Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Welcome To OSI Open System Interconnect Model: Networkforyou
Uploaded by
Partha Sarathi NandiOriginal Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Welcome To OSI Open System Interconnect Model: Networkforyou
Uploaded by
Partha Sarathi NandiCopyright:
Available Formats
Networkforyou
Welcome
To
OSI Open System
Interconnect Model
Email us: 1 of 8 WhatsApp Us : +966532984612
networkforyou4@gmail.com
Networkforyou
OSI Open Systems Interconnect Model:
• The OSI Reference model is a standard of the international Organization for Standardization (ISO).
• It is general purpose framework that characterizes and standardizes how PC’s communicate with
each other over a network.
• It is a Conceptual model.
• Its seven layered approach to data transmission divides the operations into specific related groups of
actions at each layer.
• A layer serves the layer above it and is served by the layer below it.
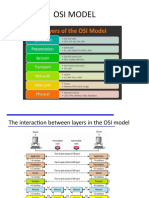
Layer 7: Application
Layer 6: Presentation
Layer5: Session
Layer4: Transport (TCP/UDP, Port)
Layer3: Network (IP Address) Router
Layer2: Data-Link (Ethernet MAC address) Switches
Layer1: Physical
We are learning this model for understanding Networking.
Email us: 2 of 8 WhatsApp Us : +966532984612
networkforyou4@gmail.com
Networkforyou
Application Layer:
• In this layer we will consider application like browsing, email, other software.
• Human-computer Interaction layer, where applications can access the network services.
• This is the only layer that directly interacts with data from the user.
• Software applications like web browsers and email clients rely on the application layer to initiate
communications.
Presentation Layer:
• This layer is primarily responsible for preparing data so that is can be used by the application
layer.
• In other words, layer 6 makes the data presentable for applications to consume.
• This layer is responsible for translation, encryption and compression of data.
• This layer is responsible for presentation data to application layer.
• In simple words we can say this layer will be responsible for data format etc. Like jpg or png for
image etc.
• When we have two host communicating to each other, we need to make sure that the
application layer one side can read the data from the host on the other side.
• In Short, the presentation layer here makes sure that application layer on both sides read each
other data.
Session Layer:
• This layer is responsible for sessions it creates and maintains the sessions.
• Session is nothing but time frame between client and server.
• This is the layer responsible for opening and closing communication between the two devices.
• The time between when the communication is opened and closed is known as the session.
• The session layer ensures that the session stays open long enough to transfer all the data being
exchanged and then promptly closes the session in order to avoid wasting resources.
Transport Layer:
• This layer is responsible for data delivery from source to destination.
• We use TCP or UDP protocol for transfer of data.
• TCP stand for Transmission Control Protocol.
• UDP stand for User datagram protocol.
• Layer 4 is responsible for End to End Communication between the two devices.
Email us: 3 of 8 WhatsApp Us : +966532984612
networkforyou4@gmail.com
Networkforyou
Network Layer:
• This layer is responsible for adding source and destination IP address.
• Network layer is responsible routing and delivering data.
• Data forwarding end to end.
Datalink Layer:
• This layer is responsible to adding source and destination MAC Address.
• This Data link layer is use to Data forwarding on the local link.
• In this Layer we have error correction.
• Data link we use Ethernet.
Physical Layer:
• This layer is nothing but as physical connection like cable or signal.
• It describes about stuff like voltages levels and physical data rates etc.
• Like everything what you touch as it is physical layer.
TCP/IP Model:
• It is a protocol which consists of multiple protocols include TCP (Transmission Control Protocol)
and IP (Internet Protocol).
• It is the main protocol used in computer operations today.
• Whereas the OSI Reference Model is conceptual, the TCP/IP used to transfer data in production
networks.
• TCP/IP is also have layered but does not use all of the OSI layers.
Let see
Email us: 4 of 8 WhatsApp Us : +966532984612
networkforyou4@gmail.com
Networkforyou
• As we can see the upper three layers are now combined to the "Application Layer". The
network layer is called the "Internet" layer and the bottom 2 layers are combined into the
"Network Access layer".
Email us: 5 of 8 WhatsApp Us : +966532984612
networkforyou4@gmail.com
Networkforyou
Let compare this two.
• Basically, it is the same idea for this both only some layers combined and different names.
• The physical and data link layer is combined into the network Access.
• The network layer is now the internet layer and the session, presentation and application layer
are combined into a single application layer.
Email us: 6 of 8 WhatsApp Us : +966532984612
networkforyou4@gmail.com
Networkforyou
Compare TCP to UDP:
As we know that we require a transport protocol to send our IP packets.
Transport Protocols that are used Most of the time to send our IP Packets are TCP or UDP
• TCP (Transmission Control Protocol)
• UDP (User Datagram Protocol)
TCP UDP
Connection Types: Connection Oriented Connectionless
Sequencing Yes No
Usage Downloads VOIP
Data Sending Slower Faster
TCP Header (20 or 60 Bytes):
Email us: 7 of 8 WhatsApp Us : +966532984612
networkforyou4@gmail.com
Networkforyou
Let discuss about all fields:
Source Port: This is 2 bytes (16 Bit) field that specifies the port number of the sender.
Destination Port: This is 2 bytes (16 Bit) field that specifies that port number of the receiver.
Sequence Number: It is 4 Bytes (32 Bit) and it indicates how much data is sent during the TCP session.
Acknowledgment Number: It is 4 Bytes (32 Bit) it is used by the receiver to request the next TCP
segments. This value will be the sequence number incremented by 1.
Do (data offset): It is 4-bit data offset field, also known as the header length. It indicates the length of
the TCP header so with this we know from where our actual data begins.
Reserved Field (RSV): It is 3 bits for the reserved field. It is unused and are always set to 0.
Flags: It is 9 bits we also call them control bits. Generally, we use to establish connections, send data
and terminate connection.
Window: It is 2 Bytes (16 bit) Window field specifies how many bytes the receiver is willing to receive.
Checksum: It is 2 Bytes (16 bits) used for a checksum to check if the TCP header is ok or not.
Urgent Pointer: It is 2 Bytes (16 bits) used for setting Urgent bit.
Options: This field is optional and can be anywhere between 0 and 320 bits.
UDP Header (8 Bytes):
Email us: 8 of 8 WhatsApp Us : +966532984612
networkforyou4@gmail.com
You might also like
- CCNA Interview Questions You'll Most Likely Be Asked: Job Interview Questions SeriesFrom EverandCCNA Interview Questions You'll Most Likely Be Asked: Job Interview Questions SeriesNo ratings yet
- Interview QuestionsDocument7 pagesInterview QuestionsaimslifeNo ratings yet
- Lecture 2 TCP, OSIDocument36 pagesLecture 2 TCP, OSImubeen naeemNo ratings yet
- Osi Model NotesDocument7 pagesOsi Model NotesSuman KumarNo ratings yet
- Week2-Application Layer FixDocument38 pagesWeek2-Application Layer FixBaekhyuneeNo ratings yet
- Network Chapter ThreeDocument46 pagesNetwork Chapter ThreeDaniel AshagrieNo ratings yet
- Osimodel 170406162300 PDFDocument42 pagesOsimodel 170406162300 PDFPvkkiy EceNo ratings yet
- TCP CharacteristicsDocument38 pagesTCP CharacteristicsgidumafayeraNo ratings yet
- CCNADocument14 pagesCCNAshripal singhNo ratings yet
- Socialism in EraDocument15 pagesSocialism in ErafesfNo ratings yet
- Presentation Topic: Tcp/Ip Presented By: Iftakhar Hussain Roll No: 2019-BSIT-043 Department: Cs & ItDocument14 pagesPresentation Topic: Tcp/Ip Presented By: Iftakhar Hussain Roll No: 2019-BSIT-043 Department: Cs & ItIftakhar HussainNo ratings yet
- Pundra University of Science & Technology: AssignmentDocument8 pagesPundra University of Science & Technology: AssignmentJahid HasanNo ratings yet
- Dypit Qbank AnsDocument8 pagesDypit Qbank Ansvanshikakubde2No ratings yet
- Chapter 4 - Internetworking-1Document91 pagesChapter 4 - Internetworking-1Goitom HaileNo ratings yet
- The OSI and TCPDocument8 pagesThe OSI and TCPSreejith VaneryNo ratings yet
- TCP:IP Reference ModelDocument12 pagesTCP:IP Reference Modelsocekay372No ratings yet
- Protocols Invovled in TcipDocument23 pagesProtocols Invovled in TcipFiremandeheavenly InamenNo ratings yet
- How OSI 7 Layer Model WorksDocument9 pagesHow OSI 7 Layer Model WorksRanjit SinghNo ratings yet
- Section 1:-Introduction To Networking Concepts NetworkingDocument35 pagesSection 1:-Introduction To Networking Concepts NetworkingManoj SainiNo ratings yet
- Chapter 2. Network Fundamental ConceptsDocument125 pagesChapter 2. Network Fundamental ConceptsBereketNo ratings yet
- Ccna Ipv4 AddressingDocument103 pagesCcna Ipv4 AddressingntimamaoNo ratings yet
- Internet and Protocol-3Document16 pagesInternet and Protocol-3Par VeenNo ratings yet
- It 1Document48 pagesIt 1mitalisgawadeNo ratings yet
- NetworkingDocument28 pagesNetworkingRichard SugboNo ratings yet
- Bcs 052 1Document19 pagesBcs 052 1ak9122459681No ratings yet
- Modulo 1Document172 pagesModulo 1Juan Jose Rios AnabiaNo ratings yet
- TCP IpDocument6 pagesTCP Ipkannanperu123No ratings yet
- What Is NetworkDocument7 pagesWhat Is Networkshripal singhNo ratings yet
- 5 Internet ProtocolsDocument41 pages5 Internet Protocolsstephenhilario3434No ratings yet
- Investigacion Modelo OSI, IP HeaderDocument5 pagesInvestigacion Modelo OSI, IP HeaderKnowhereDLNo ratings yet
- Fundamental Network ModelsDocument9 pagesFundamental Network ModelsSailas Khulumani TshabanguNo ratings yet
- Submitted To: Submitted By: Mrs. Ruchi Nanda Diksha Mangal Kajal JainDocument13 pagesSubmitted To: Submitted By: Mrs. Ruchi Nanda Diksha Mangal Kajal Jainpooja guptaNo ratings yet
- NetworkDocument82 pagesNetworkDavidoffNo ratings yet
- Network Protocol ArchitecturesDocument17 pagesNetwork Protocol Architecturesamash.emillyNo ratings yet
- The Bits and Bytes of Computer NetworkingDocument55 pagesThe Bits and Bytes of Computer NetworkingAravind Dhananjeyan83% (6)
- Lecture44 18807 Lecture567Document42 pagesLecture44 18807 Lecture567AbhayNo ratings yet
- Different Networking Systems Advantages and DisadvantagesDocument71 pagesDifferent Networking Systems Advantages and Disadvantagesshabir AhmadNo ratings yet
- Linux Unit 5Document22 pagesLinux Unit 5Adeefa AnsariNo ratings yet
- Tcp-Ip ModelDocument3 pagesTcp-Ip ModelTaimoor ZubairNo ratings yet
- 19-203-0802 Computer Commu-Nication and Net - Working: Professional Elective - IV SEM-8Document45 pages19-203-0802 Computer Commu-Nication and Net - Working: Professional Elective - IV SEM-8Ťèjùźź ȚèjùNo ratings yet
- The Internet Protocol SuiteDocument5 pagesThe Internet Protocol SuiteErwinMacaraigNo ratings yet
- CN Basics 5-6-7Document51 pagesCN Basics 5-6-7F. B. I.No ratings yet
- Secure Communication ProtocolsDocument33 pagesSecure Communication Protocolsdrrana.alshabiNo ratings yet
- OSI Reference Model and TCPDocument6 pagesOSI Reference Model and TCPKommireddy Siva Kumar100% (1)
- Unit 2 - Advance Computer Networks - WWW - Rgpvnotes.inDocument21 pagesUnit 2 - Advance Computer Networks - WWW - Rgpvnotes.inprince keshriNo ratings yet
- Networking Theory (Part 1)Document54 pagesNetworking Theory (Part 1)Irsan EhcNo ratings yet
- Module - 1Document89 pagesModule - 1Lochan Singh D - F37No ratings yet
- Ministry of Water Resources and ElectricityDocument26 pagesMinistry of Water Resources and ElectricitymeshelNo ratings yet
- It Sec NotesDocument74 pagesIt Sec NotesShamima AkhterNo ratings yet
- #17 TCP-IP ModelDocument11 pages#17 TCP-IP ModelPatel NayakNo ratings yet
- Network Programming (NP) Unit Wise MaterialsDocument139 pagesNetwork Programming (NP) Unit Wise MaterialsPrashanthNo ratings yet
- Unit IDocument172 pagesUnit IPraveen SaravananNo ratings yet
- Lecture.2.21-22-Network Models.Document30 pagesLecture.2.21-22-Network Models.murshidalbimaanyNo ratings yet
- Computer Networking Refers To Connected Computing Devices 222Document13 pagesComputer Networking Refers To Connected Computing Devices 222RAY COOLNo ratings yet
- Chapter 2:reference Model: Layer 7 - ApplicationDocument13 pagesChapter 2:reference Model: Layer 7 - ApplicationWatiri SteveNo ratings yet
- Network Protocol and TCPDocument5 pagesNetwork Protocol and TCPJoshua SantillanaNo ratings yet
- Data Communication and NetworkingDocument52 pagesData Communication and Networkingjanurag1993100% (1)
- OSI Model & Tcp/Ip ProtocolDocument31 pagesOSI Model & Tcp/Ip ProtocolSauabh SrivastavaNo ratings yet
- OSI and TCP IP MODELDocument29 pagesOSI and TCP IP MODELHarsh IsamaliaNo ratings yet
- 6 Marks in Question BankDocument22 pages6 Marks in Question BankPRIYAM XEROXNo ratings yet
- Cisco Meraki TrainingDocument3 pagesCisco Meraki TrainingPartha Sarathi NandiNo ratings yet
- Pre TestDocument3 pagesPre TestPartha Sarathi NandiNo ratings yet
- Pre TestDocument3 pagesPre TestPartha Sarathi NandiNo ratings yet
- IP Parameters For ClientsDocument9 pagesIP Parameters For ClientsPartha Sarathi NandiNo ratings yet
- IP AddressingDocument8 pagesIP AddressingPartha Sarathi NandiNo ratings yet
- 9.CDP and LLDPDocument11 pages9.CDP and LLDPPartha Sarathi NandiNo ratings yet
- 4 CISCO+RouterDocument12 pages4 CISCO+RouterPartha Sarathi NandiNo ratings yet
- 3 CISCO+SwitchDocument22 pages3 CISCO+SwitchPartha Sarathi NandiNo ratings yet
- 8 +vlanDocument18 pages8 +vlanPartha Sarathi NandiNo ratings yet
- AWS Architect Associate Course ContentDocument6 pagesAWS Architect Associate Course ContentAslam AnsariNo ratings yet
- CCNA - Icnd1.100 105.certification - study.guide.B07CJ81SNRDocument497 pagesCCNA - Icnd1.100 105.certification - study.guide.B07CJ81SNRJuan GarciaNo ratings yet
- CCNA Exploration Scope Sequence v4 0Document15 pagesCCNA Exploration Scope Sequence v4 0Evan WoodyNo ratings yet
- COMP1154 Week5 - Protocol-SuiteDocument46 pagesCOMP1154 Week5 - Protocol-SuiteSo SaNo ratings yet
- Networking FundaDocument4 pagesNetworking Fundar_p32sNo ratings yet
- CompTIA Network (N10-008) (Study Notes)Document202 pagesCompTIA Network (N10-008) (Study Notes)Tuong tran vinhNo ratings yet
- Technical English Class 2Document16 pagesTechnical English Class 2Tallyson ChavesNo ratings yet
- CompTIA Network Plus Training Kit Exam N10-005Document704 pagesCompTIA Network Plus Training Kit Exam N10-005bibivee50% (2)
- Unit 5 Complete NotesDocument54 pagesUnit 5 Complete NotesNikhil SuryawanshiNo ratings yet
- Networking MCQs Test For CITS CSADocument33 pagesNetworking MCQs Test For CITS CSARajesh KumarNo ratings yet
- Cyber Security Requirements and Related Standards - ABBDocument11 pagesCyber Security Requirements and Related Standards - ABBsriramv93No ratings yet
- Comparison and Contrast Between The OSI and TCP/IP ModelDocument44 pagesComparison and Contrast Between The OSI and TCP/IP Modeldody_7070No ratings yet
- Advanced Computer ArchitectureDocument12 pagesAdvanced Computer Architecturegangadhar_aspnetNo ratings yet
- Cisco Aci VMDCDocument39 pagesCisco Aci VMDCFaisal Abdul Gaffoor100% (1)
- 5 GDocument26 pages5 GRani ManugrahaniNo ratings yet
- DCN One Word 2023Document10 pagesDCN One Word 2023Sri GayuNo ratings yet
- Chapter 1. Introduction To TCPIP NetworkingDocument15 pagesChapter 1. Introduction To TCPIP NetworkingPoojitha NagarajaNo ratings yet
- Data Communications and Computer NetworksDocument38 pagesData Communications and Computer Networkskumararchana0% (1)
- Lecture 2 Introduction To Client Server ComputingDocument19 pagesLecture 2 Introduction To Client Server ComputingericNo ratings yet
- CCNA Cisco Network Fundamentals FINAL ExamDocument14 pagesCCNA Cisco Network Fundamentals FINAL Examsabriel69100% (2)
- System AdministratorDocument29 pagesSystem Administratorajitskhot108100% (9)
- Computer Networks Unit-I-NewDocument102 pagesComputer Networks Unit-I-NewPonnusamy S PichaimuthuNo ratings yet
- The Osi Model: International Standards Organization (ISO)Document29 pagesThe Osi Model: International Standards Organization (ISO)ミM I G H T YNo ratings yet
- Nodeb Data Configuration: InternalDocument57 pagesNodeb Data Configuration: InternalcurtiskamotoNo ratings yet
- Transport Layer: Pawan Kumar Assistantprofessor Gjus&T, HisarDocument26 pagesTransport Layer: Pawan Kumar Assistantprofessor Gjus&T, HisarG100 -vishantNo ratings yet
- 30i - Communication Specifications - V1.4Document96 pages30i - Communication Specifications - V1.4IbrahimMoussaM7No ratings yet
- Introduction To Transport LayerDocument57 pagesIntroduction To Transport LayerkjhofboaNo ratings yet
- Aws Load BalancingDocument2 pagesAws Load BalancingBharathNo ratings yet
- Network Communication ProtocolsDocument1 pageNetwork Communication ProtocolsArben Prruthi100% (1)
- Case Study of Tcp/ip and Osi ModelDocument13 pagesCase Study of Tcp/ip and Osi Modelsatyam goyalNo ratings yet
- EuroRadio - PaperDocument11 pagesEuroRadio - PaperpassworldgerezNo ratings yet