Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Common Polyatomic Ions: ZN Zinc CD Cadmium
Uploaded by
Lesly Justin FuntechaOriginal Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Common Polyatomic Ions: ZN Zinc CD Cadmium
Uploaded by
Lesly Justin FuntechaCopyright:
Available Formats
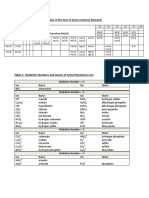
Common Polyatomic Ions
2+ charge 1- charge 2- charge
2+
Zn Zinc C2H3 O2- Acetate C2O4 2-
Oxalate
Cd2+ Cadmium CN- Cyanide CO32- Carbonate
- 2-
ClO Hypochlorite CrO4 Chromate
ClO2- Chlorite Cr2 O72- Dichromate
1+ charge ClO3- Chlorate HPO42- Hydrogen phosphate
NH4+ Ammonium ClO4- Perchlorate O22- Peroxide
Hg22+ Mercury (I) HCO3- Hydrogen (bi)carbonate SO32- Sulfite
Ag+ Silver H2PO4- Dihydrogen phosphate SO42- Sulfate
HSO3- Hydrogen sulfite SiO3 2-
Silicate
HSO4- Hydrogen (bi)sulfate
MnO4- Permanganate
NCS- Thiocyanate 3- charge
NO2- Nitrite AsO43- Arsenate
NO3- Nitrate PO33- Phosphite
- 3-
OH Hydroxide PO4 Phosphat
Prefixes For Binary Common Acids Common Acids with Oxygen
Molecular Compounds Name Formula Name Formula
Prefix Number Hydrobromic Acid HBr Acetic Acid HC2H3 O2
mono- 1 Hydrochloric Acid HCl Carbonic Acid H2CO3
di 2 Hydrocyanic Acid HCN Nitric Acid HNO3
tri- 3 Hydroflouric Acid HF Nitrous Acid HNO2
tetra- 4 Hydroiodic Acid HI Oxalic Acid H2C2 O4
penta- 5 Hydrosulfuric H2S Perchloric Acid HClO4
hexa- 6 Phosphoric Acid H3PO4
hepta- 7 Sulfuric Acid H2SO4
octa- 8 Sulfurous Acid H2SO
nona- 9
deca- 10
Formulas and Names of Common Metal Ions with More than One Ionic Charge
Formula Stock Name Classical Name Formula Stock Name Classical Name
Co2+ Cobalt(II) ion Cobaltous ion Co3+ Cobalt(III) ion Cobaltic ion
Cr2+ Chromium(II) ion Chromous ion Cr3+ Chromium(III) ion Chromic ion
Cu+ Copper(I) ion Cuprous ion Cu2+ Copper(II) ion Cupric ion
Fe2+ Iron(II) ion Ferrous ion Fe3+ Iron(III) ion Ferric ion
Hg22+ Mercury(I) ion Mercurous ion Hg2+ Mercury(II) ion Mercuric ion
Mn2+ Manganese(II) ion Manganous ion Mn3+ Manganese(III) ion Manganic ion
Pb2+ Lead(II) ion Plumbous ion Pb4+ Lead(IV) ion Plumbic ion
Sn2+ Tin(II) ion Stannous ion Sn4+ Tin(IV) ion Stannic ion
Simple Rules for the Solubility of Salts in Water
1. Most salts containing nitrates (NO3-), hydrogencarbonates (H2CO32-), or ethanoates (-CH2CO2C2 H5) salts are
soluble.
2. Most salts containing alkali metal ions (Li +, Na+, K+, Cs +, Rb +) or the ammonium ion (NH4+) are soluble.
3. Most chloride, bromide, and iodide salts are soluble. Notable exceptions are salts containing Ag +, Pb2+, and
Hg22+ ions.
4. Most sulfate salts are soluble. Notable exceptions are BaSO4, PbSO4, HgSO4, and CaSO4.
5. Most hydroxide salts are only slightly soluble. The important soluble hydroxides are NaOH and KOH. The
compounds Ba(OH)2, Sr(OH)2, and Ca(OH)2 are marginally soluble.
6. Most sulfide (S2-), carbonate (CO32-), chromate (CrO42-), and phosphate (PO43-) salts are only slightly soluble.
You might also like
- AP Chemistry Polyatomic List: Ion Name Ion Name Ion Name Ion NameDocument2 pagesAP Chemistry Polyatomic List: Ion Name Ion Name Ion Name Ion NameHarpreet KaurNo ratings yet
- တက္ကသိုလ်ဝင်တန်း ဓာတုဗေဒ Dr.Soe Kyaw KyawDocument322 pagesတက္ကသိုလ်ဝင်တန်း ဓာတုဗေဒ Dr.Soe Kyaw KyawKhin OosweNo ratings yet
- Inorganic ListDocument7 pagesInorganic ListWeronika OstrowskaNo ratings yet
- 5.9 Polyatomic CompoundsDocument3 pages5.9 Polyatomic Compoundsmichael.delaney8541No ratings yet
- Inorganic Compounds List for Medical TestsDocument4 pagesInorganic Compounds List for Medical TestsNguyên NguyễnNo ratings yet
- General Chemistry Nomenclature and Formulas GuideDocument2 pagesGeneral Chemistry Nomenclature and Formulas GuideCamille AquinoNo ratings yet
- Symbols and Charges for Monoatomic IonsDocument3 pagesSymbols and Charges for Monoatomic IonsKelvin Mark KaabayNo ratings yet
- Table 1: Common Element Ion Oxidation NumbersDocument1 pageTable 1: Common Element Ion Oxidation Numbersliam leeNo ratings yet
- Symbols and Charges For Monoatomic IonsDocument2 pagesSymbols and Charges For Monoatomic IonsaNo ratings yet
- Common Ion Sheet Symbols and ChargesDocument2 pagesCommon Ion Sheet Symbols and Chargeskarl0% (1)
- Chemistry Info SheetDocument3 pagesChemistry Info SheetClara GreenNo ratings yet
- ions ref sheetDocument2 pagesions ref sheetmoyston.jade2No ratings yet
- List of Ions: I. CationsDocument4 pagesList of Ions: I. CationsJamille GamboaNo ratings yet
- Polyatomics PDFDocument1 pagePolyatomics PDFisseylimboNo ratings yet
- Polyatomics PDFDocument1 pagePolyatomics PDFValine Cysteine MethionineNo ratings yet
- PolyatomicsDocument1 pagePolyatomicsNubar MammadovaNo ratings yet
- Polyatomics PDFDocument1 pagePolyatomics PDFDaryl De VeraNo ratings yet
- Polyatomicions PDFDocument1 pagePolyatomicions PDFIDate DanielNo ratings yet
- Polyatomics PDFDocument1 pagePolyatomics PDFImy MalagsicNo ratings yet
- Polyatomics PDFDocument1 pagePolyatomics PDFabdul halimNo ratings yet
- Common polyatomic and metal ion formulasDocument1 pageCommon polyatomic and metal ion formulasXhevatNo ratings yet
- Common Polyatomic Ions Name(s) Formula Name(s) FormulaDocument1 pageCommon Polyatomic Ions Name(s) Formula Name(s) FormulaMark Randell BalerosNo ratings yet
- Polyatomics PDFDocument1 pagePolyatomics PDFisseylimboNo ratings yet
- Common polyatomic and metal ion formulasDocument1 pageCommon polyatomic and metal ion formulasIDate DanielNo ratings yet
- Polyatomics PDFDocument1 pagePolyatomics PDFAle TriguerosNo ratings yet
- ASM_33333333333Document2 pagesASM_33333333333p5jp29697cNo ratings yet
- Symbols and Names of Common Metal Ions With More Than One Ionic Charge Symbol Stock Name Classical NameDocument2 pagesSymbols and Names of Common Metal Ions With More Than One Ionic Charge Symbol Stock Name Classical NameLilyNo ratings yet
- Cation and AnionDocument2 pagesCation and AnionNBT OONo ratings yet
- List of Common IonsDocument3 pagesList of Common IonsangelonicoNo ratings yet
- Complex Ions: Al C N F Si P CL K Ba BR RB SR I Cu Ag Fe H PB ZNDocument2 pagesComplex Ions: Al C N F Si P CL K Ba BR RB SR I Cu Ag Fe H PB ZNelizabethNo ratings yet
- Symbols and Charges-Monoatomic IonsDocument20 pagesSymbols and Charges-Monoatomic Ionsjon_kasilagNo ratings yet
- ChemistryDocument3 pagesChemistryJanna Althea S. BaruzoNo ratings yet
- Ions SheetDocument1 pageIons Sheetapi-408461912No ratings yet
- Naming Compounds Cheat SheetDocument2 pagesNaming Compounds Cheat SheetYSA BELLENo ratings yet
- Cations and Anions ListDocument1 pageCations and Anions ListjonNo ratings yet
- PR Table - IonsDocument1 pagePR Table - IonsmayerhendrixNo ratings yet
- Ion Sheet With Solubility Rules-2Document1 pageIon Sheet With Solubility Rules-2kwilsonNo ratings yet
- List of AnionsDocument2 pagesList of AnionsKwien AustriaNo ratings yet
- Naming CompoundsDocument2 pagesNaming CompoundsTeresa Marie CorderoNo ratings yet
- ApsummerDocument5 pagesApsummerLayleeNo ratings yet
- Stuff I Should Know For The Ap Test But Do Not Know Yet: Ions ListDocument2 pagesStuff I Should Know For The Ap Test But Do Not Know Yet: Ions ListedeceNo ratings yet
- Polyatomic Ions List: Honors ChemistryDocument2 pagesPolyatomic Ions List: Honors ChemistrymandaNo ratings yet
- Summer Assignment For AP Chemistry Class 2020-2021Document5 pagesSummer Assignment For AP Chemistry Class 2020-2021shelly zhangNo ratings yet
- AP Chemistry Summer Assignment 2017Document44 pagesAP Chemistry Summer Assignment 2017John SmithNo ratings yet
- Chem 1 List of IonsDocument2 pagesChem 1 List of IonsJean Angelove SantosNo ratings yet
- General Chemistry 2 Module 3Document6 pagesGeneral Chemistry 2 Module 3Jason Vinluan CarinanNo ratings yet
- Zapamti - Kiseline, Lu Ine, SoliDocument2 pagesZapamti - Kiseline, Lu Ine, SolidragoNo ratings yet
- Symbols and Names For Common Polyatomic IonsDocument1 pageSymbols and Names For Common Polyatomic IonsElixirNo ratings yet
- #1 Notes Polyatomic IonsDocument1 page#1 Notes Polyatomic IonsInes VergaraNo ratings yet
- Nomenclature: General Chemistry Pro-KnowledgeDocument2 pagesNomenclature: General Chemistry Pro-KnowledgemohammedNo ratings yet
- MANTARA - Docx ACTIVITY#5 PART BDocument3 pagesMANTARA - Docx ACTIVITY#5 PART BFarks Mantara0% (1)
- Common IonsDocument3 pagesCommon IonsabdallaaNo ratings yet
- Common Ions and Their Charges: From The Table: Ions To Memorize Cations Name Cations NameDocument2 pagesCommon Ions and Their Charges: From The Table: Ions To Memorize Cations Name Cations NameChantelle W. SHUMNo ratings yet
- Chem IndexDocument2 pagesChem IndexSiewan Taeny KimNo ratings yet
- Polyatomic Ions PDFDocument1 pagePolyatomic Ions PDFmaniz442No ratings yet
- Chemical NamingDocument1 pageChemical NamingV8LNo ratings yet
- JRS Tutorials: Chemistry IITDocument58 pagesJRS Tutorials: Chemistry IITtusharr11.mobNo ratings yet
- Common Ions - Polyatomic IonsDocument2 pagesCommon Ions - Polyatomic IonsMak ItiNo ratings yet
- Inorganic Hydrides: The Commonwealth and International Library: Chemistry DivisionFrom EverandInorganic Hydrides: The Commonwealth and International Library: Chemistry DivisionNo ratings yet
- Reading MaterialsDocument8 pagesReading MaterialsLesly Justin FuntechaNo ratings yet
- Activity Work No.1 SDG ContributionsDocument1 pageActivity Work No.1 SDG ContributionsLesly Justin FuntechaNo ratings yet
- Resume (Nisha)Document2 pagesResume (Nisha)Lesly Justin FuntechaNo ratings yet
- Biochemistr Y: What Is A Biochemistry?Document10 pagesBiochemistr Y: What Is A Biochemistry?Lesly Justin FuntechaNo ratings yet
- VISIONDocument3 pagesVISIONLesly Justin FuntechaNo ratings yet
- NCM 100 (TFN) Reminder: Assessment / Evaluation Should Be Done Every After Chapter/lessonDocument5 pagesNCM 100 (TFN) Reminder: Assessment / Evaluation Should Be Done Every After Chapter/lessonLesly Justin FuntechaNo ratings yet
- The Usda Food Guide Pyramid and MypyramidDocument12 pagesThe Usda Food Guide Pyramid and MypyramidLesly Justin FuntechaNo ratings yet
- ROCKSDocument21 pagesROCKSLesly Justin FuntechaNo ratings yet
- Types of InformationDocument10 pagesTypes of InformationLesly Justin FuntechaNo ratings yet
- Survey QuestionnaireDocument2 pagesSurvey QuestionnaireLesly Justin FuntechaNo ratings yet
- Providers of InformationDocument5 pagesProviders of InformationLesly Justin FuntechaNo ratings yet
- Front PageDocument1 pageFront PageLesly Justin FuntechaNo ratings yet
- HHHHDocument3 pagesHHHHLesly Justin FuntechaNo ratings yet
- Survey QuestionnaireDocument2 pagesSurvey QuestionnaireLesly Justin FuntechaNo ratings yet
- Mitochondria and ChloroplastDocument20 pagesMitochondria and ChloroplastLesly Justin FuntechaNo ratings yet
- According To Jiggy Manicad A Former Communicate Columnist and Was A Senatorial Candidate Said That While President Rodrigo DuterteDocument2 pagesAccording To Jiggy Manicad A Former Communicate Columnist and Was A Senatorial Candidate Said That While President Rodrigo DuterteLesly Justin FuntechaNo ratings yet
- Application (Nisha)Document1 pageApplication (Nisha)Lesly Justin FuntechaNo ratings yet
- Lesson 5Document5 pagesLesson 5Lesly Justin FuntechaNo ratings yet
- Chloroplast: Science TeacherDocument18 pagesChloroplast: Science TeacherLesly Justin FuntechaNo ratings yet
- How Can You Love Someone For So Long and So Real and Then Just StopDocument2 pagesHow Can You Love Someone For So Long and So Real and Then Just StopLesly Justin FuntechaNo ratings yet
- Meiosis Explained in 40 CharactersDocument14 pagesMeiosis Explained in 40 CharactersLesly Justin FuntechaNo ratings yet
- Bio PhysDocument7 pagesBio Physfiona altabanoNo ratings yet
- FallaciesDocument25 pagesFallaciesLesly Justin FuntechaNo ratings yet
- Chapter IIIDocument1 pageChapter IIILesly Justin FuntechaNo ratings yet
- Survey - Questionnaire Name: - Club: - Directions: The Statement Below Describes The Governance and Management ofDocument3 pagesSurvey - Questionnaire Name: - Club: - Directions: The Statement Below Describes The Governance and Management ofLesly Justin FuntechaNo ratings yet
- Fourth GComp U3 W2Document12 pagesFourth GComp U3 W2Lesly Justin FuntechaNo ratings yet
- Cell Division: The Process of MitosisDocument22 pagesCell Division: The Process of MitosisLesly Justin FuntechaNo ratings yet
- AcknowledgeDocument1 pageAcknowledgeLesly Justin FuntechaNo ratings yet
- Continental Drift Theory EvidenceDocument15 pagesContinental Drift Theory EvidenceLesly Justin FuntechaNo ratings yet
- Club Governance and Management ThesisDocument1 pageClub Governance and Management ThesisLesly Justin FuntechaNo ratings yet
- Anomalous Foam-Fractional-Flow Solutions at High-Injection Foam QualityDocument11 pagesAnomalous Foam-Fractional-Flow Solutions at High-Injection Foam QualitymnoriegalNo ratings yet
- EDC-DTS-LV004 - LV Distribution Board For Pole Mounted SubstationDocument35 pagesEDC-DTS-LV004 - LV Distribution Board For Pole Mounted SubstationJoe bilouteNo ratings yet
- Pollution: Causes, Effects and SolutionsDocument16 pagesPollution: Causes, Effects and SolutionsVibNo ratings yet
- Mdhs 96Document24 pagesMdhs 96Hồ Lương ThưởngNo ratings yet
- Unit 1 MCQ QuestionsDocument24 pagesUnit 1 MCQ Questionsanand anithaNo ratings yet
- Extlistjuly2023 DiscontDocument21 pagesExtlistjuly2023 DiscontHien PhamNo ratings yet
- Ammonia-Urea Industry in BangladeshDocument28 pagesAmmonia-Urea Industry in BangladeshHumayun Rashid Khan100% (1)
- Effect of Shielding GasesDocument7 pagesEffect of Shielding GasesMayank SinglaNo ratings yet
- Introduction To Analytical ChemistryDocument4 pagesIntroduction To Analytical ChemistryCHRISTINE JOY RETARDONo ratings yet
- Analysis of Polymers ATR FTIR AN PDFDocument3 pagesAnalysis of Polymers ATR FTIR AN PDFHasan MahmudNo ratings yet
- 1 s2.0 S0142941819323955 MainDocument7 pages1 s2.0 S0142941819323955 MainCristina GomesNo ratings yet
- Experiment No. 2 Worker Performance Under Rushed Conditions AUGUST 15, 2007Document11 pagesExperiment No. 2 Worker Performance Under Rushed Conditions AUGUST 15, 2007api-26570979100% (2)
- Cement Additives Improve High-Performance BindersDocument7 pagesCement Additives Improve High-Performance Bindersimsurender87No ratings yet
- Thrope Ziegler Cyclization SearchDocument4 pagesThrope Ziegler Cyclization SearchahmedramadanNo ratings yet
- Isotonic and Alligation MethodDocument46 pagesIsotonic and Alligation Methodabdullah2020100% (1)
- EN 12255-9-2002 - enDocument20 pagesEN 12255-9-2002 - enSolid VanadiumNo ratings yet
- HB-0202-006 HB QA CirculatingNucAcid 0819 WWDocument64 pagesHB-0202-006 HB QA CirculatingNucAcid 0819 WWnandha pratamaNo ratings yet
- Air Pollution Control DevicesDocument53 pagesAir Pollution Control DevicesVinay Dogra50% (2)
- Eg Bremsgleichrichter enDocument21 pagesEg Bremsgleichrichter enAllan AlbaracinNo ratings yet
- Aluminio BRONMETAL enDocument12 pagesAluminio BRONMETAL enPerica RakićNo ratings yet
- Gasunie Boek Physical Properties of Natural GasesDocument251 pagesGasunie Boek Physical Properties of Natural GasesRobin ZwartNo ratings yet
- Cationic Polymerization: From Photoinitiation To PhotocontrolDocument10 pagesCationic Polymerization: From Photoinitiation To Photocontrol章晴昱No ratings yet
- Strainer Air Eliminator EC 31-EC 32 - EC 39: Description - Installation ServicingDocument10 pagesStrainer Air Eliminator EC 31-EC 32 - EC 39: Description - Installation ServicingFredwash RichardNo ratings yet
- Hindi PDF NewDocument5 pagesHindi PDF NewAstro Counselor KaranNo ratings yet
- Chang General Chemistry Questions and AnswersDocument26 pagesChang General Chemistry Questions and AnswersHan Tsu0% (1)
- Physics Assignment: Suraj SinghDocument8 pagesPhysics Assignment: Suraj SinghNikhil YadavNo ratings yet
- Uhde Painting SpecificationDocument34 pagesUhde Painting Specificationmohamed elmasryNo ratings yet
- 515 1Document33 pages515 1AlexSNo ratings yet
- TensorDocument6 pagesTensorVaishnav SankarkNo ratings yet
- PAT-1 Safety Analysis Report Addendum Author Responses To Request For Additional InformationDocument95 pagesPAT-1 Safety Analysis Report Addendum Author Responses To Request For Additional Informationsandia_docsNo ratings yet