Professional Documents
Culture Documents
JACOB
Uploaded by
Franzen PalermoCopyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
JACOB
Uploaded by
Franzen PalermoCopyright:
Available Formats
1.
CHICKEN POX - Chickenpox is an illness caused by
the varicella-zoster virus. It brings on an itchy rash with
small, fluid-filled blisters. Chickenpox spreads very easily
to people who haven't had the disease or haven't gotten
the chickenpox vaccine. Chickenpox used to be a
widespread problem, but today the vaccine protects
children from it. The chickenpox vaccine is a safe way to
prevent this illness and the other health problems that can
happen during it.
2. Sore eyes or Conjunctivitis - is defined by the
Department of Health (DOH) as a redness and
inflammation of the membranes (conjunctiva) covering the
whites of the eyes and the inner parts of the eyelids. It has
many causes, but in most cases it results from viral
infection, but can also be from bacteria or
allergen. Conjunctivitis also has other symptoms, which
may vary, depending on the cause. These symptoms can
be used to diagnose the type of conjunctivitis. Common
symptoms are eye redness, stinging and foreign body
sensation, itching, and sticky eye discharge. Vision may
become blurred from excessive tearing, discharges and from photophobia (or extreme
glare), caused by the inflammation. It is self-limiting, lasting 7-10 days, but with some
amount of variability depending on the viral strain. Conjunctivitis can be diagnosed by
history and examination alone. Laboratory tests are usually not needed.
Treatment is aimed at reducing discomfort as there is no definitive medication against
the viral infection. Cool compresses, ocular vasoconstrictors and antihistamine are
helpful. As we all know by now, the infection is highly contagious, often resulting in
epidemics, as it spreads easily by hand-to-eye primarily and to a lesser degree, droplet
contamination.
3. Ringworm - is a common skin infection that is caused
by a fungus. It’s called “ringworm” because it can cause a
circular rash (shaped like a ring) that is usually red and
itchy. Anyone can get ringworm. The fungi that cause this
infection can live on skin, surfaces, and on household
items such as clothing, towels, and bedding.
Ringworm goes by many names. The medical terms are
“tinea” or “dermatophytosis.” Other names for ringworm are
based on its location on the body – for example, ringworm
on the feet is also called “athlete’s foot.”
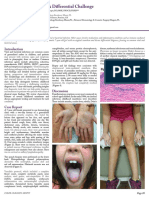
4. Hand-foot-and-mouth disease - is a mild, contagious
viral infection common in young children. Symptoms
include sores in the mouth and a rash on the hands and
feet. Hand-foot-and-mouth disease is most commonly
caused by a coxsackievirus.
There's no specific treatment for hand-foot-and-mouth
disease. Frequent hand-washing and avoiding close
contact with people who have hand-foot-and-mouth
disease may help lower your child's risk of infection.
5. Flu - is a contagious respiratory illness caused by
influenza viruses that infect the nose, throat, and
sometimes the lungs. It can cause mild to severe illness,
and at times can lead to death. The best way to prevent flu
is by getting a flu vaccine each year.
Flu Symptoms
Influenza (flu) can cause mild to severe illness, and at
times can lead to death. Flu symptoms usually come on
suddenly. People who have flu often feel some or all of
these symptoms:
fever* or feeling feverish/chills
cough
sore throat
runny or stuffy nose
muscle or body aches
headaches
fatigue (tiredness)
some people may have vomiting and diarrhea, though this is more common in
children than adults.
1. Asthma - is a disease that affects your lungs. It causes
repeated episodes of wheezing, breathlessness, chest
tightness, and nighttime or early morning coughing. Asthma
can be controlled by taking medicine and avoiding the
triggers that can cause an attack. You must also remove
the triggers in your environment that can make your asthma
worse.
2. Alzheimer’s disease - is the most common type of
dementia.
It is a progressive disease beginning with mild
memory loss and possibly leading to loss of the
ability to carry on a conversation and respond to the
environment.
Alzheimer’s disease involves parts of the brain that
control thought, memory, and language.
It can seriously affect a person’s ability to carry out
daily activities.
3. The appendix is a thin tube that is joined to the large
intestine. It sits in the lower right part of your belly
(abdomen). When you are a young child, your appendix is a
working part of your immune system, which helps your body
to fight disease. When you are older, your appendix stops
doing this and other parts of your body keep helping to fight
infection.
The appendix can get infected. If not treated it can burst
(rupture). This can happen as soon as 48 to 72 hours after you have symptoms.
Because of this, appendicitis is a medical emergency. If you have symptoms, see a
doctor right away to avoid more infection, which can be life-threatening.
4. Cancer - is a disease in which some of the body’s cells
grow uncontrollably and spread to other parts of the body.
Cancer can start almost anywhere in the human body,
which is made up of trillions of cells. Normally, human cells
grow and multiply (through a process called cell division) to
form new cells as the body needs them. When cells grow
old or become damaged, they die, and new cells take their
place.
Sometimes this orderly process breaks down, and abnormal or damaged cells grow and
multiply when they shouldn’t. These cells may form tumors, which are lumps of tissue.
Tumors can be cancerous or not cancerous (benign).
Cancerous tumors spread into, or invade, nearby tissues and can travel to distant
places in the body to form new tumors (a process called metastasis). Cancerous tumors
may also be called malignant tumors. Many cancers form solid tumors, but cancers of
the blood, such as leukemias, generally do not.
Benign tumors do not spread into, or invade, nearby tissues. When removed, benign
tumors usually don’t grow back, whereas cancerous tumors sometimes do. Benign
tumors can sometimes be quite large, however. Some can cause serious symptoms or
be life threatening, such as benign tumors in the brain.
5. Diabetes - is a chronic disease that occurs either when
the pancreas does not produce enough insulin or when the
body cannot effectively use the insulin it produces. Insulin
is a hormone that regulates blood glucose.
Hyperglycaemia, also called raised blood glucose or raised
blood sugar, is a common effect of uncontrolled diabetes
and over time leads to serious damage to many of the body's systems, especially the
nerves and blood vessels.
MAPEH 4
HEALTH
MGA URI NG NAKAKAHAWA
AT HINDI NAKAKAHAWANG SAKIT
NAME: AIDAN JACOB O. MATAWARAN
GRADE & SECTION: 4 – ORION
TEACHER: MS. MONINA L. BALIGNASAY
You might also like
- Simple Shingles CureDocument26 pagesSimple Shingles CureSpencer Shupe0% (1)
- MeningitisDocument6 pagesMeningitisCheena DolormenteNo ratings yet
- Common Pediatric Cases in OpdDocument90 pagesCommon Pediatric Cases in OpdJamie Sebastian100% (3)
- Viral Exanthems PDFDocument67 pagesViral Exanthems PDFChristopher AdhisasmitaNo ratings yet
- Common Viral Infections in The Oral Cavity: 1. Acute Herpetic Gingivostomatitis DNA VirusDocument6 pagesCommon Viral Infections in The Oral Cavity: 1. Acute Herpetic Gingivostomatitis DNA VirusChristineMartinNo ratings yet
- Chapter 6 - Dimension of Development - Health AwarenessDocument12 pagesChapter 6 - Dimension of Development - Health AwarenessAsh MooreNo ratings yet
- MCQ Oktober 02 2019Document15 pagesMCQ Oktober 02 2019Yosepha Jo100% (1)
- Different Fungal Infections, A Simple Guide To The Condition, Diagnosis, Treatment And Related ConditionsFrom EverandDifferent Fungal Infections, A Simple Guide To The Condition, Diagnosis, Treatment And Related ConditionsNo ratings yet
- Pediatric Rashes GuideDocument33 pagesPediatric Rashes GuideEskilda LucildaNo ratings yet
- Hand - Foot - Mouth Disease: Prepared By: Dr. NGUYEN QUANG DIEN Emergency DepartmentDocument24 pagesHand - Foot - Mouth Disease: Prepared By: Dr. NGUYEN QUANG DIEN Emergency DepartmentRayhan CeinNo ratings yet
- Causes, Symptoms and Treatment of EncephalitisDocument7 pagesCauses, Symptoms and Treatment of EncephalitisWiljohn de la CruzNo ratings yet
- Communicable Disease Prevention and Control GuideDocument10 pagesCommunicable Disease Prevention and Control Guidepedro calungsodNo ratings yet
- Microbial ResearchDocument12 pagesMicrobial Researchharshit kumarNo ratings yet
- Q3 Health 8 Module 4Document42 pagesQ3 Health 8 Module 4cpaloma664No ratings yet
- 13 QN ANSWRS Why Do We Fall IllDocument3 pages13 QN ANSWRS Why Do We Fall IllceoNo ratings yet
- Medicated Hand KerchiefsDocument31 pagesMedicated Hand Kerchiefsscribd_lostandfoundNo ratings yet
- Emerging and Re-emerging Diseases: Leptospirosis, Meningococcemia, AH1N1, HFMD, SARS, Chikungunya, Avian Flu, COVID-19Document11 pagesEmerging and Re-emerging Diseases: Leptospirosis, Meningococcemia, AH1N1, HFMD, SARS, Chikungunya, Avian Flu, COVID-19Josielyn Valladolid0% (1)
- What is Histoplasmosis? Fungal Lung Infection Causes and SymptomsDocument7 pagesWhat is Histoplasmosis? Fungal Lung Infection Causes and SymptomsLessaNo ratings yet
- Description of The Lesson:: Hello There! Are You Ready? Alright That's Nice To Hear It From You .Get Ready! Aja!Document12 pagesDescription of The Lesson:: Hello There! Are You Ready? Alright That's Nice To Hear It From You .Get Ready! Aja!Rci-Ched Mira CaparasNo ratings yet
- Information On DiseasesDocument7 pagesInformation On DiseasessachumasterNo ratings yet
- Wound ManagementDocument33 pagesWound ManagementDeSi BiLLaNo ratings yet
- Differences between bacteria, viruses, fungi and parasites and infections they causeDocument4 pagesDifferences between bacteria, viruses, fungi and parasites and infections they causegemmaNo ratings yet
- WH Questions About Illnesses - CamilaDocument2 pagesWH Questions About Illnesses - CamilaJuank RamírezNo ratings yet
- Health Q3 M2Document15 pagesHealth Q3 M2olameonfrixandrei486No ratings yet
- in Health 8 Leson 2Document33 pagesin Health 8 Leson 2api-613352174No ratings yet
- Medical Terms Kind of IlnessDocument11 pagesMedical Terms Kind of IlnessFani KimerliNo ratings yet
- NSTP Unit 4Document14 pagesNSTP Unit 4Sophie DatuNo ratings yet
- Patho Unit 5Document37 pagesPatho Unit 5Shafiya ShaikNo ratings yet
- Paper For Bio Theme Virus WD X-4Document8 pagesPaper For Bio Theme Virus WD X-4Muhammad RafiNo ratings yet
- Chapter 1: Introduction 1.1 General BackgroundDocument19 pagesChapter 1: Introduction 1.1 General Backgroundram gopal dasNo ratings yet
- Influenza: A Highly Contagious Viral DiseaseDocument10 pagesInfluenza: A Highly Contagious Viral DiseaseDevanyNo ratings yet
- Signs, Symptoms and Treatment of Bacterial, Viral, Fungal and Parasitic InfectionsDocument48 pagesSigns, Symptoms and Treatment of Bacterial, Viral, Fungal and Parasitic InfectionsHenie Louise HinanayNo ratings yet
- Bio Project-Small PoxDocument5 pagesBio Project-Small Poxapi-494770168No ratings yet
- Histopatho Lec - Assignment No. 1Document4 pagesHistopatho Lec - Assignment No. 1Manelli Faten BuenaventuraNo ratings yet
- LESSON 1: The Coronavirus: What Scientists Have Learned So FarDocument55 pagesLESSON 1: The Coronavirus: What Scientists Have Learned So FarAira Geramie ReyesNo ratings yet
- 6B-Biology Notes - Diseases and HygieneDocument13 pages6B-Biology Notes - Diseases and HygieneJagrity SinghNo ratings yet
- Respiratory DiseasesDocument17 pagesRespiratory DiseasesAlexamiz AldimNo ratings yet
- Erregersteckbrief en de DataDocument2 pagesErregersteckbrief en de DataDescargar scribdNo ratings yet
- Health EducationDocument10 pagesHealth Educationrjay pascualNo ratings yet
- Path o PhysiologyDocument31 pagesPath o PhysiologyjayamohanNo ratings yet
- Giardia: PROTOZOA Is A Group of Phyla That Comprises The Single-Celled Microscopic Animals, WhichDocument5 pagesGiardia: PROTOZOA Is A Group of Phyla That Comprises The Single-Celled Microscopic Animals, WhichAilah OtaganNo ratings yet
- Meehleib, Rachelle Ayn S. Pepino, Stephanie Kate ADocument16 pagesMeehleib, Rachelle Ayn S. Pepino, Stephanie Kate ARachelle AynNo ratings yet
- Activity 14Document4 pagesActivity 14acrehell8No ratings yet
- Measles: Supporting Details 2 - Measles Begins With ADocument5 pagesMeasles: Supporting Details 2 - Measles Begins With Adr israrNo ratings yet
- Nama: Khusnul Maisaroh NIM: P27820521022Document7 pagesNama: Khusnul Maisaroh NIM: P27820521022Khusnul MaisarohNo ratings yet
- 09 Science Notes ch13 Why Do We Fall Ill PDFDocument3 pages09 Science Notes ch13 Why Do We Fall Ill PDFthiruNo ratings yet
- CWTS NewDocument32 pagesCWTS NewnerlynNo ratings yet
- Aids (Acquired Immunodeficiency Syndrome) : The Joint United Nations Programme On AIDS (UNAIDS)Document3 pagesAids (Acquired Immunodeficiency Syndrome) : The Joint United Nations Programme On AIDS (UNAIDS)Micaella CastroNo ratings yet
- 2020 Abt Health and Safety in The SalonDocument21 pages2020 Abt Health and Safety in The SalonAlexis O'SullivanNo ratings yet
- Health Study GuideDocument6 pagesHealth Study GuideZaira Beatrice CruzNo ratings yet
- Preliminary (Pendahuluan) A. BackgroundDocument5 pagesPreliminary (Pendahuluan) A. BackgroundAbadiNo ratings yet
- CBSE Class 9 Science Revision Notes Chapter - 13 Why Do We Fall Ill?Document3 pagesCBSE Class 9 Science Revision Notes Chapter - 13 Why Do We Fall Ill?pdf.downloadNo ratings yet
- Form 2 Chap 4 DiseasesDocument15 pagesForm 2 Chap 4 Diseasesscribble_55No ratings yet
- Lesson 4 Health PDFDocument25 pagesLesson 4 Health PDFRomeo BalingaoNo ratings yet
- Human Health and Disease What Is Health?Document40 pagesHuman Health and Disease What Is Health?JANE ONGNo ratings yet
- Bio AssignmentDocument7 pagesBio AssignmentDana ReyesNo ratings yet
- NCMB 312 - : Bachelor of Science in Nursing Communicable Disease NursingDocument17 pagesNCMB 312 - : Bachelor of Science in Nursing Communicable Disease NursingDona Mae TaberaNo ratings yet
- CH 13 - Why Do Fall Ill - SA Type 2Document7 pagesCH 13 - Why Do Fall Ill - SA Type 2vishnu babuNo ratings yet
- Bio Investigatory ProjectDocument16 pagesBio Investigatory ProjectZenab MohamedNo ratings yet
- Communicable DiseasesDocument15 pagesCommunicable DiseasesAnushka JaiswalNo ratings yet
- Diseases and IllnessesDocument28 pagesDiseases and IllnessesKath rynNo ratings yet
- Causes of Mortality and MorbidityDocument8 pagesCauses of Mortality and MorbiditypurletpunkNo ratings yet
- Chicken Pox HandoutsDocument4 pagesChicken Pox Handoutsmaglangitjoannamarie1920No ratings yet
- The Common ColdDocument2 pagesThe Common ColdNur fauziahNo ratings yet
- Types of DiseasesDocument8 pagesTypes of DiseasesDawa Lakje Sherpa100% (1)
- 2018 - Johor (Kota Tinggi) - P2Document20 pages2018 - Johor (Kota Tinggi) - P2AIMANNo ratings yet
- Hand, Foot, and Mouth Disease and Herpangina - UpToDateDocument42 pagesHand, Foot, and Mouth Disease and Herpangina - UpToDateFer45No ratings yet
- Pidsr Weekly Notifiable Report 1Document2 pagesPidsr Weekly Notifiable Report 1Gladdy CabrezaNo ratings yet
- PPS UPEC PIDSP Rashes in Children ModuleDocument232 pagesPPS UPEC PIDSP Rashes in Children ModuleIda Marionne ArriolaNo ratings yet
- Sample ReflectionDocument2 pagesSample ReflectionRhiza Joy HiposNo ratings yet
- HerpanginaDocument8 pagesHerpanginaWendy Nadya Vitasani HalohoNo ratings yet
- 1) - Oral Exam Revealed A White Strawberry Tongue: Ecker, Habashy, SkopitDocument5 pages1) - Oral Exam Revealed A White Strawberry Tongue: Ecker, Habashy, SkopitAngela DuangchitNo ratings yet
- HFMD Parent Orientation Narrative ReportDocument7 pagesHFMD Parent Orientation Narrative ReportGerald CiudadNo ratings yet
- 8 Childhood Viral Skin Rashes: Chickenpox, Measles and MoreDocument9 pages8 Childhood Viral Skin Rashes: Chickenpox, Measles and MoreErik OrtegaNo ratings yet
- Hand Foot and Mouth DiseaseDocument3 pagesHand Foot and Mouth DiseaseAisah AisahNo ratings yet
- HFMD Guide to Viral Illness in ChildrenDocument2 pagesHFMD Guide to Viral Illness in ChildrenBimantoro SaputroNo ratings yet
- NOTES CD Lecture Generic 2022Document182 pagesNOTES CD Lecture Generic 2022Meryville JacildoNo ratings yet
- Protocol For Management of Hand, Foot and Mouth Disease (HFMD) and Herpangina at Clinics and Hospitals in SarawakDocument17 pagesProtocol For Management of Hand, Foot and Mouth Disease (HFMD) and Herpangina at Clinics and Hospitals in SarawakbabytwelveNo ratings yet
- Comprehensive Guide on Hand, Foot and Mouth DiseaseDocument13 pagesComprehensive Guide on Hand, Foot and Mouth DiseaseradicalmpNo ratings yet
- HFMD FINAL - AzaniDocument8 pagesHFMD FINAL - AzaniGrace BlaiseNo ratings yet
- Oet SpeakingDocument19 pagesOet SpeakingChristina DienteNo ratings yet
- Oral Infections GuideDocument2 pagesOral Infections GuideSoojung NamNo ratings yet
- Coxsackievirus: Incubation Period: 2-9 DaysDocument4 pagesCoxsackievirus: Incubation Period: 2-9 DaysrachellesliedeleonNo ratings yet
- Higgs BosonDocument20 pagesHiggs BosonWiljohn de la CruzNo ratings yet
- Hand Foot MouthDocument2 pagesHand Foot MouthCrystal Rodis-ConcepcionNo ratings yet
- PusoDocument4 pagesPusoStephanie SundiangNo ratings yet
- Hand Foot and Mouth DiseaseDocument16 pagesHand Foot and Mouth DiseaseCaroline TecsonNo ratings yet
- Pediatric Research and Child HealthDocument3 pagesPediatric Research and Child HealthdantiNo ratings yet
- Viral Infections of HumansDocument89 pagesViral Infections of HumansMark Vincent JanoyogNo ratings yet