Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Bio 2
Uploaded by
Kyla Jane Gabica0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
6 views3 pagesOriginal Title
BIO 2 - Google Docs
Copyright
© © All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
6 views3 pagesBio 2
Uploaded by
Kyla Jane GabicaCopyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
You are on page 1of 3
PLANTS’ SPECIALIZED STRUCTURES
• Plant organs are made of three tissue systems.
1. Dermal tissue covers the outside of a plant.
– protects the plant
– secretes cuticle of leaves
– forms outer bark of trees
VOCABULARY Made of Epidermis and Cuticle
Histology •Epidermis
•study of animal and plant tissues. - a protective tissue that covers the entire surface of the
plant. The epidermis protects the plant from infection and
Microtome water loss.
• an instrument used to cut tissues into
ultrathin sections. •Cuticle
– the outermost layer of plants, which covers leaves, fruits,
flowers, and non-woody stems of higher plants. It helps to
prevent evaporation from the leaf surface.
2. Ground tissue is found inside a plant.
– provides support
– stores materials in roots and stems.
– most commonly made of parenchyma.
3. Vascular tissue transports water, minerals and organic
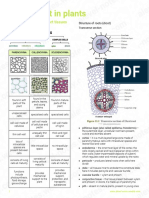
Plant Cells and Tissues
compounds.
KEY CONCEPT
– two networks of hollow tubes.
● Plants have specialized cells and tissue systems.
– xylem transports water and minerals.
– phloem transports photosynthetic products.
• Water and dissolved minerals move through xylem.
* Xylem contains specialized cells.
– vessel elements are short and wide
– tracheid cells are long and narrow
– xylem cells die at maturity
• Phloem carries sugars from photosynthesis
throughout the plant.
* Phloem contains specialized cells.
– sieve tube elements have holes at ends.
– companion cells help sieve tube elements.
– unlike xylem, phloem tissue is alive.
• Transpiration is the loss of water vapor through leaves.
– water vapor exits leaf stomata.
– helps pull water to the top branches.
• Roots anchor plants and absorb mineral nutrients from
soil.
• Roots provide many functions.
– support the plant
– absorb, transport, and store nutrients
– root hairs help absorption
•There are several parts of a root.
– root cap covers the tip
– apical meristem is an area of growth
– vascular cylinder contains xylem and phloem.
KEY CONCEPT
● Leaves absorb light and carry out photosynthesis.
• Most leaves share some similar structures.
*The blade is usually broad and flat.
– collects sunlight for photosynthesis.
– connects to the stem by a petiole.
• Guard cells surround each stoma.
– Stomata open and close when guard cells
change shape.
– When stomata are open, water evaporates
and gas exchanges.
– Stomata close at night and when plant loses
too much water.
You might also like
- Theories of The Origin of Solar SystemDocument18 pagesTheories of The Origin of Solar SystemGWYNETH REIN CARI�ONo ratings yet
- Plants Specialized StructuresDocument38 pagesPlants Specialized StructuresKyla Jane GabicaNo ratings yet
- ELSC Week13 Plant Survival PDFDocument43 pagesELSC Week13 Plant Survival PDFarriane BaladadNo ratings yet
- Plants Specialized StructuresDocument38 pagesPlants Specialized StructuresKyla Jane GabicaNo ratings yet
- Leaf StructureDocument10 pagesLeaf StructureKristina PonceNo ratings yet
- Week 2 Plant TissuesDocument20 pagesWeek 2 Plant Tissueskevin愛No ratings yet
- Leaf StructureDocument10 pagesLeaf StructureMeanNo ratings yet
- Plant Form and FunctionsDocument2 pagesPlant Form and FunctionsJason TaburnalNo ratings yet
- 21 Plant Structure and FunctionDocument50 pages21 Plant Structure and FunctionRoan James OcampoNo ratings yet
- Plant Structure FunctionDocument58 pagesPlant Structure Functionno siNo ratings yet
- Plant Structure, Growth, & Development Plant Structure, Growth, & DevelopmentDocument74 pagesPlant Structure, Growth, & Development Plant Structure, Growth, & DevelopmentSophia AbatayNo ratings yet
- Biology Plant Based PresentationDocument86 pagesBiology Plant Based PresentationImCubanBeNo ratings yet
- The Plant Tissues.Document41 pagesThe Plant Tissues.JenniferNo ratings yet
- Absorption and Translocation in PlantsDocument39 pagesAbsorption and Translocation in PlantsChelsie Fae SantosNo ratings yet
- 21 Plant Structure and Function - 032212Document45 pages21 Plant Structure and Function - 032212Nudiya SappalNo ratings yet
- Meristematic Tis: Plants AnimalsDocument6 pagesMeristematic Tis: Plants AnimalsRajat ChauhanNo ratings yet
- PlanttissuesDocument25 pagesPlanttissuesphuongchi53100% (1)
- General Biology 2Document10 pagesGeneral Biology 2kristineNo ratings yet
- Plant Tissues EDITEDDocument44 pagesPlant Tissues EDITEDJonoel TaborNo ratings yet
- Genbio Long Quiz 2 ReviewerDocument42 pagesGenbio Long Quiz 2 ReviewerEthan Erika BionaNo ratings yet
- 7 Transport in PlantsDocument7 pages7 Transport in PlantsTina EtoileNo ratings yet
- Plant TissuesDocument32 pagesPlant TissuesVikneswaran Gunahlan Nesh100% (2)
- Leaves:: Form and StructureDocument37 pagesLeaves:: Form and StructureJane ManalusNo ratings yet
- AAPostLab The Plant BodyDocument87 pagesAAPostLab The Plant BodyAlla KanaNo ratings yet
- PMA LeavesDocument37 pagesPMA Leavesalaiza.reblandoNo ratings yet
- BIOL223-Lab 10Document60 pagesBIOL223-Lab 10chicken friesNo ratings yet
- Plant Tissues 2Document43 pagesPlant Tissues 2Francis MacasioNo ratings yet
- Plant TissuesDocument30 pagesPlant TissuesAra May B. Olis100% (1)
- TISSUES - Class Notes - SprintDocument40 pagesTISSUES - Class Notes - SprintMr Vinod yadavNo ratings yet
- 35 Lecture Presentation 0Document76 pages35 Lecture Presentation 0Catherina PurbaNo ratings yet
- Mauseth Chapter 05 PDFDocument2 pagesMauseth Chapter 05 PDFCharlotte AmanteNo ratings yet
- GS BIO 206. Functional Organization in PlantsDocument9 pagesGS BIO 206. Functional Organization in PlantsChary Johanne MenesesNo ratings yet
- LeavesDocument30 pagesLeavesjada tuckerNo ratings yet
- Plant TissueDocument8 pagesPlant TissueAlana DariesNo ratings yet
- Lecture 14 Plant Cell Wall 2019Document38 pagesLecture 14 Plant Cell Wall 2019jeozbapqfpugltpsrbNo ratings yet
- Miedy Corazon Tabang Sta. Monica High School PhilippinesDocument68 pagesMiedy Corazon Tabang Sta. Monica High School PhilippinesArman Austria100% (1)
- Chapter 5 Tissues and Primary Growth of StemsDocument47 pagesChapter 5 Tissues and Primary Growth of StemsJenilyn FarnacioNo ratings yet
- Plant Organs System: Roots & Stem Leaf Flower & FruitsDocument38 pagesPlant Organs System: Roots & Stem Leaf Flower & FruitsSweet EmmeNo ratings yet
- General Biology 2Document5 pagesGeneral Biology 2Nolrene TbcNo ratings yet
- L-6 Plant TissuesDocument34 pagesL-6 Plant TissuesIshita PandeyNo ratings yet
- Report-Major 1 (Crop Science)Document29 pagesReport-Major 1 (Crop Science)Princess Rena RamosNo ratings yet
- Tissues, Roots, Stems, LeavesDocument128 pagesTissues, Roots, Stems, LeavesAlfonso PlantillaNo ratings yet
- Bio 11 LE 2 ReviewerDocument2 pagesBio 11 LE 2 ReviewerLara GreyjoyNo ratings yet
- Plant Anatomy Chu ChuDocument39 pagesPlant Anatomy Chu Chucultjin2No ratings yet
- Plant TissuesDocument10 pagesPlant TissuesAndrea CruzNo ratings yet
- 3.5 PlantsDocument37 pages3.5 PlantsthumpthumpNo ratings yet
- BOTANI 8 - Anatomi Morfologi DaunDocument42 pagesBOTANI 8 - Anatomi Morfologi DaunNabila IstiqomahNo ratings yet
- Lecture - Chapter 42 - Stems, Roots, and LeavesDocument31 pagesLecture - Chapter 42 - Stems, Roots, and LeavesJan Marlon GoritNo ratings yet
- Anatomy of Flowering Plants NotesDocument9 pagesAnatomy of Flowering Plants NotesVansh SinghNo ratings yet
- Bio - CH 2 TissuesDocument92 pagesBio - CH 2 TissuesPagli MonkeyNo ratings yet
- Plant Cells and TissuesDocument20 pagesPlant Cells and TissuesROWENANo ratings yet
- Transport in Plants and Animals.Document135 pagesTransport in Plants and Animals.Kiprono Mathew100% (11)
- Transport in Plants and Animals.Document126 pagesTransport in Plants and Animals.Kiama GitahiNo ratings yet
- Lecture 7 - Organs: Leaves: Lakehead UniversityDocument40 pagesLecture 7 - Organs: Leaves: Lakehead UniversityClara HrestakNo ratings yet
- 1.2 Plants Organ SystemDocument32 pages1.2 Plants Organ SystemkitsujinnNo ratings yet
- NCERT CLASS 9 CH-6 TissuesDocument42 pagesNCERT CLASS 9 CH-6 TissuesJoshiNo ratings yet
- Internal Structure of A LeafDocument38 pagesInternal Structure of A Leafnozel77100% (1)
- BiologyIIforNonMajorsII 07Document78 pagesBiologyIIforNonMajorsII 07Mmoh87No ratings yet
- LeavesDocument3 pagesLeavessssfiresssNo ratings yet
- How Plants Grow - With Information on the Biology of Plant Cells, Roots, Leaves and FlowersFrom EverandHow Plants Grow - With Information on the Biology of Plant Cells, Roots, Leaves and FlowersNo ratings yet
- Group 9Document1 pageGroup 9Kyla Jane GabicaNo ratings yet
- Reviewer in Entrep 2nd QuarterDocument5 pagesReviewer in Entrep 2nd QuarterKyla Jane GabicaNo ratings yet
- 21 STDocument2 pages21 STKyla Jane GabicaNo ratings yet
- Waiting (21st)Document19 pagesWaiting (21st)Kyla Jane GabicaNo ratings yet
- PR (2nd)Document2 pagesPR (2nd)Kyla Jane GabicaNo ratings yet
- SACRA 1 ReviewerDocument2 pagesSACRA 1 ReviewerKyla Jane GabicaNo ratings yet
- Notes of CH Tissues Class 9Document20 pagesNotes of CH Tissues Class 9PrabhaNo ratings yet
- Short Answers Question Chapter: Life ProcessDocument1 pageShort Answers Question Chapter: Life ProcessShreya Home TutorialsNo ratings yet
- Plant AnatomyDocument17 pagesPlant AnatomyPradyuman Choubey100% (1)
- English Worksheet Solution of Class XDocument29 pagesEnglish Worksheet Solution of Class XShrutiNo ratings yet
- TERM 2 Chapter 7 Topical Revision Bio STPMDocument59 pagesTERM 2 Chapter 7 Topical Revision Bio STPMKeertana SubramaniamNo ratings yet
- Pharmacognosy 11250071Document124 pagesPharmacognosy 11250071KabirNo ratings yet
- Dra. Victoria Fernández - Foliar FertilizationDocument144 pagesDra. Victoria Fernández - Foliar Fertilizationmmarcon1973No ratings yet
- Background Information Year 5-6, Unit 2: Survival: AdaptationDocument3 pagesBackground Information Year 5-6, Unit 2: Survival: AdaptationsairaNo ratings yet
- Factors Affecting Crop ProductionDocument36 pagesFactors Affecting Crop ProductionPca ZdnNo ratings yet
- Gesc101 PDFDocument10 pagesGesc101 PDFlakhuindiaNo ratings yet
- Soal PAT B. ING Kelas XI K13Document9 pagesSoal PAT B. ING Kelas XI K13Meylyn HwangNo ratings yet
- Bamboo: Class: Class 7 - Section A Subject: Science Chapter: Nutrition in Plants TitleDocument2 pagesBamboo: Class: Class 7 - Section A Subject: Science Chapter: Nutrition in Plants TitleArvind Murali50% (2)
- New Trends in Icse Biology 7 PDFDocument22 pagesNew Trends in Icse Biology 7 PDFkumar74% (19)
- Biology Write UpDocument7 pagesBiology Write UpAnnie Cristobal EscotoNo ratings yet
- IJCRT2106647Document10 pagesIJCRT2106647Darshan RNo ratings yet
- GCSE AQA Biology Unit 3Document10 pagesGCSE AQA Biology Unit 3Fasih AhmadNo ratings yet
- C Evapo TranspirationDocument49 pagesC Evapo Transpirationjuliyet strucNo ratings yet
- AdaptationsDocument24 pagesAdaptationsDinesh Kumar.vNo ratings yet
- CH 7 Respiration StudentDocument25 pagesCH 7 Respiration StudentHamirah Abd HamidNo ratings yet
- Soalan pt3Document8 pagesSoalan pt3wkt6133No ratings yet
- Chapter 6 Lesson 1 PhotosynthesisDocument31 pagesChapter 6 Lesson 1 PhotosynthesisAli waleed AbdalmoatyNo ratings yet
- Caie Igcse Biology 0610 Theory v2Document33 pagesCaie Igcse Biology 0610 Theory v2HibsNo ratings yet
- FST 1Document3 pagesFST 1muscularindian0% (1)
- 0010 1A Book Angol 01 Novenyelettan PDFDocument121 pages0010 1A Book Angol 01 Novenyelettan PDFketakeeNo ratings yet
- Science PortfolioDocument81 pagesScience PortfolioVismaya ViswanathanNo ratings yet
- Leaves and Pigments PDFDocument16 pagesLeaves and Pigments PDFnurul annisa lubisNo ratings yet
- Phil West-Growing Plantation Forests (2006) PDFDocument305 pagesPhil West-Growing Plantation Forests (2006) PDFJunior MendesNo ratings yet
- Keenan Et Al, 2013Document5 pagesKeenan Et Al, 2013Marcela LúciaNo ratings yet
- FAO Irrigation and Drainage Paper 56 EvapotranspirationDocument326 pagesFAO Irrigation and Drainage Paper 56 EvapotranspirationFabrício Brito Silva100% (2)
- Photosynthesis Play: Disclaimer & Limitation of LiabilityDocument3 pagesPhotosynthesis Play: Disclaimer & Limitation of LiabilityPrepa Abierta IspeeaNo ratings yet