Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Amines Short Notes
Amines Short Notes
Uploaded by
Advik Gupta0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
4 views2 pagesThe document discusses amines, including their classification, preparation methods, chemical reactions, physical properties, and tests. Amines are classified as primary (1o), secondary (2o), or tertiary (3o) depending on the number of alkyl or aryl groups bonded to the nitrogen atom. They can be prepared through various substitution and reduction reactions such as ammonolysis, alkylation of azides, and reduction of nitro compounds. Amines undergo reactions characteristic of both bases and organic compounds, such as forming salts with acids and undergoing electrophilic aromatic substitution. Primary and secondary amines have higher boiling points and solubility than tertiary amines due to hydrogen bonding.
Original Description:
Original Title
Amines Short notes
Copyright
© © All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentThe document discusses amines, including their classification, preparation methods, chemical reactions, physical properties, and tests. Amines are classified as primary (1o), secondary (2o), or tertiary (3o) depending on the number of alkyl or aryl groups bonded to the nitrogen atom. They can be prepared through various substitution and reduction reactions such as ammonolysis, alkylation of azides, and reduction of nitro compounds. Amines undergo reactions characteristic of both bases and organic compounds, such as forming salts with acids and undergoing electrophilic aromatic substitution. Primary and secondary amines have higher boiling points and solubility than tertiary amines due to hydrogen bonding.
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
4 views2 pagesAmines Short Notes
Amines Short Notes
Uploaded by
Advik GuptaThe document discusses amines, including their classification, preparation methods, chemical reactions, physical properties, and tests. Amines are classified as primary (1o), secondary (2o), or tertiary (3o) depending on the number of alkyl or aryl groups bonded to the nitrogen atom. They can be prepared through various substitution and reduction reactions such as ammonolysis, alkylation of azides, and reduction of nitro compounds. Amines undergo reactions characteristic of both bases and organic compounds, such as forming salts with acids and undergoing electrophilic aromatic substitution. Primary and secondary amines have higher boiling points and solubility than tertiary amines due to hydrogen bonding.
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
You are on page 1of 2
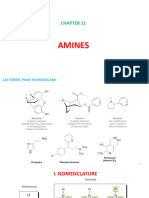
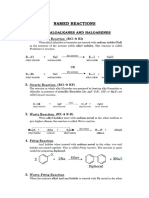
Amines
▪ Basic Nomenclature and Classification of Amines ▪ Chemical reactions of Amine
a. 1o amine 1. Reactions showing with basic nature
b. 2o amine i. Reaction with acids to form salts
c. 3o amine ii. Reaction with Chloro Platinic/Auric acid
iii. Reaction with H2O
▪ Preparation of Amines 2. Benzoylation reaction
1. Ammonolysis of alkyl halide 3. Reaction with Tilden reagent(NOCl)
→ NH3/ /-HX 4. Reaction with Phosgene(COCl2)
→ SN2 mechanism 5. Electrophilic Substitution reaction
→ Order of reactivity : RI > RBr > RCl > RF i. Sulphonation
→ 1o,2o,3o and Quarternary ammonium salt are formed ii. Friedel Crafts Alkylation/ Acylation❌
2. Ammonolysis of alcohols iii. Ipso substitution(-COOH, -SO3H)
→ NH3/Al2O3/ 6. Reaction with HNO2
→ Quarternary ammonium salt is not formed due to steric hindrance i. 1o amine
→ In excess ammonia is used, then main product will be 1 o amine ii. 2o amine
3. Alkylation of Azide ion and Reduction iii. 3o amine
→ Much better method to prepare 1o amine iv. 3o aryl amine
→ R-X, LAH 7. Diazonium salt, Diazotisation reaction
→ SN2 attack by Azide ion ▫ Coupling reaction of BDC
4. Hoffmann exhaustive alkylation ▫ Preparation of Benzene Diazonium salt
→ 1o, 2o , 3o amine to 4o ammonium salt 8. Libermann's nitro reaction
→ Reagent = CH3I → Phenol reacts with (HONO)
→ Quarternary ammonium halide salt react with moist Ag 2O to give → Forms p-nitrosophenol
silver halide as precipitate → Tautomerism occurs
→ Quarternary ammonium hydroxide on at 400K, undergoes → In presence of conc. H2SO4 = GRB
elimination and produces alkene
5. Hoffmann Bromamide degradation
→ Amides => Amines ▪ Test involving Amines
→ For 1o aliphatic or aromatic Amide 1. Carbylamine reaction(Iso-Cyanide Test)
→ Reagent = KOH/Br2 → CHCl3/ alc. KOH/
6. Reduction of Nitro compounds → Only for 1o aliphatic or aromatic amine
→ H2/Pd or Metal+Acid or LAH → Alkyl Isocyanide => Very bad smell(Product)
7. Reduction of Nitriles and Isonitriles → Nu- = RNH2 , E+ = CCl2
8. Reduction of Oxime 2. Hinsberg's Test
9. Reduction of Amides → Ph-SO2Cl
10. Reductive of Amination → SN2 mechanism
11. Gabriel-phthalimide synthesis → 1o amine✔, 2o amine✔, 3o amine❌
→ For 1o aliphatic amines 3. Hoffmann's mustard oil test
→ Alc. KOH/ R-X/ H2O(-OH) i. CS2/ HgCl2/
→ Phthalimide => 1o aliphatic amine ii. Alkyl Isothiocyanate(Smell like mustard oil)
→ Follows SN2 mechanism
12. By Hydrosysis R-NC and RNCO
13. From Grignard Reagent(R-MgX)
14. Schmidt reaction
→ Reagent = N3H-H2SO4/
→ Acyl chloride => 1o amine
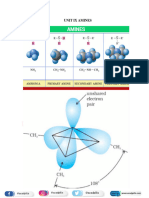
▪ Physical Properties of Amine
1. Boiling point
→ 1o amine > 2o amine > 3o amine
→ Intermolecular forces in 1o amine and 2o amine
→ H bonding
2. Solubility
→ 1o amine > 2o amine > 3o amine
→ 1o amine and 2o amine can form H-bond with water
→ Decreases with increase in size of alkyl group
3. Basic nature
→ Inductive effect(3o > 2o > 1o)
→ Steric hindrance
→ Inversely prop. to No. of resonating structure
→ Aromatic amines are less basic than Aliphatic
→ %s ∝ Electronegativity ∝ 1/Basicity
→ Aniline are more basic than substituted Aniline
→ Ortho substituted Aniline are less basic due to ortho effect
Organic Chemistry⌬ Page 1
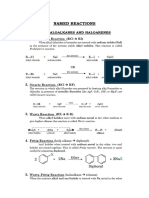
Amines
▪ Basic Nomenclature and Classification of Amines ▪ Chemical reactions of Amine
a. 1o amine 1. Reactions showing with basic nature
b. 2o amine i. Reaction with acids to form salts
c. 3o amine ii. Reaction with Chloro Platinic/Auric acid
iii. Reaction with H2O
▪ Preparation of Amines 2. Benzoylation reaction
1. Ammonolysis of alkyl halide 3. Reaction with Tilden reagent(NOCl)
→ NH3/ /-HX 4. Reaction with Phosgene(COCl2)
→ SN2 mechanism 5. Electrophilic Substitution reaction
→ Order of reactivity : RI > RBr > RCl > RF i. Sulphonation
→ 1o,2o,3o and Quarternary ammonium salt are formed ii. Friedel Crafts Alkylation/ Acylation❌
2. Ammonolysis of alcohols iii. Ipso substitution(-COOH, -SO3H)
→ NH3/Al2O3/ 6. Reaction with HNO2
→ Quarternary ammonium salt is not formed due to steric hindrance i. 1o amine
→ In excess ammonia is used, then main product will be 1 o amine ii. 2o amine
3. Alkylation of Azide ion and Reduction iii. 3o amine
→ Much better method to prepare 1o amine iv. 3o aryl amine
→ R-X, LAH 7. Diazonium salt, Diazotisation reaction
→ SN2 attack by Azide ion ▫ Coupling reaction of BDC
4. Hoffmann exhaustive alkylation ▫ Preparation of Benzene Diazonium salt
→ 1o, 2o , 3o amine to 4o ammonium salt 8. Libermann's nitro reaction
→ Reagent = CH3I → Phenol reacts with (HONO)
→ Quarternary ammonium halide salt react with moist Ag 2O to give → Forms p-nitrosophenol
silver halide as precipitate → Tautomerism occurs
→ Quarternary ammonium hydroxide on at 400K, undergoes → In presence of conc. H2SO4 = GRB
elimination and produces alkene
5. Hoffmann Bromamide degradation
→ Amides => Amines ▪ Test involving Amines
→ For 1o aliphatic or aromatic Amide 1. Carbylamine reaction(Iso-Cyanide Test)
→ Reagent = KOH/Br2 → CHCl3/ alc. KOH/
6. Reduction of Nitro compounds → Only for 1o aliphatic or aromatic amine
→ H2/Pd or Metal+Acid or LAH → Alkyl Isocyanide => Very bad smell(Product)
7. Reduction of Nitriles and Isonitriles → Nu- = RNH2 , E+ = CCl2
8. Reduction of Oxime 2. Hinsberg's Test
9. Reduction of Amides → Ph-SO2Cl
10. Reductive of Amination → SN2 mechanism
11. Gabriel-phthalimide synthesis → 1o amine✔, 2o amine✔, 3o amine❌
→ For 1o aliphatic amines 3. Hoffmann's mustard oil test
→ Alc. KOH/ R-X/ H2O(-OH) i. CS2/ HgCl2/
→ Phthalimide => 1o aliphatic amine ii. Alkyl Isothiocyanate(Smell like mustard oil)
→ Follows SN2 mechanism
12. By Hydrosysis R-NC and RNCO
13. From Grignard Reagent(R-MgX)
14. Schmidt reaction
→ Reagent = N3H-H2SO4/
→ Acyl chloride => 1o amine
▪ Physical Properties of Amine
1. Boiling point
→ 1o amine > 2o amine > 3o amine
→ Intermolecular forces in 1o amine and 2o amine
→ H bonding
2. Solubility
→ 1o amine > 2o amine > 3o amine
→ 1o amine and 2o amine can form H-bond with water
→ Decreases with increase in size of alkyl group
3. Basic nature
→ Inductive effect(3o > 2o > 1o)
→ Steric hindrance
→ Inversely prop. to No. of resonating structure
→ Aromatic amines are less basic than Aliphatic
→ %s ∝ Electronegativity ∝ 1/Basicity
→ Aniline are more basic than substituted Aniline
→ Ortho substituted Aniline are less basic due to ortho effect
Organic Chemistry⌬ Page 1
You might also like
- ENG790s2 Lab Sheet - Hilton Combustion Unit-1Document8 pagesENG790s2 Lab Sheet - Hilton Combustion Unit-1Moiz Subhan100% (1)
- Full Report: Synthesis of AspirinDocument3 pagesFull Report: Synthesis of AspirinNor Ashikin IsmailNo ratings yet
- Amines, Amide and Derivatives: Edit and Compiled By: Hafiz Abdul Rafay Latif KayaniDocument26 pagesAmines, Amide and Derivatives: Edit and Compiled By: Hafiz Abdul Rafay Latif KayaniPalwasha KardarNo ratings yet
- Non-Asbestos Gasket: Catalogue No. Zy03Document24 pagesNon-Asbestos Gasket: Catalogue No. Zy03Wh NgNo ratings yet
- IR Spectrum Table by Frequency Range: Frequency Range Absorption (CM) Appearance Group Compound Class CommentsDocument7 pagesIR Spectrum Table by Frequency Range: Frequency Range Absorption (CM) Appearance Group Compound Class CommentsRyo CaesarNo ratings yet
- Alcohol and Ether CompleteDocument2 pagesAlcohol and Ether CompleteAdvik GuptaNo ratings yet
- AminesDocument12 pagesAminesEmelda BanumathyNo ratings yet
- Chapter 11 - AminesDocument40 pagesChapter 11 - AminesHoài Nguyễn Phan VũNo ratings yet
- AminesDocument13 pagesAminesSohamNo ratings yet
- Amines NotesDocument26 pagesAmines Notessamay gujratiNo ratings yet
- Amines All SheetDocument9 pagesAmines All SheetMahendra ShahNo ratings yet
- CBSE Class 12 Chem Notes Question Bank Amines PDFDocument21 pagesCBSE Class 12 Chem Notes Question Bank Amines PDFMr bhupendra Singh rathoreNo ratings yet
- AMINESDocument7 pagesAMINESpathakgourav0302No ratings yet
- 12th - Genral - Named Organic Reaction Sheet Class NotesDocument5 pages12th - Genral - Named Organic Reaction Sheet Class Notesaaravtrivedi313No ratings yet
- Amines: KOH CH CL 3Document2 pagesAmines: KOH CH CL 3Yuvaraj HebbalNo ratings yet
- Class 12 - AminesDocument34 pagesClass 12 - AminesRidhi AgarwalNo ratings yet
- NamereactionorganicDocument13 pagesNamereactionorganicdeykrishna654100% (1)
- Xii - CH13 - Organic Compounds Containing NitrogenDocument5 pagesXii - CH13 - Organic Compounds Containing NitrogenYash RajNo ratings yet
- Chapter 24 NotesDocument37 pagesChapter 24 NotesTiffany YehNo ratings yet
- General Organic ChemistryDocument10 pagesGeneral Organic ChemistryRiddhi Chatterjee100% (2)
- Naming Reaction FinalDocument9 pagesNaming Reaction FinalRajendra ThamerciNo ratings yet
- Amines Ic19770Document6 pagesAmines Ic19770Satendra KumarNo ratings yet
- Amine DPP 02Document4 pagesAmine DPP 02Dharmvir TantyNo ratings yet
- Cbse Test Paper - 01 Class - 12 Chemistry (Amines)Document7 pagesCbse Test Paper - 01 Class - 12 Chemistry (Amines)Tamil SelviNo ratings yet
- Nitrogen Containing Compuonds-01-TheoryDocument20 pagesNitrogen Containing Compuonds-01-TheoryRaju SinghNo ratings yet
- Sesion - Aldehidos y CetonasDocument54 pagesSesion - Aldehidos y CetonasdiversestoresupplyonlineNo ratings yet
- (Topic 2) Carbonyl Chemistry 2 2022Document31 pages(Topic 2) Carbonyl Chemistry 2 2022VirginiaNo ratings yet
- Chemistry Evaluation QuestionsDocument9 pagesChemistry Evaluation Questions21additional12No ratings yet
- Activity 7 Post Lab - NotesDocument10 pagesActivity 7 Post Lab - Notes2241689No ratings yet
- Named RXNDocument10 pagesNamed RXNssatechies62No ratings yet
- Reaksi Reaksi AminaDocument4 pagesReaksi Reaksi AminaWildan KPNo ratings yet
- Module 5 - XII NEET - ChemistryDocument128 pagesModule 5 - XII NEET - ChemistryGhanshyam MatlaneNo ratings yet
- CHEM F311 Lecture 2 Oxiding and Reducing AgentsDocument16 pagesCHEM F311 Lecture 2 Oxiding and Reducing AgentsSAYAN RAYNo ratings yet
- 12 Chemistry Notes ch13 Amines-1Document8 pages12 Chemistry Notes ch13 Amines-1mv7602456No ratings yet
- 12 Chemistry Notes ch13 AminesDocument11 pages12 Chemistry Notes ch13 AminesAkNo ratings yet
- NH NH: Solution Class 12 - Chemistry AminesDocument2 pagesNH NH: Solution Class 12 - Chemistry AminesTarique MasoodNo ratings yet
- Chemistry - Amines NotesDocument22 pagesChemistry - Amines NotesJshdhdNo ratings yet
- Plij Gib Me BookDocument16 pagesPlij Gib Me BookDarsheel AmbasthaNo ratings yet
- Lecture 10 (02!02!2024) Alcohol OxidationDocument24 pagesLecture 10 (02!02!2024) Alcohol OxidationericktNo ratings yet
- Class 12 Chemistry Chapter 13 Amines NotesDocument10 pagesClass 12 Chemistry Chapter 13 Amines Notescharusrirajkumar27No ratings yet
- Notes For Chemistry Class 12 Chapter 13 AminesDocument22 pagesNotes For Chemistry Class 12 Chapter 13 AminesVanshika JainNo ratings yet
- NotesDocument10 pagesNotespovikanimathiNo ratings yet
- AMINESDocument58 pagesAMINESHarsh Shah100% (1)
- Amines 3Document15 pagesAmines 3rosariopraveen007No ratings yet
- CH 19 Problem Answers (All)Document26 pagesCH 19 Problem Answers (All)sorinavramescuNo ratings yet
- CBSE Class-12 Chemistry Quick Revision Notes Chapter-13: Amines AminesDocument8 pagesCBSE Class-12 Chemistry Quick Revision Notes Chapter-13: Amines AminesAryan MeenaNo ratings yet
- Easy Way To Score in Organic ChemistryDocument2 pagesEasy Way To Score in Organic ChemistryRoopa KhenedNo ratings yet
- Notes On Preparation of HaloalkanesDocument18 pagesNotes On Preparation of Haloalkanesranjana roy100% (1)
- Chapter 1amine Student Hand OutDocument67 pagesChapter 1amine Student Hand OuthazimNo ratings yet
- OC - Lectures15-16 3Document27 pagesOC - Lectures15-16 3aa aaNo ratings yet
- Chapter 8 - Alcohol Phenol 2022Document55 pagesChapter 8 - Alcohol Phenol 2022Hoài Nguyễn Phan VũNo ratings yet
- AminesDocument31 pagesAminesJoseph YayenNo ratings yet
- ChemLab NotesDocument4 pagesChemLab NotesDale P. PolvorosaNo ratings yet
- Class 12 Organic Name ReacyionDocument7 pagesClass 12 Organic Name Reacyioncyeditz10101No ratings yet
- CH 22 PracticeDocument6 pagesCH 22 PracticeKeenaLiNo ratings yet
- AminesDocument6 pagesAminesAirome CorpuzNo ratings yet
- C38 - Hydrocarbons - Ajay - Send For Edit To PublicationDocument25 pagesC38 - Hydrocarbons - Ajay - Send For Edit To PublicationPrince ThakurNo ratings yet
- Name Reactions of Organic ChemistryDocument6 pagesName Reactions of Organic Chemistryvishi162007No ratings yet
- Name Reactions of Organic ChemistryDocument7 pagesName Reactions of Organic Chemistryaashishdevkota185No ratings yet
- L7 Amines and Amino AcidsDocument16 pagesL7 Amines and Amino AcidsCheng FuNo ratings yet
- AminesDocument10 pagesAminesDUHA GORASHINo ratings yet
- Name Reactions of Organic ChemistryDocument7 pagesName Reactions of Organic ChemistryNaynam SharmaNo ratings yet
- Annual Reports in Organic Synthesis — 1971From EverandAnnual Reports in Organic Synthesis — 1971John McMurryNo ratings yet
- Annual Reports in Organic Synthesis — 1970From EverandAnnual Reports in Organic Synthesis — 1970John McMurryNo ratings yet
- Fiber Manu ProcessDocument3 pagesFiber Manu ProcessMrugesh ShahNo ratings yet
- Synthesis of AcetanilideDocument4 pagesSynthesis of AcetanilideMich Tolentino50% (2)
- Technology 1Document9 pagesTechnology 1Prabhu KalpakkamNo ratings yet
- A Comparison of BS en 287 Part 1 and ISO 9606Document3 pagesA Comparison of BS en 287 Part 1 and ISO 9606Joe ClarkeNo ratings yet
- New Applications of Catalytic Chain Transfer PolymerizationDocument11 pagesNew Applications of Catalytic Chain Transfer PolymerizationQuan Nguyen HaiNo ratings yet
- Basnet Et Al. - 2018 - A Review On Bio-Synthesized Zinc Oxide NanoparticlDocument21 pagesBasnet Et Al. - 2018 - A Review On Bio-Synthesized Zinc Oxide NanoparticlRodrigo SilvaNo ratings yet
- Guide Dissolved Oxygen MeasurementDocument40 pagesGuide Dissolved Oxygen Measurementrafael_111No ratings yet
- Zinc, Casting, Properties and ApplicationDocument76 pagesZinc, Casting, Properties and Applicationadelina ednandaNo ratings yet
- Sorbead R: Product Data SheetDocument2 pagesSorbead R: Product Data Sheetpmfg847633No ratings yet
- Uop304 08Document13 pagesUop304 08Muhannad NasifNo ratings yet
- CFNS Experiment 75 - Making Nylon - The Nylon Rope TrickDocument3 pagesCFNS Experiment 75 - Making Nylon - The Nylon Rope TrickJohnson KendekNo ratings yet
- Shiri2010 Chem Rev 2010 Synth BIMs TIMsDocument44 pagesShiri2010 Chem Rev 2010 Synth BIMs TIMsLuân NguyễnNo ratings yet
- Floating Drug Delivery System-: An Approach To Prolong Gastric RetentionDocument29 pagesFloating Drug Delivery System-: An Approach To Prolong Gastric Retentionapi-19985983No ratings yet
- 12 Received Fabrics 2023Document19 pages12 Received Fabrics 2023ini jawabanNo ratings yet
- Lanco 1400 SFDocument2 pagesLanco 1400 SFmgamal1080No ratings yet
- Chapter 82 Advanced Theories of Covalent BondingDocument94 pagesChapter 82 Advanced Theories of Covalent BondingcheruNo ratings yet
- DDB Board Resolution No. 4, S 2007-Operation Private EyeDocument3 pagesDDB Board Resolution No. 4, S 2007-Operation Private EyeCrizalde de DiosNo ratings yet
- Why Your RO Membrane Cleaning May Not Be Effective. The Benefits of Reverse CleaningDocument10 pagesWhy Your RO Membrane Cleaning May Not Be Effective. The Benefits of Reverse Cleaningzerocool86No ratings yet
- AttachmentDocument71 pagesAttachmentAhmad ibrahimNo ratings yet
- Boron HydrideDocument10 pagesBoron HydrideZul AndriNo ratings yet
- Packaging of Fats and OilDocument32 pagesPackaging of Fats and OilKajal VermaNo ratings yet
- BeeswaxDocument6 pagesBeeswaxmuahdib11No ratings yet
- Electrochimica Acta: Abhilash Sankaran, Christopher Staszel, Farzad Mashayek, Alexander L. YarinDocument14 pagesElectrochimica Acta: Abhilash Sankaran, Christopher Staszel, Farzad Mashayek, Alexander L. Yarinely sianNo ratings yet
- Catalysis and Physical Organic ChemistryDocument49 pagesCatalysis and Physical Organic ChemistryAnandarup GoswamiNo ratings yet
- Oleic Acid MSDS: Section 1: Chemical Product and Company IdentificationDocument5 pagesOleic Acid MSDS: Section 1: Chemical Product and Company Identificationdian_2108No ratings yet
- Achievements in The Life SciencesDocument8 pagesAchievements in The Life Sciencessameer sahaanNo ratings yet