Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Maternal Notes
Maternal Notes
Uploaded by
nicolerejelaradillos3Original Description:
Original Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Maternal Notes
Maternal Notes
Uploaded by
nicolerejelaradillos3Copyright:
Available Formats
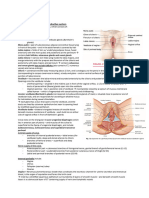
2 undifferentiated ducts (mesonephric (wolfian) & paramesoRephric (mullerian)
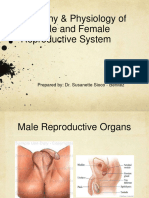
external structures of male repro (stp)
internal structures " " " (epididymis, vas deferens ,prostate gland,bulbourethral gland ,urethra)
segments of fallopian tube (interstitial, isthmus, ampulla, infundibullum)
exercises to strengthen perenial body (kegel, tailor sitting, squatting)
layers of ovaries (tunica albuginea, cortex, medulla)
identify:
beginning of breast development (thelarche)
beginning of mens (menarche)
production of sperm( spermatogenesis)
it separates each sac (midline septum)
what cells produce testosterone (interstitial cells/leydig's cells)
also known as cowper's glands (bulbourethral glands)
short segment between the body and cervix ( isthmus)
lowest portion of uterus which is usually 2-5cm long (cervix)
inner layer of mucous membrane innermost layer (endometrium)
middle layer of muscle fibers (myometrium)
outer layer of connective tissue (perimetrium)
condition where it will lead to hemiation of rectum to vagina ( rectocele)
overstretching lead to hemiation of bladder to vagina (cystocele)
has a similar function to clitoris (glans)
torn during childbirth & site of episiotomy (fourchette)
located in urinary meatus + PRODUCES ALKALINE MUCUS FOR LUBRICATION AND PROTECTION
(paraurethral gland / skene's gland)
located in each side of vaginal opening + SECRETES ALKALINE SUBSTANCES TO LUBRICATE VAGINAL
ORIFICIE & NEUTRALIZE ACIDITY OF VAGINA (paravaginal glamds / bartholin's glands) + also the site of
bartholinitis
elastic tissue that coverd vagina (hymen)
bartholin's cyst and infection ( bartholinitis)
a hymen so complete that blocks passage of mens until surgucally incised (imperforate hymen)
hormone of woman (estrogen)
best time for breast self exam (5-7 days aft mens)
areola appears rpugh due to sebacious glands (montgomery's tubercles)
note: inner endometrium, myometrium middle, perimetrium outer
at birth : 2 milliom immature ova
7yrs = 500T per ovsry
22 yrs = 300,000 ova
menopause: none left
///
segments of ft:
interstitial - most proximal, most dangerous site for ectopic pregnancy, lies within uterine 1 cm
isthmus - next distal, exteremly narrow, site of sterilization or BTL (BILATERAL TUBAL LIGATION)
ampulla = 3rd & longedt portion 5cm, site of fertilization
infundibullum= most distal, funnel shaped, rim covered by fimbriae(small hairs) that help guide to fallopian tube
//. retroversion = tipped backward
anteversion= forward
anteflexiom= m bent sharply forward at junction of cervix
retroflexion= bent sharply backward before cervix
septum= divides uterus
bicornuate uterus= horns at junction of FALLOPIAN TUBE
vagina - hollow rugated canal
fornices - recess at cervical end of vagina
bulbocavernosus muscle- voluntary sphincter (kegel's exercise strengthen the muscles)
nipple - composed of smooth muscles can cause erectioj or sucking stimulation, 15-20 small openings
mammary - divided into 15-20 lobes divided into lobules
lobules - cluster of acinar cells/acini (saclike terminal parts,,,, secretes milk & colostrum)
hormones that influ mg
estrogen - development of ductike M structure of breast
progesterone - acinar structurs of breast
human placental lactogen or hpl - breast development during pregnancy
oxytocin - letdown reflex or milk ejection rf
prolactin - stimulates milk prod.
2 division of pelvis
false pelvis - upper half ( supports uterus during late month of preg & aids in directing fetus into true pelvis for birth
true pelvis - lower half, long bony, curved canal has three parts (inlet, pelvic cavity, outlet)
anterior & lateral portion made up of>
2 innominate hipbones DIVIDED INTO:
ilium
ischium
pubis
posterior position :
sacrum
coccyx
linea terminalis / brim : line from sacral promontory to superior border of sp which divides pelvis into true & false pelvis
You might also like
- FemalereproductiveorganDocument57 pagesFemalereproductiveorganIwan MongayNo ratings yet
- Female Reproductive System PDFDocument48 pagesFemale Reproductive System PDFTeppy the GreatNo ratings yet
- Last Minute Embryology: Human embryology made easy and digestible for medical and nursing studentsFrom EverandLast Minute Embryology: Human embryology made easy and digestible for medical and nursing studentsNo ratings yet
- Section 2 The Female Genital Organs: Gonad - Conveying Ducts - Accessory GlandsDocument29 pagesSection 2 The Female Genital Organs: Gonad - Conveying Ducts - Accessory Glandssomebody_maNo ratings yet
- Anatomy Lec 22 (FGOs)Document49 pagesAnatomy Lec 22 (FGOs)Humraz100% (1)
- Anatomy and PhysiologyDocument8 pagesAnatomy and PhysiologyAironne ManguilimotanNo ratings yet
- Maternal and Child Health Nursing Reviewer-CompleteDocument66 pagesMaternal and Child Health Nursing Reviewer-Completeposh003892% (39)
- 2013 Maternal and Child Health Nursing Reviewer CompleteDocument40 pages2013 Maternal and Child Health Nursing Reviewer CompleteHarley Justiniani Dela CruzNo ratings yet
- Maternal and Child Nursing From Tina CompleteDocument51 pagesMaternal and Child Nursing From Tina CompleteArgee AlonsabeNo ratings yet
- Maternal Child Nursing (MCN) PDFDocument94 pagesMaternal Child Nursing (MCN) PDFirene8000No ratings yet
- Reproductive SystemDocument4 pagesReproductive Systemclar29No ratings yet
- Lecture 2 - Embryology of The Female Genital Tract & Anatomy of Female Pelvis & Fetal SkullDocument11 pagesLecture 2 - Embryology of The Female Genital Tract & Anatomy of Female Pelvis & Fetal SkullBrandonRyanF.MosidinNo ratings yet
- The Anatomy, Histology and Development of The Uterine Tube and Uterus PDFDocument16 pagesThe Anatomy, Histology and Development of The Uterine Tube and Uterus PDFredderdatNo ratings yet
- Obstetrics and Gynecology Notes 2-1 (AutoRecovered)Document109 pagesObstetrics and Gynecology Notes 2-1 (AutoRecovered)Kate GafarNo ratings yet
- Female GenitaliavDocument39 pagesFemale GenitaliavKathlyn PactorananNo ratings yet
- ModuleDocument8 pagesModuleKarnina MagbuhosNo ratings yet
- Femalereproductiveorgan 150117083020 Conversion Gate01Document57 pagesFemalereproductiveorgan 150117083020 Conversion Gate01SARABIA, ARVIN JR.No ratings yet
- Maternal Lectures EditedDocument77 pagesMaternal Lectures EditedSHEENA MAE DE LOS REYESNo ratings yet
- Gynecological Anatomy & PhysiologyDocument39 pagesGynecological Anatomy & Physiologynursereview100% (3)
- Human ReproductionDocument15 pagesHuman ReproductionAnkit PruthwirajNo ratings yet
- Human Anatomy The Reproductive System: Dr. Ali MohsinDocument3 pagesHuman Anatomy The Reproductive System: Dr. Ali Mohsinpathanedeepshikha09No ratings yet
- P3 ReproductiveDocument24 pagesP3 ReproductiveZach DanielNo ratings yet
- Human ReproductionDocument60 pagesHuman ReproductionOmiNo ratings yet
- Unit XDocument18 pagesUnit XPreeti ChouhanNo ratings yet
- Chapter: 3. Human Reproduction: The Male Reproductive SystemDocument12 pagesChapter: 3. Human Reproduction: The Male Reproductive Systemlogi nageshNo ratings yet
- Physiology - Ii Year BemsDocument10 pagesPhysiology - Ii Year BemsKumar M V ScNo ratings yet
- Bio NotesDocument180 pagesBio NotesjyotibhalaNo ratings yet
- Human Reproduction Logo NotesDocument25 pagesHuman Reproduction Logo Notespajice8959No ratings yet
- Ma. Elizabeth F. FontanillaDocument48 pagesMa. Elizabeth F. Fontanillatam mei100% (1)
- Female RSystemDocument71 pagesFemale RSystemicliftonguytonNo ratings yet
- Ob Notes EditedDocument28 pagesOb Notes EditedJake IliganNo ratings yet
- Xii Zool Ch3 Human Reproduction HssliveDocument8 pagesXii Zool Ch3 Human Reproduction HsslivePrituNo ratings yet
- Reproductive System of Human-80Document7 pagesReproductive System of Human-80joshidipesh770No ratings yet
- Anatomy and Physiology Reproductive System: ComponentsDocument7 pagesAnatomy and Physiology Reproductive System: ComponentsMark Nel Nuñez100% (1)
- Anatomy & Physiology of Female Reproductive System Lecturer .Mahabad.M.koyiDocument36 pagesAnatomy & Physiology of Female Reproductive System Lecturer .Mahabad.M.koyiKarwan DilmanyNo ratings yet
- UNIT 11 (Reproductive System)Document12 pagesUNIT 11 (Reproductive System)Workinesh Kaynabo KambaloNo ratings yet
- Scanned With CamscannerDocument12 pagesScanned With CamscannerDr. Mohammad JamaliNo ratings yet
- OB NormalsDocument14 pagesOB NormalsLouie John AbilaNo ratings yet
- X. Anatomy & Physiology Cervix: VaginaDocument8 pagesX. Anatomy & Physiology Cervix: VaginaNicaMariannePañaNo ratings yet
- The Growing Fetus FertilizationDocument6 pagesThe Growing Fetus FertilizationJustJ ThingsNo ratings yet
- Human Reproduction and Reproductive HealthDocument16 pagesHuman Reproduction and Reproductive HealthHemanth GowdaNo ratings yet
- Anatomy & Physiology of Female Reproductive System: Dr. Aida Abd El-RazekDocument96 pagesAnatomy & Physiology of Female Reproductive System: Dr. Aida Abd El-RazekJennifer DixonNo ratings yet
- Module 1..lesson 1,2&3Document26 pagesModule 1..lesson 1,2&3Carlyn100% (1)
- Female RSsystem 2Document90 pagesFemale RSsystem 2icliftonguytonNo ratings yet
- Pre-Reading For Reproductive SystemDocument16 pagesPre-Reading For Reproductive SystemRill VasanthNo ratings yet
- Reproductive SystemDocument6 pagesReproductive SystemJared Bien TagolimotNo ratings yet
- The Reproductive System - EDITEDDocument6 pagesThe Reproductive System - EDITEDgilissaNo ratings yet
- Screenshot 2022-03-28 at 10.17.47 PMDocument127 pagesScreenshot 2022-03-28 at 10.17.47 PMqdvvqvxn7gNo ratings yet
- Female Reproductive SystemDocument2 pagesFemale Reproductive SystemVishesh KumarNo ratings yet
- The Reproductive SystemDocument10 pagesThe Reproductive SystemSenthereng MoaisiNo ratings yet
- Structure and Function of The Reproductive SystemDocument83 pagesStructure and Function of The Reproductive SystemMagy Tabisaura GuzmanNo ratings yet
- Anatomy and Physiology of The Male and Female Reproductive System Female Reproductive Anatomy and PhysiologyDocument6 pagesAnatomy and Physiology of The Male and Female Reproductive System Female Reproductive Anatomy and PhysiologyJustJ ThingsNo ratings yet
- Maternal & Child Nursing ANATOMY & PHYSIOLOGY SECTION 1Document102 pagesMaternal & Child Nursing ANATOMY & PHYSIOLOGY SECTION 1emma rose lutella100% (1)
- CMCA Study Set 1 by MangloDocument6 pagesCMCA Study Set 1 by MangloYesha LouiseNo ratings yet
- Assignment # 3Document12 pagesAssignment # 3usaeed00000No ratings yet
- MCN Jane Lou GargaritanoDocument918 pagesMCN Jane Lou GargaritanoJanelle Estrabela GargaritanoNo ratings yet
- 2 Study of Female Reproductive SystemDocument6 pages2 Study of Female Reproductive SystemShreeya SharmaNo ratings yet
- Dwnload Full Fundamentals of Anatomy and Physiology 9th Edition Martini Test Bank PDFDocument36 pagesDwnload Full Fundamentals of Anatomy and Physiology 9th Edition Martini Test Bank PDFwaterycobstone.yg9zl100% (6)
- Organization and General Plan of The BodyDocument4 pagesOrganization and General Plan of The BodyJeanNo ratings yet
- Histopathological Photos - Part 2Document65 pagesHistopathological Photos - Part 2solom islamNo ratings yet
- Practical Task 2 Starfish DevelopmentDocument4 pagesPractical Task 2 Starfish DevelopmentBuhle PhaswaneNo ratings yet
- Formatif - C2 Cell Biology and Organisation KSSMDocument22 pagesFormatif - C2 Cell Biology and Organisation KSSMadamNo ratings yet
- Bio100 - Le3 ReviewerDocument20 pagesBio100 - Le3 ReviewerMariel De Leon GinesNo ratings yet
- Plant Anatomy ThesisDocument6 pagesPlant Anatomy Thesisbcreq2m5100% (2)
- Cross Sections of Leaf Stem and RootDocument15 pagesCross Sections of Leaf Stem and Rootlwandlemkhonza96No ratings yet
- Exercise G11Document5 pagesExercise G11zyhfqz25zwNo ratings yet
- Lab Report 2 Final - Botany1Document9 pagesLab Report 2 Final - Botany1Jonathan SerranoNo ratings yet
- BM - PPT Lesson Slides - C09Document71 pagesBM - PPT Lesson Slides - C09shannonNo ratings yet
- ThehumanbodypackDocument11 pagesThehumanbodypackLuciana ArandaNo ratings yet
- Extraembryonic MembranesDocument3 pagesExtraembryonic MembranesSimon RaoNo ratings yet
- Landmarks and Body Orientation WSDocument2 pagesLandmarks and Body Orientation WSLyrics DistrictNo ratings yet
- Worksheet 2 - Organization of The Body + IntegumentaryDocument17 pagesWorksheet 2 - Organization of The Body + IntegumentaryNoriel BaldeviaNo ratings yet
- Liver HistologyDocument8 pagesLiver HistologyAishaNo ratings yet
- Nutrition in AnimalsDocument6 pagesNutrition in AnimalsRenuNo ratings yet
- BIO LE2 ReviewerDocument16 pagesBIO LE2 ReviewerMark JimenezNo ratings yet
- Destor V.W - Lab Exercise 15 - Digestive System - dvm2fDocument31 pagesDestor V.W - Lab Exercise 15 - Digestive System - dvm2fAbdul Rahman OgagangNo ratings yet
- Iam Free Jan'24 MRCS ADocument4 pagesIam Free Jan'24 MRCS AthanitoNo ratings yet
- 5 Chapter AnaphyDocument8 pages5 Chapter Anaphyjeanbecera19No ratings yet
- 2 AQA Biology Organisation Knowledge MAT Part 2 GCSEDocument4 pages2 AQA Biology Organisation Knowledge MAT Part 2 GCSEMN NgọcNo ratings yet
- A7 Structural Organization in Animals MinDocument1 pageA7 Structural Organization in Animals MinDME MPonlineNo ratings yet
- RO_GenBio_SMILE_LP2_Q1_WEEK2Document14 pagesRO_GenBio_SMILE_LP2_Q1_WEEK2jeknendoNo ratings yet
- Integumentary System NotesDocument7 pagesIntegumentary System NotesDale Gil JuliaNo ratings yet
- Dystrophy 1Document15 pagesDystrophy 1Ammar NasirNo ratings yet
- SCIENCE 6 q2 MODULE 2 - NOTEBOOK LONGDocument35 pagesSCIENCE 6 q2 MODULE 2 - NOTEBOOK LONGPortia Dulce Patatag ToqueroNo ratings yet
- 9 SM Science Um 2022 23Document456 pages9 SM Science Um 2022 23poppat gamerNo ratings yet
- Human Form and Development (HFD)Document1 pageHuman Form and Development (HFD)Ologunja PaulNo ratings yet
- Glandular EpitheliumDocument10 pagesGlandular EpitheliumAbby Claire SomeraNo ratings yet