100% found this document useful (2 votes)
5K views4 pagesVectors Short Notes
1. The document discusses various vector and geometry concepts such as the dot product, cross product, projections of vectors, and properties of parallelotopes and tetrahedrons.
2. It provides formulas for the dot product, cross product, cosine formula, and definitions of perpendicular and parallel vectors.
3. Several geometric concepts are defined, including the projection of one vector onto another vector, the area of a parallelogram formed by two vectors, and the volume of a parallelotope.
Uploaded by
ShaankariCopyright
© © All Rights Reserved
We take content rights seriously. If you suspect this is your content, claim it here.
Available Formats
Download as PDF, TXT or read online on Scribd
100% found this document useful (2 votes)
5K views4 pagesVectors Short Notes
1. The document discusses various vector and geometry concepts such as the dot product, cross product, projections of vectors, and properties of parallelotopes and tetrahedrons.
2. It provides formulas for the dot product, cross product, cosine formula, and definitions of perpendicular and parallel vectors.
3. Several geometric concepts are defined, including the projection of one vector onto another vector, the area of a parallelogram formed by two vectors, and the volume of a parallelotope.
Uploaded by
ShaankariCopyright
© © All Rights Reserved
We take content rights seriously. If you suspect this is your content, claim it here.
Available Formats
Download as PDF, TXT or read online on Scribd
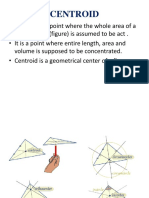
- Properties of Vectors: Details properties of vectors including scalar and vector products, and coplanar vectors.
- Vector Introduction: An introduction to vectors, discussing basic concepts and properties with initial sketches.
- Advanced Vector Concepts: Explores advanced concepts such as reciprocal system of vectors and related mathematical proofs.
- Vector Theorems: Covers various theorems related to vectors, including those in the plane and in space.


![unit vecto
coplanor with ae
TaxB)x2]
calay
prod
c
4vectors
lag aenges identity
Ca xF).(2 x3)
- .E.
Bor pood
c
cop](https://screenshots.scribd.com/Scribd/252_100_85/192/699594690/3.jpeg)