Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Networking PDF
Uploaded by
onmywaytoplaygame0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
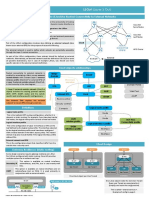
9 views2 pagesNetworking is the practice of connecting computers and devices to share resources and information. It allows for communication in today's digital age. There are different types of networks like local area networks (LANs) within a building and wide area networks (WANs) spanning larger distances. Key networking components include routers, switches, hubs, and modems. Protocols like TCP/IP, HTTP/HTTPS, DNS, and DHCP enable communication and manage network tasks. Common network topologies are bus, star, ring, and mesh configurations. Security measures involve firewalls, encryption, and authentication to protect networks. The internet and intranets differ in scope but both enable collaboration and data sharing. Cloud computing provides data access from anywhere
Original Description:
Networking presentation
Original Title
Networking.pdf
Copyright
© © All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentNetworking is the practice of connecting computers and devices to share resources and information. It allows for communication in today's digital age. There are different types of networks like local area networks (LANs) within a building and wide area networks (WANs) spanning larger distances. Key networking components include routers, switches, hubs, and modems. Protocols like TCP/IP, HTTP/HTTPS, DNS, and DHCP enable communication and manage network tasks. Common network topologies are bus, star, ring, and mesh configurations. Security measures involve firewalls, encryption, and authentication to protect networks. The internet and intranets differ in scope but both enable collaboration and data sharing. Cloud computing provides data access from anywhere
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
9 views2 pagesNetworking PDF
Uploaded by
onmywaytoplaygameNetworking is the practice of connecting computers and devices to share resources and information. It allows for communication in today's digital age. There are different types of networks like local area networks (LANs) within a building and wide area networks (WANs) spanning larger distances. Key networking components include routers, switches, hubs, and modems. Protocols like TCP/IP, HTTP/HTTPS, DNS, and DHCP enable communication and manage network tasks. Common network topologies are bus, star, ring, and mesh configurations. Security measures involve firewalls, encryption, and authentication to protect networks. The internet and intranets differ in scope but both enable collaboration and data sharing. Cloud computing provides data access from anywhere
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
You are on page 1of 2
Certainly!
Let's expand on each point for a more detailed overview:
Slide 1: Introduction
- **Definition of Networking:** Networking is the practice of connecting computers and other
devices to share resources and information.
- **Importance in the Digital Age:** Networking is crucial for communication, resource sharing,
and accessing information, especially in today's interconnected world.
Slide 2: Types of Networks
- **Local Area Network (LAN):** A network within a limited geographic area, like an office or a
building.
- **Wide Area Network (WAN):** Spans larger distances, connecting LANs across cities or
countries.
- **Wireless Networks:** Utilizes wireless technologies like Wi-Fi for connectivity.
Slide 3: Network Components
- **Routers:** Directs data between devices in different networks.
- **Switches:** Connects devices within the same network and manages data traffic efficiently.
- **Hubs:** Basic networking devices that connect multiple computers in a LAN.
- **Modems:** Converts digital data from a computer into a signal suitable for transmission over
communication lines.
Slide 4: Protocols
- **TCP/IP:** Fundamental suite of protocols ensuring reliable data transfer.
- **HTTP/HTTPS:** Protocols for web communication, securing data with HTTPS.
- **DNS:** Translates domain names into IP addresses.
- **DHCP:** Assigns IP addresses dynamically to devices on a network.
Slide 5: Network Topologies
- **Bus:** Single central cable connecting all devices.
- **Star:** Devices connected to a central hub or switch.
- **Ring:** Devices connected in a circular fashion.
- **Mesh:** Devices interconnected for redundancy and reliability.
Slide 6: Network Security
- **Firewalls:** Protects a network by controlling incoming and outgoing traffic.
- **Encryption:** Secures data transmission to prevent unauthorized access.
- **Authentication:** Verifies the identity of users or devices accessing the network.
Slide 7: Internet and Intranet
- **Differences:** Internet is a global network of networks, while an intranet is a private network
within an organization.
- **Use Cases:** Internet for global communication, intranet for internal collaboration and
resource sharing.
Slide 8: Cloud Computing
- **Basics:** Storing and accessing data and programs over the internet instead of a local
computer.
- **Advantages for Networking:** Scalability, flexibility, and accessibility from anywhere with an
internet connection.
Slide 9: IPv4 vs. IPv6
- **Addressing:** IPv4 uses 32-bit addresses, while IPv6 uses 128-bit addresses, providing
more unique combinations.
- **Transition Challenges:** The move from IPv4 to IPv6 is essential due to address exhaustion
in IPv4.
Slide 10: Troubleshooting
- **Common Network Issues:** Connectivity problems, slow performance, and security issues.
- **Diagnostic Tools:** Ping, traceroute, and network analyzers help identify and resolve
problems.
Slide 11: Future Trends
- **5G Technology:** Enables faster and more reliable wireless communication.
- **Internet of Things (IoT):** Interconnectivity of everyday devices for data exchange.
- **Edge Computing:** Processing data closer to the source to reduce latency.
Slide 12: Conclusion
- **Recap of Key Points:** Summarize the essential aspects covered in the presentation.
- **Q&A:** Open the floor for questions and discussions.
You might also like
- Project Report On Computer NetworksDocument45 pagesProject Report On Computer NetworksCutie81% (59)
- User Manual - zNID 2424A1 PDFDocument58 pagesUser Manual - zNID 2424A1 PDFericssonboyNo ratings yet
- A Level CS CH 2 9618Document20 pagesA Level CS CH 2 9618calvin esauNo ratings yet
- DIT 0411 Mobile Computing Outline - Jan 2023Document4 pagesDIT 0411 Mobile Computing Outline - Jan 2023Stephen MainaNo ratings yet
- NetworkingDocument2 pagesNetworkingShankar DakoliaNo ratings yet
- Computer NetworksDocument18 pagesComputer Networksacharyay72No ratings yet
- Computer NetworkDocument64 pagesComputer NetworkMariane PalomoNo ratings yet
- Q.1 To 10. NTDocument13 pagesQ.1 To 10. NTninjamekwan10No ratings yet
- 16 Al 17 InglesDocument5 pages16 Al 17 InglesApolo GreenNo ratings yet
- Scribd (Network)Document2 pagesScribd (Network)vladbedarev1109No ratings yet
- Chapter-1 Computer NetworkDocument41 pagesChapter-1 Computer NetworkmelkamuyirgaNo ratings yet
- Network Security and Administration Group WorkDocument44 pagesNetwork Security and Administration Group WorkMunene KelvinNo ratings yet
- New Section 1Document16 pagesNew Section 1sharransri1122No ratings yet
- Cisco ITE Chapter 7 Exam & AnswersDocument4 pagesCisco ITE Chapter 7 Exam & AnswersNoor Shahumi Abu ShaharNo ratings yet
- The Internet ICTDocument37 pagesThe Internet ICTJuma RamadhaniNo ratings yet
- Computer NetworkDocument34 pagesComputer NetworkYunus RashidNo ratings yet
- Chapter 03 - Understand Computer NetworkingDocument19 pagesChapter 03 - Understand Computer NetworkingJaye 99No ratings yet
- 803 Web Application Class XI 1Document254 pages803 Web Application Class XI 1Naina KanojiaNo ratings yet
- Computer Network & Data Communication f3Document16 pagesComputer Network & Data Communication f3ayissi jeanNo ratings yet
- Computer NetworksDocument13 pagesComputer NetworkselvinajaconNo ratings yet
- Chapter - 1: 1.1 NetworkingDocument44 pagesChapter - 1: 1.1 NetworkingKing RagnarNo ratings yet
- 4.2 Computer Network & Data CommunicationDocument26 pages4.2 Computer Network & Data CommunicationMaxim TawoutiaNo ratings yet
- Introduction To IoT (Internet of Things) Chapter 1 NotesDocument19 pagesIntroduction To IoT (Internet of Things) Chapter 1 NoteskpadmajaNo ratings yet
- CCNA 1 Chapter 1 v5+v6 Exam Answer 2017Document9 pagesCCNA 1 Chapter 1 v5+v6 Exam Answer 2017Abdo Alabed100% (1)
- Chapter OneDocument118 pagesChapter Onetaha azadNo ratings yet
- Chapter 2 ITE2513 2022Document35 pagesChapter 2 ITE2513 2022isma farizNo ratings yet
- Q.B For It SkiilsDocument15 pagesQ.B For It SkiilsSwapnil ShirkeNo ratings yet
- Multinet: Connecting To Multiple Ieee 802.11 Networks Using A Single Wireless CardDocument22 pagesMultinet: Connecting To Multiple Ieee 802.11 Networks Using A Single Wireless CardValentin OfiterescuNo ratings yet
- Computer Network & Data CommunicationDocument24 pagesComputer Network & Data CommunicationRonic DakNo ratings yet
- CCNA 1 v6.0 Study Material - Chapter 1 Explore The NetworkDocument15 pagesCCNA 1 v6.0 Study Material - Chapter 1 Explore The NetworkfiraolNo ratings yet
- Study of InternetworkingDocument10 pagesStudy of InternetworkingPravendra KushwahaNo ratings yet
- CCNA 1 Final Exam Answers 2017 v51v60 Introduction To NetworksDocument65 pagesCCNA 1 Final Exam Answers 2017 v51v60 Introduction To NetworksÐâvid Ĵesus Morales SeguraNo ratings yet
- Introduction To Computer NetworksDocument12 pagesIntroduction To Computer NetworksfarooqNo ratings yet
- CCNA 1 Final Exam Answers v6.0Document42 pagesCCNA 1 Final Exam Answers v6.0Ahmad FajriNo ratings yet
- Grade 10-12 - Week 4Document5 pagesGrade 10-12 - Week 4Oliver C SilvanoNo ratings yet
- CN Unit-IDocument167 pagesCN Unit-I18W91A0C0No ratings yet
- PT Lesson1 Computer-NetworkDocument16 pagesPT Lesson1 Computer-NetworkRodelynn PaduaNo ratings yet
- Chapter-5-Computer 9th ClassDocument8 pagesChapter-5-Computer 9th ClassMudassar NaseemNo ratings yet
- Chapter - 2 Internet and NetworkingDocument4 pagesChapter - 2 Internet and NetworkingbaljitNo ratings yet
- GR 12 ICT2 TNotes 3Document19 pagesGR 12 ICT2 TNotes 3Nuha RiyadNo ratings yet
- Practical 1Document18 pagesPractical 1Harsh PatelNo ratings yet
- Unit 8 Internet Internet ServicesDocument71 pagesUnit 8 Internet Internet ServicesBIGYAN PAUDYALNo ratings yet
- The InternetDocument2 pagesThe InternetJosh SalmonsNo ratings yet
- InternetDocument18 pagesInternetNaseer AhmedNo ratings yet
- Submodule Introduction To Communication NetworksDocument18 pagesSubmodule Introduction To Communication Networksmohamedmwakuzimu9966No ratings yet
- Chapter 1 Networking FundamentalsDocument100 pagesChapter 1 Networking FundamentalsnuhonoNo ratings yet
- Chapter 4 Computer Network and The Internet2Document33 pagesChapter 4 Computer Network and The Internet2Mehari KirosNo ratings yet
- CCNA 1 Chapter 1 v5Document13 pagesCCNA 1 Chapter 1 v5Ian NarcisoNo ratings yet
- Introduction To Computer Networks - PpsDocument12 pagesIntroduction To Computer Networks - PpsVikas DhimanNo ratings yet
- CN 21 Scheme 1-5Document109 pagesCN 21 Scheme 1-5Knightfury MilanNo ratings yet
- Telecommunications and Networking in Today's Business WorldDocument43 pagesTelecommunications and Networking in Today's Business WorldNazrul Hosen Ayon100% (4)
- CCDN NotesDocument35 pagesCCDN NotesYeekshu ChouhanNo ratings yet
- AssignmentDocument8 pagesAssignmentmakuvisemichael43No ratings yet
- Questions From Chapter 7Document4 pagesQuestions From Chapter 7Syeda Wahida SabrinaNo ratings yet
- CNE Question Bank Unit 1 and 2 Answers-1Document39 pagesCNE Question Bank Unit 1 and 2 Answers-1Aryan DamaniaNo ratings yet
- New Version: CCNA 1 Final Exam Answers v6.0Document25 pagesNew Version: CCNA 1 Final Exam Answers v6.0cNo ratings yet
- CHAPTER FOUR Networks and Cloud ComputingDocument24 pagesCHAPTER FOUR Networks and Cloud ComputingEndalkachew EmareNo ratings yet
- Sicso Networking Academy Chapter 6 v5Document6 pagesSicso Networking Academy Chapter 6 v5Sopheap SangNo ratings yet
- Dr. Nagesh YagnamDocument63 pagesDr. Nagesh YagnamSonata Conjo DaryNo ratings yet
- Operating System 12thDocument6 pagesOperating System 12thashu21dollNo ratings yet
- REMOTE ACCESS VPN- SSL VPN: A deep dive into SSL VPN from basicFrom EverandREMOTE ACCESS VPN- SSL VPN: A deep dive into SSL VPN from basicRating: 5 out of 5 stars5/5 (1)
- Difference Between Straight Through and Crossover CableDocument1 pageDifference Between Straight Through and Crossover CableJonathan PalerNo ratings yet
- ScaNv6 instructorPPT Chapter4Document30 pagesScaNv6 instructorPPT Chapter4sochea domjsNo ratings yet
- Network Switch: From Wikipedia, The Free EncyclopediaDocument7 pagesNetwork Switch: From Wikipedia, The Free EncyclopediashravandownloadNo ratings yet
- CCNA 1 v7 Modules 11 - 13 - IP Addressing Exam Answers FullDocument23 pagesCCNA 1 v7 Modules 11 - 13 - IP Addressing Exam Answers Fullwafa hopNo ratings yet
- Huawei Train4sure H12-261 v2021-04-28 by Liuwei 164qDocument83 pagesHuawei Train4sure H12-261 v2021-04-28 by Liuwei 164qhoussemNo ratings yet
- srx1600 Firewall DatasheetDocument6 pagessrx1600 Firewall DatasheetfvalenNo ratings yet
- Ad MCQDocument6 pagesAd MCQSuguna PriyaNo ratings yet
- Iot Sudip MishraDocument426 pagesIot Sudip MishraLipika B MNo ratings yet
- Valix, C. - FA2 Solutions Manual (2015)Document247 pagesValix, C. - FA2 Solutions Manual (2015)Elisabeth HenangerNo ratings yet
- CV Hesham HamadDocument2 pagesCV Hesham Hamadhello.ass.hooleNo ratings yet
- Lab 5 SolDocument8 pagesLab 5 SolSujal PrakashNo ratings yet
- Plano de Instalação PABX MitelDocument447 pagesPlano de Instalação PABX MitelRenato Silveira DionysioNo ratings yet
- Zybersafe Trafficcloak - Ethernet EncryptionDocument2 pagesZybersafe Trafficcloak - Ethernet EncryptionRamon CuevasNo ratings yet
- Fact Sheet: Bently Nevada Asset Condition Monitoring ADAPT 3701/46 Hydro MonitorDocument2 pagesFact Sheet: Bently Nevada Asset Condition Monitoring ADAPT 3701/46 Hydro MonitorViet DinhTrongNo ratings yet
- MMC-18EC743-Module-1 NotesDocument17 pagesMMC-18EC743-Module-1 Notesmkhushim83No ratings yet
- 3.1 OSI ModelDocument6 pages3.1 OSI ModelSuyasha JainNo ratings yet
- IT 104 FinalsDocument22 pagesIT 104 FinalsKiethNo ratings yet
- RouterOS by Example Stephen Discher PDFDocument236 pagesRouterOS by Example Stephen Discher PDFAntonioNo ratings yet
- Cisco ACI L3Out (Layer 3 Out)Document3 pagesCisco ACI L3Out (Layer 3 Out)Shashank TripathiNo ratings yet
- Enterprise-Class Universal Network Management Controller: Industrial-Grade Physical HardwareDocument5 pagesEnterprise-Class Universal Network Management Controller: Industrial-Grade Physical HardwareelochoNo ratings yet
- Computer Networks Compiled NotesDocument55 pagesComputer Networks Compiled NotesFredrick OrigaNo ratings yet
- Wireless-G USB Adapter WUSB54G ManualDocument25 pagesWireless-G USB Adapter WUSB54G ManualAdal LopezNo ratings yet
- Iptvswitch: Streaming ServerDocument2 pagesIptvswitch: Streaming ServerNam Khánh Đỗ VănNo ratings yet
- End Term Examination-ONLINE MODE (Non-CBCS) (May, 2021)Document3 pagesEnd Term Examination-ONLINE MODE (Non-CBCS) (May, 2021)EASHYATA EASHYATANo ratings yet
- Network +Document19 pagesNetwork +Tolea TolNo ratings yet
- Public Switched Telephone Network (PSTN) : Voice and Data Delivery NetworksDocument180 pagesPublic Switched Telephone Network (PSTN) : Voice and Data Delivery NetworksAlas Mallari DonatoNo ratings yet
- Assignm End Sem NetworkingDocument3 pagesAssignm End Sem NetworkinganukalpkumarthakurNo ratings yet
- LT1001 AT CommandsDocument44 pagesLT1001 AT CommandsraedNo ratings yet