Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Pancreas
Uploaded by
VinayCopyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Pancreas
Uploaded by
VinayCopyright:
Available Formats
Pancreas
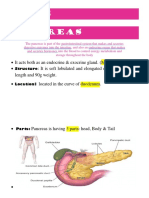
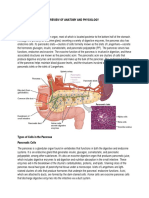
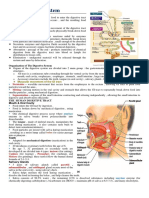
The pancreas is an organ located near the stomach and duodenum that has both
endocrine and exocrine functions. The exocrine cells are called acinar cells, and
they release digestive enzymes through a duct into the duodenum of the small
intestine. Ductal epithelial cells release bicarbonate to help neutralize the acidic
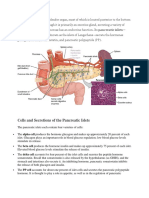
chyme leaving the stomach. The endocrine cells are called the islets of
Langerhans. Within them, beta cells release insulin, which helps absorb glucose
from the bloodstream and reduce blood sugar levels. Alpha cells release glucagon,
which promotes the conversion of glycogen to glucose and releases into the
bloodstream to increase blood sugar levels. Finally, delta cells release
somatostatin, which inhibits both alpha and beta cells and plays a large role in
enzyme regulation pathways.
PLAY PICMONIC
Characteristics
Acinar Cells Release Digestive Enzymes
Acai-berry releasing Digestive Fish-enzymes
The pancreatic acini are the exocrine part of the pancreas. They produce and secrete digestive enzymes into the duodenum of the small intestine.
Ductal Epithelial Cells Release Bicarbonate
Duck releasing Bi-car-bombs
The ductal epithelial cells in the exocrine pancreas release bicarbonate ions into the duodenum to neutralize the acidic chyme entering the duodenum
from the stomach.
Islets of Langerhans
Island of Long-horn-palms
The endocrine section of the pancreas is made up of islets of Langerhans. The section constitutes only 1-2% of the mass of the pancreas, and is
responsible for regulating blood sugar levels.
Beta Cells Release Insulin
Beta-fish with Insect-syringe
Insulin is synthesized in the beta cells of the islets of Langerhans. Beta cells are about 65-80% of cells in the endocrine area of the pancreas. Insulin
activates beta cells and inhibits alpha cells. It also causes liver cells, skeletal muscles, and fat tissue to absorb glucose and decrease blood sugar levels.
Alpha Cells Release Glucagon
Afro Glue-King-Kong
Glucagon is secreted by alpha cells of the islets of Langerhans, which are located in a specific endocrine portion of the pancreas. Glucagon activates
alpha cells and inhibits beta cells. Glucagon stimulates the liver to convert glycogen to glucose and release it into the blood.
Delta Cells Release Somatostatin
Delta-triangle Releases Sumo-Santa
Somatostatin is secreted by the delta cells of the pancreas, but is also found in the stomach and intestine.
Somatostatin Inhibits Alpha and Beta Cells
Sumo-Santa landing on Afro and Beta-fish
Somatostatin is an inhibitory hormone, and prevents the release of insulin and glucagon. It also inhibits growth hormone (GH) and thyroid-stimulating
hormone (TSH).
Sign up for FREE at picmonic.com
You might also like
- Healthy Habits for Managing & Reversing Prediabetes: 100 Simple, Effective Ways to Prevent and Undo PrediabetesFrom EverandHealthy Habits for Managing & Reversing Prediabetes: 100 Simple, Effective Ways to Prevent and Undo PrediabetesNo ratings yet
- Anatomy and PhysiologyDocument4 pagesAnatomy and PhysiologyJohn Rey Abad67% (3)
- Anaphy PancreasDocument6 pagesAnaphy PancreasAELYN SEVILLANo ratings yet
- Pancreas PancreasDocument18 pagesPancreas PancreasZzeba KhanNo ratings yet
- Salivary SecretionDocument10 pagesSalivary SecretionMahadi Hasan KhanNo ratings yet
- Ms - Anu Sebastian: B.Pharm M.Pharm Assistant Professor, Dept. of Pharmacology Nirmala College of Pharmacy Muvattupuzha, Ernakulam, KeralaDocument18 pagesMs - Anu Sebastian: B.Pharm M.Pharm Assistant Professor, Dept. of Pharmacology Nirmala College of Pharmacy Muvattupuzha, Ernakulam, KeralaZzeba KhanNo ratings yet
- Mouth: Lingual Lipase LipidDocument9 pagesMouth: Lingual Lipase LipidOscar Villados Jr.No ratings yet
- Endocrine SystemDocument7 pagesEndocrine SystemKelly Camero ÜNo ratings yet
- Hepatopancreatic Ampulla: Common Bile DuctDocument7 pagesHepatopancreatic Ampulla: Common Bile DuctnanasNo ratings yet
- Physiology of The PancreasDocument4 pagesPhysiology of The PancreasKetan PatelNo ratings yet
- Anatomy and Physiology Endocrine System: HypothalamusDocument3 pagesAnatomy and Physiology Endocrine System: HypothalamusPearl JuntillaNo ratings yet
- Role of Digestive EnzymesDocument8 pagesRole of Digestive EnzymesvasaviNo ratings yet
- Liver and Pancreas FinalDocument47 pagesLiver and Pancreas FinalmosabNo ratings yet
- 4M TheoryDocument10 pages4M TheoryGwenn SalazarNo ratings yet
- Review of Anatomy and PhysiologyDocument7 pagesReview of Anatomy and PhysiologyKyla CalzadoNo ratings yet
- Periodic TestDocument3 pagesPeriodic TestDebapriya HazraNo ratings yet
- Anatomy and Physiology DMDocument3 pagesAnatomy and Physiology DMJisel-Apple Bulan100% (3)
- Script ReportDocument3 pagesScript ReportVannJayson CaseresNo ratings yet
- The PancreasDocument2 pagesThe Pancreasf6v9pqg2zzNo ratings yet
- Biochemical Structure & Function of Glucagon & SomatostatinDocument21 pagesBiochemical Structure & Function of Glucagon & SomatostatinSyedSaqibHussainNo ratings yet
- Anatomy and PhysiologyDocument2 pagesAnatomy and PhysiologyJeffrey Calicdan BucalaNo ratings yet
- The Role of Enzymes in The Digestive SystemDocument2 pagesThe Role of Enzymes in The Digestive SystemJeanAnzurezNo ratings yet
- Anatomy of PancreasDocument2 pagesAnatomy of PancreasAubrey MacNo ratings yet
- Gi Hormones: Dr. Sharon M. PDocument50 pagesGi Hormones: Dr. Sharon M. PAleenaNo ratings yet
- Digestive GlandDocument22 pagesDigestive GlandMalinus TorquatusNo ratings yet
- Islets of LangerhansDocument2 pagesIslets of LangerhansJc TeohNo ratings yet
- Cells and Secretions of The Pancreatic IsletsDocument4 pagesCells and Secretions of The Pancreatic IsletsSophia OcayNo ratings yet
- Hormonal Secretion of PancreasDocument17 pagesHormonal Secretion of PancreasNazia WasimNo ratings yet
- Digestive GlandsDocument17 pagesDigestive GlandsPrazwal RegmiNo ratings yet
- PancreasDocument24 pagesPancreasJeanette RiosNo ratings yet
- Dogfishsharkdissection Doc-2Document5 pagesDogfishsharkdissection Doc-2api-318477724No ratings yet
- Pancreatic HormonesDocument42 pagesPancreatic Hormonesmustafa aliNo ratings yet
- Regulation of Blood GlucoseDocument21 pagesRegulation of Blood GlucoseDimple PatelNo ratings yet
- Pancreas: Cells and Secretions of The Pancreatic IsletsDocument8 pagesPancreas: Cells and Secretions of The Pancreatic IsletsansahNo ratings yet
- Module 3: The Gastrointestinal System: Learning ObjectivesDocument1 pageModule 3: The Gastrointestinal System: Learning ObjectivesZeina SharkasNo ratings yet
- PancreasDocument36 pagesPancreasANZC-chetana singhNo ratings yet
- Physiology of The PancreasDocument4 pagesPhysiology of The PancreasClayton VerBerkmösNo ratings yet
- Medical School Notes On Pancreatic IssuesDocument26 pagesMedical School Notes On Pancreatic IssuesDeji KajiNo ratings yet
- Cañonero Juanico Jaco Talamor TarrazonaDocument19 pagesCañonero Juanico Jaco Talamor TarrazonaEej EspinoNo ratings yet
- Lecture-5 Hormonal Regulation of Intestinal MotilityDocument4 pagesLecture-5 Hormonal Regulation of Intestinal Motilityمرتضى حسين عبدNo ratings yet
- Gastrointestinal System Secretion and Functions of Pancreas and Gallbladder and Their RegulationDocument7 pagesGastrointestinal System Secretion and Functions of Pancreas and Gallbladder and Their RegulationSHANJIDA ALI RIANo ratings yet
- LiverDocument3 pagesLiverrahniNo ratings yet
- Physiology of GIT (2) (Autosaved)Document67 pagesPhysiology of GIT (2) (Autosaved)RISALATUL KHOIROTUNISANo ratings yet
- RgergDocument3 pagesRgergqaisjan123No ratings yet
- Structure Appearance FunctionDocument6 pagesStructure Appearance FunctionKennee Eve CantilNo ratings yet
- Biology PancreasDocument10 pagesBiology Pancreasjavier orellana mejiaNo ratings yet
- 2.6 Kontrol Saraf Hormon DigestivusDocument19 pages2.6 Kontrol Saraf Hormon DigestivusDewi Kartika SariNo ratings yet
- Pancreatic Enzyme DeficiencyDocument3 pagesPancreatic Enzyme DeficiencyMarie Louie MonforteNo ratings yet
- Hormonal Control of GitDocument42 pagesHormonal Control of GitM. Shahin Uddin KazemNo ratings yet
- The Digestion ProcessDocument7 pagesThe Digestion ProcessKim Szydney RachoNo ratings yet
- Gastric Juice RegulationDocument22 pagesGastric Juice Regulationjanuian75% (4)
- Understanding Diabetes: Anatomy and PhysiologyDocument3 pagesUnderstanding Diabetes: Anatomy and PhysiologyJas Castro JoveroNo ratings yet
- Digestive Hormones and EnzymesDocument2 pagesDigestive Hormones and EnzymesTiannaNo ratings yet
- Biochemistry of Specialized Tissues (Liver)Document24 pagesBiochemistry of Specialized Tissues (Liver)Uloko ChristopherNo ratings yet
- محاضرات الكيمياء كاملة PDFDocument124 pagesمحاضرات الكيمياء كاملة PDFفراس الموسويNo ratings yet
- Anatomy and PhysiologyDocument13 pagesAnatomy and PhysiologyernestoNo ratings yet
- HORMONES-PHYSIO NotesDocument1 pageHORMONES-PHYSIO NotesANGELICA ADVIENTONo ratings yet
- 61.functions of The Liver and BileDocument2 pages61.functions of The Liver and BileNek TeroNo ratings yet
- The Digestive System MODULEDocument3 pagesThe Digestive System MODULEBen Moldenhaur100% (2)
- Pancreatic Juice SecretionDocument3 pagesPancreatic Juice SecretionBilal SaidNo ratings yet
- Breast Engrogement FinalDocument41 pagesBreast Engrogement FinalSharmistha DebnathNo ratings yet
- Introduction To Animal Science An Sci 1Document70 pagesIntroduction To Animal Science An Sci 1princesspuro966No ratings yet
- Planes Systems OrganizationDocument36 pagesPlanes Systems OrganizationR. EssoNo ratings yet
- Introduction To Anatomy and Physiology BookDocument42 pagesIntroduction To Anatomy and Physiology BookAnge Ouedraogo100% (1)
- Please Note: Veterinary PathologyDocument45 pagesPlease Note: Veterinary PathologyRenien Khim BahayaNo ratings yet
- NEET SS New Brochures 2018 PDFDocument16 pagesNEET SS New Brochures 2018 PDFSrinivas PingaliNo ratings yet
- BioPsych Handout 4 RESTRUCTUREDDocument7 pagesBioPsych Handout 4 RESTRUCTUREDMarial JavierNo ratings yet
- Benefits of Breastfeeding (Outline Paper)Document15 pagesBenefits of Breastfeeding (Outline Paper)Bea Glory0% (3)
- Appendicitis Case StudyDocument6 pagesAppendicitis Case StudyKimxi Chiu LimNo ratings yet
- Bsc2086 Ass. 1 SummerDocument51 pagesBsc2086 Ass. 1 SummerGeico88No ratings yet
- Biology: Board - ICSE Class-8 Topic - Endocrine and AdolescenceDocument11 pagesBiology: Board - ICSE Class-8 Topic - Endocrine and AdolescenceItu Dey100% (2)
- Coeliac Trunk, Superior and Inferior Mesenteric ArteriesDocument24 pagesCoeliac Trunk, Superior and Inferior Mesenteric ArteriesKosisochukwu sixtus Ugwunnaji100% (1)
- HypokalemiaDocument40 pagesHypokalemiaNadila Putri100% (1)
- HyponatremiaDocument19 pagesHyponatremiaapi-260357356No ratings yet
- The GastroDocument25 pagesThe Gastroangel_maui100% (7)
- MCQs On Chemical Coordination and ControlDocument18 pagesMCQs On Chemical Coordination and ControlPukazhvanthen ParamanandhanNo ratings yet
- Demonstration of The Reflex Pathway in FrogsDocument12 pagesDemonstration of The Reflex Pathway in FrogsRuwiniRajakarunaNo ratings yet
- New-Onset Supraventricular Arrhythmia During Septic Shock: Prevalence, Risk Factors and PrognosisDocument8 pagesNew-Onset Supraventricular Arrhythmia During Septic Shock: Prevalence, Risk Factors and PrognosisAhmad FahroziNo ratings yet
- Anatomy-Physiology of The Eye DNB Ophthalmology Theory DnbCentral - inDocument66 pagesAnatomy-Physiology of The Eye DNB Ophthalmology Theory DnbCentral - inporuNo ratings yet
- Neuroanatomy, Cerebellum: Statpearls (Internet) - Treasure Island (FL) : Statpearls Publishing 2023 JanDocument5 pagesNeuroanatomy, Cerebellum: Statpearls (Internet) - Treasure Island (FL) : Statpearls Publishing 2023 JanANISA RIFKA RIDHONo ratings yet
- Benign Prostatic HyperplasiaDocument4 pagesBenign Prostatic Hyperplasiaエド パジャロンNo ratings yet
- Session #17 SAS - AnaPhy (Lab)Document4 pagesSession #17 SAS - AnaPhy (Lab)Nicole Ken AgdanaNo ratings yet
- Chapter 1 - The Nervous SystemDocument8 pagesChapter 1 - The Nervous SystemRadha RamineniNo ratings yet
- 5 BubbleheDocument1 page5 BubbleheErick SumicadNo ratings yet
- A Case Study On Graves DiseaseDocument46 pagesA Case Study On Graves DiseaseRenie SerranoNo ratings yet
- Cholelytiasis 2013 2015Document37 pagesCholelytiasis 2013 2015Nurul RamadhantyNo ratings yet
- The Heart and PericardiumDocument40 pagesThe Heart and PericardiumMartha Orendu Oche AttahNo ratings yet
- UNIT13 CompressedDocument27 pagesUNIT13 Compressedemerald CasinilloNo ratings yet
- Human Body Systems For KidsDocument12 pagesHuman Body Systems For Kidsnk20No ratings yet
- Pathophysiology of Acute Renal FailureDocument2 pagesPathophysiology of Acute Renal Failuresugarmontejo67% (3)