Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Bab 3
Uploaded by
nanndhini777Original Description:
Original Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Bab 3
Uploaded by
nanndhini777Copyright:
Available Formats
Jawapan Bab 3
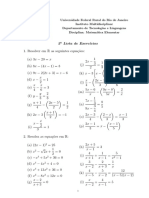
1. (a) y = 3x − 32 (b) p = 2g + 3ℎ − 5 5(x − 3y)
2. (e) =y [y]
2x
Perkara rumus f = vu 5(x – 3y)
Subject of formula l = πj2t F = ma u+v × 2x = y × 2x
seperti seperti 2x
as as
Faktor 5x − 15y = 2xy
l F f
penghubung 2xy + 15y = 5x
Relating factor 1 1
y(2x + 15) × = 5x ×
3. (a) m = 2n + 5 [n] 2x + 15 2x + 15
=m
2n + 5 5x
y=
=m–5
2n + 5 – 5 2x + 15
=m−5
2n 3
(f ) 4cd = [d]
2n ÷ 2
= (m − 5) ÷ 2 d
m–5 3
n= 4cd × d = ×d
2 d
(b) ab = x2 – b [b] 4cd2 =3
4cd ÷ 4c = 3 ÷ 4c
ab + b = x2 – b + b 3
ab + b = x2 d2 =
4c
b(a + 1) = x2 3
1 1 d =
b(a + 1) × = x2 × 4c
a+ 1 a+ 1
x2
b= 4. (a) p = rq2 + 2sq2 [q]
a+1
h j
(c) 3k = + [j ] rq2 + 2sq2 = p
2 3
q2(r + 2s) = p
h j
+ = 3k 1 1
2 3 q2(r + 2s) × =p×
r + 2s r + 2s
3h + 2j
= 3k p
2×3 q2 =
r + 2s
3h + 2j
× 6 = 3k × 6
6 p
2h + 2j = 18k
q2 =
r + 2s
3ℎ + 2j – 3h = 18k – 3h
2j = 18k – 3h p
q=
2j ÷ 2 = (18k – 3ℎ) ÷ 2 r + 2s
18k – 3h
j= k
j = 9k –
2
3h
(b) x = 5
y [y]
2
5ky = x
2
2 + 3r 2
(d) T= [r]
r
25k
2 + 3r
= x2
T×r = ×r y
r
Tr – 3r = 2 + 3r – 3r 25k
×
1 1
= x2 ×
1 y 25k 25k
1
r(T – 3) × =2× 1 x2
T–3 T–3 =
2 y 25k
r=
T–3 25k
y= 2
x
1 © Penerbitan Pelangi Sdn. Bhd.
Matematik Tingkatan 2 Bab 3
(c) V = 1 s²h [s] = 4 + 21
3 = 25
= 5
1 s²h = V
3
(b) x = 3(2 – y )
2
1 s²h × 3 = V × 3 z
3 h h = 3[2 – (–2)2]
–8
s² = 3V 3(–2)
h =
–8
3V = 6
s= 8
h
= 3
4
1 1 1
(c) + =
4 h k m
(d) V = pr 3 [r] 1 1 1
3 + =
2 k 3
4 3 1 1 1
pr = V = –
3 k 3 2
4 3 3 3 1 1
pr × =V× =–
3 4p 4p k 6
3V k = –6
r3 =
4p
4+p =t
(d)
3
r3 = 3
3V
4p
5q
4 + p = –1
5(–2)
r = 3V
3
4p 4 + p = –1(–10)
= 10
p = 10 – 4
(e) e = 1f [f ] = 6
(e) x = y²z
1 =e
f
64 = 2² z
4 z = 64
1f = e
2
2
64
z=
4
= 16
1 = e2
f z = 162
= 256
f = 12
e 6. (a) Keuntungan = Hasil jualan – Jumlah kos
Profit = Total sales – Total cost
(f ) p = h – 9
2 2
[h]
p = (4x + 5y) – (2.5x + 3y)
= 4x + 5y – 2.5x – 3y
h2 – 9 = p2
= 1.5x + 2y
h2 – 9 + 9 = p2 + 9
h2 = p2 + 9
h2 =
p2 + 9 p = (4 – 2.5)x + (5 – 3)y
= 1.5x + 2y
h =
p2 + 9
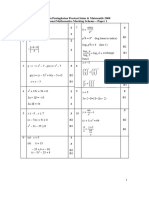
(b) (i) T = k + (k – 9)
5. (a) k =
y – 3h = 2k – 9
= 4 – 3(–7)
© Penerbitan Pelangi Sdn. Bhd. 2
Matematik Tingkatan 2 Bab 3
(ii) T = 2k – 9 (iii) Apabila / When
37 = 2k – 9 n + 4 = 89
2k = 37 + 9 n = 85
= 46 J = 3(85) + 6
k = 23 = 261
(c) (i) QR = 2
PR 3 Praktis Masteri 3
QR = PR2
3 BAHAGIAN A
2
= y
1. fg = h
2
3
L = Luas PRTU – Luas QRS 36
Area of PRTU – Area of QRS h 2
= fg
1 2y x 36
= xy – 1 21 2 ℎ 2
= 36fg
2 3 2
= xy – xy ℎ = 36fg
6
ℎ = 6 fg
= 5 xy
6 Jawapan / Answer : C
(ii) L = 5 xy 2. ab2c = 2a2 + 5c
6 −5 × (7)2 × c = 2(−5)2 + 5c
20 = (3)y5 −245c = 50 + 5c
6 250c = −50
20 = 5 y
2 c=− 1
5
y = 2 × 20
5 Jawapan / Answer : B
= 8
3. C = 1 πv2u
(d) (i) Jumlah bayaran 4
= Bayaran 5 jam pertama + Bayaran = 1 × π × 102 × 12
baki jam seterusnya 4
Total payment = 300π
= Payment for the first 5 hours + Payment for the
remaining hours Jawapan / Answer: C
K = 22 × 5 + 18(n – 5)
= 110 + 18(n – 5) BAHAGIAN B
(ii) K = 110 + 18(n – 5)
4. (i) 7 + q = 5p − 2q
= 110 + 18(9 – 5)
= 110 + 18(4) 5p = 27 + q + 2q
= 182 27 + 3q
p =
Maka, jumlah bayaran sewa kereta ialah 5
RM182.
(ii) 2q = 24q
2
Thus, the total payment of the car rental is RM182.
7p 5
(e) (i) Katakan nombor ganjil yang pertama = n 168pq = 10q
2
Let the first odd number = n
5
Tiga markah itu: p=
The three marks: 84q
n, n + 2, n + 4 5. (b)
J = n + (n + 2) + (n + 4) 5k
16 + 8g + g2 = 3 + h g=
J = 3n + 6 h(3 – h)
(ii) Julat / Range Julat = Markah tertinggi
= (n + 4) – n – Markah terendah 5k = 3g – hg
Range = Highest mark – Lowest mark g=h–1
=4 h
3 © Penerbitan Pelangi Sdn. Bhd.
Matematik Tingkatan 2 Bab 3
16 + 8g + g
2
=3+ℎ (b) (i)
6(3x) + 2(5y) = 92
18x + 10y = 92
(g + 4)
2
=3+ℎ
g+4 =3+ℎ (ii) 18(4) + 10y= 92
g =ℎ−1 72 + 10y = 92
10y = 92 – 72
5k = 3g − ℎg 10y = 20
h y=2
5k = 3gℎ − gℎ2
5k = gℎ(3 − ℎ) Bilangan coklat A
The number of chocolates A
g = 5k = 3(4) = 12 keping / pieces
h(3 – h)
Bilangan coklat B
(b) (i) ✓ The number of chocolates B
xy − 2z = 7x = 5(2) = 10 keping / pieces
xy − 7x = 2x (c) (i) p = 2(q + q + 2.5)
x(y − 7) = 2z p = 2(2q + 2.5)
x = 2z p = 4q + 5
y–7
(ii)
89 = 4q + 5
(ii) ✗ 4q = 89 – 5
xy − 2z = 7x 4q = 84
2z = xy − 7x q = 21
z = xy – 7x
2 Luas / Area = 21 × (21 + 2.5)
= 21 × 23.5
6. (a) (i)
c
= 493.5 m2
T
(ii)
(b) (i)
✗
(m + n)2 = pq
Fokus KBAT
5
(a) J = s + 2s atau / or J = 3s atau / or
2)
(1 + 2
= 9q
5 1 3
9 J = k + k atau / or J = k
=3 q 2 2
5
3 3
q = (b) J = K
5 2
q = 0.36 3
= (40) = 60
2
(ii) ✓
(c) Bilangan bola sepak / Number of soccer balls
(m + n)2 = J = 3s
pq
5 90 = 3s
(3 + 7) = p
2
s = 30
5
p = 100 Bilangan bola pingpong / Number of ping pong balls
5 = 30 × 2 = 60
p = 20
Bilangan bakul yang diperlukan untuk menyimpan
p = 400
30 biji bola sepak
The number of baskets needed to keep 30 soccer balls
BAHAGIAN C 30
= =3
7–m 10
7. (a) =p
2n Bilangan bakul yang diperlukan untuk menyimpan
7–m 60 biji bola pingpong
= p2
2n The number of baskets needed to keep 60 ping pong balls
7 – m = 2np2 60
= = 2.4 ≈ 3
–m = 2np2 – 7 25
m = 7 – 2np2 Maka, bilangan bakul yang diperlukan untuk
menyimpan kesemua bola ialah 3.
Therefore, the number of baskets needed to keep all balls is 3.
© Penerbitan Pelangi Sdn. Bhd. 4
You might also like
- Answers to Selected Problems in Multivariable Calculus with Linear Algebra and SeriesFrom EverandAnswers to Selected Problems in Multivariable Calculus with Linear Algebra and SeriesRating: 1.5 out of 5 stars1.5/5 (2)
- Model Paper PDFDocument11 pagesModel Paper PDFWan Nur AyunniNo ratings yet
- 2 Log X 5xy Xyz +Document8 pages2 Log X 5xy Xyz +primitivo rojo aguilarNo ratings yet
- Cbse Cl12 Ead Mathematics Solutions To Sample Paper 5Document9 pagesCbse Cl12 Ead Mathematics Solutions To Sample Paper 5sarthakbhardwaj075No ratings yet
- 05 Kunci Jawaban Dan Pembahasan Mat Viii ADocument86 pages05 Kunci Jawaban Dan Pembahasan Mat Viii ADicky KurniawanNo ratings yet
- Jawapan: Rumus AlgebraDocument5 pagesJawapan: Rumus AlgebraAwatif Hannani Binti Ahmad FahmiNo ratings yet
- Honors Algebra 2 Cheat SheetDocument1 pageHonors Algebra 2 Cheat SheetGreta WintersteenNo ratings yet
- Solusi Try Out Online Tka Saintek Xii Ipa (Kode: To-1113)Document9 pagesSolusi Try Out Online Tka Saintek Xii Ipa (Kode: To-1113)Suriname TurinasiNo ratings yet
- Hints & Solutions: Major Test (MT)Document8 pagesHints & Solutions: Major Test (MT)samkhya designsNo ratings yet
- MLT Set 1 ADocument3 pagesMLT Set 1 AAnnees SabreenaNo ratings yet
- AP® Exam Practice Questions For Chapter 2Document6 pagesAP® Exam Practice Questions For Chapter 2Sayar U A FourNo ratings yet
- Assorted Integration Exercise AnswerDocument1 pageAssorted Integration Exercise AnswermengleeNo ratings yet
- Algebraic Fractions RevisionDocument2 pagesAlgebraic Fractions RevisionGangka PeriasamyNo ratings yet
- Lista2 Elementar 2020Document3 pagesLista2 Elementar 2020Santana BetaNo ratings yet
- SPM Target Form 4: Chapter 1 Functions: Paper 1Document2 pagesSPM Target Form 4: Chapter 1 Functions: Paper 1radhi88No ratings yet
- Ans Prac 3Document3 pagesAns Prac 3Rowena HNo ratings yet
- Final: Problems and AnswersDocument3 pagesFinal: Problems and AnswersDoris riverosNo ratings yet
- Exercise 2Document2 pagesExercise 2Sanjay Kumar SinghNo ratings yet
- E - Iii: XerciseDocument4 pagesE - Iii: XerciseAnant DwivediNo ratings yet
- Solusi To Januari Tka Saintek 081 Set 2Document10 pagesSolusi To Januari Tka Saintek 081 Set 2Ananda DitaNo ratings yet
- 9.2 Substitution 7Document9 pages9.2 Substitution 7Hin Wa LeungNo ratings yet
- Integrales Incompletas IIDocument3 pagesIntegrales Incompletas IIneri74No ratings yet
- 11 Mathematics Straight Line Test 05 Answer k84vDocument4 pages11 Mathematics Straight Line Test 05 Answer k84vsparkling200No ratings yet
- Algebra 1 (Solutions)Document5 pagesAlgebra 1 (Solutions)Shashank BhardwajNo ratings yet
- Jawapan: Penilaian Akhir Tahun Kertas 1 1. (A) 3. (A)Document7 pagesJawapan: Penilaian Akhir Tahun Kertas 1 1. (A) 3. (A)Johari FikriNo ratings yet
- Type of Relation 1.2 Functions 1.4 Inverse FunctionDocument3 pagesType of Relation 1.2 Functions 1.4 Inverse Function纪泽勇No ratings yet
- 35 - PDFsam - 01 رياضيات 1-بDocument2 pages35 - PDFsam - 01 رياضيات 1-بMina AlbertNo ratings yet
- SPM Target Form 4: Chapter 1 Functions: Paper 1Document2 pagesSPM Target Form 4: Chapter 1 Functions: Paper 1Ybb GNo ratings yet
- 4 - 5 - Garis Lurus - Edisi 2018Document5 pages4 - 5 - Garis Lurus - Edisi 2018Nor Hijriyati IsmailNo ratings yet
- (Worksheet) Ungkapan Dan Persamaan Kuadratik 2 (Form 4)Document5 pages(Worksheet) Ungkapan Dan Persamaan Kuadratik 2 (Form 4)Ryan JeeNo ratings yet
- Gate Solved Paper - Me: y X X X P P P P X FX A B V Ydx P y X A B V XDX P XDX PDocument33 pagesGate Solved Paper - Me: y X X X P P P P X FX A B V Ydx P y X A B V XDX P XDX PHarish Jahan MohanNo ratings yet
- Jee Main 25 Jan Shift 1 Maths Memory Based Question Paper With SolutionDocument7 pagesJee Main 25 Jan Shift 1 Maths Memory Based Question Paper With SolutionHimanshu BhandariNo ratings yet
- © Science Exam Papers: Worked Solutions Edexcel C3 Paper IDocument3 pages© Science Exam Papers: Worked Solutions Edexcel C3 Paper I유리No ratings yet
- Penyelesaian Lengkap: Topik 7 (Tingkatan 4) : Kertas 1 1Document8 pagesPenyelesaian Lengkap: Topik 7 (Tingkatan 4) : Kertas 1 1Fatin IrdinaNo ratings yet
- 29 - PDFsam - 01 رياضيات 1-بDocument2 pages29 - PDFsam - 01 رياضيات 1-بMina AlbertNo ratings yet
- Chapt 3 - Differentiation IDocument29 pagesChapt 3 - Differentiation IJeremiah NakibingeNo ratings yet
- Maths Transition Pack QuestionsDocument18 pagesMaths Transition Pack QuestionsBenNo ratings yet
- Alevelsb p1 Ex2cDocument1 pageAlevelsb p1 Ex2cAnnaNo ratings yet
- Ial Pm1 Ex8gDocument1 pageIal Pm1 Ex8gNabeeha SyedNo ratings yet
- NCERT Solutions For Class 7 Maths 8may Chapter 12 Algebraic Expressions Exercise 12.1Document12 pagesNCERT Solutions For Class 7 Maths 8may Chapter 12 Algebraic Expressions Exercise 12.1arvinda1981No ratings yet
- NCERT Solutions For Class 7 Maths 8may Chapter 12 Algebraic ExpressionsDocument42 pagesNCERT Solutions For Class 7 Maths 8may Chapter 12 Algebraic ExpressionsVarun BOSS BOSSNo ratings yet
- 1b. Equations of Straight Lines - AnswersDocument3 pages1b. Equations of Straight Lines - AnswersMacwise IngabireNo ratings yet
- SPM Trial 2009 AddMath2 Ans PenangDocument17 pagesSPM Trial 2009 AddMath2 Ans PenangSimPorNo ratings yet
- خاصيات القوى+الحساب الحرفيDocument1 pageخاصيات القوى+الحساب الحرفيcherazerNo ratings yet
- Adobe Scan 13-Nov-2021Document10 pagesAdobe Scan 13-Nov-2021kiran lodikaNo ratings yet
- SPM - IntegrationDocument8 pagesSPM - IntegrationFatin NabilaNo ratings yet
- Mathematics As The Science of Patterns: AnswersDocument10 pagesMathematics As The Science of Patterns: Answersmathworld_0204No ratings yet
- Ans Sol JEEMain 2023 PH 2-10-04 2023 Morning MathematicsDocument4 pagesAns Sol JEEMain 2023 PH 2-10-04 2023 Morning MathematicsmoonNo ratings yet
- Selangor Add Math P1 Ans 2008Document3 pagesSelangor Add Math P1 Ans 2008gigi_panNo ratings yet
- Integration of Integrals Involving Quadratic FunctionsDocument12 pagesIntegration of Integrals Involving Quadratic FunctionsNaseeb AliiNo ratings yet
- SIMULTANEOUSEQUATIONS - Substitution12Document6 pagesSIMULTANEOUSEQUATIONS - Substitution12Zacariah SaadiehNo ratings yet
- 02s Coordinate Geometry and MatricesDocument36 pages02s Coordinate Geometry and MatricesCobraコブラNo ratings yet
- Perabola Ex1Document3 pagesPerabola Ex1Anant Preet SinghNo ratings yet
- Cheena Francesca Luciano-WORKSHEET-in-PRECALCULUS-Graphs-of-Trigonometric-FunctionDocument2 pagesCheena Francesca Luciano-WORKSHEET-in-PRECALCULUS-Graphs-of-Trigonometric-FunctionCheena Francesca LucianoNo ratings yet
- Grade 10 Graded Classwork October 2020 Instructions: Answer ALL QuestionsDocument3 pagesGrade 10 Graded Classwork October 2020 Instructions: Answer ALL QuestionsTyrell RobinsonNo ratings yet
- P2 Trial 2019 (MS) SPI SerembanDocument5 pagesP2 Trial 2019 (MS) SPI SerembanPeng Peng KekNo ratings yet
- Suggested Answer: Additional MathematicsDocument20 pagesSuggested Answer: Additional Mathematicsapi-19650882No ratings yet
- Integrals Wo WatermarkDocument12 pagesIntegrals Wo Watermarkmeghashyam.raju1210No ratings yet
- EcuacionesDocument3 pagesEcuacionesSara Ruth Bernal GuzmanNo ratings yet
- E1Ageo CDocument2 pagesE1Ageo Cfun snapsNo ratings yet
- Power System RelayingDocument4 pagesPower System RelayingfadihsNo ratings yet
- Boonrak 417-Task 1Document4 pagesBoonrak 417-Task 1Teerapol KhoonburanNo ratings yet
- MKTG103 - Lesson 1Document24 pagesMKTG103 - Lesson 1Chona MarieNo ratings yet
- Ihtm Rohtak Syllabus BHMDocument60 pagesIhtm Rohtak Syllabus BHMManish PooniaNo ratings yet
- Sumilang Et AlDocument277 pagesSumilang Et AlAngelica AguilarNo ratings yet
- Hicub Synergies With Ness Ii: Overall TaskDocument5 pagesHicub Synergies With Ness Ii: Overall TaskNew England SustainabilityNo ratings yet
- Signal Toothpaste: Group (D) MembersDocument23 pagesSignal Toothpaste: Group (D) MembersReem AmrNo ratings yet
- Mass Marketing EmptyDocument4 pagesMass Marketing EmptyvalenciaNo ratings yet
- The Product Life CycleDocument13 pagesThe Product Life CycleishakembhaviNo ratings yet
- Syllabus EntrepreneurshipDocument12 pagesSyllabus EntrepreneurshipBhaskar SharmaNo ratings yet
- Executive SummaryDocument23 pagesExecutive SummarySuresh KumarNo ratings yet
- Question Bank - Practical QuestionsDocument10 pagesQuestion Bank - Practical QuestionsNeel KapoorNo ratings yet
- CH - 1Document29 pagesCH - 1Say KyekNo ratings yet
- Summary Chapter 6: Entrepreneurship and Starting Small BusinessDocument19 pagesSummary Chapter 6: Entrepreneurship and Starting Small BusinessriskaNo ratings yet
- CH 5. Reach Beyond Existing DemandDocument10 pagesCH 5. Reach Beyond Existing Demandtaghavi1347No ratings yet
- Oreo Product MarketingDocument19 pagesOreo Product MarketingTapan JariwalaNo ratings yet
- Marketing Tools and Techniques Assignment: Amity University, Uttar PradeshDocument7 pagesMarketing Tools and Techniques Assignment: Amity University, Uttar PradeshKanika AroraNo ratings yet
- Sample Cease & Desist LetterDocument2 pagesSample Cease & Desist Letterjsconrad12No ratings yet
- Tata Tritvam Assigmnet by Sarwar AlamDocument19 pagesTata Tritvam Assigmnet by Sarwar AlammdsarwaralamNo ratings yet
- Print Summer2017Document92 pagesPrint Summer2017Celeo Ramos100% (1)
- Chipotle 1Document13 pagesChipotle 1cpaking23No ratings yet
- TagsDocument7 pagesTagsdangminhNo ratings yet
- Domino's Pizza Inc.: DPZ Delivers ConsistencyDocument26 pagesDomino's Pizza Inc.: DPZ Delivers ConsistencySanket Maheshwari0% (1)
- Reinvention:: Taking Personal Advantage of The Project Failure ProblemDocument4 pagesReinvention:: Taking Personal Advantage of The Project Failure Problemjwpaprk1No ratings yet
- BA115 Carpenter PPT Chapter 05fill - inDocument40 pagesBA115 Carpenter PPT Chapter 05fill - inJayadatta Shreepada SNo ratings yet
- Unit Test 2 Term 1 S4 (2022 - 2023)Document3 pagesUnit Test 2 Term 1 S4 (2022 - 2023)Olieve Jacqueline FangNo ratings yet
- HND Business AssignmentDocument2 pagesHND Business AssignmentShahzaib AzharNo ratings yet
- Week 6 Entrepreneurial Marketing PDFDocument29 pagesWeek 6 Entrepreneurial Marketing PDFAsifIsmayilovNo ratings yet
- KnowMore Test TasksDocument6 pagesKnowMore Test TasksMonnu montoNo ratings yet
- Project On Mahindra TractorsDocument55 pagesProject On Mahindra TractorsVineeth Vijaykumar83% (18)