Professional Documents
Culture Documents
3rd Monthly Test Reviewer
Uploaded by
Laxen Junio0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
11 views5 pagesReviewer
Copyright
© © All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
DOCX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentReviewer
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as DOCX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
11 views5 pages3rd Monthly Test Reviewer
Uploaded by
Laxen JunioReviewer
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as DOCX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
You are on page 1of 5
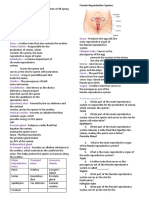
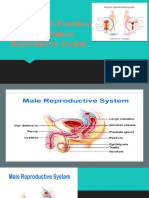
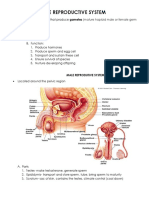
Science Sertoli cells - supports and nourish the
Male Reproductive System immature sperm cells by giving them
o Functions: nutrients and blood products.
- To produce sperm (spermatogenesis), o Sperm Production
- To produce hormones to control the Spermatogonia – sperm producing
development of secondary sex cells found in the tubule walls
characteristics Sertoli cells
o Parts: Leydig cells – found in the tubule;
testes or testicles – male sex glands or produce male hormones.
reproductive organs; secrete hormone Epididymis -is a tightly coiled mass
Seminiferous tubules – produce sperm of thin tubes that carries sperm from
cells or spermatozoa the testes to the ductus deferens in
Epididymis – a temporary storage place of the male reproductive system.
sperms, located along the sides of the o Sperm Transportation
testes Vas deferens
Testosterone - male sex hormone which Ejaculatory duct - is created when
controls the development of secondary sex the seminal vesicle's duct merges
characteristics, making a man feel and look with the vas deferens.
like a man Seminal vesicle
Vas deferens – receive sperms from Prostate gland
epididymis and carries them up, and Urethra - travels through the penis
delivers them into the urethra and also carries semen.
Seminal vesicle – a gland that produces Cowper’s gland/Bulbourethral
part of the seminal secretion; a side pouch gland
near the urethra; Penis
Scrotum – a bag or pouch for testes; has Female Reproductive System
involuntary muscle fibers as part of the skin o Functions
Prostate gland – produces a thin, watery, - To produce egg (oogenesis),
alkaline secretion that mixes with sperm - To receive sperm and provide a place
cells and other secretion to form the semen where fertilization of the egg by the sperm
- Prostatic secretion makes the sperm can take place
cells start to swim vigorously - To provide for the development of the
Cowper’s gland/Bulbourethral gland – embryo, and
located together with the prostate gland - To produce hormones to control the
near the upper end of the male urethra development of secondary sex
Penis – mass of erectile tissue, characteristics
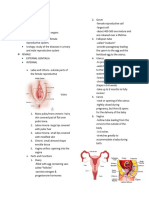
surrounded by a fibrous case arranged in o Parts
three columns; ordinarily hangs down in Follicle – Ovarian cell
front of the scrotum Fallopian tube/ Oviduct/ Uterine Tube -
Foreskin or prepuce – covers the Uterus (womb) - Placed where the fertilized
sensitive head of the penis often so long ovum is implanted
and tight Cervix – Opening of the uterus
o Parts of Spermcells Vagina – The channel leading to the uterus
Consists of four major parts to the external opening of the genital canal
- Head (flattened oval shaped) - Hymen – soft ring of tissue which narrows
- Neck the lower part of the vagina; stretched or
- Connecting piece torn during the first sexual experience
- Tail Vulva - The external parts of the female
Flagellum – organelle that makes sperm genitalia
movement possible; has mitochondria to Mamary gland (Breast) – Produces milk
transform energy - Nipple
Acrosome – capsule located at the head - Areola
of sperm; filled with special dissolving
enzymes
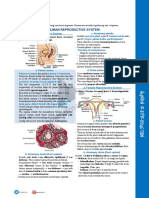
o The Ovarian and Uterine Cycles – Fertalization of the egg
Hormonal Functions - Egg – enclosed by a layer called
Hormones – coordinate the corona radiata
development of ovum and the uterus - Zona pellucida – another barrier of
Follicle – formed when a mass of an egg which composed mainly of
ovarian cells released an ovum or jelly-like substances
egg Ovulation - the process of generating the
FSH (follicle stimulating hormone) egg cell, takes place between the tenth and
- stimulates follicle maturation and the sixteenth day of the average menstrual
estrogen production cycle
- estrogen – stimulates egg to ripen Embryo – any developing organism whose
Corpus luteum –produces a body form has not yet acquired the
hormone called progesterone characteristics that make it recognizable as
LH (Luteinizing hormone) – a member of a particular animal species;
controls the yellow body formation of last for 6 weeks
follicles o Significant stages during embryonic
Progesterone – causes breast development
enlargement during pregnancy; Blastula – a development of the
maintains the growth of the mucus embryo
lining of the uterus Gastrula – an early stage of
Menstruation - The breakdown and embryonic development during
discharge of the soft uterine tissues and the which the second germ layer is
unfertilized egg. formed
Menarche - The first menstrual Embryonic Membranes
discharge of blood from the vagina o Extraembryonic membrane – a membrane
- Most obvious signal of the onset of forms around the mass of dividing cells
puberty in females o Chorion – produces enzymes to enable the
- Signals the beginning of the cyclic villi to sink into the uterine membrane
changes in the ovary o Amnion – contain fluid that protects the
o Cycle developing embryo from mechanical injury
Blood Flow – 1 to 5 day and keeps its moist
Follicular – 6 to 13 day o Placenta – serves to transport food and
waste materials between the mother and
Ovulation – 14 day
the developing young
Luteal – 15 to 28 day
o Umbilical cord – connects embryo to the
o Human fertilization and Development
placenta
- Fertilization – the union of gametes
o Navel – the scar that marks the location of
or the fusion of the egg cell nucleus
the umbilical cord
and the sperm cell nucleus
Growth of germ layers
- External fertilization – sperm cells
Ectoderm - Inner ear, cochlea, skin,
and egg cells are shed by their
hair, nails, nervous system, tooth
donors in a surrounding medium
enamel, inner lining of nose and
where they unite
mouth
- Internal fertilization – occurs in a
female reproductive tract Mesoderm - Skeleton, muscles
- Syngamy fertilization – merging (cardiac, smooth, skeletal), excretory
process of sperm’s and egg’s system and reproductive structures,
nucleus blood vessels and blood
Sexual Reproduction Endoderm - Lining of the digestive
- Male and female parents both system, lining of the respiratory tract,
release their sex cells (gametes) liver, pancreas, thyroid, parathyroid
which join together to produce a cell Fatal Development (per month)
called a zygote, it grows into an 1. By the end of the first month, the embryo
embryo and then in an independent is about 1/10 of an inch long. The heart,
new organism which is no larger than a poppy seed,
has begun beating
2. The embryo is about 1 inch long and has In females, gonorrhea can also
distinct, slightly webbed fingers. Veins are infect the cervix.
clearly visible. The heart has divided into o Syphilis - a common bacterial
right and left chambers. infection that’s spread through sex.
Syphilis is easily cured with antibiotic
3. By now the fetus is 2 1/2 to 3 inches long medicine, but it can cause
and is fully formed. He has begun permanent damage if you don’t get
swallowing and kicking. All organs and treated.
muscles have formed and are beginning o Epididmitis – Inflammation of the
to function. epididymis
4. Your baby is covered with a layer of thick, o Prostate Cancer - A disease in
downy hair called lanugo. His heartbeat which cancer cells grow in the
can be heard clearly. This is when you prostate
may feel your baby's first kick. o Male Infertility – produces no
5. A protective coating called vernix sperm cell; caused by an inherited
caseosa begins to form on baby's skin. condition like chromosomal
By the end of this month, your baby will be abnormalities
nearly 8 inches long and weigh almost a o Cervical Cancer – Cancer cells
pound. grow on the cervix
6. Eyebrows and eyelids are visible. Your o Dysmenorrhea – severe pain during
baby's lungs are filled with amniotic fluid, menstruation
and he has started breathing motions. If o Amenorrhea – Abnormal absence
you talk or sing, he can hear you. of menstruation
7. By the end of the seventh month, your o Oligomenorrhea – Abnormal and
baby weighs about 3 1/2 pounds and is infrequent period
about 12 inches long. His body is well- o Sterility – unable to produce
formed. Fingernails cover his fingertips offspring
8. Your baby is gaining about half a pound o Vaginitis – A vaginal infection or
per week, and layers of fat are piling on. irritation
He has probably turned head-down in Dangers from Unregulated application of
preparation for birth. He weighs between certain technological advances
4 and 6 pounds. In vitro fertilization - a medical
9. Your baby is a hefty 6 to 9 pounds and procedure whereby an egg is
measures between 19 and 22 inches. As fertilized by sperm in a test tube or
he becomes more crowded, you may feel elsewhere outside the body.
him move around less. Artificial Insemination and
Diseases of the Reproductive System Surrogate Montherhood - the
Sexually Transmitted Diseases (STD) - are injection of semen into the vagina or
infections passed or transmitted from person to uterus other than by sexual
person through sexual contact or intercourse. intercourse
o Chlamydia - caused by bacteria - a woman who bears a child on
called Chlamydia trachomatis. It can behalf of another woman, either from
infect both men and women. Women her own egg fertilized by the other
can get chlamydia in the cervix, woman's partner, or from the
rectum, or throat. Men can get implantation in her uterus of a
chlamydia in the urethra (inside the fertilized egg from the other woman.
penis), rectum, or throat. Cloning - replicate (a fragment of
o Genital Herpes - causes herpetic DNA placed in an organism) so that
sores, which are painful blisters there is enough to analyze or use in
(fluid-filled bumps) that can break protein production.
open and ooze fluid.
o Gonorrhea - an infection caused by
a Neisseria gonorrhoeae bacteria
that can infect both males and
females. Gonorrhea most often
affects the urethra, rectum or throat.
English
Definition Essay - A definition
Essay Writing essay gives the meaning of a word,
o Essay - is a literary composition devoted to term or concept.
the presentation of the writer’s own ideas on - The denotation of a word is its
a topic and generally addressing a particular dictionary definition.
aspect of the subject. - The connotation of a word is its
o Forms of Essay informal or slang meaning in daily
The Formal Essay – is a reflection usage.
of life in a rather serious tone. Its Persuasive Essay - you are writing
tone, language, and subject matter to get your audience to accept your
are extremely formal. The writer’s point of view and think like you do.
purpose is to explain, to persuade, Essay Format
and to instruct.
The Informal Essay –also known as
the familiar essay, does not dwell on Thesis Introduction
serious or scholarly ideas because Statement
its subjects are the interesting and
unique thoughts of writers. It’s
usually playful or conversational. Body
o Types of Essay
Narrative Essay - A narrative essay
tells a story. Conclusion
- It can be either fictional or real-life.
- The more “real” it is for you, the
better you will tell it. (Sometimes our
o Introduction
imaginations are more real to us
- Try to capture the reader’s attention.
than our daily lives.)
- Introduction Format
Descriptive Essay - A descriptive - Attention getter
essay paints a picture with words.
- It appeals to the senses: sight, - State your problem
hearing, taste, touch and smell. - Bridge or transition sentences
- It can also appeal to emotions. - Thesis statement (always at the
- Explain something: to give an end)
account of something by giving Make a bridge to connect the
details of its characteristics. attention getting sentence(s) to your
Illustration Essay - In an illustration thesis statement
essay, you give examples of your Common way to make a bridge is to
topic. explain why the topic is important.
- Examples are very helpful to readers This bridge is often a few sentences
who may be unfamiliar with your long.
subject. Conclude introductory paragraph
- Something that helps to explain with the most important idea of the
something: an example or essay-THE THESIS STATEMENT
comparison that helps to clarify or o Thesis Statement
explain something - Topic: To announce the topic to the
Process Analysis Essay - Process reader
Analysis is a “how to do it” essay. - Opinion: To reflect a judgement
- You show in words how to get about the topic
something done: what the steps are - 3 reasons: To provide the reader
from beginning to end. with a blueprint of what is to come in
- Finally, you tell what you will have the paper
when the process is finished.
o Body - a set of paragraphs that develop the - Should follow logically from the body
idea expressed in the thesis statement. of the essay
- Make a list of main ideas that - Restate your thesis statement in
support the thesis statement. Each different words
main idea becomes the main idea - You might want to have your reader
sentence for a body paragraph. do something after reading (“call to
- Arrange the main ideas in logical action” – Example: Go write your
order (time, place, importance) Senator about this problem.)
- Plan out each body paragraph by -
listing major details that support
each main idea.
- Order the details within each
paragraph in a logical way. Each
body paragraph may end with a
concluding sentence
o The Writing Stage
After planning and arranging your main
ideas and major details, begin writing
your body paragraphs.
The number of paragraphs depends on
the topic’s complexity, inclusiveness,
and your purpose for writing.
Usually a short essay contains 3 to 5
body paragraphs, plus an introduction
and conclusion
Remember to use signal words to
make smooth transitions between
sentences and paragraphs.
o Signal/ Transition Words
For examples: For example, for
instance, to illustrate
For organization or chronological
order: The six steps are…, next,
finally first, secondly, third
For additional points: Furthermore,
in addition, also, moreover
For opposing ideas: On the other
hand, in contrast, although, however
For similar ideas: Likewise, similarly,
in comparison
For exceptions: However,
nevertheless, but, yet, still
For emphasis: Above all, finally,
more importantly
For understanding: In other words, in
essence, briefly
For summarizing: In conclusion, to
sum up, for these reasons, in a
nutshell
o Conclusion
- Leave the reader thinking about your
topic. Leave an impression on them!
- No new information in conclusion
- Be sure to recap your ideas
You might also like
- Science 10Document3 pagesScience 10Andrea JimenezNo ratings yet
- (Week 17) Reproductive SystemDocument3 pages(Week 17) Reproductive SystemDiana Leen Dela CruzNo ratings yet
- SCIENCE 10 - The Reproductive SystemDocument9 pagesSCIENCE 10 - The Reproductive SystemJyña Khura TanoNo ratings yet
- Science ReviewerDocument7 pagesScience ReviewerGilvert PanganibanNo ratings yet
- G10 3RD Quarter ScienceDocument15 pagesG10 3RD Quarter ScienceRaven MayoNo ratings yet
- Reproductive SystemDocument29 pagesReproductive SystemGrace Marfa OreñoNo ratings yet
- Enhanced Notes 3 Reproductive SystemDocument5 pagesEnhanced Notes 3 Reproductive SystemLyle CasulNo ratings yet
- Notes in ScienceDocument4 pagesNotes in ScienceKate NicoleNo ratings yet
- Reproductive SystemDocument5 pagesReproductive SystemkhakimagdalenaNo ratings yet
- 3q ScienceDocument5 pages3q Sciencemariefranchescadevelos.imcNo ratings yet
- SCIENCE REVIEWER 3rd SNZDocument7 pagesSCIENCE REVIEWER 3rd SNZcatherine mendozaNo ratings yet
- Male Gametes: OvariesDocument5 pagesMale Gametes: OvariesJasper OrilNo ratings yet
- Human ReproductionDocument69 pagesHuman Reproductionapi-202349222No ratings yet
- Human ReproductionDocument41 pagesHuman ReproductionMmabatho VilakaziNo ratings yet
- Human Reproductive SystemDocument26 pagesHuman Reproductive SystemAlmario DacalcapNo ratings yet
- Reviewers 3rd Qrtr.Document33 pagesReviewers 3rd Qrtr.Kim Jay Ann HalongongNo ratings yet
- Anatomy and Physiology of ReproductionDocument3 pagesAnatomy and Physiology of ReproductionheavenNo ratings yet
- Reproductive System Power Point AckroydDocument19 pagesReproductive System Power Point AckroydTrung Ngô Lê BảoNo ratings yet
- SCIENCE 10 3rdDocument4 pagesSCIENCE 10 3rdallyanni cabanatuanNo ratings yet
- SCIENCE Lecture b516Document2 pagesSCIENCE Lecture b516Justine Mae FeranilNo ratings yet
- Reproducrive SystemDocument15 pagesReproducrive SystemEfren GuinumtadNo ratings yet
- Summary QuestionDocument4 pagesSummary QuestionwagkangtangaNo ratings yet
- PSGUNP279020221123075249578Unit 2 - Lesson 3 - Human Reproductive System - OrgansDocument11 pagesPSGUNP279020221123075249578Unit 2 - Lesson 3 - Human Reproductive System - OrgansAshneel ChakravortyNo ratings yet
- Lesson 1 Male and Female Reproductive SystemDocument50 pagesLesson 1 Male and Female Reproductive Systempt09651934948No ratings yet
- Science 10 Reviewer 3RDDocument12 pagesScience 10 Reviewer 3RDaltheaburgas9No ratings yet
- Male Reproductive System:: Summary QuestionDocument4 pagesMale Reproductive System:: Summary QuestionwagkangtangaNo ratings yet
- 19 Reproductive SystemDocument6 pages19 Reproductive SystemEugene HerreraNo ratings yet
- Human Reproduction: Important NotesDocument6 pagesHuman Reproduction: Important NotesHema KamatNo ratings yet
- Reproductive SystemDocument5 pagesReproductive Systemmuli.michaelNo ratings yet
- Project On Reproduction: By: Aaron FreyDocument27 pagesProject On Reproduction: By: Aaron FreyLaurinda Asiedu DavisNo ratings yet
- Reproductive Systems ReviewerDocument4 pagesReproductive Systems ReviewerAustin LaurenNo ratings yet
- Lecture Notes Introduction To Reproductive SystemDocument8 pagesLecture Notes Introduction To Reproductive SystemKirstie Goc-ongNo ratings yet
- Science ReviewerDocument6 pagesScience Reviewerkristinadecastro815No ratings yet
- Reproductive SystemDocument30 pagesReproductive SystemMary Grace NovidaNo ratings yet
- S.5 BIO Reproduction in Animals NOTESDocument18 pagesS.5 BIO Reproduction in Animals NOTESmusokelukia6No ratings yet
- Human Reproduction CH-03, Bio, Class-XiiDocument69 pagesHuman Reproduction CH-03, Bio, Class-Xiisumitdhakad543No ratings yet
- Reproduction in Humans: SMPK 6 PenaburDocument24 pagesReproduction in Humans: SMPK 6 PenaburOKTAVIANI HAPSARINo ratings yet
- SCIENCEDocument4 pagesSCIENCEMa. Isabel AtanesNo ratings yet
- Physics Class 10 ICSEDocument5 pagesPhysics Class 10 ICSEmohammedumar7864521No ratings yet
- Reproductive SytemDocument2 pagesReproductive SytemHanna Rezqah P. YusophNo ratings yet
- ReproductionDocument10 pagesReproductionttvignesuwarNo ratings yet
- SXSXDocument27 pagesSXSXJoevany E. BigorniaNo ratings yet
- MATERNAL-AND-CHILD-NURSING Notes For BoardsDocument10 pagesMATERNAL-AND-CHILD-NURSING Notes For BoardsJill Margarett BongatoNo ratings yet
- Human ReproductionDocument5 pagesHuman ReproductionHimanshu Harsh 12th ANo ratings yet
- Ob Notes Normal 1Document41 pagesOb Notes Normal 1pinpindalgoNo ratings yet
- Hormones and Reproduction v2Document1 pageHormones and Reproduction v2JNo ratings yet
- Human Reproductive SystemDocument14 pagesHuman Reproductive SystemShiena marie Ma-alatNo ratings yet
- HumanreproductionpptDocument59 pagesHumanreproductionpptsugi sivamNo ratings yet
- CHAPTER 3 - Reproduction (Science Form 1)Document13 pagesCHAPTER 3 - Reproduction (Science Form 1)w pNo ratings yet
- Reproductive SystemDocument7 pagesReproductive SystemshaniaericaNo ratings yet
- 3rd Quarter Science Periodical Test NotesDocument13 pages3rd Quarter Science Periodical Test Notesmichael enriquezNo ratings yet
- Reproductive - Systems - in - Vertebrates ss2Document12 pagesReproductive - Systems - in - Vertebrates ss2Ezeh PrincessNo ratings yet
- Reproduction in HumansDocument14 pagesReproduction in HumansarnoldnsondojrNo ratings yet
- Presentation 2Document21 pagesPresentation 2ericasinamagNo ratings yet
- Biology NoteDocument9 pagesBiology NotejuliaNo ratings yet
- Science ReviewerDocument18 pagesScience Reviewer28. Pinera, Yna Angela S.No ratings yet
- Human ReproductionDocument16 pagesHuman Reproductiontamalbio7No ratings yet
- History of EmbryologyDocument35 pagesHistory of EmbryologyAdrienne Chelsea GabayNo ratings yet
- The Reproductive SystemDocument5 pagesThe Reproductive SystemPak LypNo ratings yet
- Class 12 Biology Pock BookDocument53 pagesClass 12 Biology Pock Bookbs.3136 VVS.No ratings yet
- Pretes OBGYNEDocument4 pagesPretes OBGYNEAltheaNo ratings yet
- Chap2 Lesson 1-4Document43 pagesChap2 Lesson 1-4Renalf Ezra BarbietoNo ratings yet
- Secondary 2 Science NotesDocument43 pagesSecondary 2 Science Noteszach0% (1)
- Reproduction - IGCSE Biology Notes (2020)Document22 pagesReproduction - IGCSE Biology Notes (2020)Armaaan ziyadNo ratings yet
- Endometrium in Surgical PathologyDocument129 pagesEndometrium in Surgical PathologyleartaNo ratings yet
- MenstruationDocument33 pagesMenstruationmskot100% (3)
- Class 10 Science Chapter 8 How Do Organisms Reproduce Revision NotesDocument28 pagesClass 10 Science Chapter 8 How Do Organisms Reproduce Revision NotesInnama FatimaNo ratings yet
- Chapter-3 MCQDocument10 pagesChapter-3 MCQPriya SinghNo ratings yet
- For DissertationDocument13 pagesFor DissertationRegi viniciyaNo ratings yet
- Progestogens in Obstetrics and Gynecology 2015th Edition (PRG)Document213 pagesProgestogens in Obstetrics and Gynecology 2015th Edition (PRG)amenu_bizuneh100% (4)
- Aiims Mbbs Solved Papers - 2016Document54 pagesAiims Mbbs Solved Papers - 2016ravichandran0506No ratings yet
- Anatomy and PhysioDocument5 pagesAnatomy and Physiofrances_ortezaNo ratings yet
- Decriptive Study of Garba SamagriDocument16 pagesDecriptive Study of Garba SamagriDeepthi ViswaroopanNo ratings yet
- Physiology of MenopauseDocument21 pagesPhysiology of MenopauseHellenKyakuwaire100% (1)
- Ovarian CystsDocument4 pagesOvarian CystsPriya GuptaNo ratings yet
- Feedback Mechanisms in Female Reproductive SystemDocument4 pagesFeedback Mechanisms in Female Reproductive SystemJuan Jaylou AnteNo ratings yet
- 18 Early Signs and Symptoms of Pregnancy Before Missed Period PREGNANCY SYMPTOMSDocument8 pages18 Early Signs and Symptoms of Pregnancy Before Missed Period PREGNANCY SYMPTOMSHEALTHY and FITNESSNo ratings yet
- Anaphy Finals ReviewerDocument193 pagesAnaphy Finals Reviewerxuxi dulNo ratings yet
- Gonadal Hormones and InhibitorsDocument8 pagesGonadal Hormones and InhibitorsMarianne CruzNo ratings yet
- Renr Practice Test 10 FinalDocument13 pagesRenr Practice Test 10 FinalTk100% (1)
- Science 5 LM Q1 Q4Document149 pagesScience 5 LM Q1 Q4Ludy Lyn100% (3)
- Zinc, Copper and Selenium in ReproductionDocument15 pagesZinc, Copper and Selenium in ReproductionNéstor MirelesNo ratings yet
- Nur - 100 Session 1 - SemillaDocument6 pagesNur - 100 Session 1 - SemillaVon R Semilla100% (2)
- Amenorrhoea NotesDocument17 pagesAmenorrhoea NotesPrasadNo ratings yet
- Osteoporosis in AyurvedaDocument3 pagesOsteoporosis in AyurvedaYoga FMUNo ratings yet
- Influence of Sex Hormones On The PeriodontiumDocument11 pagesInfluence of Sex Hormones On The PeriodontiumElena IancuNo ratings yet
- Natural Method To Control BirthDocument8 pagesNatural Method To Control BirthManish OliNo ratings yet
- MCNDocument13 pagesMCNJoseph Wilson MacasaNo ratings yet