Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Meiosis Explained in 40 Characters
Uploaded by
Lesly Justin Funtecha0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
2 views14 pagesThis document describes the stages of meiosis. Meiosis reduces the amount of genetic information and produces haploid gametes with 23 chromosomes. The first meiotic division results in homologous chromosomes pairing and crossing over, followed by their separation into daughter cells. The second meiotic division is similar to mitosis but does not involve DNA replication, resulting in four haploid cells from one original diploid cell. Meiosis is significant because it produces gametes for sexual reproduction and genetic variation in offspring.
Original Description:
,;;
Original Title
Meiosis
Copyright
© © All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
PPTX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentThis document describes the stages of meiosis. Meiosis reduces the amount of genetic information and produces haploid gametes with 23 chromosomes. The first meiotic division results in homologous chromosomes pairing and crossing over, followed by their separation into daughter cells. The second meiotic division is similar to mitosis but does not involve DNA replication, resulting in four haploid cells from one original diploid cell. Meiosis is significant because it produces gametes for sexual reproduction and genetic variation in offspring.
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PPTX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
2 views14 pagesMeiosis Explained in 40 Characters
Uploaded by
Lesly Justin FuntechaThis document describes the stages of meiosis. Meiosis reduces the amount of genetic information and produces haploid gametes with 23 chromosomes. The first meiotic division results in homologous chromosomes pairing and crossing over, followed by their separation into daughter cells. The second meiotic division is similar to mitosis but does not involve DNA replication, resulting in four haploid cells from one original diploid cell. Meiosis is significant because it produces gametes for sexual reproduction and genetic variation in offspring.
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PPTX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
You are on page 1of 14
MEIOSIS
MARK DAVE R. VILLAMOR
Science Teacher
Objectives
Describe the stages of mitosis and meiosis.
Discuss the crossing over and recombination in
meiosis.
Explain the significance or application of mitosis/
meiosis.
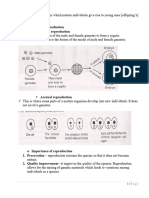
MEIOSIS
Reduces the amount of genetic information.
Produces haploid gametes with 23
chromosomes.
Gametes combine in fertilization to reconstitute
the diploid complement found in parental cells.
FIRST MEIOTIC DIVISION
Results in reducing the number of
chromosomes.
Division is accompanied by cytokinesis.
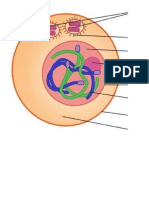
PROPHASE I
Homologous
chromosome starts to
pairs
Crossing over of
chromosomes.
(chiasma)
Centrioles replicates
Nuclear membrane
disappears.
METAPHASE I
Homologous
chromosomes starts to
align at the metaphase
plate.
Spindle fibers are
formed.
ANAPHASE I
Initiated by the separation
of sister chromatids at the
centromere.
The daughter
chromosomes move
forward to the poles.
TELOPHASE I
SECOND MEIOTIC DIVISION
Similar to mitotic division (mitosis).
Number of chromosome each daughter cells
receive is reduced to half (23).
NO ADDITIONAL REPLICATION OCCURS
PROPHASE II
Nuclear membrane
disappears again.
NO REPLICATION OF
CHROMOSOMES.
Centrioles are
replicated.
METAPHASE II
Chromosomes are
aligned at the center of
the cell known as
metaphase plate.
The spindle fibers starts
to form and attach to the
kinetochore of the
chromosome.
ANAPHASE II
Centromeres split
Individual chromosomes
are pulled to poles
TELOPHASE II
Nuclear membrane
starts to form again.
Four haploid daughter
cells results from one
original diploid cell
ASSIGNMENT (1/2)
Explain the importance of meiosis to our body.
Criteria:
Content –5
Cleanliness – 2
Organization – 3
10 points
You might also like
- Human Chromosomes: An Illustrated Introduction to Human CytogeneticsFrom EverandHuman Chromosomes: An Illustrated Introduction to Human CytogeneticsRating: 5 out of 5 stars5/5 (1)
- Mitosis & MeiosisDocument36 pagesMitosis & MeiosisxerhaianNo ratings yet
- Genetics 1 MeiosisDocument26 pagesGenetics 1 Meiosisapi-188431847No ratings yet
- Gene Editing, Epigenetic, Cloning and TherapyFrom EverandGene Editing, Epigenetic, Cloning and TherapyRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (1)
- Cell DivisionDocument67 pagesCell DivisionRylle SimonNo ratings yet
- Module-2-Meiosis-and-MitosisDocument88 pagesModule-2-Meiosis-and-MitosisSevdred CadelinaNo ratings yet
- q1 Genbio1 Slkweek5 v2 EditDocument9 pagesq1 Genbio1 Slkweek5 v2 EditInele Ellia AgReNo ratings yet
- Meiosis-Advanced_20240304_125003_0000Document25 pagesMeiosis-Advanced_20240304_125003_0000Jaja Jr. Evasco EmbarqueNo ratings yet
- Meiosis and MitosisDocument46 pagesMeiosis and MitosisJoann JacobNo ratings yet
- Class - X: Life Science Study Material: Cell DivisionDocument13 pagesClass - X: Life Science Study Material: Cell DivisionANIRBAN PALNo ratings yet
- Meiosis: Cell Division and Gamete FormationDocument17 pagesMeiosis: Cell Division and Gamete Formationandrew gauranaNo ratings yet
- Module 4Document5 pagesModule 4Ivan PaulinoNo ratings yet
- Cell Division: Mitosis and MeiosisDocument18 pagesCell Division: Mitosis and Meiosislouisse veracesNo ratings yet
- CELL DIVISIONDocument35 pagesCELL DIVISIONRosalina Bautista RamosNo ratings yet
- IB DP Biology Topic 3 - Genetics 3.3 Meiosis Study NotesDocument28 pagesIB DP Biology Topic 3 - Genetics 3.3 Meiosis Study Notespepedu aceNo ratings yet
- Mitosis MeiosisDocument8 pagesMitosis MeiosisSyndy Mae Wasing DosogNo ratings yet
- Cell DivisionDocument32 pagesCell DivisionRhea GulayNo ratings yet
- Understanding Meiosis and MitosisDocument14 pagesUnderstanding Meiosis and MitosisMary Joy ReyesNo ratings yet
- Mitosis and Meiosis ExamDocument6 pagesMitosis and Meiosis ExamAishley BerdinNo ratings yet
- SZL B206 Principles of GeneticsDocument28 pagesSZL B206 Principles of Geneticsawuors249No ratings yet
- Prometaphase: Somatic Cells Somatic CellsDocument4 pagesPrometaphase: Somatic Cells Somatic CellsMica CapistranoNo ratings yet
- MITOSISDocument19 pagesMITOSISFranshel CaldozaNo ratings yet
- Batterjee Medical College (BMC) FAST (Preparatory Year) Biology Department 2012-2013Document14 pagesBatterjee Medical College (BMC) FAST (Preparatory Year) Biology Department 2012-2013edain84No ratings yet
- MeiosisDocument3 pagesMeiosisJaja Jr. Evasco EmbarqueNo ratings yet
- Cell DivisionDocument27 pagesCell DivisionLavinia DonaldNo ratings yet
- F3 2021 REPRODUCTION IN PLANTSDocument27 pagesF3 2021 REPRODUCTION IN PLANTSlastyngugiNo ratings yet
- Biotechnology NotesDocument21 pagesBiotechnology NotesRommel BauzaNo ratings yet
- Meiosis I & 2Document17 pagesMeiosis I & 2Mar Delos ReyesNo ratings yet
- The Cell CycleDocument72 pagesThe Cell CycleJerry Jeroum RegudoNo ratings yet
- Cell DivisionDocument38 pagesCell DivisionJane Marry IgnacioNo ratings yet
- Cell Division: The Stages of Mitosis & MeiosisDocument27 pagesCell Division: The Stages of Mitosis & MeiosisTaira GraceNo ratings yet
- Mitosis V MeiosisDocument5 pagesMitosis V MeiosisddaarrsshhiittNo ratings yet
- Meiosis and Mitosis: The Cell Division ProcessesDocument17 pagesMeiosis and Mitosis: The Cell Division ProcessesMuskan ShreeNo ratings yet
- Week 2 Sci 8Document33 pagesWeek 2 Sci 8Joseph Gabriel Genuino CruzNo ratings yet
- Mitosis and MeiosisDocument2 pagesMitosis and MeiosisFrances Isko FranciscoNo ratings yet
- Science8 Q4 M2Document6 pagesScience8 Q4 M2Arabella BaldonadoNo ratings yet
- Inbound 4185024769852247435Document13 pagesInbound 4185024769852247435Chesca DacilloNo ratings yet
- Cell Division StagesDocument118 pagesCell Division StagesNora AfidaNo ratings yet
- Stages of Mitosis and Meiosis Given 2N=6Document29 pagesStages of Mitosis and Meiosis Given 2N=6rnzyrlcasinilloNo ratings yet
- MF009 4B Nuclear Division James L2Document29 pagesMF009 4B Nuclear Division James L2PikuNo ratings yet
- Grade 8 Osmeña Q4 - Week 2Document48 pagesGrade 8 Osmeña Q4 - Week 2SHAIRA LYN CUMILANGNo ratings yet
- 2.MEIOSISDocument36 pages2.MEIOSISnthabiisengNo ratings yet
- Cell Division: Mitosis and Meiosis ExplainedDocument17 pagesCell Division: Mitosis and Meiosis ExplainedGenevieve GanubNo ratings yet
- BIO T4 KSSM Chapter 6 - DLPDocument62 pagesBIO T4 KSSM Chapter 6 - DLPcikguana79No ratings yet
- Biologists Traditionally Classify All Living Organisms Into Two Major GroupsDocument2 pagesBiologists Traditionally Classify All Living Organisms Into Two Major GroupsrahafNo ratings yet
- MeiosisDocument30 pagesMeiosisJosephine VinaraoNo ratings yet
- 4 MeiosisDocument5 pages4 MeiosisVarun GoseinNo ratings yet
- The Cell Cycle-TRFDocument8 pagesThe Cell Cycle-TRFmaniiiiiiiiNo ratings yet
- Cell CycleDocument19 pagesCell CycleMoffat KaprezzoNo ratings yet
- Exercise 5Document5 pagesExercise 5holie madroneroNo ratings yet
- Cell Structure and DivisionDocument70 pagesCell Structure and DivisionAMALIA INDAH ALLIZA ALLIZANo ratings yet
- Cell DivisionDocument52 pagesCell DivisionRamachandran Ram100% (1)
- AP Bio Lab 3 FinalDocument6 pagesAP Bio Lab 3 Finalniteeshsettypalli100% (1)
- CBSE Quick Revision Notes (Class-11 Biology) Chapter-10 Cell Cycle and Cell DivisionDocument4 pagesCBSE Quick Revision Notes (Class-11 Biology) Chapter-10 Cell Cycle and Cell DivisionArnavNo ratings yet
- Mitosis: Labeled Diagram: Interphase: Gap 1 Phase (Growth), Synthesis Phase (Copy of DNA), Gap 2 Phase (OrganelleDocument7 pagesMitosis: Labeled Diagram: Interphase: Gap 1 Phase (Growth), Synthesis Phase (Copy of DNA), Gap 2 Phase (Organelleazzahra adeliaNo ratings yet
- MeiosisDocument19 pagesMeiosisDrech LanadoNo ratings yet
- Cell DivisionDocument5 pagesCell DivisionSsonko EdrineNo ratings yet
- Bio 001 Cell DivisionDocument8 pagesBio 001 Cell DivisionKnick KnackNo ratings yet
- Biochemistr Y: What Is A Biochemistry?Document10 pagesBiochemistr Y: What Is A Biochemistry?Lesly Justin FuntechaNo ratings yet
- Reading MaterialsDocument8 pagesReading MaterialsLesly Justin FuntechaNo ratings yet
- VISIONDocument3 pagesVISIONLesly Justin FuntechaNo ratings yet
- Resume (Nisha)Document2 pagesResume (Nisha)Lesly Justin FuntechaNo ratings yet
- The Usda Food Guide Pyramid and MypyramidDocument12 pagesThe Usda Food Guide Pyramid and MypyramidLesly Justin FuntechaNo ratings yet
- Application (Nisha)Document1 pageApplication (Nisha)Lesly Justin FuntechaNo ratings yet
- HHHHDocument3 pagesHHHHLesly Justin FuntechaNo ratings yet
- Activity Work No.1 SDG ContributionsDocument1 pageActivity Work No.1 SDG ContributionsLesly Justin FuntechaNo ratings yet
- Survey QuestionnaireDocument2 pagesSurvey QuestionnaireLesly Justin FuntechaNo ratings yet
- NCM 100 (TFN) Reminder: Assessment / Evaluation Should Be Done Every After Chapter/lessonDocument5 pagesNCM 100 (TFN) Reminder: Assessment / Evaluation Should Be Done Every After Chapter/lessonLesly Justin FuntechaNo ratings yet
- Front PageDocument1 pageFront PageLesly Justin FuntechaNo ratings yet
- Bio PhysDocument7 pagesBio Physfiona altabanoNo ratings yet
- Types of InformationDocument10 pagesTypes of InformationLesly Justin FuntechaNo ratings yet
- Survey QuestionnaireDocument2 pagesSurvey QuestionnaireLesly Justin FuntechaNo ratings yet
- ROCKSDocument21 pagesROCKSLesly Justin FuntechaNo ratings yet
- According To Jiggy Manicad A Former Communicate Columnist and Was A Senatorial Candidate Said That While President Rodrigo DuterteDocument2 pagesAccording To Jiggy Manicad A Former Communicate Columnist and Was A Senatorial Candidate Said That While President Rodrigo DuterteLesly Justin FuntechaNo ratings yet
- Providers of InformationDocument5 pagesProviders of InformationLesly Justin FuntechaNo ratings yet
- Cell Division: The Process of MitosisDocument22 pagesCell Division: The Process of MitosisLesly Justin FuntechaNo ratings yet
- Mitochondria and ChloroplastDocument20 pagesMitochondria and ChloroplastLesly Justin FuntechaNo ratings yet
- Lesson 5Document5 pagesLesson 5Lesly Justin FuntechaNo ratings yet
- Survey - Questionnaire Name: - Club: - Directions: The Statement Below Describes The Governance and Management ofDocument3 pagesSurvey - Questionnaire Name: - Club: - Directions: The Statement Below Describes The Governance and Management ofLesly Justin FuntechaNo ratings yet
- FallaciesDocument25 pagesFallaciesLesly Justin FuntechaNo ratings yet
- Chloroplast: Science TeacherDocument18 pagesChloroplast: Science TeacherLesly Justin FuntechaNo ratings yet
- How Can You Love Someone For So Long and So Real and Then Just StopDocument2 pagesHow Can You Love Someone For So Long and So Real and Then Just StopLesly Justin FuntechaNo ratings yet
- Fourth GComp U3 W2Document12 pagesFourth GComp U3 W2Lesly Justin FuntechaNo ratings yet
- AcknowledgeDocument1 pageAcknowledgeLesly Justin FuntechaNo ratings yet
- Club Governance and Management ThesisDocument1 pageClub Governance and Management ThesisLesly Justin FuntechaNo ratings yet
- Continental Drift Theory EvidenceDocument15 pagesContinental Drift Theory EvidenceLesly Justin FuntechaNo ratings yet
- Chapter IIIDocument1 pageChapter IIILesly Justin FuntechaNo ratings yet