Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Gensic Reviewer2 Anatomy and Physiology of Reproduction
Uploaded by
explorers.beamaepetracortaOriginal Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Gensic Reviewer2 Anatomy and Physiology of Reproduction
Uploaded by
explorers.beamaepetracortaCopyright:
Available Formats
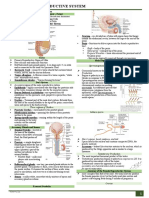
ANATOMY AND PHYSIOLOGY OF PUBERTY
REPRODUCTION
The MENSTRUAL CYCLE marks the beginning of
the puberty for females. The menstruation
begins about 14 days after ovulation (plus or
Labia Majora – outer lips surrounding all the
minus one to two days). The overall cycle is
other structures.
governed by the hypothalamus as it monitors
Labia Minora – inner lips surrounding the hormone levels in the bloodstream.
vestibule where sweat and oil glands located.
Mons Veneris – pads of fatty tissue between
MENSTRUAL CYCLE
pubic bone and skin
MENSTRUAL PHASE.
Perineum - area of skin separating the
genitalia from the anus. - This occurs if the ovum is not fertilized and
does not implant itself into the uterine lining.
Prepuce - clitoral hood
The continued high levels of estrogen and
Urethral Opening – end of the tube connecting progesterone causes the pituitary gland to stop
to bladder and used for urination. releasing FSH and LH.
Vaginal Opening – also known as the introitus PROLIFERATIVE PHASE.
Vestibule - area surrounding the urethral It occurs when the hypothalamus stimulates
opening and vagina. the pituitary gland to release FSH that
stimulates ovaries to produce estrogen and
Vulva – all the external genital structures taken causes ova to mature in the ovarian follicles.
together. The endometrium is repaired, thickens, and
becomes well-vascularized in response to
increasing levels of estrogens.
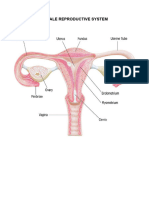
INTERNAL PARTS
SECRETORY PHASE.
Cervix - small end of uterus to which vagina
leads. It is the opening to interior uterus. It occurs when the pituitary gland releases LH
causes the ovary to release a mature ovum and
Fallopian Tube - it carries the egg cells from causes the remaining portion of the follicle to
ovaries to uterus, also this is where the develop into the corpus luteum.
fertilization occurs.
Ovaries – it produces estrogen, progesterone,
and ova or egg cells. PROBLEMS ASSOCIATED WITH THE
MENSTRUAL CYCLE
Uterus – Womb, organ within pelvic zone
where fetus is carried.
Vagina – collapsible canal extending from the PREMENSTRUAL SYNDROME (PMS)
vaginal opening back and upward into body to DYSMENORRHEA
cervix and uterus.
AMENORRHEA
MENOPAUSE Seminal Vesicles – two glands that produce
alkaline fluid rich in fructose sugar, comprising
70% of semen volume.
SECONDARY SEXUAL CHARACTERISTICS
Testes – produces androgen, particularly large
Widening of hips and pelvis quantities of testosterone, and sperm cells.
Enlargement of breasts Urethra – tube within the penis that carries
sperm and semen the rest of the way to the
opening of the penis.
MALE Vas Deferens – travels from testicle toward
urethra carrying sperm;
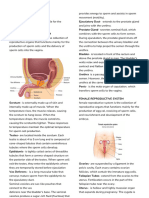
EXTERNAL PARTS
Corona – rim of glans where it arises from the THE PROCESS OF REPRODUCTION
shaft TERMS
Frenulum – is the thin strip of skin connecting OVULATION
the glans and shaft on the underside of the
penis. - the process when a mature ovum is released
from the ovary and travels to the fallopian
Penis – glans that is particularly sensitive to tube for possible fertilization.
stimulation.
FERTILIZATION
Perineum - area of skin separating the
genitalia from the anus. - union of the sperm and the ovum.
Prepuce – foreskin covering the head of the PREGNANCY
penis
- the process when an offspring develops
Scrotum – it is the sac that encloses the two within the mother’s womb
compartments housing the testes.
PREGNANCY
Urethral Opening – found on head of penis this
It officially starts when a fertilized egg implants
is the end tube connected to bladder and used
in the lining of the uterus. Pregnancy happens
for urination.
2-3 weeks after sexual intercourse.
The conception is the process that begins with
INTERNAL PARTS the fertilization of an egg and ends with the
implantation.
Ejaculatory Ducts – connect vas deferens to
urethra Once the embryo attaches to the inner lining of
the uterus, a fetus develops within five to
Prostate – gland producing alkaline secretions seven days from a ball of cells floating in the
that account for about 30% of semen volume. uterus, which officially begins pregnancy.
A normal pregnancy lasts 37-42 weeks (nine
months). This is measured from the first day of
the last period. Pregnancy is discussed in
terms of TRIMESTERS.
After eight weeks, the embryo is officially
referred to as a fetus.
WHAT ARE THE HEALTH EFFECTS OF EARLY
PREGNANCY IN THE GROWING ADOLESCENT?
There are serious health risks associated with
early pregnancy because a young woman’s
body is not mature enough to handle bearing a
child.
OBSTRUCTED LABOR
FISTULA
You might also like
- Anatomy and Physiology of ReproductionDocument27 pagesAnatomy and Physiology of ReproductionÆRO YT CHANNELNo ratings yet
- Biomedical PerpectiveDocument22 pagesBiomedical Perpectiveedmaration 2002No ratings yet
- Reproductive SystemDocument5 pagesReproductive SystemkhakimagdalenaNo ratings yet
- Reproductive SystemDocument6 pagesReproductive Systemmoramabel950No ratings yet
- Lesson 1 Male and Female Reproductive SystemDocument50 pagesLesson 1 Male and Female Reproductive Systempt09651934948No ratings yet
- Reproductive SystemDocument29 pagesReproductive SystemGrace Marfa OreñoNo ratings yet
- Anatomy and Physiology of ReproductionDocument3 pagesAnatomy and Physiology of ReproductionAstorias Jayv B.No ratings yet
- Lesson 4 Biomedical Perspective in Gender Sexuality 2Document28 pagesLesson 4 Biomedical Perspective in Gender Sexuality 2Nikka GoenettNo ratings yet
- Male Reproductive SystemDocument9 pagesMale Reproductive SystemLatrell GelacioNo ratings yet
- S10 Q3 WEEK1 Reproductive System LECTUREDocument35 pagesS10 Q3 WEEK1 Reproductive System LECTUREREGLOS, Marie Nhelle K.No ratings yet
- REPRODUCTIONDocument78 pagesREPRODUCTIONglaizaNo ratings yet
- Reproduction AnfismanDocument43 pagesReproduction AnfismanSyahirahNo ratings yet
- SCIENCE 10 - The Reproductive SystemDocument9 pagesSCIENCE 10 - The Reproductive SystemJyña Khura TanoNo ratings yet
- (Week 17) Reproductive SystemDocument3 pages(Week 17) Reproductive SystemDiana Leen Dela CruzNo ratings yet
- Lesson 4-7 ReviewerDocument4 pagesLesson 4-7 Reviewermaryjoycelaqui.mlNo ratings yet
- 2 The Reproductive SystemDocument122 pages2 The Reproductive SystemBryan Lloyd Ballestar RayatNo ratings yet
- Reproductive System ReviewerDocument4 pagesReproductive System ReviewerJewel Arcega PartoNo ratings yet
- Anatomy and Physiology of ReproductionDocument3 pagesAnatomy and Physiology of ReproductionheavenNo ratings yet
- Reproduksi SistemDocument27 pagesReproduksi SistemAndriW.IraNo ratings yet
- Reproductive System - Bio 2 - 12 Stem - l11Document4 pagesReproductive System - Bio 2 - 12 Stem - l11Lyka Lobido CabeltesNo ratings yet
- Handout Maternity Nursing Female Reproductive OrgansDocument3 pagesHandout Maternity Nursing Female Reproductive OrgansPaul Christian P. Santos, RN100% (2)
- Inbound 7864817067318640141Document55 pagesInbound 7864817067318640141Rijane Mae Castillo GabaNo ratings yet
- Female Reproductive SystemDocument17 pagesFemale Reproductive SystemYsthanamhire TolentinoNo ratings yet
- REPRODUCTIVEDocument89 pagesREPRODUCTIVEJohn MichaelMackayNo ratings yet
- LESSON 1 - Reproductive System and Its DiseasesDocument45 pagesLESSON 1 - Reproductive System and Its DiseasesMikela DelatoreNo ratings yet
- Science 10 Reviewer 3RDDocument12 pagesScience 10 Reviewer 3RDaltheaburgas9No ratings yet
- Reproduction in Humans: SMPK 6 PenaburDocument24 pagesReproduction in Humans: SMPK 6 PenaburOKTAVIANI HAPSARINo ratings yet
- Final Anatomy and PhysiologyDocument22 pagesFinal Anatomy and PhysiologyJohn BretanaNo ratings yet
- Care of The Mother and Fetus During The Perinatal PeriodDocument37 pagesCare of The Mother and Fetus During The Perinatal PeriodSana ChanNo ratings yet
- LESSON-4 Anatomy and Physiology of ReproductionDocument16 pagesLESSON-4 Anatomy and Physiology of ReproductionJane EdullantesNo ratings yet
- Anatomy and PhysiologyDocument7 pagesAnatomy and PhysiologyKristine Alejandro100% (1)
- Male Reproductive System Female Reproductive SystemDocument1 pageMale Reproductive System Female Reproductive SystemEunimae VillanuevaNo ratings yet
- Human Reproductive SystemDocument3 pagesHuman Reproductive SystemKrishnan Nicolai MiguelNo ratings yet
- Reproduction System PhysiologyDocument40 pagesReproduction System PhysiologySalman KhanNo ratings yet
- CMCA Study Set 1 by MangloDocument6 pagesCMCA Study Set 1 by MangloYesha LouiseNo ratings yet
- Science Reviewer Q3Document7 pagesScience Reviewer Q3Zoren JovenNo ratings yet
- Reproductive SystemDocument43 pagesReproductive SystemDoc Zay VillafuerteNo ratings yet
- 1 ConceptionDocument104 pages1 ConceptionAnuchithraRKNo ratings yet
- Uts 3Document12 pagesUts 3kurtyuiNo ratings yet
- Reproductive SystemDocument32 pagesReproductive SystemPrincess Nicole HernaezNo ratings yet
- Soft Mound of Fatty Tissue in Front ofDocument6 pagesSoft Mound of Fatty Tissue in Front ofKhristin Joy GamponiaNo ratings yet
- Reproductive System For ReviewerDocument50 pagesReproductive System For Reviewerzyrle (zayrieeo)No ratings yet
- OB NormalsDocument14 pagesOB NormalsLouie John AbilaNo ratings yet
- Anatomy and Physiolog MyomaDocument3 pagesAnatomy and Physiolog MyomaJisel-Apple BulanNo ratings yet
- Female Reproductive Ogans Internal Organs of ReproductionDocument22 pagesFemale Reproductive Ogans Internal Organs of ReproductionAecille VillarNo ratings yet
- Female Reproductive Ogans Internal Organs of ReproductionDocument22 pagesFemale Reproductive Ogans Internal Organs of ReproductionAngela NeriNo ratings yet
- Anatomy and Physiology CompleteDocument9 pagesAnatomy and Physiology CompleteJohn BretanaNo ratings yet
- 3rd Monthly Test ReviewerDocument5 pages3rd Monthly Test ReviewerLaxen JunioNo ratings yet
- QUARTER 3 Reproductive SystemDocument30 pagesQUARTER 3 Reproductive Systemespinajeff07No ratings yet
- Human Reproduction: Important NotesDocument6 pagesHuman Reproduction: Important NotesHema KamatNo ratings yet
- Reproductive SystemDocument33 pagesReproductive Systemjheannegabriellea.ylaganNo ratings yet
- Science 10Document3 pagesScience 10Andrea JimenezNo ratings yet
- Science 3rd QuarterDocument22 pagesScience 3rd QuarterBethel AquinoNo ratings yet
- UNIT 11 (Reproductive System)Document12 pagesUNIT 11 (Reproductive System)Workinesh Kaynabo KambaloNo ratings yet
- Reporductive SystemDocument31 pagesReporductive SystemEmma Joel OtaiNo ratings yet
- Human Repro Prelim ReviewerDocument2 pagesHuman Repro Prelim ReviewerMaryGrace Cruz-MatienzoNo ratings yet
- Female Reproductive System: Dominguez, Nikka EDocument51 pagesFemale Reproductive System: Dominguez, Nikka EGwyneth100% (1)
- Reproductive System AnatomyDocument7 pagesReproductive System AnatomyEdDa LaIne TotillaNo ratings yet
- Class 10 Biology Chapter 11 Revision NotesDocument8 pagesClass 10 Biology Chapter 11 Revision NotesShayon BeraNo ratings yet
- lastCleanException 20210728200429Document83 pageslastCleanException 20210728200429Alicja FeltynowskaNo ratings yet
- Research Proposal - ICMR STS 2019 1. Title: Thyroid Auto-Immune Response in Pregnant Women With Gestational Diabetes Mellitus 2. ObjectiveDocument4 pagesResearch Proposal - ICMR STS 2019 1. Title: Thyroid Auto-Immune Response in Pregnant Women With Gestational Diabetes Mellitus 2. Objectivesiddarth reddyNo ratings yet
- Maternity Case 9: Fatime Sanogo (Core) : Guided Reflection QuestionsDocument2 pagesMaternity Case 9: Fatime Sanogo (Core) : Guided Reflection QuestionsDai NguyenNo ratings yet
- Mapeh 8 Periodical Q2 FinalsDocument2 pagesMapeh 8 Periodical Q2 FinalsJac PolidoNo ratings yet
- Care of Mother, Child, and Adolescent: Prepared by Donna Belle Sumugat RN ManDocument26 pagesCare of Mother, Child, and Adolescent: Prepared by Donna Belle Sumugat RN ManLaurence Docog100% (1)
- PB 1 - NP 2 (Final)Document17 pagesPB 1 - NP 2 (Final)AnnizaNo ratings yet
- Bahasa Inggris NURHALIMAH-1Document3 pagesBahasa Inggris NURHALIMAH-1NurhalimahNo ratings yet
- The Philippine Family Planning ProgramDocument40 pagesThe Philippine Family Planning ProgramAlexandria P. OrcajadaNo ratings yet
- Fetal Membranes and PlacentaDocument4 pagesFetal Membranes and Placentavanobestoon223No ratings yet
- Example QuizDocument17 pagesExample QuizDianne LabisNo ratings yet
- SurrogasyDocument29 pagesSurrogasyArshi KhanNo ratings yet
- The Legal and Ethical Dilemmas in Keeping Abreast With Innovations in Medical SciencesDocument4 pagesThe Legal and Ethical Dilemmas in Keeping Abreast With Innovations in Medical ScienceslampatNo ratings yet
- Ginecologia Ro An 2022 NR 1 1Document52 pagesGinecologia Ro An 2022 NR 1 1DaianaAdrianaNo ratings yet
- Maternal & Child Health Nursing - Care of The Childbearing & Childrearing FamilyDocument292 pagesMaternal & Child Health Nursing - Care of The Childbearing & Childrearing FamilyFlorence GuerraNo ratings yet
- Tugas Koding Pregnan Rosifatiya Kurnia (22032517)Document5 pagesTugas Koding Pregnan Rosifatiya Kurnia (22032517)BagaszoNo ratings yet
- Ovarian Apoplexy and Its Impact On Reproductive HealthDocument8 pagesOvarian Apoplexy and Its Impact On Reproductive HealthCentral Asian StudiesNo ratings yet
- Columbia Sexuality and Gender Law Clinic - Surrogacy Law and Policy Report - June 2016 PDFDocument90 pagesColumbia Sexuality and Gender Law Clinic - Surrogacy Law and Policy Report - June 2016 PDFShantanu AgnihotriNo ratings yet
- Family Reproductive Life PlanningDocument11 pagesFamily Reproductive Life PlanningIsabel BangalaoNo ratings yet
- Healthy Women in Georgia A ReportDocument44 pagesHealthy Women in Georgia A ReportViren SharmaNo ratings yet
- Module 3Document3 pagesModule 3Charles JoseNo ratings yet
- PEB Format Jurnal Revisi 1Document17 pagesPEB Format Jurnal Revisi 1wika_MWNo ratings yet
- Articles: BackgroundDocument12 pagesArticles: BackgroundChristian YzaguirreNo ratings yet
- Omnibus Policies On The Availment of Leave Privileges 111Document8 pagesOmnibus Policies On The Availment of Leave Privileges 111Diana HermidaNo ratings yet
- Uterine Fibroids (Leiomyomas) : Issues in Pregnancy - UpToDateDocument23 pagesUterine Fibroids (Leiomyomas) : Issues in Pregnancy - UpToDaterilla saeliputriNo ratings yet
- 3 Wives One Husband 2Document508 pages3 Wives One Husband 2relebohilelehasa2No ratings yet
- Komunikasi Terapeutik Bidan Dan Pasien Pasca Melahirkan Operasi Pada Rumah Sakit Muhammadiyah Palangka RayaDocument13 pagesKomunikasi Terapeutik Bidan Dan Pasien Pasca Melahirkan Operasi Pada Rumah Sakit Muhammadiyah Palangka RayaSelvyra Eka MasturinaNo ratings yet
- Abortion - PPT For 2nd MSCDocument121 pagesAbortion - PPT For 2nd MSCsindhujojo33% (3)
- Ultrasound of Congenital Fetal Anomalies: Differential Diagnosis and Prognostic Indicators. Second EditionDocument30 pagesUltrasound of Congenital Fetal Anomalies: Differential Diagnosis and Prognostic Indicators. Second EditionDevanshNo ratings yet
- Bundle of Joy The Protection Journey: Vital Care PlusDocument1 pageBundle of Joy The Protection Journey: Vital Care PlusMustaza Abu BakarNo ratings yet
- Evaluate The Size of The Pelvis and Cervix Trusted SourceDocument2 pagesEvaluate The Size of The Pelvis and Cervix Trusted SourceDjoudji ngoune AmabelleNo ratings yet