Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Tutorial 1 - Answers
Tutorial 1 - Answers
Uploaded by
David Rivera Arjona0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
3 views1 pageThis document summarizes the answers to 4 tutorial questions about clean combustion technologies:
1) It provides the values calculated for constants and equivalence ratio in the first question.
2) It lists the absolute enthalpy and mass fractions calculated for the mixture in the second question.
3) It gives the high and low heating values calculated for the third question considering different products of H2O.
4) It states that the adiabatic flame temperature calculated was 2318K and provides additional analysis and calculations considering variable specific heats and dissociation for the fourth question.
Original Description:
Original Title
Tutorial 1 -answers
Copyright
© © All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentThis document summarizes the answers to 4 tutorial questions about clean combustion technologies:
1) It provides the values calculated for constants and equivalence ratio in the first question.
2) It lists the absolute enthalpy and mass fractions calculated for the mixture in the second question.
3) It gives the high and low heating values calculated for the third question considering different products of H2O.
4) It states that the adiabatic flame temperature calculated was 2318K and provides additional analysis and calculations considering variable specific heats and dissociation for the fourth question.
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
3 views1 pageTutorial 1 - Answers
Tutorial 1 - Answers
Uploaded by
David Rivera ArjonaThis document summarizes the answers to 4 tutorial questions about clean combustion technologies:
1) It provides the values calculated for constants and equivalence ratio in the first question.
2) It lists the absolute enthalpy and mass fractions calculated for the mixture in the second question.
3) It gives the high and low heating values calculated for the third question considering different products of H2O.
4) It states that the adiabatic flame temperature calculated was 2318K and provides additional analysis and calculations considering variable specific heats and dissociation for the fourth question.
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
You are on page 1of 1
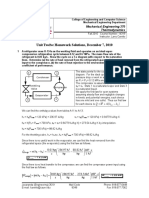
Tutorial 1- answers
CP533 Clean Combustion Technologies (CCT)
Q1. 𝑎𝑠𝑡𝑜𝑖 = 15.5, 𝑏 = 0.5, and equivalence ratio 𝛷 = 0.968
Q2. Absolute enthalpy of the mixture:
−58339.1 𝑘𝐽/𝑘𝑚𝑜𝑙𝑚𝑖𝑥
−1869.12 𝑘𝐽/𝑘𝑔𝑚𝑖𝑥
Mass fractions of the three component gases:
𝑌𝐶𝑂 = 0.0897
𝑌𝐶𝑂2 = 0.2820
𝑌𝑁2 = 0.6282
Comments: Both molar and mass units are frequently used in combustion. Because of this,
you should be quite comfortable with their interconversions.
Q3. Considering the product of H2O as liquid, the high heating value is:
∆ℎ̅𝑐 = 6830096 𝑘𝐽/𝑘𝑚𝑜𝑙𝐶10𝐻22 (or 48003 𝑘𝐽/𝑘𝑔𝐶10𝐻22 );
when considering the product of H2O as gas, the low heating value is:
∆ℎ̅𝑐 = 6345986 𝑘𝐽/𝑚𝑜𝑙𝐶10𝐻22 (or 44601 𝑘𝐽/𝑘𝑔𝐶10𝐻22 );
Q4. 𝑇𝑎𝑑 = 2318 𝐾
Comments: Considering the crudeness of the assumptions, this result appears to be rather
surprisingly good agreement. Removing assumption 2 and recalculating 𝑇𝑎𝑑 using variable
specific heats, i.e.,
𝑇
ℎ̅𝑖 = ℎ̅𝑓,𝑖
0
+ ∫ 𝑐𝑃,𝑖 𝑑𝑇
298
Yields 𝑇𝑎𝑑 = 2328 𝐾. You could see, this result (2328K) is quite close to the constant-𝐶𝑝
solution (2318K), we can conclude that the ~100K difference is the result of neglecting
dissociation. Note, dissociation causes a lowering of 𝑇𝑎𝑑 since more energy is tied up in
chemical bonds (enthalpies of formation) at the expense of the sensible enthalpy.
You might also like
- Solutions Manual Fluid Mechanics 5th EdiDocument8 pagesSolutions Manual Fluid Mechanics 5th EdiАпцгдк Ьфш БгднчллNo ratings yet
- Introduction To Chemical Processes Murphy Chapter06 SolutionsDocument94 pagesIntroduction To Chemical Processes Murphy Chapter06 SolutionsEric Barnett29% (7)
- The ClausiusDocument12 pagesThe ClausiusjokishNo ratings yet
- Chem 1 Week 4 Stoichiometry CompilerDocument7 pagesChem 1 Week 4 Stoichiometry CompilerMelcorr MontesclarosNo ratings yet
- Ctdcha 2Document10 pagesCtdcha 2TKNo ratings yet
- Lecture 1 - IntroductionDocument20 pagesLecture 1 - IntroductionDavid Rivera Arjona100% (1)
- FALLSEM2022 23 - BCHY101L - TH - VL2022230105172 - Reference - Material - II - 03 12 2022 - 1a Numericals Mod 1 F 22 23 ClassDocument24 pagesFALLSEM2022 23 - BCHY101L - TH - VL2022230105172 - Reference - Material - II - 03 12 2022 - 1a Numericals Mod 1 F 22 23 ClassVenkat BalajiNo ratings yet
- Module 10 - UNIT II - Fuels (Part 2)Document7 pagesModule 10 - UNIT II - Fuels (Part 2)Jhess GaliciaNo ratings yet
- CPC2 Lecture 7-1Document14 pagesCPC2 Lecture 7-1Adu GilbertNo ratings yet
- Phy Chem Course WorkDocument6 pagesPhy Chem Course Workpacoto livingstoneNo ratings yet
- CHEN2000 FinalDocument10 pagesCHEN2000 FinalKHÁNH VÂN DIỆPNo ratings yet
- General Chemistry - Problem SolvingDocument2 pagesGeneral Chemistry - Problem SolvingGemma Noelle AragonNo ratings yet
- Contoh Soal CreDocument11 pagesContoh Soal CreMuhammad Irfan SalahuddinNo ratings yet
- Synthron Case Study Write UpDocument10 pagesSynthron Case Study Write UpTallo CruzNo ratings yet
- Thermo ChemistryDocument5 pagesThermo ChemistryroythomascNo ratings yet
- Task #1Document9 pagesTask #1EmptySilenceNo ratings yet
- Thermodynamic IiDocument4 pagesThermodynamic Iis221110888No ratings yet
- Obaidullah Waheed 20099517 CENG0034 Natural Gas Processing Coursework 2Document6 pagesObaidullah Waheed 20099517 CENG0034 Natural Gas Processing Coursework 2ganeshNo ratings yet
- Powerplant Final CEPDocument7 pagesPowerplant Final CEPzayyanraajpoot456No ratings yet
- Student Experiment - ChemistryDocument9 pagesStudent Experiment - ChemistryJimNo ratings yet
- Rekayasa TermalDocument5 pagesRekayasa TermalHydra ZineNo ratings yet
- Numericals: Thermodynamics and Chemical KineticsDocument8 pagesNumericals: Thermodynamics and Chemical KineticsBhavya AnandNo ratings yet
- ChE 209 Chemical Process Calculations - L19 2Document46 pagesChE 209 Chemical Process Calculations - L19 2v4hz8swm9tNo ratings yet
- Technological University of The Philippines Ayala Boulevard, Ermita, Manila, Philippines College of Engineering Mechanical Engineering DepartmentDocument11 pagesTechnological University of The Philippines Ayala Boulevard, Ermita, Manila, Philippines College of Engineering Mechanical Engineering DepartmentmarkNo ratings yet
- Appendix C Design Calculations For Gas Power Generation Plant Design Alternative 2: Option ADocument44 pagesAppendix C Design Calculations For Gas Power Generation Plant Design Alternative 2: Option AAaronn RaphaaNo ratings yet
- Tutorial Problems-Ch 5Document36 pagesTutorial Problems-Ch 5nonstopforever9266No ratings yet
- Ps Gs PDFDocument10 pagesPs Gs PDFVivek MauryaNo ratings yet
- Chemical Equilibrium and DissociationDocument14 pagesChemical Equilibrium and DissociationSpr FANo ratings yet
- E20 025 Junker's CalorimeterDocument9 pagesE20 025 Junker's Calorimetersajeevanrs1216No ratings yet
- Esercizi Sulla Combustione - TurnsDocument5 pagesEsercizi Sulla Combustione - TurnsMario TodiscoNo ratings yet
- Energy BalanceDocument16 pagesEnergy BalanceFirdaus SaudNo ratings yet
- In The Last Lectures We Saw How Mass and Energy Balance Is DoneDocument22 pagesIn The Last Lectures We Saw How Mass and Energy Balance Is DoneThebe Tshepiso MaitshokoNo ratings yet
- Thermochemistry: What Is The Difference Between Exothermic and Endothermic Reactions?Document7 pagesThermochemistry: What Is The Difference Between Exothermic and Endothermic Reactions?riza amoresNo ratings yet
- S2012 ChE234 S Exam - 2Document6 pagesS2012 ChE234 S Exam - 2jrobs314No ratings yet
- 5 - Availability & IrreversibilityDocument13 pages5 - Availability & IrreversibilitySaurabh KalitaNo ratings yet
- Unit 26 Assign. 1Document5 pagesUnit 26 Assign. 1Hasan Ahmed100% (1)
- 32 Vaporization TNDocument4 pages32 Vaporization TNAjeng FadillahNo ratings yet
- Revision - Energy BalanceDocument4 pagesRevision - Energy BalancePorkkodi SugumaranNo ratings yet
- Lesson 04: Thermochemistry Unit 02: Thermochemical Equations Learning ObjectivesDocument7 pagesLesson 04: Thermochemistry Unit 02: Thermochemical Equations Learning ObjectivesLelouchNo ratings yet
- Respuestas Termoquimica ChangDocument8 pagesRespuestas Termoquimica ChangIsabelNo ratings yet
- Refri - STTFDocument5 pagesRefri - STTFAli AkbarNo ratings yet
- Solution Tutorial 6 2022fDocument3 pagesSolution Tutorial 6 2022fcompasscuriosityNo ratings yet
- Assumptions 1 Steady Operating Conditions Exist. 2 The Mixing Chamber Is Well-Insulated So That Heat LossDocument1 pageAssumptions 1 Steady Operating Conditions Exist. 2 The Mixing Chamber Is Well-Insulated So That Heat LossHafiz Mahar28No ratings yet
- By J. Gutow 8/2007 Fuel ValuesDocument2 pagesBy J. Gutow 8/2007 Fuel ValuesMiriam TorreNo ratings yet
- Assignment 4Document1 pageAssignment 4Kanchan SavitaNo ratings yet
- Chapter 6Document33 pagesChapter 6Victor M. JakiNo ratings yet
- 2018-6-14 Advanced Environmental ProtectionDocument10 pages2018-6-14 Advanced Environmental ProtectionSoveasna ChanNo ratings yet
- Chemical Process Calculations: Autumn 2021Document23 pagesChemical Process Calculations: Autumn 2021Ujjwal AnandNo ratings yet
- Chap 14 PracDocument6 pagesChap 14 PracArturo Hernández MoralesNo ratings yet
- Topic18 AnswersDocument40 pagesTopic18 AnswersEduardoNo ratings yet
- Lab - Activity No. 6 - Rimbao, Alona Jane V.Document5 pagesLab - Activity No. 6 - Rimbao, Alona Jane V.Alona Jane RimbaoNo ratings yet
- Topic 17 - Equilibrium HL - AnswersDocument7 pagesTopic 17 - Equilibrium HL - Answers赵倞No ratings yet
- Lec2 Heat Engine and Carnot Cycle PostDocument51 pagesLec2 Heat Engine and Carnot Cycle PostAniruddha NarkhedeNo ratings yet
- Reactor Design QuestionsDocument3 pagesReactor Design QuestionsellieNo ratings yet
- Chapter 12 (Vapor Power Systems) : Actual Rankine CycleDocument8 pagesChapter 12 (Vapor Power Systems) : Actual Rankine CycleNagham MuradNo ratings yet
- Lesson 6 Slides - The Rankine Power Cycle PDFDocument18 pagesLesson 6 Slides - The Rankine Power Cycle PDFPheza AndrewNo ratings yet
- HW 13Document5 pagesHW 13muru0105No ratings yet
- A Modern Course in Statistical PhysicsFrom EverandA Modern Course in Statistical PhysicsRating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (2)
- Tutorial 5 - AnswersDocument1 pageTutorial 5 - AnswersDavid Rivera ArjonaNo ratings yet
- Tutorial 3 - AnswersDocument1 pageTutorial 3 - AnswersDavid Rivera ArjonaNo ratings yet
- Absolute EnthalpyDocument2 pagesAbsolute EnthalpyDavid Rivera ArjonaNo ratings yet
- Tutorial 2 - AnswerDocument1 pageTutorial 2 - AnswerDavid Rivera ArjonaNo ratings yet
- Lecture 5 - EB IntroductionDocument16 pagesLecture 5 - EB IntroductionDavid Rivera ArjonaNo ratings yet