blockers
o NA/V/ Constipation o delirium o Famotidine// ranitidine
o hypotension o Phlebitis (Diazepam) - Antihistamines
o o diphenhydramine
Multimodal agents Others Corticosteroids
- various MOAs - propofol
Antipsychotics
- various SEs - dexmedtomidine
- first gen haloperidol
- ketamine
- second gen (atypical)
o quetiapine o risperidone
o olanzapine o ziprasidone
Overall summary - use validated tools for assessment
- pain addressed prior to sedation
o opioids are first line, but multimodal agents should be utilized as adjunct therapy to reduce opioid use
o intermittent dosing should be tried prior to continuous infusion
o ideal agent is rapid acting, has a short DUA, no active metabolites and unlikely to accumulate
- light sedation > deep sedation
o mech. Vented patients only use deep sedation if NECESSARY
o benzos limited due to risk of delirium, increased ventilation durations, and length of ICU stay
o nurse driven sedation protocols and spontaneous awakening trials can decrease duration of mech. Ventilation, sedation, and ICU stay
- delirium affects a significant number of ICU patients and is associated with worse outcomes
o prevention is key
o no meds improve outcomes for prevention or tx
o it may be appropriate to use antipsychotic to treat hyperactive delirium
You might also like
- Drug Abuse & DependenceDocument3 pagesDrug Abuse & DependenceJustin HulinNo ratings yet
- Risperidone: Generic Name: ClassificationsDocument9 pagesRisperidone: Generic Name: ClassificationsColeen Mae CamaristaNo ratings yet
- Fo Analgetik Opioid - Blok6Document65 pagesFo Analgetik Opioid - Blok6Rhena Fitria KhairunnisaNo ratings yet
- PsychiatryDocument5 pagesPsychiatryJohn SmithNo ratings yet
- CH 28 Nausea/VomitingDocument2 pagesCH 28 Nausea/VomitingkandeeNo ratings yet
- Delirium Protocol PDFDocument1 pageDelirium Protocol PDFPablo RamirezNo ratings yet
- DRUG STUDY (Zuclopenthixol Decanoate) - SANGUYO, CB.Document5 pagesDRUG STUDY (Zuclopenthixol Decanoate) - SANGUYO, CB.Camille SanguyoNo ratings yet
- SchizopDocument43 pagesSchizopapi-548578435No ratings yet
- Schizophrenia (DS)Document7 pagesSchizophrenia (DS)Al TheóNo ratings yet
- Schizophrenia DSDocument2 pagesSchizophrenia DSCatungal RophineNo ratings yet
- PsychotropicsDocument4 pagesPsychotropicsGeoffrey KernsNo ratings yet
- Antipsychotics - AMBOSS PDFDocument7 pagesAntipsychotics - AMBOSS PDFOpio Isaac100% (1)
- Painsedationdelirium Topic Discussion HandoutDocument7 pagesPainsedationdelirium Topic Discussion Handoutapi-641524095No ratings yet
- DrUG STUDY PSYCHEDocument52 pagesDrUG STUDY PSYCHELiza MPNo ratings yet
- Early Parkinsons Disease - Rev2 - Dr. AndradiDocument27 pagesEarly Parkinsons Disease - Rev2 - Dr. AndradiEka Surya MahendraNo ratings yet
- Injections: 2.5mg/ml in CNS: Drowsiness,: DroperidolDocument3 pagesInjections: 2.5mg/ml in CNS: Drowsiness,: DroperidolthesarayoNo ratings yet
- Intro To PsychopharmacologyDocument8 pagesIntro To Psychopharmacologyprettykiran7No ratings yet
- Case StudyDocument14 pagesCase Studyapi-592376639No ratings yet
- Agents Used For Schizophrenia (Antipsychotic) : Novita CaroliaDocument17 pagesAgents Used For Schizophrenia (Antipsychotic) : Novita CaroliaDetty NoviantyNo ratings yet
- Anti PsychoticDocument38 pagesAnti PsychoticAsep Cece IrhamNo ratings yet
- Sedation in ICUDocument14 pagesSedation in ICUIhtesham Ul HaqNo ratings yet
- MethadoneDocument2 pagesMethadoneIvanne HisolerNo ratings yet
- Sedation, Analgesics, and Paralysis For MV Patients: Sedatives Promote Sleep, Reduce Anxiety and AgitationDocument3 pagesSedation, Analgesics, and Paralysis For MV Patients: Sedatives Promote Sleep, Reduce Anxiety and Agitationفاطِمه سيد ابراهيمNo ratings yet
- Table of Sedative, Hypnotic, AntianxietyDocument4 pagesTable of Sedative, Hypnotic, AntianxietyirfanzukriNo ratings yet
- Week 7 Course TaskDocument13 pagesWeek 7 Course TaskRachelle CambaNo ratings yet
- Psychotherapeutic AgentsDocument2 pagesPsychotherapeutic AgentsjustinahorroNo ratings yet
- Hypertension: 1. Systolic and Diastolic HypertensionDocument3 pagesHypertension: 1. Systolic and Diastolic HypertensionJulia Rae Delos SantosNo ratings yet
- Antipsychotic Present and FutureDocument34 pagesAntipsychotic Present and FuturepabitraNo ratings yet
- Drug Study: Phinma - University of Iloilo College of Allied Health SciencesDocument3 pagesDrug Study: Phinma - University of Iloilo College of Allied Health Scienceslhie cabanlitNo ratings yet
- Systemic PharmacologyDocument37 pagesSystemic PharmacologyMoNiruzzaman MoNirNo ratings yet
- 117a MidtermDocument2 pages117a MidtermJonathan MangawiliNo ratings yet
- Ativan (Lorazepam) Drug StudyDocument3 pagesAtivan (Lorazepam) Drug StudyCHERISE CORDOVA100% (2)
- Drug Study: Midazolam: RecommendedDocument5 pagesDrug Study: Midazolam: RecommendedShara Lailanie A. AzisNo ratings yet
- (Issues and Orders To Cover) : - DyspneaDocument1 page(Issues and Orders To Cover) : - DyspneaAngelNo ratings yet
- Dug Study PsycheDocument33 pagesDug Study PsycheAziil LiizaNo ratings yet
- FOP 2019 Pediatric Tics Tourette SyndromeDocument29 pagesFOP 2019 Pediatric Tics Tourette SyndromeJosé SalasNo ratings yet
- Drug Study (Burn Injury) ManuscriptDocument4 pagesDrug Study (Burn Injury) ManuscriptEricka VillanuevaNo ratings yet
- Antipsychotics: Mary A. Wittler and Eric J. LavonasDocument5 pagesAntipsychotics: Mary A. Wittler and Eric J. LavonasSNo ratings yet
- CNSDocument102 pagesCNSNoriko MatsumotoNo ratings yet
- Schizophrenia - PharmacologyDocument1 pageSchizophrenia - PharmacologyJohn Nine ErispeNo ratings yet
- Assessment Algorithm For Sedated Adult ICU Patients: No YesDocument18 pagesAssessment Algorithm For Sedated Adult ICU Patients: No YeshendraNo ratings yet
- Sedation & Neuromuscular Blockade: Pediatric Critical Care Medicine Emory University Children's Healthcare of AtlantaDocument58 pagesSedation & Neuromuscular Blockade: Pediatric Critical Care Medicine Emory University Children's Healthcare of AtlantaZEMENAY TRUNEHNo ratings yet
- Psychiatric EmergenciesDocument26 pagesPsychiatric EmergenciesKai Zi (凯)No ratings yet
- Sedative HypnoticDocument60 pagesSedative HypnoticNeeraj KumarNo ratings yet
- Pharmacology IV L5Document4 pagesPharmacology IV L5سلطان القلحNo ratings yet
- Menpin Drug StudyPenthidineDocument2 pagesMenpin Drug StudyPenthidineVine CastroNo ratings yet
- 28 - PHAR0004!9!7 Anxiolytic Hypnotic Lecture 2023Document30 pages28 - PHAR0004!9!7 Anxiolytic Hypnotic Lecture 2023Zara KhanNo ratings yet
- Sedatives & HypnoticsDocument49 pagesSedatives & HypnoticsShubha DiwakarNo ratings yet
- Prevention and Management of Pain, AgitationDocument44 pagesPrevention and Management of Pain, AgitationSiriporn PongpattarapakNo ratings yet
- 33 Psych EmergenciesDocument3 pages33 Psych EmergenciesGAPL WijesekaraNo ratings yet
- Obat2 Yang Bekerja Pada Ganguan Kesadaran: Elly Usman Bagian Farmakologi Dan Terapi, Fakultas Kedokteran, UnandDocument29 pagesObat2 Yang Bekerja Pada Ganguan Kesadaran: Elly Usman Bagian Farmakologi Dan Terapi, Fakultas Kedokteran, UnandKhairani HakimNo ratings yet
- Drug Study-PtsdDocument4 pagesDrug Study-PtsdWILMARIE SAPANTANo ratings yet
- Psychotropic DrugsDocument29 pagesPsychotropic DrugsBahaa ShaabanNo ratings yet
- Lui Sh-Colored Lips and Finger Nails Blur Red VisionDocument1 pageLui Sh-Colored Lips and Finger Nails Blur Red VisionMagdayao Romamea100% (1)
- Pcol 1 Prefinals Part 1 PDFDocument9 pagesPcol 1 Prefinals Part 1 PDFJillian Mae DacerNo ratings yet
- PromethazineDocument3 pagesPromethazineGwyn RosalesNo ratings yet
- TRAMADOL HCL (Ultram)Document2 pagesTRAMADOL HCL (Ultram)karenmichellelecarozNo ratings yet
- Al-Zaytoonah Private University of Jordan: Psychiatric Nursing DepartmentDocument29 pagesAl-Zaytoonah Private University of Jordan: Psychiatric Nursing DepartmentHeba_Al_KhozaeNo ratings yet
- 3 Treatment of HypertensionDocument7 pages3 Treatment of HypertensiontiaraNo ratings yet
- Blood Products Production From Transgenic AnimalsDocument25 pagesBlood Products Production From Transgenic AnimalsRekha Lakshmi Narayanan0% (2)
- Ob 2Document9 pagesOb 2Danica Chiara Motia100% (1)
- Medison - Sonoace 8000liveDocument6 pagesMedison - Sonoace 8000liveJohnatan MonjesNo ratings yet
- Beneficence and Non-MaleficenceDocument3 pagesBeneficence and Non-MaleficenceRathin BanerjeeNo ratings yet
- Betz Rebecca ResumeDocument2 pagesBetz Rebecca Resumeapi-316054946No ratings yet
- Sickle CellDocument21 pagesSickle CellLeon0% (1)
- Joint Commission Emergency Management Requirements For HospitalsDocument4 pagesJoint Commission Emergency Management Requirements For HospitalsFrances CorreaNo ratings yet
- List of Medical Professionals-SPADocument8 pagesList of Medical Professionals-SPANoemí GuzmartNo ratings yet
- Common Medical AbbreviationsDocument1 pageCommon Medical Abbreviationskedwards108No ratings yet
- Physiology of HemoglobinDocument15 pagesPhysiology of HemoglobinIbrahim YahyaNo ratings yet
- Underwriting PacketDocument9 pagesUnderwriting Packetapi-207980596No ratings yet
- RBC PathologyDocument7 pagesRBC PathologyKent CruzNo ratings yet
- The Fig and Olive MiracleDocument2 pagesThe Fig and Olive MiracleIman Syafar100% (1)
- What's Bugging Your Teen?-The Microbiota and Adolescent Mental HealthDocument13 pagesWhat's Bugging Your Teen?-The Microbiota and Adolescent Mental HealthPaula Manalo-SuliguinNo ratings yet
- Bone Marrow BiopsyDocument2 pagesBone Marrow BiopsySatinder SinghNo ratings yet
- Understanding Receiver Operating Characteristic Roc CurvesDocument2 pagesUnderstanding Receiver Operating Characteristic Roc CurvesOlievia Herinda AdhiafebriantyNo ratings yet
- SDS en-US SimpleGreenLimeScaleRemoverDocument5 pagesSDS en-US SimpleGreenLimeScaleRemoverjoelcarhuanchoNo ratings yet
- InflammationDocument41 pagesInflammationbharath goNo ratings yet
- Fractura e FalangsDocument16 pagesFractura e FalangsJulio Cesar Guillen MoralesNo ratings yet
- Total Protein SpinreactDocument1 pageTotal Protein Spinreactariyan khanNo ratings yet
- Dissertation 7Document18 pagesDissertation 7Sidhartha KumarNo ratings yet
- Daftar Obat Untuk Formularium RSHBH FinalDocument13 pagesDaftar Obat Untuk Formularium RSHBH FinalReza Yuni SandraNo ratings yet
- Meena 2021Document11 pagesMeena 2021As MaaNo ratings yet
- Appeal LetterDocument1 pageAppeal Letterdate6No ratings yet
- Why Medical Anthropology MattersDocument3 pagesWhy Medical Anthropology MattersBárbara HerreraNo ratings yet
- May 17, 2013 Strathmore TimesDocument36 pagesMay 17, 2013 Strathmore TimesStrathmore TimesNo ratings yet
- SOAP Notes: AuthorsDocument6 pagesSOAP Notes: AuthorsRanita Kumalasari100% (4)
- Bear 1000Document2 pagesBear 1000elabsNo ratings yet
- AIIMS Question PaperDocument6 pagesAIIMS Question Papersharu4291100% (1)
- ATELEKTASISDocument37 pagesATELEKTASISGalih Arief Harimurti WawolumajaNo ratings yet