Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Cheat Sheet 2
Uploaded by
gaming accountOriginal Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Cheat Sheet 2
Uploaded by
gaming accountCopyright:
Available Formats
test z-test single-t ind-1 chi-square
when to use: - 1 sample mean - no pop. SD - compare 2 sample means - nominal IV
- pop. parameters - compare 1 sample mean to - no pop. parameters - frequency data
- pop. SD another value
variables: pop parameters - 𝝁 = other value - M = sample mean - N = total # of responses
- 𝝁 = pop. mean - M = sample mean - k = # of columns, cells,
- 𝝈 = pop. SD - there is SD choices
- M = mean - fo = freq. obs.
- SD = standard dev. - fe = freq. exp.
(# of pp. by chance)
formula: 𝑀−µ 𝑀−µ 𝑀1−𝑀2 fe = (# row) + (# col) ÷
𝑧 = 𝑆𝐸𝑚
𝑡= 𝑒𝑠𝑡. 𝑆𝐸𝑚
𝑡= 𝑒𝑠𝑡. 𝑆𝐸𝑑𝑖𝑓𝑓 total #
σ 𝑆𝐷 2
2
𝑆𝐸𝑚 = 𝑒𝑠𝑡. 𝑆𝐸𝑀 = 𝑆𝐷𝑎 2 𝑆𝐷𝑏 2
𝑥 =
(𝑓𝑜−𝑓𝑒)
𝑁 𝑁−1 𝑆𝐸𝑑 = ( ) +( ) 𝑓𝑒
𝑁𝑎−1 𝑁𝑏−1
df n/a 𝑑𝑓 = 𝑛 − 1 𝑑𝑓 = (𝑁𝑎 + 𝑁𝑏) − 2 𝑑𝑓 = 𝑘 − 1
effect size (𝑀−µ) 𝑡 𝑑 = 𝑡( 𝑁𝑎 + 𝑁𝑏/(𝑁𝑎 * 𝑁𝑏)
𝑑= σ
𝑑= 𝑥
2
𝑁 𝑑= 2
s: 0.2 𝑁+𝑥
m: 0.5
l: 0.8
conf. inter. C.I = M ± Zcrit. (SEm) C.I = M ± Tcrit. (Est. SEm) C.I = (Ma-Mb) ± Tcrit. (Est. SEdiff) n/a
steps 1. calc SEm 1. calc est. SEm 1. calc SEdiff 1. draw contingency table
2. calc z 2. calc t 2. calc t 2. calc fe for each cell
3. compare z and z critical 3. calc df 3. calc df 2
3. calc 𝑥 for each cell
0.05 or 95% +- 1.96 4. compare t and t critical 4. compare t and t critical and add everything
0.01 or 99% +- 2.58 5. calc effect size (d) (if t beats 5. calc effect size (if t beats critical) 4. calc df
4. calc effect size (if z beats critical) 2 2
critical) 5. compare 𝑥 and 𝑥
critical
6. calc effect size
keywords - population SD - random sample - is there a sig. diff. between ____ and - yes or no outcome
- parameter mean _____ - counts not scores
- compared on continuous outcome
concepts - difference between M and 𝝁 - difference between M and 𝝁 or - difference between 2 sample means - differences between
when you have 𝝈 between M and another value observed and expected
frequencies
You might also like
- CombinepdfDocument2 pagesCombinepdfgaming accountNo ratings yet
- CombinepdfDocument2 pagesCombinepdfgaming accountNo ratings yet
- CombinepdfDocument2 pagesCombinepdfgaming accountNo ratings yet
- CHAPTER 3 - Laplace Transforms (2B) (1)Document7 pagesCHAPTER 3 - Laplace Transforms (2B) (1)Camille SalmasanNo ratings yet
- 4) AC CircuitsDocument40 pages4) AC CircuitsS x DNo ratings yet
- Formula SheetDocument1 pageFormula SheetNoemi LayogNo ratings yet
- Electrical Simulation LabDocument51 pagesElectrical Simulation LabRithwakNo ratings yet
- DC and AC Power Fundamentals SAPDocument51 pagesDC and AC Power Fundamentals SAPPaul Danniel AquinoNo ratings yet
- Csitnepal: UNIT:-1 Principles of Analyzing Algorithms and ProblemsDocument83 pagesCsitnepal: UNIT:-1 Principles of Analyzing Algorithms and ProblemsKiran KhanalNo ratings yet
- Today:: + Cos + Sin ,:, Arg Arg + Arg +Document20 pagesToday:: + Cos + Sin ,:, Arg Arg + Arg +IbrahimNo ratings yet
- Daily Number of New Covid Cases in UKDocument37 pagesDaily Number of New Covid Cases in UKCəvahir AğazadəNo ratings yet
- Field From A Uniformly Charged Disk Solutions: ElectricDocument2 pagesField From A Uniformly Charged Disk Solutions: ElectricNarendra KumarNo ratings yet
- Csmodel NotesDocument79 pagesCsmodel NotesbrentsoanNo ratings yet
- Ms of Dispersion - Part 3Document4 pagesMs of Dispersion - Part 3Kunal DesaiNo ratings yet
- Stat 5002 Final Exam Formulas W 21Document7 pagesStat 5002 Final Exam Formulas W 21PaolaCastelwhiteNo ratings yet
- 4.2 Differentiation in Parameters - Part 1Document4 pages4.2 Differentiation in Parameters - Part 1Jericho CunananNo ratings yet
- Lecture 5Document6 pagesLecture 5Debayan BiswasNo ratings yet
- Equation Sheet SemesterDocument2 pagesEquation Sheet SemesterakNo ratings yet
- Chap 9 Simple Harmonic Motion SummaryDocument2 pagesChap 9 Simple Harmonic Motion SummarySyakirah MunirNo ratings yet
- Machine Learning and Pattern Recognition Week 8_backpropDocument8 pagesMachine Learning and Pattern Recognition Week 8_backpropzeliawillscumbergNo ratings yet
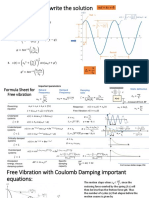
- Formula Sheet For Free VibrationDocument5 pagesFormula Sheet For Free VibrationCesar MolinaNo ratings yet
- Sph4ue - Formula Sheet 2023Document2 pagesSph4ue - Formula Sheet 2023speedyz3377No ratings yet
- Stat2 2023 Syllabus B v1.0 Weeks 5-6-7Document41 pagesStat2 2023 Syllabus B v1.0 Weeks 5-6-7Andrei PopaNo ratings yet
- Math 4361 Homework 1 Student Herp McderpDocument4 pagesMath 4361 Homework 1 Student Herp McderpJuliana GomezNo ratings yet
- Tutorial 3 2020 - MemoDocument14 pagesTutorial 3 2020 - MemoLouise FrylinckNo ratings yet
- Calc 2.10 PacketDocument3 pagesCalc 2.10 Packetha haNo ratings yet
- Calculus 1 With Analytic Geometry Bsed - 2Document20 pagesCalculus 1 With Analytic Geometry Bsed - 2Dindo HiocoNo ratings yet
- hw1 - Solution Grade 100Document6 pageshw1 - Solution Grade 100Ravid CohenNo ratings yet
- Lec 9Document5 pagesLec 9شوقي الزوارNo ratings yet
- math project activities 1Document6 pagesmath project activities 1api-696786602No ratings yet
- Aadt or Adt ×K DHV ×D DDHVDocument9 pagesAadt or Adt ×K DHV ×D DDHVnasserNo ratings yet
- Eda FormulasDocument2 pagesEda FormulasLee Angus SantosNo ratings yet
- Chapter 2 Basic Features: 2.1 Simple MathDocument10 pagesChapter 2 Basic Features: 2.1 Simple MathSameer ShaikhNo ratings yet
- Kinematics problemsDocument4 pagesKinematics problemsFiyah Can Ttp RiecaNo ratings yet
- Continuous Probability Distribution: Business Statistics Prepared By: Ikram-E-KhudaDocument31 pagesContinuous Probability Distribution: Business Statistics Prepared By: Ikram-E-KhudaAsharNo ratings yet
- Analog - Module - 2 - Rectifiers - ECE 1001Document11 pagesAnalog - Module - 2 - Rectifiers - ECE 1001sanjit0907_982377739No ratings yet
- Exponential FunctionDocument4 pagesExponential FunctionErica Mamauag100% (1)
- Where: A and B Are Real Numbers. I.E. & (Real Set) C: Complex No. I: Imaginary Unit For WhichDocument4 pagesWhere: A and B Are Real Numbers. I.E. & (Real Set) C: Complex No. I: Imaginary Unit For WhichAdnan NajemNo ratings yet
- Computing Roots Modulo PDocument3 pagesComputing Roots Modulo PoliverjohnboydNo ratings yet
- Physics 12 Data SheetDocument3 pagesPhysics 12 Data SheetfesNo ratings yet
- Formula Scanner Class 10 New PatternDocument1 pageFormula Scanner Class 10 New Patternnitesh kotianNo ratings yet
- 9856 S - 2020 Jan Algebra 2 Indi Test SOLUTIONSDocument5 pages9856 S - 2020 Jan Algebra 2 Indi Test SOLUTIONSBhav JainNo ratings yet
- Many Cheerful FactsDocument17 pagesMany Cheerful Factsbobmiller94No ratings yet
- Formula Notes Industrial Engin 891686837008983Document30 pagesFormula Notes Industrial Engin 891686837008983Somu SinghNo ratings yet
- Compendium List of Formulae: 1. Number SystemDocument30 pagesCompendium List of Formulae: 1. Number SystemNishantNo ratings yet
- Measures of Central Tendency and Partition ValuesDocument4 pagesMeasures of Central Tendency and Partition ValuesAditya MessiNo ratings yet
- Chapter 1 Simple Linear Regression ModelDocument2 pagesChapter 1 Simple Linear Regression ModelNermine LimemeNo ratings yet
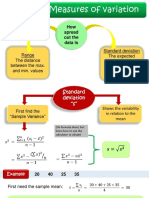
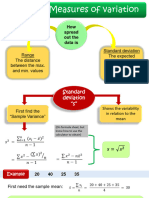
- Sec 2.5 - Measures of VariabilityDocument8 pagesSec 2.5 - Measures of VariabilitySiinozuko MasentseNo ratings yet
- SpeedMath ShortCutsVol2Document15 pagesSpeedMath ShortCutsVol2Karan KakkarNo ratings yet
- Isolate The Following Variable From Each of The Equations.: V + A T V + 2a DDocument1 pageIsolate The Following Variable From Each of The Equations.: V + A T V + 2a DDr. Sanjay kajalNo ratings yet
- Sec 2.5 - Measures of Variability - 2021Document8 pagesSec 2.5 - Measures of Variability - 2021sthembisoandile059No ratings yet
- Advance Mathematical Physics in Cylindrical CoordinatesDocument6 pagesAdvance Mathematical Physics in Cylindrical CoordinatesRaufAhmedNo ratings yet
- Inverse Trigonometric FunctionDocument15 pagesInverse Trigonometric FunctionEric BulalaNo ratings yet
- DERIVATIVEDocument8 pagesDERIVATIVENoel S. De Juan Jr.No ratings yet
- attachment_1 (39)Document21 pagesattachment_1 (39)anthony.onyishi.242680No ratings yet
- Marking Scheme of MAT1164Document10 pagesMarking Scheme of MAT1164KhabiNo ratings yet
- A-level Maths Revision: Cheeky Revision ShortcutsFrom EverandA-level Maths Revision: Cheeky Revision ShortcutsRating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (8)
- Trigonometric Ratios to Transformations (Trigonometry) Mathematics E-Book For Public ExamsFrom EverandTrigonometric Ratios to Transformations (Trigonometry) Mathematics E-Book For Public ExamsRating: 5 out of 5 stars5/5 (1)
- Application of Derivatives Tangents and Normals (Calculus) Mathematics E-Book For Public ExamsFrom EverandApplication of Derivatives Tangents and Normals (Calculus) Mathematics E-Book For Public ExamsRating: 5 out of 5 stars5/5 (1)
- Senior High Statistics and Probability Lecture Note SummaryDocument7 pagesSenior High Statistics and Probability Lecture Note SummaryKyle BARRIOSNo ratings yet
- Week 6 Central Limit Theorem NotesDocument32 pagesWeek 6 Central Limit Theorem NotesNicole Anne SocoNo ratings yet
- Stats Yr2 Chapter 3::: Normal DistributionDocument46 pagesStats Yr2 Chapter 3::: Normal DistributionmethNo ratings yet
- Topic Wise s2Document82 pagesTopic Wise s2Rayalakshmi RajyalakshmiNo ratings yet
- Sampling Distribution of Sample MeansDocument33 pagesSampling Distribution of Sample MeansDia CoraldeNo ratings yet
- Probability and Statistics 2019 June QBDocument16 pagesProbability and Statistics 2019 June QBsravaniNo ratings yet
- Simple Random SamplingDocument18 pagesSimple Random Samplinghimanshu pachouriNo ratings yet
- Sampling Distributions ExplainedDocument8 pagesSampling Distributions ExplainedRizah HernandezNo ratings yet
- 2019 JC2 H2 Math SA2 Nanyang JCDocument48 pages2019 JC2 H2 Math SA2 Nanyang JCJasmine TanNo ratings yet
- Reading 5 Sampling and EstimationDocument29 pagesReading 5 Sampling and EstimationARPIT ARYANo ratings yet
- Short Quiz StatDocument21 pagesShort Quiz StatKeziah Ventura69% (13)
- Bbs14e PPT ch07Document31 pagesBbs14e PPT ch07Nguyen Thi Nhung (K16HL)No ratings yet
- Statistics 1B Lecture Notes: Author: T. FarrarDocument129 pagesStatistics 1B Lecture Notes: Author: T. FarrarEnKay 11No ratings yet
- Statistics and ProbabilityDocument20 pagesStatistics and ProbabilityAngel Lorayne SalvacionNo ratings yet
- Stat and Prob - Q3 Week 2 - Module 2Document18 pagesStat and Prob - Q3 Week 2 - Module 2JessicaNo ratings yet
- NJC Sampling Lecture NotesDocument24 pagesNJC Sampling Lecture NotesbhimabiNo ratings yet
- Sampling Distribution of The Sample Mean (When The Variance Is Unknown)Document13 pagesSampling Distribution of The Sample Mean (When The Variance Is Unknown)Yuki MuraNo ratings yet
- 4.1 Sampling Distributions of Sample MeansDocument10 pages4.1 Sampling Distributions of Sample MeansOlebogengPNo ratings yet
- IGNOU Statistics Guide Explains Hypothesis TestingDocument16 pagesIGNOU Statistics Guide Explains Hypothesis TestingKingKaliaNo ratings yet
- Jntuh Cse 2-1 r13 SyllabusDocument11 pagesJntuh Cse 2-1 r13 SyllabusVinay KandulaNo ratings yet
- Sampling Distribution and StatisticsDocument15 pagesSampling Distribution and StatisticsNatnael AsfawNo ratings yet
- Statistics and Probability: Quarter 3 - Module 16: Identifying Sampling Distribution of StatisticsDocument27 pagesStatistics and Probability: Quarter 3 - Module 16: Identifying Sampling Distribution of StatisticsMoreal QazNo ratings yet
- Week 7 STUDY GUIDE Statistics Probability 1Document16 pagesWeek 7 STUDY GUIDE Statistics Probability 1Hannah MartinezNo ratings yet
- Robust Statistics - How Not To Reject OutliersDocument5 pagesRobust Statistics - How Not To Reject OutliersEduardoNo ratings yet
- 15chap 3.1 Sampling DistributionDocument33 pages15chap 3.1 Sampling DistributionNyah MargarettNo ratings yet
- Numerical Descriptive TechniquesDocument65 pagesNumerical Descriptive Techniquesa,sajsdoqjsNo ratings yet
- Isom 2500Document58 pagesIsom 2500JessicaLiNo ratings yet
- Munier Hossain - Making Sense of Medical Statistics (2021, Cambridge University Press) - Libgen - LiDocument199 pagesMunier Hossain - Making Sense of Medical Statistics (2021, Cambridge University Press) - Libgen - LijonahiNo ratings yet
- Statistics For The Behavioral Sciences 10th Edition Gravetter Test BankDocument19 pagesStatistics For The Behavioral Sciences 10th Edition Gravetter Test Bankedithelizabeth5mz18100% (26)
- Analisis KlasifikasiDocument41 pagesAnalisis KlasifikasihastiaNo ratings yet