Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Wre Micro Project
Uploaded by
ajajkhan22659Original Description:
Original Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Wre Micro Project
Uploaded by
ajajkhan22659Copyright:
Available Formats
WRE Micro project
Foundation Engineering (Zeal College of Engineering and Research)
Studocu is not sponsored or endorsed by any college or university
Downloaded by Ajaj Khan (ajajkhan22659@gmail.com)
MAHARASHRA STATE BOARD OF TECHNICAL EDUCATION
ZEAL EDUCATION SOCIETY`S
ZEAL POLYTECHNIC
MICRO PROJECT
Academic year: 2023-24
TITAL OF PROJECT
Prepare Report On Drip Irigation Project Along With Its Operation And
Maintainance
Program: Civil Engineering Program code: TYCE
Course: Water Resource Engineering Course code: 22501
Downloaded by Ajaj Khan (ajajkhan22659@gmail.com)
MAHARASHTRA STATE BOARD OF TECHNICAL EDUCATION
Certificate
This is to certify that Mr. Santosh Shankrappa Rathod Roll No. of 5th Semester of
Diploma in TYCE-A Civil Engineering of Institute, ZEAL POLYTECHNIC (0988) has
Completed the Micro Project satisfactorily Water Resource Engineering in subject (22501)
for the academic year 2023 – 2024 as prescribed in the curriculum.
Place: Pune Enrolment No.:2109880148
Date: / /2023 Exam Seat no.: ……………
Subject teacher Head of the Department Principal
Downloaded by Ajaj Khan (ajajkhan22659@gmail.com)
Group Details:
Sr. No. Name of Group members Roll no. Enrolment no. Seat no.
1 Santosh S.Rathod CE-A-321 2109880148
2 Pranay S. Sable CE-A-322 2109880150
3 Shaikh Adnan Saif Arif CE-A-323 2109880157
4 Shaikh Nusrat Nafiz Arif CE-A-324 2109880158
Name of the Guide: Prof. Khade sir
Downloaded by Ajaj Khan (ajajkhan22659@gmail.com)
INDEX
Page
Sr.no. Content
no.
ABSTRACT
1
CONTENT
2
CONCLUSION
3
4 REFRANCE & SOURCES
5 WEEKLY REPORT
6 ANNAXURE II
Downloaded by Ajaj Khan (ajajkhan22659@gmail.com)
PROJECT ABSTRACT
in india, perhaps more than 80 per cent of the available water is used for
irrigation. irrigation is the controlled application of water through man-made
systems to meet the water requirements of agriculture. irrigation is an artificial
application of water to crops or plants, especially when an agricultural field does
not get enough water through rains. having perhaps the largest irrigated area in
the world, india faces acute water scarcity. we need to adopt irrigation methods
that help in not only in saving freshwater, but also provide sufficient water to
plants for growth. one such method now being followed in india is
‘microirrigation’.
Microirrigation is the slow application of continuous drips, tiny streams or
miniature sprays of water above or below the soil surface. In this Session, you
will learn about the main features of microirrigation system and its classification
microirrigation system can be broadly classified into two categories:
(1) drip irrigation system
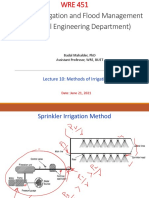
(2) sprinkler irrigation system
however, there are distinct differences in the water flow rate, operating pressure
requirement and measurement of the wetted area between drip and sprinkler
irrigation systems. water flow rate means the amount of water discharged in an
area at a particular time. it is expressed in litre/minute (lpm) or gallons/ minute
(gpm). the system operating pressure must compensate for pressure losses
through system components and field elevation effects
Downloaded by Ajaj Khan (ajajkhan22659@gmail.com)
MAIN CONTENT
DRIP IRRIGATION SYSTEM
drip irrigation system, also known as ‘trickle irrigation system’, is a method of
applying the required
amount of water directly to the root zones of plants through drippers or emitters
at frequent intervals. in this system, water is applied drop-by-drop or by a micro
jet on the soil surface or sub-surface at a rate lower than the infiltration rate of
the soil. the emitters dissipate pressure from the distribution system by means of
orifices, vortexes and tortuous or long flow paths, thus, allowing a limited
volume of water to be discharged. most emitters are placed on ground but they
can also be buried. the emitted water moves within the soil system largely by
unsaturated flow. the water moves into the soil and wets the root zones of plants
vertically by gravity and laterally by capillary action. the lateral movement of
water beneath the surface is greater in medium to heavy soil as compared to
sandy soil. the wetted soil area for widely spaced emitters will, normally, be
elliptical in shape. drip irrigation can be used on windy days and during various
land operations
types of drip irrigation system
drip irrigation system can be classified into the following:
(i) surface drip irrigation
(ii) sub-surface drip irrigation
(iii) family drip
(iv) online drip
(v) in-line drip
surface drip
irrigation
surface drip irrigation is used to irrigate perennial crops (plants that live for more
than two years) and annual crops (plants that germinate, produce seeds, flower
and die in one year). typical surface drip irrigation system consists of the
following.
pump unit: it comprises a pump and a power unit to supply electricity to the
pump. the pump draws water from the source and provides the right pressure for
its delivery into the pipe system.
Downloaded by Ajaj Khan (ajajkhan22659@gmail.com)
6
Downloaded by Ajaj Khan (ajajkhan22659@gmail.com)
head control unit: it consists of shut-off, air and check (non-return) valves to
control the discharge and pressure of water in the entire system. a pressure relief
valve is installed after the pump unit to return excess water when the system is
not operated at its full capacity. it may also have filters to clear the water. the
filters remove sediment and debris, which can clog the system. disc filters are
commonly used to filter water from ponds, reservoirs, tanks and other sources
that contain algae. some head control units contain a fertiliser or nutrient tank to
supply fertiliser solution to plants.
tubings: it consists of a main line, sub-main lines or sub-mains and laterals. the
main line conveys water from the source and distributes it to the sub-mains. the
sub-mains convey water to the laterals, which in turn supply it to the emmiters or
drippers. the laterals are, usually, 13–32 mm in diameter and supply water into
fields through the head control unit.
emitters or drippers: these devices are used to control the discharge of water from
the laterals to plants. they are made of high density polythylene (hdpe) plastic.
water enters the drippers at approximately 1 kg/cm2 pressure and is delivered at
zero pressure in the form of droplets at a low rate of 1–2.4 litre/hour. there are
mainly two types of emitters.
Downloaded by Ajaj Khan (ajajkhan22659@gmail.com)
(a) online emitters: these are small plastic devices, which convey small streams
of water from polyethylene (pe) tubing to the soil. the water, then, moves through
the soil via capillary flow and creates a wetted circle, the size of which depends
on the soil type, flow rate and irrigation schedule. online emitters are attached to
the pe tubing wall by inserting the emitters’ barb-shaped base through a punched
hole. these can be placed anywhere along the length of the pipe. some emitters
have self-piercing barbs. the diameter of pipes used for installing online
emmitters is usually, between 12 and 20 mm.
(b) in-line emitters or drip lines: these consist of small plastic emission devices,
which are pre-inserted into the pe tubing at specified intervals during the tubing
extrusion process. their rate of water flow depends on the inlet pressure. with
lower inlet pressure, the water flow decreases, whereas, with high pressure, it
increases. this emitter is available in 0.8 lph to 4 lph discharge rate.
surface drip irrigation system is, generally, used to irrigate high-value
vegetable crops, such as tomato, broccoli, celery, cauliflower, spinach, kohlrabi,
leaf lettuce, etc.
sub-surface drip irrigation
sub-surface drip irrigation is a method of irrigating crops through buried plastic
tubes, containing embedded emitters located at regular spacings. a sub-surface
drip irrigation system has a similar design as surface drip irrigation system. but in
this case, the drip tubes are typically located 38–84″ (97–213 cm) apart and 6–
Downloaded by Ajaj Khan (ajajkhan22659@gmail.com)
10″ (15–25 cm) below the soil surface. in sub-surface drip irrigation,
evaporation is minimised and water is used more efficiently as compared to
surface irrigation. in sub-surface irrigation, the effects of surface infiltration like
crusting, water losses via evaporation and surface run-off are eliminated. water is
applied directly to the root zone of a crop as opposed to surface irrigation, in
which most weed seeds hibernate. water application is efficient and uniform in
this system. sub-surface drip irrigation helps in water conservation in open field
agriculture, often resulting in saving up to 25–50 per cent water as compared to
the flood
irrigation system.
family drip or gravity fed drip irrigation
family drip or ‘gravity fed drip irrigation’ system is a low-cost system developed
for small family plots. it is suitable for house gardening and
peri-urban agriculture. it can also be used to demonstrate the working of drip
irrigation system. family drip system is designed for areas measuring 500–1000
m2. it consists of five components — elevated tank, shut-off valve, filter, main
line and drip line.
generally, a family drip irrigation system comprises a drum, control or shut-off
valve, filter (small disc or screen filter), main line and drip laterals. the drip
outlets are spaced at 30 cm. no central pressurised water system or power source
is required in this system. therefore, it is cheap, easy to install and operate
online drip irrigation
in this system, emitters or drippers are fixed externally on the laterals at
designed spacings. thus, the drippers can be checked and cleaned easily in case
of
Downloaded by Ajaj Khan (ajajkhan22659@gmail.com)
9
Downloaded by Ajaj Khan (ajajkhan22659@gmail.com)
clogging. the dripper spacing can be changed any time to cover the increased root
zone of a plant. online dripper system is used in orchards, vineyards, artificial
landscapes and nurseries. it is, generally, used for irrigating horticultural plants
like mango, coconut, orange, lemon, banana, grapes, pomegranate, papaya,
sapota, guava, teakwood, bamboo, amla (indian gooseberry), etc.
in-line drip irrigation
in this system, drippers are fixed in the lateral tube at designed spacings at the
time of manufacturing to meet the requirement of various crops. it is effective for
row crops like cotton, sugarcane, groundnut, vegetables and flowering crops.
dripper spacing depends on the water
requirement of a crop and the water-holding capacity of the soil. once installed,
the dripper spacing cannot be changed.
10
Downloaded by Ajaj Khan (ajajkhan22659@gmail.com)
CONCLUSION
drip irrigation was developed initially for home, lawn,farm’s
care and garden water use. however, while spray irrigation technology was
developed for personal use, it is such a useful technology that it has quickly
become one of the most common types of irrigation systems in agriculture.by
using of drip irrigation method water can be saved the government of india
launched the pradhan mantri krishi sinchai yojana (pmksy) or prime minister’s
agriculture irrigation programme, with the slogan ‘per drop more crop’ in july
2015. it is a policy initiative to shift towards microirrigation so as to ‘save’ water
in agriculture and boost crop yield.
REFERENCE :
1. Water resource engineering , coad(22501) ,Nishant a. Upadhye
2. www.google .com
11
Downloaded by Ajaj Khan (ajajkhan22659@gmail.com)
WEEKLY PROGRESS REPORT
MICRO PROJECT
SR.NO. WEEK ACTIVITY PERFORMED SIGN OF GUIDE DATE
1 1ST Discussion and finalization of topic
2 2ND Preparation and submission of abstract
3 3RD Literature Review
4 4TH Collection of Date
5 5TH Collection of Date
6 6TH Discussion and outline of Content
7 7TH Formulation of Content
8 8TH Editing and proof Reading of Content
9 9TH Compilation of report and Presentation
10 10TH Seminar
11 11TH Viva voce
12 12TH Final submission of Micro Project
Sign of the Student Sign of the Faculty
12
Downloaded by Ajaj Khan (ajajkhan22659@gmail.com)
ANEEXURE II
Evaluation Sheet for the Micro Project
Academic Year: 2023-24 Name If The Faculty: Prof.M.V.Khade
Course: Water Resource Engineering Course Code: 22501 Semester: 5TH
Title of the Project: Prepare Report On Drip Irigation Project Along With Its Operation
And Maintainance
Co’s addressed by Micro Project:
Tick the CO
CO No. Course Outcomes Statements
Addressed
CO204.1 Estimate hydrological parameters
Estimate crop water requirements of a command area and capacity of
CO204.2 canals
CO204.3 Maintain irrigation structures.
CO204.4 Execute the Minor and Micro Irrigation Schemes.
CO004.5 Select the relevant Diversion Head works for the specific site conditions
Comments/suggestions about team work/leadership/inter-personal communication (If any)
………………………………………………………………………………………………….
Marks out
of 6 for Marks out of 4
Roll
Student Name performance for performance Total out of 10
no
in group in
activity oral/presentation
1. Santosh S.Rathod
2. Pranay S. Sable
3. Shaikh Adnan Saif Arif
4. Shaikh Nusrat Nafiz Arif
(Signature of Faculty)
13
Downloaded by Ajaj Khan (ajajkhan22659@gmail.com)
You might also like
- Civil Drip Irrigation Report - 2Document20 pagesCivil Drip Irrigation Report - 2Deepak kumar YADAV57% (7)
- GSM Based Irrigation SystemDocument122 pagesGSM Based Irrigation Systemmayur_rughani86% (7)
- (Template) Sprinkler and Micro Irrigation Systems Manual - PROOF 21072020Document84 pages(Template) Sprinkler and Micro Irrigation Systems Manual - PROOF 21072020Lakum Ravi N.No ratings yet
- Drip Irrigation : Efficient Water Delivery for Crop GrowthFrom EverandDrip Irrigation : Efficient Water Delivery for Crop GrowthNo ratings yet
- 9 - Drip IrrigationDocument58 pages9 - Drip Irrigationgregorio roaNo ratings yet
- Paper53254 258Document6 pagesPaper53254 258ShrikantNo ratings yet
- Irrigation SystemDocument7 pagesIrrigation System185412No ratings yet
- Drip Irrigation - Management and MaintenanceDocument3 pagesDrip Irrigation - Management and Maintenancepfdc GuwahatiNo ratings yet
- Irrigation Systems - Type of Irrigation (According To The Water Distribution System)Document34 pagesIrrigation Systems - Type of Irrigation (According To The Water Distribution System)Jaston MwicheNo ratings yet
- Paper53254 258Document6 pagesPaper53254 258Aayush KumarNo ratings yet
- Paper53254 258Document6 pagesPaper53254 258swapna2No ratings yet
- Drip Irrigation and Fertigation Drip Irrigation SystemDocument20 pagesDrip Irrigation and Fertigation Drip Irrigation SystemRudra Goud100% (1)
- Datta Meghe College of Engineering.: Project Report OnDocument45 pagesDatta Meghe College of Engineering.: Project Report OnDarshan Patel67% (3)
- A Project Report On Rainwater Harv Seting 2Document50 pagesA Project Report On Rainwater Harv Seting 2Gps BhanogNo ratings yet
- NAbard Model Bank ProjectsDocument44 pagesNAbard Model Bank ProjectsSrinivasan SakthivelNo ratings yet
- Hydrology, Irrigation and Flood Management L4/T1 (Civil Engineering Department)Document21 pagesHydrology, Irrigation and Flood Management L4/T1 (Civil Engineering Department)Mirza Md. Nazmus SakibNo ratings yet
- Sprinkler Irrigation FinalDocument44 pagesSprinkler Irrigation FinalBirjesh Yaduvanshi100% (1)
- Planning & Designining Rain Water Harvesting Syst.Document64 pagesPlanning & Designining Rain Water Harvesting Syst.Samuel DavisNo ratings yet
- Design of Rapid Gravity Filter Using AUTOCAD and CDocument44 pagesDesign of Rapid Gravity Filter Using AUTOCAD and CBinyam Kebede100% (4)
- Smart Drip Irrigation System (Sdis) Using Moisture and Rain SensorsDocument8 pagesSmart Drip Irrigation System (Sdis) Using Moisture and Rain SensorsMOHAMED BOUKAFNo ratings yet
- A Project Report On Design of Rainwater Harvesting System For Lingaya'S University CampusDocument50 pagesA Project Report On Design of Rainwater Harvesting System For Lingaya'S University CampusVasanthi VijayNo ratings yet
- Pedal Powered Centrifugal Pump Purified Water Supply DeviceDocument10 pagesPedal Powered Centrifugal Pump Purified Water Supply Deviceramarao6No ratings yet
- Final Report Awfs1Document30 pagesFinal Report Awfs1Sahana ReddyNo ratings yet
- A Project Report On Rainwater Harv Seting 2Document50 pagesA Project Report On Rainwater Harv Seting 2ayushNo ratings yet
- Seminar ReportDocument38 pagesSeminar ReportDaya Nandaj100% (2)
- Pedal Operated Water Filtration System (Mobifilt) : Research ArticleDocument5 pagesPedal Operated Water Filtration System (Mobifilt) : Research ArticleGajanan MaliNo ratings yet
- Drip IrrigationDocument23 pagesDrip IrrigationFree fire LoverNo ratings yet
- A Project Report On Rainwater Harv Seting 2Document50 pagesA Project Report On Rainwater Harv Seting 2Harishwar ReddyNo ratings yet
- A Project Report On Design of Rainwater Harvesting System For Lingaya'S University CampusDocument50 pagesA Project Report On Design of Rainwater Harvesting System For Lingaya'S University CampusAftab ShaikhNo ratings yet
- A Project Report On Rainwater Harv Seting 2Document50 pagesA Project Report On Rainwater Harv Seting 2Abhiraj Abhiraj100% (1)
- Project CivilDocument50 pagesProject CivilAbhishek YadavNo ratings yet
- Drip Irrigation ProjectDocument8 pagesDrip Irrigation Projectfebous100% (1)
- Irrigation TypesDocument22 pagesIrrigation TypesJonathan La CruzNo ratings yet
- Drip IrrigationDocument17 pagesDrip IrrigationLohithReddyNo ratings yet
- AE 152 Lab 6 - Irrigation Control StructuresDocument5 pagesAE 152 Lab 6 - Irrigation Control Structuresgregorio roa100% (1)
- THE RIVER ... : A LifestyleDocument42 pagesTHE RIVER ... : A Lifestylesilantknife_1841No ratings yet
- Drip Irrigation by RamyaDocument12 pagesDrip Irrigation by RamyaNuthi RamyaNo ratings yet
- A Project Report On Design of Rainwater Harvesting System For Lingaya'S University CampusDocument50 pagesA Project Report On Design of Rainwater Harvesting System For Lingaya'S University CampusMohamoud AbdulahiNo ratings yet
- Techniques OF Drip Irrigation and FertigationDocument25 pagesTechniques OF Drip Irrigation and FertigationBhuvnesh Kumar100% (2)
- History: Micro-Irrigation Water Roots Soil Root Zone Evaporation Valves Pipes Tubing Emitters Surface IrrigationDocument6 pagesHistory: Micro-Irrigation Water Roots Soil Root Zone Evaporation Valves Pipes Tubing Emitters Surface IrrigationnanaoNo ratings yet
- Water Jet Machining: An Advance Manufacturing Process: April 2015Document6 pagesWater Jet Machining: An Advance Manufacturing Process: April 2015palak mohodNo ratings yet
- 19.hydraulic Properties of Buried Pipe Distribution SystemDocument12 pages19.hydraulic Properties of Buried Pipe Distribution Systemaktarul bauNo ratings yet
- Kapasitas Daya Dukung Jaringan Pipa Air Bersih Dan Ven Gedung Lembaga Pengembangan Dan Penjaminan Mutu Pendidikan Universitas Negeri YogyakartaDocument13 pagesKapasitas Daya Dukung Jaringan Pipa Air Bersih Dan Ven Gedung Lembaga Pengembangan Dan Penjaminan Mutu Pendidikan Universitas Negeri YogyakartaAgustino DaniNo ratings yet
- Trickling Filters: Introduction: Trickling Filter (Otherwise Known As PercolatingDocument4 pagesTrickling Filters: Introduction: Trickling Filter (Otherwise Known As PercolatingthebammanNo ratings yet
- Akhil SeminarDocument13 pagesAkhil SeminarAkhil ManilalNo ratings yet
- Civil Engineering Seminar Topics - Drip IrrigationDocument12 pagesCivil Engineering Seminar Topics - Drip IrrigationVinod KumarNo ratings yet
- Microcontroller Based Automation of Drip Irrigation SystemDocument6 pagesMicrocontroller Based Automation of Drip Irrigation Systemzinabuhaile26No ratings yet
- Research Paper On Micro Irrigation SystemDocument5 pagesResearch Paper On Micro Irrigation Systemegxnjw0k100% (1)
- Study On Sewage Treatment Plant Comming Up at Bhagwati Nagar JammuDocument33 pagesStudy On Sewage Treatment Plant Comming Up at Bhagwati Nagar Jammuanupam rainaNo ratings yet
- Volume 2 Issue 12 December 2020 Pages 76 78shivaniDocument4 pagesVolume 2 Issue 12 December 2020 Pages 76 78shivaniSaloua ElboustatiNo ratings yet
- Septic Systems: January 2019Document16 pagesSeptic Systems: January 2019mahendra DHNo ratings yet
- WS - Chap 1& 2&3Document28 pagesWS - Chap 1& 2&3Eng Bagaragaza RomualdNo ratings yet
- Volume 2 Issue 12 December 2020 Pages 76 78shivaniDocument4 pagesVolume 2 Issue 12 December 2020 Pages 76 78shivaniPramod 1sk19cv020No ratings yet
- Sprinkler-System PDFDocument136 pagesSprinkler-System PDFEmerito PerezNo ratings yet
- Siva ProjectDocument12 pagesSiva ProjectSravan KumarNo ratings yet
- Design and Construction of A Battery Powered Jet Spray Cylinder For Micro-Irrigation SchemeDocument13 pagesDesign and Construction of A Battery Powered Jet Spray Cylinder For Micro-Irrigation SchemeInternational Journal of Innovative Science and Research TechnologyNo ratings yet
- Seminar ReportDocument25 pagesSeminar ReportSaurabh100% (1)
- Course Outcomes 3 1Document3 pagesCourse Outcomes 3 1ajajkhan22659No ratings yet
- Connection Newsletter Issue 6Document23 pagesConnection Newsletter Issue 6ajajkhan22659No ratings yet
- Nikhil 3 IDocument2 pagesNikhil 3 Iajajkhan22659No ratings yet
- DSR Micro Project Final AjajDocument30 pagesDSR Micro Project Final Ajajajajkhan22659No ratings yet
- Entry Req EngDocument4 pagesEntry Req EngMatheus StefaniNo ratings yet
- Thesis Topics On Social EntrepreneurshipDocument6 pagesThesis Topics On Social EntrepreneurshipCollegePapersToBuySingapore100% (2)
- CSEC Spanish June 2011 P2Document9 pagesCSEC Spanish June 2011 P2AshleyNo ratings yet
- 2 PassivetransportDocument8 pages2 PassivetransportFayeNo ratings yet
- Your Initial Task. Find Out What's in Me!Document6 pagesYour Initial Task. Find Out What's in Me!Earl MontecastroNo ratings yet
- The Yocum Library Online Database Passwords: All SubjectsDocument3 pagesThe Yocum Library Online Database Passwords: All SubjectsJHSNo ratings yet
- Scribd Sap SD Pricing in Depth Configuration GuideDocument136 pagesScribd Sap SD Pricing in Depth Configuration GuideRavi SubramanianNo ratings yet
- Shashika Boteju Mathematics Grade 9Document12 pagesShashika Boteju Mathematics Grade 9Dilruk GallageNo ratings yet
- Siri Jack-Up PlatformDocument7 pagesSiri Jack-Up Platformnaren_013No ratings yet
- Httpsauthors - Library.caltech - edu10520914TR000574 05 Chapter-5 PDFDocument41 pagesHttpsauthors - Library.caltech - edu10520914TR000574 05 Chapter-5 PDFKiệt LýNo ratings yet
- Surigao Del Sur State University: Mathematics in The Modern World Module Number 2Document11 pagesSurigao Del Sur State University: Mathematics in The Modern World Module Number 2TOP ERNo ratings yet
- IS30 IS50 WM CWL WM-L Schnittstellendoku enDocument250 pagesIS30 IS50 WM CWL WM-L Schnittstellendoku enspidigeNo ratings yet
- Mechanisms of Nutrient Uptake of Plant Root Cells From SoilDocument47 pagesMechanisms of Nutrient Uptake of Plant Root Cells From SoilMaha ChaudharyNo ratings yet
- How To ApplyDocument129 pagesHow To ApplySasa KasaNo ratings yet
- The Igloo PartyDocument11 pagesThe Igloo PartyRaghav MalhotraNo ratings yet
- Notes - Market Failure-Ch 13Document3 pagesNotes - Market Failure-Ch 13Rodney MonroeNo ratings yet
- Torque SpecsDocument21 pagesTorque SpecssaturnayalaNo ratings yet
- Solved Problems: Single Degree Free VibrationDocument14 pagesSolved Problems: Single Degree Free Vibrationprem adhikariNo ratings yet
- Misamis Oriental Vs Cagayan ElectricDocument7 pagesMisamis Oriental Vs Cagayan ElectricJovhilmar E. BrinquezNo ratings yet
- English Compulsory (1) PrintDocument15 pagesEnglish Compulsory (1) PrintZakir KhanNo ratings yet
- The Sniper - Storey PDFDocument177 pagesThe Sniper - Storey PDFJose Luis95% (19)
- BS 6089 - 2010 - Assessment of Insitu Compressive TestDocument40 pagesBS 6089 - 2010 - Assessment of Insitu Compressive TestMike Chan100% (2)
- CC W3 AWS Basic InfraDocument57 pagesCC W3 AWS Basic InfraMuhammad Tehseen KhanNo ratings yet
- Pneumatic Valve With Diaphragm: Instruction, Use and Maintenance ManualDocument50 pagesPneumatic Valve With Diaphragm: Instruction, Use and Maintenance ManualRicardo CalderonNo ratings yet
- Cone of ExperienceDocument7 pagesCone of ExperienceErica GalorNo ratings yet
- IBP1941 14 Fatigue of Pipelines Subjecte PDFDocument10 pagesIBP1941 14 Fatigue of Pipelines Subjecte PDFAnjani PrabhakarNo ratings yet
- Adime 2Document13 pagesAdime 2api-496164982No ratings yet
- List of RAs UpdatedDocument12 pagesList of RAs UpdatedThe SuperstarNo ratings yet
- Vibrational SpectrosDocument6 pagesVibrational Spectrosprasant906No ratings yet
- Assembly Senate Response.2.10.21. Final PDFDocument16 pagesAssembly Senate Response.2.10.21. Final PDFZacharyEJWilliamsNo ratings yet