Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Skeletal System Fuctions
Skeletal System Fuctions
Uploaded by
Erica RosislifeOriginal Description:
Original Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Skeletal System Fuctions
Skeletal System Fuctions
Uploaded by
Erica RosislifeCopyright:
Available Formats
The skeletal system, comprising bones, cartilage, ligaments, and tendons, performs several
crucial functions in the human body:
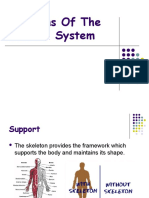
1. **Support:** Bones provide structural support for the entire body, maintaining its shape
and preventing it from collapsing.
2. **Protection:** The skeletal system protects vital organs. For example, the skull protects
the brain, and the rib cage shields the heart and lungs.
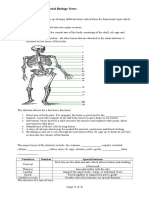
3. **Movement:** Skeletal muscles, attached to bones by tendons, allow voluntary
movement. Joints, formed where bones meet, facilitate smooth and controlled motions.
4. **Blood Cell Production:** In the bone marrow, certain bones produce red and white
blood cells, contributing to the body’s immune system and oxygen transport.
5. **Mineral Storage:** Bones store essential minerals like calcium and phosphorus,
releasing them into the bloodstream as needed for various physiological functions.
6. **Storage of Fat:** Yellow bone marrow stores fat, providing an energy reserve for the
body.
7. **Endocrine Regulation:** Certain bones, such as the bones in the endocrine system
(e.g., the pituitary gland), play a role in the regulation of hormones.
In essence, the skeletal system is integral for support, protection, movement, blood cell
production, mineral storage, fat storage, and endocrine regulation in the human body.
You might also like
- The Musculoskeletal SystemDocument23 pagesThe Musculoskeletal SystemEduardoAlejoZamoraJr.100% (5)
- Human Body StructureDocument72 pagesHuman Body Structuredeepak dwivedi94% (16)
- Skeleton SystemDocument4 pagesSkeleton Systemlevyan.alakesan9736No ratings yet
- The Skeletal SystemDocument2 pagesThe Skeletal Systemaya.silvereyeNo ratings yet
- 10 - Fisiologi TulangDocument19 pages10 - Fisiologi TulangRaditya PangestuNo ratings yet
- Teaching Notes - Muscle TissueDocument2 pagesTeaching Notes - Muscle TissueSusan FNo ratings yet
- Essential of Muscular SystemDocument1 pageEssential of Muscular SystemErica RosislifeNo ratings yet
- Parts of The BodyDocument2 pagesParts of The BodyJohnreeNo ratings yet
- Osteosarcoma-Ana and PhysiologyDocument4 pagesOsteosarcoma-Ana and PhysiologyNeirfla WassabiNo ratings yet
- Unit Five-Human Body SystemDocument5 pagesUnit Five-Human Body SystemKedir MohammedNo ratings yet
- The Skeletal SystemDocument1 pageThe Skeletal SystemMaxlynBangsilanNo ratings yet
- The Main Functions of The Skeletal SystemDocument4 pagesThe Main Functions of The Skeletal SystemLaura EslavaNo ratings yet
- Functions of The Skeletal SystemDocument12 pagesFunctions of The Skeletal SystemJared Philip Marquez CondezNo ratings yet
- Structure and Function of A Skeletal SystemDocument4 pagesStructure and Function of A Skeletal Systemapi-280073172No ratings yet
- Chapter 1Document2 pagesChapter 1Vivath LyNo ratings yet
- 1the Functions of The Skeletal SystemDocument27 pages1the Functions of The Skeletal SystemRuffa May OlayaNo ratings yet
- Skeletal System Fact FileDocument2 pagesSkeletal System Fact FileAsma AbbasNo ratings yet
- Module Skeletal SystemDocument10 pagesModule Skeletal SystemEMEM QUENNo ratings yet
- 11 Physical Education Keynotes Ch08 Fundamental of AnatomyDocument3 pages11 Physical Education Keynotes Ch08 Fundamental of AnatomyAkashNo ratings yet
- Phy 8Document3 pagesPhy 8AniketNo ratings yet
- Human BodyDocument2 pagesHuman Bodyzainab.fatima1150No ratings yet
- Skeleton: What Are Bones?Document6 pagesSkeleton: What Are Bones?Tik TokNo ratings yet
- Skeletal SystemDocument10 pagesSkeletal Systemapi-276387510No ratings yet
- CSEC - Form 4 Human and Social Biology NotesDocument4 pagesCSEC - Form 4 Human and Social Biology NotesLeon Abel80% (5)
- Skeletal and Muscular SystemDocument12 pagesSkeletal and Muscular Systemapi-296946092100% (1)
- (Bones 5)Document12 pages(Bones 5)Khan KingNo ratings yet
- What Is The Skeletal System?Document21 pagesWhat Is The Skeletal System?Ezekiel A. NavarroNo ratings yet
- P.E Pre-Activity - DiongzonDocument9 pagesP.E Pre-Activity - DiongzonAnalie DiongzonNo ratings yet
- Human Body: Ribonucleic Acid (RNA) Is ADocument35 pagesHuman Body: Ribonucleic Acid (RNA) Is AkiruthikaNo ratings yet
- Unctions of Ones: Mechanical Functions of BonesDocument2 pagesUnctions of Ones: Mechanical Functions of Bonessneh SankpalNo ratings yet
- Skeletal SystemDocument28 pagesSkeletal SystemAivee SumulongNo ratings yet
- Bone As A Living Dynamic TissueDocument14 pagesBone As A Living Dynamic TissueSuraj_Subedi100% (6)
- The Human Skeleton - 2023Document5 pagesThe Human Skeleton - 2023Milagro GeronimoNo ratings yet
- By:Pricyllia Herfianty Putri 8.2Document23 pagesBy:Pricyllia Herfianty Putri 8.2Pricyllia Herfianty PutriNo ratings yet
- NCMDocument2 pagesNCMHeherson_Taban_2403No ratings yet
- The Skeletal SystemDocument4 pagesThe Skeletal SystemJoya Sugue AlforqueNo ratings yet
- Skeletal SystemDocument12 pagesSkeletal SystemRojan V Min KookNo ratings yet
- Function of Internal OrganDocument3 pagesFunction of Internal Organerika damayantiNo ratings yet
- Working Body OrgansDocument29 pagesWorking Body OrgansRASSEL DULOSNo ratings yet
- Presentation AvyvsDocument3 pagesPresentation Avyvs10 Lê Viết Hiển 12.13No ratings yet
- Chapter 8Document6 pagesChapter 8Abhinaba PaulNo ratings yet
- Skeletal SystemDocument9 pagesSkeletal SystemLotusNo ratings yet
- Anatomy and Physiology Lecture Assignment (Skeletal System)Document4 pagesAnatomy and Physiology Lecture Assignment (Skeletal System)Destined UbaldoNo ratings yet
- Studyguide360: The Skeletal System Is The Bony Framework of Our BodyDocument3 pagesStudyguide360: The Skeletal System Is The Bony Framework of Our BodyAman DalalNo ratings yet
- Skeletal SYatemDocument188 pagesSkeletal SYatemJasmine GañganNo ratings yet
- Animal TissuesDocument10 pagesAnimal TissuesAlvin PaboresNo ratings yet
- Anatomy and PhysiologyDocument4 pagesAnatomy and PhysiologyMark Ianne AngNo ratings yet
- Human Musculoskeletal System 5Sn3Document10 pagesHuman Musculoskeletal System 5Sn3Muhammad Firdauz Abdul RaisNo ratings yet
- BIOLOGYDocument5 pagesBIOLOGYKimberling SandovalNo ratings yet
- Unit 5Document4 pagesUnit 5Kedir MohammedNo ratings yet
- 20201012-20201019-1149-Skeletal SystemDocument61 pages20201012-20201019-1149-Skeletal Systemdrin zekaNo ratings yet
- Orthopedic NursingDocument237 pagesOrthopedic Nursingɹǝʍdןnos100% (24)
- UNIT - 7 Skeletal SystemDocument163 pagesUNIT - 7 Skeletal SystemChandan ShahNo ratings yet
- Bio Lesson 1Document2 pagesBio Lesson 13bada.kan3anNo ratings yet
- 6.1 The Functions of The Skeletal System - Anatomy & PhysiologyDocument13 pages6.1 The Functions of The Skeletal System - Anatomy & PhysiologyA.No ratings yet
- The Musculo Skeletal SystemDocument2 pagesThe Musculo Skeletal Systemenzopark773No ratings yet
- Bones and Muscles and Organs, Oh My! | Anatomy and PhysiologyFrom EverandBones and Muscles and Organs, Oh My! | Anatomy and PhysiologyNo ratings yet
- Bones in The Human Body: 2nd Grade Science Workbook | Children's Anatomy Books EditionFrom EverandBones in The Human Body: 2nd Grade Science Workbook | Children's Anatomy Books EditionNo ratings yet
- Benefits of Integumentary SystemDocument1 pageBenefits of Integumentary SystemErica RosislifeNo ratings yet
- 3Document1 page3Erica RosislifeNo ratings yet
- 1Document1 page1Erica RosislifeNo ratings yet
- Tle 10Document4 pagesTle 10Erica RosislifeNo ratings yet
- English 7Document3 pagesEnglish 7Erica RosislifeNo ratings yet