Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Airport Handling
Uploaded by
aadyacharan3Original Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Airport Handling
Uploaded by
aadyacharan3Copyright:
Available Formats
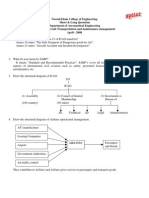
AIRPORT HANDLING
Passengers routing
Security check of baggage-Baggage screened through X-Ray machine
and locks sealed with security tags.
Check in-Ticket, passport and visa verified. Baggage weighed and
baggage tag is put on the luggage. Cabin baggage also tagged.
Boarding card.
Immigration.
Customs.
Holding area security check.
Waiting lounge.
Boarding gate.
Aerodrome/Airport-defined area on land or water intended to be used either
fully or in part for arrival, departure and movement of aircraft.
AAI-Airport Authority of India is an organization working under the
ministry of India.
Functions-
1) Controls & management of the Indian airspace extending beyond
the territorial limits of the country, as accepted by ICAO.
2) Design development, operation and maintenance of international
and domestic airports and civil enclaves.
3) Construction, modification and management of passenger
terminals.
4) Development and management of cargo terminals at international
& domestic airports.
5) Provision of passenger facilities and information system at the
passenger terminal at airports.
6) Expansion and strengthening of operation area viz.runways,
aprons, taxiway etc.
7) Provision of visual aids.
8) Provision of communication and navigation aids viz ILS,
(Instrument landing System) DVOR, DME,(Distance Measuring
equipment) Radar etc.
Revenue- generated from landing/parking fees, late fees.
IGHC (IATA Ground Handling Council)
1) IGHC bring together over 350 airlines, ground handlers, airports and
authorities.
2) Serves as a platform where matters of mutual concern regarding ground
operation can be discussed.
3) Standards are developed on how ground handling activities at airports
are conducted.
DGCA-They are responsible for implementing, controlling and supervising
air worthiness standards safety operations and crew training in India.
BCAS-BCAS monitoring the implementation of security rules and
regulations & carrying out survey of security needs.
Ensures that the persons implementing security controls are appropriately
trained & possess all competencies required to perform their duty.
Planning and coordination of aviation security matters.They are in charge
of issuing Airport Entry Permit (AEP).
DIAL (Delhi International Airport Limited)-operates and manages develops
Indira Gandhi International Airport.
GMR- Gandhi Mallikarnajuna Rao
Immigration- The department where records of passengers arriving and
departing into a country are kept with details names of passengers,
passport details, and visa details.
Custom-Customs is a government department responsible for import &
export, excise department and internal duties and taxes of all kind. Checks
baggage of arriving passengers into a country for any duty to be levied on
the goods brought by the passengers. Examines and checks cargo which
has to be exported out of the country and import cargo which is coming into
a country.
CISF-secures airport premises and guards the boundary of airport and also
check vehicular, passenger and staff movements within the airport and
monitoring the airport & movement of incoming & outgoing calls.
Airlines-
1) Airlines require handling of aircrafts between the time of arrival and
departure.
2) Ensure safety of aircraft.
3) Minimum ground time.
4) To ensure on-time departure.
Nature of ground handling-
1) Series of processes required to separate an aircraft from its load
(passengers, baggage & cargo) on arrival and combine it with its load
prior to departure.
2) Key task is to reduce aircraft ground time thus, increasing aircraft
productivity.
Ground Handling Services-Many airlines sub contract ground handling
to one of the following ground handling players-
1) Airline owned ground handling companies e.g.:-Lufthansa airport
services.
2) Independent handlers e.g.:-SATs (Singapore Airport Terminal Services),
DNATA (Dubai National Air Travel Agency), AISATs.
Ground handling services:-
1) Ramp services.
2) Aircraft marshaling/push back.
3) Loading & unloading.
4) Passenger’s steps.
5) Load control/weight & balance.
Passenger’s service:-Check in, gate boarding, customer service, baggage
service. BBA (Baggage Break-up Area), BMA (Baggage Make-up Area).
Aircraft Cabin Cleaning:-
1) Cleans cabins/gallery.
2) Clear garbage.
3) Clean Lavatories.
Above the wing:-is the operation passenger handling & related.
Passenger Services (above the wing)
Check-in
Gates
Ticketing
Lobby management
Lounge management
Customer assistance with self-serve products and irregular
operations
Special needs handling
Baggage services
• Lost and found bags
• Claims
• Baggage tracing
Below the wing operations.
Aircraft loading and unloading
Cabin grooming
Aircraft towing
De-icing services
Components of an airport layout:-
1) Runway is the area where aircraft lands or take off.
2) Terminal buildings:-These buildings are the spaces where passengers
board or alight from flights. These buildings houses all the necessary
facilities for passengers to check-in their luggage’s, ticket counters,
security check clean customs and have lounges to wait before boarding
the flight.
Terminals have cafes, lounges and bars to serve waiting passengers
large airports have more than one terminal that are connected to one
another through link ways such as walkways, sky bridge or trans.
FAA:-Federal Aviation Administration.
3) Apron (ramp):-A defined area in an airport to accommodate aircraft for
purposes of loading or unloading of passengers, cargo, refueling,
parking or maintenance.
4) Taxiway:-A taxiway is a path on an airport connecting runways with
apron (ramp), hangers & terminal etc.
5) Hanger:-A hanger is a closed building structure to hold aircraft in
protective storage.
6) Control tower:-A tower at an airfield from which air traffic is controlled by
radio and observed physically and by radar.
No show:-A pax who had a reservation on a flight and is shown on the PNL
but failed to use the reservation for reason other than miss connection.
Standby or go show passenger:-A potential revenue passenger at a check
in location and who is prepared to accept space subject to availability.
Load sheet:-A completed load sheet contains weight and balance data
pertaining to a particular flight including the weight of the aircraft, crew,
pantry, fuel, passenger, baggage, cargo & mail. It contains the detailed
distribution of this load.
Code share:-It is an agreement between two or more air carriers to share
each other’s inventory for optimal utilization. The company who actually
operates the flight is called operating carrier.
The company who does not operate flight but markets it under its own
airline code and flight number is called marketing carrier.
Interline:-Anything involving two or more.
Interline point:-Any point in the itinerary at which the pax is to change from
the flight of one airline to the flight of another.
Interline transfer:-Transfer from the service of one carrier to the service of
another.
Documents accompany the flight are:-
1) General Declaration (GD)-list of crew members operating flights.
2) Passengers manifest.
3) Cargo manifest.
PIR-Property Irregularity Report.
(When pax reports missing baggage fill in the PIR in presence of pax.)
1) DPR-Damaged Property Report.
3) EBT-Excess Baggage Ticket.
4) DIPB-Diplomatic Baggage.
5) CBBG-Cabin Baggage.
6) PSM-Passenger Service Message.
7) PNL-Passenger Name List.
8) FIM-Flight Interruption Manifest.
9) CIP-Commercially Important Pax.
10) MASS-Meet and Assist.
Passenger baggage:-
1) Baggage: - Baggage means such articles, effects and other personal
property of a passenger as are necessary or appropriate for wear, use
comfort or convenience in connection with a trip. Unless otherwise
specified it includes both checked and unchecked baggage of the
passenger.
2) Checked baggage:-means baggage of which carrier takes sole custody
and for which carrier has issued a baggage tag.
3) Unchecked baggage:-means any baggage of the passenger other than
checked baggage.
4) Accompanied baggage:-means baggage carried on the same aircraft as
that on which the passenger is carried.
5) Unaccompanied baggage:-means the baggage not carried on the same
aircraft as that on which passenger is carried.
6) Free baggage allowance:-means baggage which may be carried without
payment of a charge in addition to the fare.
7) Excess baggage:-means that part of baggage which is in excess of the
free baggage allowance.
Weight system:-for first class-40kg, business class-30kg and economy
class-20kg.
Air India free baggage allowance for travel from/to USA.
1) First class & executive class:-2pc/32kgs each. The sum of three
dimensions (length+breadth+height) must not exceed 62 inches or 158
cms for each piece. The minimum weight permissible for a single piece
of baggage is 32 kgs.
2) Economy class:-2pc/23kgs each. The sum of three dimensions
(length+breadth+height) of both must not exceed 107 inches. Moreover,
the linear dimension of each piece should not exceed 62 inches. The
weight of each bag must not exceed 23kilos.
3) Infant in all classes-1pc/10kgs.
Carry on items free of cost:-
1) A handbag, pocket book or purse.
2) An overcoat, wrap or blanket.
3) An umbrella or walking stick.
4) A still camera and/or a pair of binoculars.
5) A reasonable amount of reading matter for the flight.
6) Infant food for consumption in flight.
7) Infant-carrying basket or bassinet.
Accompanied blind person:-
1) A blind person who is accompanied by an adult passenger will be
accepted as a regular passenger.
2) When the blind person is accompanied by a seeing eye dog, the
handling of such passenger should be as follows:-
1) The Seeing Eye dog will be accepted free of charge for carriage in the
passenger compartment provided that:-
a) The dog should remain at the feet of his master during the flight.
b) The dog is properly harnessed and muzzled.
c) All permit required for the dog to enter the country of destination, en
route are prepared.
d) The dog will not be fed, except for water in the cabin during the flight.
But in case of a long trip and the feeding of the dog is necessary en
route, the feeding should be done on the ground during the transit hours.
The food should be prepared by the passenger and the cost of the food,
if any should be borne by the passenger.
Excess baggage (Air India’s domestic sector):-
Should your baggage exceed the limitation of the free baggage allowance,
an excess baggage charge needs to be paid. For domestic sectors within
India, the excess baggage rate is INR250 per kg per coupon.
Excess baggage weight system international:-
In the weight system the excess baggage charges per kilo is 1.5% of the
highest normal direct one way economy class fare.
Eg1) -Journey-DEL to LON, allowance-20kg, fare-INR25000, pax carry-
30kg. ANS:-Excess baggage-10kg
1.5% of 25000=375 .Excess baggage for 1kg = INR 375
Excess baggage for 10kg = INR 375*10 = INR 3750
Eg2) = Journey-DEL to SIN, allowance-20kg, fare-INR 20000, pax carry-
32kg.
ANS:-Excess baggage = 12kg .1.5% of 20000 = 300
Excess baggage for 1kg = INR300
Excess baggage for 12kg = INR300*12 = INR3600.
Piece system (excess baggage for travel between India and USA).
Excess baggage more than 23kgs up to 32kgs charges (per piece)
USD100 per piece. 3rd and additional piece up to 23kg USD200 per piece.
Restricted baggage classified into following categories:-
1) Prohibited articles.
2) Articles unaccepted as baggage.
3) Articles acceptable as baggage under certain conditions.
Articles unacceptable as baggage (dangerous goods)
Class 1= Explosives.
Class 2= Gases.
Class 3=Flammable liquids.
Class 4= Flammable solids, substances liable to spontaneous combustion,
substances which in contact with water emit flammable gases.
Class 5= Oxidizing substances and organic peroxides.
Class 6= Toxic and infectious substances.
Class 7= Radioactive material.
Class 8= Corrosives.
Class 9 = Miscellaneous dangerous goods.
Prohibited articles:-
1) Any article which is forbidden by the applicable laws, government’s
regulations or orders of any country to be flown from, into or over.
2) Any article which is likely to endanger the aircraft, persons or property.
3) Any article whose weight, size or character is unsuitable for carriage on
the aircraft.
4) Any article which is likely to be damaged by air carriage.
5) Any article unsuitably packed.
6) Any other article whose carriage specially restricted or prohibited by
tariffs and regulations of the airline.
Labels and tags:-
Check labels & tags on baggage and ensures old labels and tags are
removed to avoid mishandling/misrouting.
Labels:-Checked baggage stickers are stucked on the boxes that are
checked in by passengers at the terminal building counter.
Fragile label must be stuck on baggage to alert the baggage handlers to
handle the baggage with care.
Tags:-All check-in baggage must be tag with an airline baggage tag
showing the carrier (airline), destination and the routing.
There are many different types of baggage tags that are used different
purposes:-
1) Hand baggage tags.
2) Priority tag.
3) Limited release tag.
4) Meet and assist tag.
5) Heavy tag.
OHS limit (occupational, health and safety) limit is 32kg per piece.
Through check-in:-Baggage of through check-in passengers can be
checked through to their final destinations, if they have confirmed tickets.
The minimum connecting time (MCT) must be met for their connecting
flights.
Overbooking:-overbooking is when the number of seats sold on a flight
exceeds aircrafts passenger seating capacity.
Reasons for overbooking are:-
1) Failure to show for the flight (no show).
2) Yield management.
Denied boarding: - It is due to -
1) Overbooking.
2) Change of scheduled aircraft.
3) Booking error made by the reservation staff.
Codes:-
1) MEDA: - Medical case – company medical clearance may be required.
2) STCR: - Stretcher passenger.
3) WCHR: - Wheelchair- R for ramp.
4) WCHS: - Wheelchair- S for steps.
5) WCHC: - Wheelchair- C for cabin.
6) BLND: - Blind passenger.
7) DEAF: - Deaf passenger.
8) UMNR: - Unaccompanied minor.
9) MAAS: - Meet and Assist.
10) LANG: - Language Assistant Needed.
11) PREG: - Pregnant passenger.
12) DEPA: - Deported passenger travelling with an escort.
13) DEPU: - Deported passenger travelling without an escort.
Special seating requirement:-
1) AVIH – Live Animal in Hold.
2) BSCT – Bassinet Seating Requested for Infant.
3) EXST – Extra Seat Required.
4) INF – Booking Contains an Infant.
5) PETC – Passenger is travelling with an assistance dog/pet in cabin.
6) YPTA – Young passenger travelling alone.
Special Meal -
1) AVML – Asian Vegetarian Meal.
2) BBML – Baby/Infant Meal.
3) CHML – Child Meal.
4) DBML – Diabetic Meal.
5) FPML – Fruit Platter Meal.
6) JPML – Japanese Meal.
7) KSML – Kosher Meal.
8) MOML – Muslim Meal.
9) SPML – Special Meal.
10) VGML – Vegetarian Vegan Meal.
11) VJML – Jain Meal.
12) VLML – Vegetarian Lacto – Ovo Meal.
A Alpha Al fah
B Bravo Brah Voh
C Charlie Char Lee
D Delta Dell Tah
E Echo Eck Oh
F Foxtrot Foks Trot
G Golf Golf
H Hotel Hoh Tell
I India In Dee Ah
J Juliett Jew Lee Ett
K Kilo Key Loh
L Lima Lee Mah
M Mike Mike
N November No Vem Ber
O Oscar Oss Car
P Papa Pah Pah
Q Quebec Keh Beck
R Romeo Row Me Oh
S Sierra See Air Ah
T Tango Tang Go
U Uniform You Nee Form
V Victor Vik Tah
W Whiskey Wiss Key
X X Ray Ecks Ray
Y Yankee Yang Key
Z Zulu Zoo Loo
You might also like
- Practical Airport Operations, Safety, and Emergency Management: Protocols for Today and the FutureFrom EverandPractical Airport Operations, Safety, and Emergency Management: Protocols for Today and the FutureRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (5)
- Research Paper: International AirportDocument10 pagesResearch Paper: International AirportGladdelyn Piencenaves100% (1)
- Airbus SWOT AnalysisDocument4 pagesAirbus SWOT AnalysisTameem NadeemNo ratings yet
- Essentials of Aviation ManagementDocument30 pagesEssentials of Aviation ManagementAbid RanaNo ratings yet
- Passenger Service Agent Course 2019Document139 pagesPassenger Service Agent Course 2019ElshaikhNo ratings yet
- Airbus A320 Ceo NeoDocument2 pagesAirbus A320 Ceo NeoAjay KumarNo ratings yet
- Pgs (6marks) Set 3Document3 pagesPgs (6marks) Set 3NivieNo ratings yet
- L8 Air TransportDocument28 pagesL8 Air TransportNiran NadarajaNo ratings yet
- Passenger, Baggage and Aircraft HandlingDocument13 pagesPassenger, Baggage and Aircraft HandlingNikiNo ratings yet
- Line Operation ServicesDocument52 pagesLine Operation ServicesandrewpunNo ratings yet
- BIA Report PDFDocument33 pagesBIA Report PDFUditha NarawitaNo ratings yet
- Aviation terms, departure and arrival fromalitiesDocument3 pagesAviation terms, departure and arrival fromalitiesSabeerNo ratings yet
- Itts Final ReviewerDocument30 pagesItts Final ReviewerShaira GrafilNo ratings yet
- Domestic Airport Building ResearchDocument10 pagesDomestic Airport Building ResearchJared Cuento TransfiguracionNo ratings yet
- Module 2. Airport and Airline Process (Operations Management)Document9 pagesModule 2. Airport and Airline Process (Operations Management)MARITONI MEDALLANo ratings yet
- First Part: CHAPTER I. Definitions. Chapter S I ObjectiveDocument4 pagesFirst Part: CHAPTER I. Definitions. Chapter S I ObjectiveJosé Guadalupe JaimesNo ratings yet
- Air Transport Unit-5Document21 pagesAir Transport Unit-5Aditi TomarNo ratings yet
- Airport TerminologyDocument5 pagesAirport Terminologyajaynadda2804No ratings yet
- Test Pour Agent D'acceuilDocument5 pagesTest Pour Agent D'acceuilMed JabrNo ratings yet
- BBA AM - Unit 3Document35 pagesBBA AM - Unit 3Mahen parvathaneniNo ratings yet
- AirportDocument45 pagesAirportJay PatelNo ratings yet
- L.N - Aas - Unit - 2Document14 pagesL.N - Aas - Unit - 2Nambi RajanNo ratings yet
- Manual de Limba EnglezaDocument52 pagesManual de Limba EnglezaMaria SolomonNo ratings yet
- AirportDocument8 pagesAirportShiela CedronNo ratings yet
- Mba Avi Sem 4 Airline Operations and Scheduling: Unit 2 Passenger TerminalDocument19 pagesMba Avi Sem 4 Airline Operations and Scheduling: Unit 2 Passenger TerminalfranklinNo ratings yet
- Lecture Notes - TOU4003 L9 10 - Airport and Terminal OperationsDocument10 pagesLecture Notes - TOU4003 L9 10 - Airport and Terminal OperationsChang Hay Yu,MirandaNo ratings yet
- Prepare B737 Flight with 12 Safety ChecksDocument14 pagesPrepare B737 Flight with 12 Safety ChecksFerhat JaidiNo ratings yet
- Air Cargo Management Power Point 1Document82 pagesAir Cargo Management Power Point 1AromalNo ratings yet
- 01 - Airport Lecture 1-2Document90 pages01 - Airport Lecture 1-2Najwa Dhea DenintaNo ratings yet
- Airport Facilities & Services Provided to AirlinesDocument11 pagesAirport Facilities & Services Provided to AirlinesJeff YamsNo ratings yet
- IATA ManualDocument44 pagesIATA ManualjasdsbNo ratings yet
- Networkin AssignmentDocument5 pagesNetworkin AssignmentCollins MunuoNo ratings yet
- SAMUI International AirportDocument20 pagesSAMUI International AirportAhsan AfzaalNo ratings yet
- Air Transport - UNIT-1Document30 pagesAir Transport - UNIT-1Aditi TomarNo ratings yet
- Air Cargo and Ground Handling ServicesDocument22 pagesAir Cargo and Ground Handling ServicesAbdul RehmanNo ratings yet
- Transportation Development & Airport FunctionsDocument29 pagesTransportation Development & Airport Functionsjace molds100% (1)
- Chapter 5 Boarding Gate and Flight Finalizing ProceduresDocument12 pagesChapter 5 Boarding Gate and Flight Finalizing ProcedurespotatosaysNo ratings yet
- Cargo Airline Management Information SystemDocument7 pagesCargo Airline Management Information SystemTEJUS PRABHU 2148116No ratings yet
- Air Transport Management Unit-4Document25 pagesAir Transport Management Unit-4Aditi TomarNo ratings yet
- AIRPORTDocument17 pagesAIRPORTCorrine BonocanNo ratings yet
- Chapter 3 AirFreight ForwardingDocument37 pagesChapter 3 AirFreight ForwardingThomas Anderson100% (1)
- Aircraft Ground HandlingDocument15 pagesAircraft Ground HandlingAlien AnnNo ratings yet
- Aviation Assignment WrittenDocument13 pagesAviation Assignment Writtenvishalsinghtomar145No ratings yet
- Aviation SecurityDocument22 pagesAviation SecurityYash Sawant100% (1)
- Airline and Travel AgencyDocument66 pagesAirline and Travel AgencyPat Lanre ArijeritaNo ratings yet
- Passenger HandlingDocument88 pagesPassenger Handlingsir peterNo ratings yet
- Airport Operations Arrival/Departure Final PresentationDocument14 pagesAirport Operations Arrival/Departure Final PresentationSyeda Azka AliNo ratings yet
- Air FreightDocument34 pagesAir FreightAnonymous GAulxiINo ratings yet
- Sub Code 46-2rd Year-unit -5Document24 pagesSub Code 46-2rd Year-unit -5RenjithNo ratings yet
- ICAO Annexes and Aircraft Accident InvestigationDocument15 pagesICAO Annexes and Aircraft Accident InvestigationArif Abdul RahmanNo ratings yet
- New Microsoft Word DocumentDocument6 pagesNew Microsoft Word DocumentPranav Manohar DeshmukhNo ratings yet
- ICAO Annexes and SARP for Aircraft MaintenanceDocument15 pagesICAO Annexes and SARP for Aircraft MaintenanceRameez FaroukNo ratings yet
- GRCCCM NOTES Aviation Management IntroductionDocument24 pagesGRCCCM NOTES Aviation Management IntroductionchandanNo ratings yet
- Airport Engineering Explained: Runways, Terminals & Air Traffic ControlDocument44 pagesAirport Engineering Explained: Runways, Terminals & Air Traffic ControlFuaad Abdirizak Elmi100% (1)
- Processing of Departing PassengersDocument20 pagesProcessing of Departing PassengersMaritoni MedallaNo ratings yet
- Aeronautical English Guide: Aeronáutica Margarita Betancourt C.ADocument19 pagesAeronautical English Guide: Aeronáutica Margarita Betancourt C.ANicol VelasquezNo ratings yet
- BandaraDocument22 pagesBandaraApay SafariNo ratings yet
- Lec 17-Intro To Airport Engineering - Runway EngineeringDocument26 pagesLec 17-Intro To Airport Engineering - Runway Engineeringmwaqas250No ratings yet
- Unit 3Document36 pagesUnit 3Aditi TomarNo ratings yet
- Thailand - SatyamDocument9 pagesThailand - Satyamaadyacharan3No ratings yet
- RI 7 Areas of FocusDocument1 pageRI 7 Areas of Focusaadyacharan3No ratings yet
- m204 PDFDocument12 pagesm204 PDFRahul SinghNo ratings yet
- Oratorical Competition - Fundamental DutiesDocument3 pagesOratorical Competition - Fundamental Dutiesaadyacharan3No ratings yet
- Anti-Bullying WorkshopDocument1 pageAnti-Bullying Workshopaadyacharan3No ratings yet
- Maths Class 9 Linear Equations in Two VariablesDocument20 pagesMaths Class 9 Linear Equations in Two Variablesaadyacharan3No ratings yet
- Unit 12 Test 3Document2 pagesUnit 12 Test 3ThanhDâuNo ratings yet
- THE-FRUIT-STAND Aircraft LibraryDocument17 pagesTHE-FRUIT-STAND Aircraft LibraryMuhammad Akmal AbrarNo ratings yet
- Sumit Chauhan - Bhopal-DELDocument1 pageSumit Chauhan - Bhopal-DELMONISH NAYARNo ratings yet
- Reading Test Mavo - Texts (KB 16-2)Document8 pagesReading Test Mavo - Texts (KB 16-2)Daniel MarchenaNo ratings yet
- SummaryDocument5 pagesSummaryaceasistido56No ratings yet
- BeechcraftDocument128 pagesBeechcraftСтанислав Строкаш100% (1)
- TicketDocument2 pagesTicketManish SinghNo ratings yet
- Prova 5Document9 pagesProva 5Andre BorinNo ratings yet
- S&SCorp ICAO-IVAO Military Flight Plan Form-7233-S1MDocument2 pagesS&SCorp ICAO-IVAO Military Flight Plan Form-7233-S1MSantiago Herrera PalacioNo ratings yet
- Santiago Chile Flight ItineraryDocument3 pagesSantiago Chile Flight Itineraryhenry fernandezNo ratings yet
- Transcript For Test 14Document9 pagesTranscript For Test 14Tố UyênNo ratings yet
- Travel Reservation NovemberDocument1 pageTravel Reservation Novemberahmed sobhyNo ratings yet
- Vocabulary at The AirportDocument5 pagesVocabulary at The AirportEnglish with Chloe'No ratings yet
- Air France Flight 8969 Hijacking Case StudyDocument12 pagesAir France Flight 8969 Hijacking Case StudyFrancene FelipeNo ratings yet
- Egyptair Training CenterDocument30 pagesEgyptair Training CenterMohamedNo ratings yet
- Flying cars could transform commutes with air taxisDocument5 pagesFlying cars could transform commutes with air taxisHarshaVardhan RNo ratings yet
- Ieltsfever Academic Reading Practice Test 51 PDFDocument8 pagesIeltsfever Academic Reading Practice Test 51 PDFHarpreet BhullarNo ratings yet
- IF23072436624795 ETicketDocument3 pagesIF23072436624795 ETicketContract CounselNo ratings yet
- Medan Kuala Lumpur: DepartureDocument4 pagesMedan Kuala Lumpur: DepartureGayaNo ratings yet
- Wizz Air - First OfficerDocument2 pagesWizz Air - First OfficerdavidNo ratings yet
- The Airport Book From Landing Field To Modern TerminalDocument198 pagesThe Airport Book From Landing Field To Modern TerminalAviation LibraryNo ratings yet
- Cleartrip Flight E-TicketDocument2 pagesCleartrip Flight E-TicketMishrafashion HubNo ratings yet
- English Manual CiaacDocument70 pagesEnglish Manual CiaacJET MAN SKYNo ratings yet
- QualityWings - Ultimate 146 Collection Users ManualDocument326 pagesQualityWings - Ultimate 146 Collection Users Manualpresencia6275% (4)
- English Question Paper For H S Final Exam 2022Document16 pagesEnglish Question Paper For H S Final Exam 2022Shivajit DuttaNo ratings yet
- Wbcviii PDFDocument1,192 pagesWbcviii PDFDaniel PinheiroNo ratings yet
- Indonesian Aviation Regulations and ICAO StandardsDocument7 pagesIndonesian Aviation Regulations and ICAO StandardsAmirAli MohebbiNo ratings yet