Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Pka Table
Uploaded by
Eman Badry0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
5 views1 pagePka values
Original Title
pka_table
Copyright
© © All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentPka values
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
5 views1 pagePka Table
Uploaded by
Eman BadryPka values
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
You are on page 1of 1
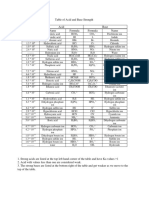
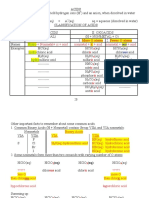
• Acid and base strengths
acid pKa base pKb
HClO4 perchloric acid ∼ −7 ClO− 4 ∼ 21
HCl hydrogen chloride ∼ −3 Cl− ∼ 17
H2 SO4 sulfuric acid ∼ −3 HSO− 4 ∼ 17
HNO3 nitric acid −1 NO− 3 15
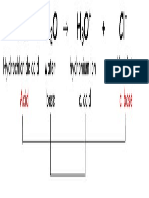
H3 O+ hydronium ion 0 H2 O 14
H2 SO3 sulfurous acid 1.8 HSO− 3 12.2
HSO− 4 bisulfate 1.9 SO2−
4 12.1
H3 PO4 phosphoric acid 2.12 H2 PO− 4 11.88
[Fe(H2 O)6 ]3+ aquo ferric ion 2.10 [Fe(H2 O)5 OH]2+ 11.90
HF hydrofluoric acid 3.2 F− 10.8
CH3 COOH acetic acid 4.7 CH3 COO− 9.3
[Al(H2 O)6 ]3+ aquo aluminum ion 4.9 [Al(H2 O)5 OH]2+ 9.1
H2 CO3 total dissolved CO2 a 6.3 HCO− 3 7.7
H2 S hydrogen sulfide 7.04 HS− 6.96
H2 PO− 4 dihydrogen phosphate 7.2 H2 PO2− 4 6.8
HSO− 3 bisulfite ion 7.21 SO2−
3 6.79
HOCl hypochlorous acid 8.0 OCl− 6.0
HCN hydrogen cyanide 9.2 CN− 4.8
H3 BO4 boric acid 9.30 B(OH)− 4 4.70
NH+ 4 ammonium ion 9.25 NH3 4.75
Si(OH)4 o-silicic acid 9.50 SiO(OH)− 3 4.50
HCO− 3 bicarbonate 10.33 CO2−3 3.67
HPO2− 4 hydrogen phosphate 12.32 PO3−
4 1.67
SiO(OH)− 3 silicate 12.6 SiO2 (OH)2− 2 1.4
H2 O water b 14 OH− 0
HS− bisulfide c ∼ 19 S2− ∼ −5
NH3 ammonia ∼ 23 NH− 2 ∼ −9
OH− hydroxide ion ∼ 24 O2− ∼ −10
a The acid H CO is only a minority species in aqueous carbon dioxide solutions, which contain mainly CO
2 3 2(aq) .
The pKa of 6.3 that is commonly given is calculated on the basis of the total CO2 in the solution. The true pKa of
H2 CO3 is about 3.5.
b If water is acting as a solute, as it must if the acid strength of H O is being compared with that of other very
2
weak acids, then pKa ≈ 16 should be used. See J. Chem. Education 1990: 67(5) 386-388.
c Many tables still give 14 as pK for H S; this is now known to be incorrect.
2 2
Table 1: pK values of acids and bases in aqueous solutions at 25 ◦ C
Chem1 General Chemistry Reference Text 7 Acid-base equilibria and calculations
You might also like
- An Analysis of Stravinsky's Symphony of Psalms Focusing On Tonality and HarmonyDocument68 pagesAn Analysis of Stravinsky's Symphony of Psalms Focusing On Tonality and Harmonyr-c-a-d100% (2)
- Ansys ManualDocument124 pagesAnsys ManualUdamanNo ratings yet
- Acid-Base TitrationDocument150 pagesAcid-Base TitrationKukkiboNo ratings yet
- Scania SOPS ParametersDocument32 pagesScania SOPS Parametersjose breno vieira silva89% (19)
- Acids and Bases NotesDocument17 pagesAcids and Bases NotesNap DoNo ratings yet
- Defects in Fusion WeldingDocument83 pagesDefects in Fusion WeldingBalakumar100% (1)
- ISO 10110 Optical Drawing StandardsDocument17 pagesISO 10110 Optical Drawing Standardskalvino314No ratings yet
- Schwarzer Schmarsow - The Emergence of Architectural Space August Schmarsows Theory of RaumgestaltungDocument15 pagesSchwarzer Schmarsow - The Emergence of Architectural Space August Schmarsows Theory of RaumgestaltungDimitra BilliaNo ratings yet
- Product Position and Overview: Infoplus.21 Foundation CourseDocument22 pagesProduct Position and Overview: Infoplus.21 Foundation Courseursimmi100% (1)
- PVD PreloadingDocument104 pagesPVD PreloadingAkriti Kothiala100% (1)
- Power Semiconductor Applications - Philips-NXPDocument609 pagesPower Semiconductor Applications - Philips-NXPnanditonanaman100% (2)
- Castable RefractoryDocument4 pagesCastable RefractorySarbajitMannaNo ratings yet
- Wärtsilä NOXDocument35 pagesWärtsilä NOXDeepesh MerchantNo ratings yet
- Bok:978 94 017 9664 4Document215 pagesBok:978 94 017 9664 4fivalen1_443898619100% (2)
- Solutions 222Document8 pagesSolutions 222estellasr00No ratings yet
- Answers Acids and Bases Review 12-13 2Document2 pagesAnswers Acids and Bases Review 12-13 2Noel SiudutNo ratings yet
- APChemDocument8 pagesAPChemMacie CareyNo ratings yet
- Table of Acid and Base StrengthDocument1 pageTable of Acid and Base StrengthNgoc Tham VoNo ratings yet
- Chem 102 Week 5Document65 pagesChem 102 Week 5CAILA CACHERONo ratings yet
- Name: KEY Nomenclature - Covalent (Molecular) Compounds Part A: Name The Following Covalent Compounds. Part B: Write The Chemical Formula For Each of The Following CompoundsDocument2 pagesName: KEY Nomenclature - Covalent (Molecular) Compounds Part A: Name The Following Covalent Compounds. Part B: Write The Chemical Formula For Each of The Following CompoundsTrung LuongNo ratings yet
- Ebook Chemical Principles The Quest For Insight 7Th Edition Atkins Solutions Manual Full Chapter PDFDocument67 pagesEbook Chemical Principles The Quest For Insight 7Th Edition Atkins Solutions Manual Full Chapter PDFJaniceMarqueznxed100% (11)
- Chem Principles 7e ISM Focus 06 Even FINALDocument112 pagesChem Principles 7e ISM Focus 06 Even FINALSelma MeloNo ratings yet
- Solution 805196Document4 pagesSolution 805196scNo ratings yet
- Chemistry SummaryDocument22 pagesChemistry SummaryEmma Isabella GraceNo ratings yet
- Activity 2.1 - Acids and Bases NMNMDocument3 pagesActivity 2.1 - Acids and Bases NMNMClarise CanANo ratings yet
- Reflection Worksheet - Balancing ReactionsDocument2 pagesReflection Worksheet - Balancing ReactionsParth NataniNo ratings yet
- For JEE Aspirants: Complete Inorganic Chemistry ReactionsDocument56 pagesFor JEE Aspirants: Complete Inorganic Chemistry ReactionsLakshmi AnandNo ratings yet
- Acid and BaseDocument7 pagesAcid and BaseSHARMAN A/L KAILASA PILLAI MUDALIAR MoeNo ratings yet
- Acids, Bases and SaltsDocument8 pagesAcids, Bases and Saltsaakashb1918No ratings yet
- Tugas Transcript Naskah-DRA-20036074-Shafira Dwinanda JafandevaDocument2 pagesTugas Transcript Naskah-DRA-20036074-Shafira Dwinanda JafandevaShafira DwinandaNo ratings yet
- Chapter 3 Acid - BaseDocument98 pagesChapter 3 Acid - BaseNhan PhướcNo ratings yet
- IOC All ReactionsDocument56 pagesIOC All ReactionsKeerthana MNo ratings yet
- Chapter 3 Acid - BaseDocument98 pagesChapter 3 Acid - BaseKhoa Nguyen Viet DangNo ratings yet
- Calventas Lab ReportDocument5 pagesCalventas Lab ReportGodwayneNo ratings yet
- Asam BasaDocument13 pagesAsam Basaaliefyan4769No ratings yet
- Chapter 3 Acid - BaseDocument98 pagesChapter 3 Acid - BasePHƯƠNG ĐẶNG YẾNNo ratings yet
- Balance EquationsDocument1 pageBalance EquationsLayna HarrisonNo ratings yet
- Ib Chem Answers 8Document2 pagesIb Chem Answers 8baguette baguettoNo ratings yet
- Chap 05 - Ionic Equilibrium MindNotes by Arnav SirDocument10 pagesChap 05 - Ionic Equilibrium MindNotes by Arnav SirKhushi RoyNo ratings yet
- Balancing Equations: Practice ProblemsDocument10 pagesBalancing Equations: Practice ProblemsAyesha TauseefNo ratings yet
- PKa Table of AcidsDocument1 pagePKa Table of AcidsGuery SaenzNo ratings yet
- 12e1 PDFDocument5 pages12e1 PDFwastequestNo ratings yet
- 12th Chemistry CH-4NotesDocument6 pages12th Chemistry CH-4NotesMajid HafeezNo ratings yet
- Chapter 7 Acid-Base ReactionDocument111 pagesChapter 7 Acid-Base ReactionUMMU MARDHIAH ABDUL HALIMNo ratings yet
- Balancing Questions PracticeDocument5 pagesBalancing Questions PracticeZunaira SafdarNo ratings yet
- Balancing Questions PracticeDocument5 pagesBalancing Questions PracticeZunaira SafdarNo ratings yet
- Balancing Equations: Practice ProblemsDocument10 pagesBalancing Equations: Practice ProblemsSheryl Nishmae Bernardo SantosNo ratings yet
- တက္ကသိုလ်ဝင်တန်း ဓာတုဗေဒ Dr.Soe Kyaw KyawDocument322 pagesတက္ကသိုလ်ဝင်တန်း ဓာတုဗေဒ Dr.Soe Kyaw KyawKhin OosweNo ratings yet
- Ap ChemDocument2 pagesAp ChemEthan NguyenNo ratings yet
- 1.11 CHEM FINAL Chapter 11 Sulfuric AcidDocument21 pages1.11 CHEM FINAL Chapter 11 Sulfuric AcidSudhanshuNo ratings yet
- Balancing EquationsDocument6 pagesBalancing Equationssyed abdul ahadNo ratings yet
- Teorias Ácido-BaseDocument47 pagesTeorias Ácido-BaseFernando Silva BetimNo ratings yet
- WEDNESDAY 12:00 - 2:00 PM: Oceña, Margarito Jr. ODocument8 pagesWEDNESDAY 12:00 - 2:00 PM: Oceña, Margarito Jr. ONivla GenesisNo ratings yet
- Hydro Hydro Hydro: + Nonmetal+ Ic + Acid Nonmetal + Ic + Acid Nonmetal + + AcidDocument21 pagesHydro Hydro Hydro: + Nonmetal+ Ic + Acid Nonmetal + Ic + Acid Nonmetal + + AcidHani TamimiNo ratings yet
- Chap 02cDocument10 pagesChap 02cRCNo ratings yet
- 05 - The Chemistry of Acids and Bases Complete - RevisedDocument63 pages05 - The Chemistry of Acids and Bases Complete - RevisedKabesang TalesNo ratings yet
- Worksheet Chapter 4.I ANSWERSDocument2 pagesWorksheet Chapter 4.I ANSWERSkhalid badranNo ratings yet
- Conjugate Acid and Base PairsDocument1 pageConjugate Acid and Base Pairsfelisita wisangNo ratings yet
- 1288 PhenolsDocument29 pages1288 PhenolsX ThrxNo ratings yet
- Reactions of Copper 1Document14 pagesReactions of Copper 1jw wNo ratings yet
- Chapter 2 Acid - Base - EngDocument98 pagesChapter 2 Acid - Base - Englong.vuongbz188No ratings yet
- Reactions of Copper 2Document14 pagesReactions of Copper 2jw wNo ratings yet
- Dicarboxylic Acids: - Bromoadipic AcidDocument32 pagesDicarboxylic Acids: - Bromoadipic AcidByakuya BleachNo ratings yet
- Balancing Equations: Practice Problems: Equation Balancing Chemistry Assignment: No 1Document4 pagesBalancing Equations: Practice Problems: Equation Balancing Chemistry Assignment: No 1Sher KhanNo ratings yet
- SulphurDocument12 pagesSulphurUJJWAL JHANo ratings yet
- Notes - Unit of Acid and Bases - Answer Key PacketDocument47 pagesNotes - Unit of Acid and Bases - Answer Key PacketLizeth PautaNo ratings yet
- ANAL CHEM SAMPLE With Answer 9Document37 pagesANAL CHEM SAMPLE With Answer 9BugsbunnyNo ratings yet
- Tobias, Mark Denzel B. Bse 1B Science: Worksheet - Bronsted-Lowry Acids and Bases Name: Year and Section: DateDocument2 pagesTobias, Mark Denzel B. Bse 1B Science: Worksheet - Bronsted-Lowry Acids and Bases Name: Year and Section: DateMaden betoNo ratings yet
- 3.ii. BASES AND ACIDS OF CHOICEDocument110 pages3.ii. BASES AND ACIDS OF CHOICEKeith OmwoyoNo ratings yet
- CH 10 OxidesDocument8 pagesCH 10 Oxidesapi-3774259No ratings yet
- Common Polyatomic Ions: ZN Zinc CD CadmiumDocument1 pageCommon Polyatomic Ions: ZN Zinc CD CadmiumLesly Justin FuntechaNo ratings yet
- IS30 IS50 WM CWL WM-L Schnittstellendoku enDocument250 pagesIS30 IS50 WM CWL WM-L Schnittstellendoku enspidigeNo ratings yet
- 31-12-2022 - SR - Super60 - NUCLEUS & STERLING - BT - Jee-Main-PTM-16 - KEY & Sol'SDocument12 pages31-12-2022 - SR - Super60 - NUCLEUS & STERLING - BT - Jee-Main-PTM-16 - KEY & Sol'SSameena LoniNo ratings yet
- Efficiency Analysis of An Aerospike Nozzle: Dipak J. Choudhari, Uday V. AsolekarDocument5 pagesEfficiency Analysis of An Aerospike Nozzle: Dipak J. Choudhari, Uday V. AsolekarAswith R ShenoyNo ratings yet
- Tracking Field OperationsDocument9 pagesTracking Field OperationsWilberZangaNo ratings yet
- Itp582b-515-01-Ib 2Document12 pagesItp582b-515-01-Ib 2Cara & Drei Amazing JourneyNo ratings yet
- Polymer-Plastics Technology and EngineeringDocument6 pagesPolymer-Plastics Technology and Engineeringsamuelben87No ratings yet
- CS6411 Network Lab Manual - 2013 - Regulation PDFDocument71 pagesCS6411 Network Lab Manual - 2013 - Regulation PDFjayaprasanna123No ratings yet
- Vdot Training TabelDocument7 pagesVdot Training TabelVarto RazvanNo ratings yet
- Che 243 Fluid Dynamics: Problem Set #4 Solutions: SolutionDocument9 pagesChe 243 Fluid Dynamics: Problem Set #4 Solutions: SolutionKyungtae Park100% (2)
- Air-Pollution-Meteorology UNIT IIDocument91 pagesAir-Pollution-Meteorology UNIT IIDR. Ramesh ChandragiriNo ratings yet
- TEMPLATE School Data Analysis Report 1st Periodic TestDocument3 pagesTEMPLATE School Data Analysis Report 1st Periodic TestDaisy Reyes CayabyabNo ratings yet
- Solar and Wind Hybrid Power GenerationDocument35 pagesSolar and Wind Hybrid Power Generationlatest advance guruji 2018No ratings yet
- Skin and Its AppendagesDocument3 pagesSkin and Its AppendagesMarchylle Faye JimenezNo ratings yet
- Unit 3 Study Guide and ExercisesDocument2 pagesUnit 3 Study Guide and ExercisesTuan NguyenNo ratings yet
- Mathematics - Iii: Instructions To CandidatesDocument2 pagesMathematics - Iii: Instructions To Candidatessimar batraNo ratings yet
- Understanding & Programming The PIC16C84: A Beginners' Tutorial Jim BrownDocument35 pagesUnderstanding & Programming The PIC16C84: A Beginners' Tutorial Jim BrownCornelius CampbellNo ratings yet
- Mathematical Model of Transportation ProblemDocument14 pagesMathematical Model of Transportation ProblemwasimghghNo ratings yet
- Basics of Circuit Analysis: RC RLCDocument18 pagesBasics of Circuit Analysis: RC RLCdavissblaineNo ratings yet