Professional Documents
Culture Documents
2.2 Atomic Structure and Periodic Table
Uploaded by
Abdul RasheedOriginal Description:
Original Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
2.2 Atomic Structure and Periodic Table
Uploaded by
Abdul RasheedCopyright:
Available Formats
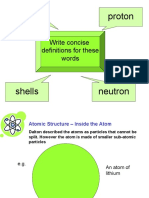
Structure of an atom
An atom is the smallest uncharged particle that can take part in a
chemical change.
om
• An atom contains a centrally
located nucleus.
.c
• The nucleus contains positively
es
charged protons and neutral
neutrons.[Protons + neutrons=
rc
nucleon number or mass number]
u
• The electrons revolve around the
shells or energy levels. so
nucleus in fixed orbits called electron
re
• An atom is electrically neutral as the number of protons
m
(+vely charged) are equal to the number of electrons (-vely
charged).
xa
• Position of elements in the periodic table is based on their
te
atomic number.
ar
------------------------------------------------------
m
Subatomic Symbol Relative mass Relative charge
particles
.s
PROTON p 1 +1
w
NEUTRON n 1 No charge
ELECTRON e 0.00054 -1
w
-----------------------------------------------------
w
Copyright-Smart Exam Resources 1
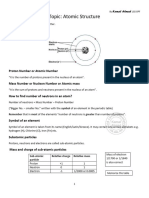
Define:
• Proton number ( Atomic number): It is the number of protons
in the nucleus of an atom.
• Nucleon number ( Mass number): It is the total number of
om
protons and neutrons in the nucleus of an atom.
.c
es
u rc
so
re
m
xa
te
ar
m
.s
w
w
w
Copyright-Smart Exam Resources 2
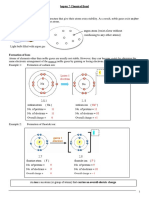
Electronic configuration for the atoms and ions of first 10
elements
om
Atom E.C. Type of ions Reason for no ion
formed formation
.c
Hydrogen 1 H+ , H-
es
Helium- 2 Ni ion It has a completely
rc
Group-8 formation filled outer shell
u
Lithium 2,1 Li+
Group-1
Beryllium 2,2 Be2+ so
re
Group-2
m
Boron 2,3 B3+
Group-3
xa
Carbon 2,4 No ion It has a tendency
te
Group-4 formation to share electrons
ar
Nitrogen 2,5 N3-
Group-5
m
Oxygen 2,6 O2-
.s
Group-6
w
Fluorine 2,7 F-
Group-7
w
Neon 2,8 No ion It has a completely
w
Group-8 formation filled outer shell
Copyright-Smart Exam Resources 3
Electronic configuration for the atoms and ions of from atomic
number 11-20 of the periodic table:
om
Atom E.C. Type of ions Reason for no ion
formed formation
.c
Sodium 1,8,1 Na+
Group-1
es
Magnesium 2,8,2 Mg2+
rc
Group-2
Aluminium 2,8,3 Al3+
u
Group-3
Silicon 2,8,4 No ionso It has a tendency
re
Group-4 formation to share electrons
m
Phosphorous 2,8,5 P3-
Group-5
xa
Sulfur 2,8,6 S2-
te
Group-6
Chlorine 2,8,7 Cl-
ar
Group-7
m
Argon 2,8,8 No ion It has a completely
.s
Group-8 formation filled outer shell
w
Potassium 2,8,8,1 K+
Group-1
w
Calcium 2,8,8,2 Ca2+
w
Group-2
Copyright-Smart Exam Resources 4
Note:
• Group 8 noble gases have a fuller outer shell
Example:
om
Atom E.C. Type of ions Reason for no ion
formed formation
Helium- 2 Ni ion It has a completely
.c
Group-8 formation filled outer shell
es
Neon 2,8 No ion It has a completely
Group-8 formation filled outer shell
rc
Argon 28,8 No ion It has a completely
u
Group-8 formation filled outer shell
so
re
m
xa
te
ar
m
.s
w
w
w
Copyright-Smart Exam Resources 5
• The number of outer shell electrons is equal to the group
number in groups 1 to VII
Example:
om
Atom E.C. Type of ions Reason for no ion
formed formation
.c
Sodium 2,8,1 Na+
Group-1
es
Magnesium 2,8,2 Mg2+
rc
Group-2
Aluminium 2,8,3 Al3+
u
Group-3
Silicon 2,8,4 No ionso It has a tendency
re
Group-4 formation to share electrons
m
Phosphorous 2,8,5 P3-
Group-5
xa
Sulfur 2,8,6 S2-
te
Group-6
Chlorine 2,8,7 Cl-
ar
Group-7
m
.s
w
w
w
Copyright-Smart Exam Resources 6
• The number of occupied electron shells is equal to the
period number:
Example:
om
Element Period Number of occupied electron shells
Lithium 2 2
.c
es
rc
Beryllium 2 2
u
so
re
m
Boron 2 2
xa
te
ar
m
.s
w
w
w
Copyright-Smart Exam Resources 7
You might also like
- Book H.W CH 1Document21 pagesBook H.W CH 1Raiyad RezaNo ratings yet
- Structure of The AtomDocument24 pagesStructure of The AtomKunalNo ratings yet
- Unit 2 Atoms and Nucleus - Reg - 2019 - REVDocument66 pagesUnit 2 Atoms and Nucleus - Reg - 2019 - REVRecilia MarthaNo ratings yet
- ATOMIC STRUCTURE-moduleDocument6 pagesATOMIC STRUCTURE-modulejudith cue100% (1)
- Chapter 5 - Structure of AtomsDocument4 pagesChapter 5 - Structure of AtomsAdil Yaqub - 74665/TCHR/CNTBNo ratings yet
- Atomic StructureDocument13 pagesAtomic Structurerenan.masangya-18No ratings yet
- 9C Summer Vacations HomeworkDocument9 pages9C Summer Vacations HomeworkKinret WarisNo ratings yet
- Bond TypesDocument28 pagesBond Typesvigneshs.me23No ratings yet
- 929-Mass Numbers Inc Isotopes PresentationDocument18 pages929-Mass Numbers Inc Isotopes PresentationB.Ed. Wing SundargarhNo ratings yet
- ScienceDocument10 pagesScienceAmber RoselNo ratings yet
- Atomic Structure-OL-NotesDocument4 pagesAtomic Structure-OL-Notesshlaibat13No ratings yet
- 4 Structure OftheatomDocument15 pages4 Structure OftheatomVaibhav V VeenajNo ratings yet
- Level 2 Notes 2024 - 04chemical BondingDocument25 pagesLevel 2 Notes 2024 - 04chemical BondingMatthew TanNo ratings yet
- 1.1 Atoms and Molecules PDFDocument39 pages1.1 Atoms and Molecules PDFKKNo ratings yet
- Atoms, Elements and CompoundsDocument20 pagesAtoms, Elements and CompoundsMenaga Ilangkovan100% (1)
- The Atom Activities: Discovery of Electron Democritus Proposes The Word "Atom" Current ModelDocument8 pagesThe Atom Activities: Discovery of Electron Democritus Proposes The Word "Atom" Current ModelHunter PpollNo ratings yet
- Atomic Structure For Grade 10Document4 pagesAtomic Structure For Grade 10Aja AndersonNo ratings yet
- Structure of The AtomDocument15 pagesStructure of The AtomJeetNo ratings yet
- Atomic Theory Q2 Week1 G9 For StudentsDocument19 pagesAtomic Theory Q2 Week1 G9 For Studentsforonlygames08No ratings yet
- Chapter - 4: Structure of The AtomDocument15 pagesChapter - 4: Structure of The Atomuma mishraNo ratings yet
- Atoms, Molecules and IonsDocument58 pagesAtoms, Molecules and IonsJunaid Alam100% (1)
- Ncert Solutions For Class 9 Science Jan14 Chapter 4 Structure of The AtomDocument18 pagesNcert Solutions For Class 9 Science Jan14 Chapter 4 Structure of The AtomMannat MadanNo ratings yet
- Topic.4 Chemical Bonding and CatalysisDocument19 pagesTopic.4 Chemical Bonding and Catalysispoonamwaingade_20095No ratings yet
- Structure of AtomDocument14 pagesStructure of AtomSiddh PatelNo ratings yet
- IQ2 Atomic Structure and Atomic MassDocument26 pagesIQ2 Atomic Structure and Atomic MassLuke DavisNo ratings yet
- Ncert Sol For Cbse Class 9 Sci Chapter 4 Structure of The AtomDocument18 pagesNcert Sol For Cbse Class 9 Sci Chapter 4 Structure of The AtomShah RukhNo ratings yet
- Unit 7 Microscopic World 1 S3AC Answers 220811 175227Document10 pagesUnit 7 Microscopic World 1 S3AC Answers 220811 1752274A10 HUI OI YU KATRINANo ratings yet
- Notes - Structure of AtomDocument8 pagesNotes - Structure of AtomHardikNo ratings yet
- UntitledDocument58 pagesUntitledMuhammad Harith Hilmi Zen AzharNo ratings yet
- 2 Chapter 02 Atomic BondingDocument17 pages2 Chapter 02 Atomic BondingZain FarhanNo ratings yet
- Atomic Structure Bohr Model Periodic Trends Student Notes Practice Problems 1Document10 pagesAtomic Structure Bohr Model Periodic Trends Student Notes Practice Problems 1api-255434272No ratings yet
- Module in Chemical BondingDocument36 pagesModule in Chemical BondingJaycee De LeonNo ratings yet
- Chapter 3 (Notes and Activities)Document10 pagesChapter 3 (Notes and Activities)Ahmed MutwakilNo ratings yet
- DevisDocument24 pagesDevisKiyingi GodfreyNo ratings yet
- Atomic StructureDocument24 pagesAtomic StructureKris DookharanNo ratings yet
- Chapter 1 Material ScienceDocument69 pagesChapter 1 Material ScienceFadhli JapryNo ratings yet
- Structure and Bonding - Lesson 3 - Ionic BondingDocument19 pagesStructure and Bonding - Lesson 3 - Ionic Bondingcharlie markouNo ratings yet
- Chapter-Structure of Atom-Writing Chemical Formulae: Page 1/3Document3 pagesChapter-Structure of Atom-Writing Chemical Formulae: Page 1/3Perajothi PalanirajaNo ratings yet
- Numbers of Electrons in The Outermost ShellDocument46 pagesNumbers of Electrons in The Outermost ShellGianna SaludoNo ratings yet
- Physical Science SHS 4.1 Counting Valence ElectronsDocument29 pagesPhysical Science SHS 4.1 Counting Valence ElectronsMaricris Jane PeranteNo ratings yet
- C1 Revision SheetsDocument7 pagesC1 Revision Sheetsakio haruNo ratings yet
- Atomic Structure: Note: Note: Maximum No. of Electrons in Any Shell 2nDocument2 pagesAtomic Structure: Note: Note: Maximum No. of Electrons in Any Shell 2nmujeebc 1972No ratings yet
- Chemistry Worksheet - IonsDocument2 pagesChemistry Worksheet - IonsDon RexaNo ratings yet
- The Band of Stability - Nuclear Decay Graphing Activity InstructionsDocument3 pagesThe Band of Stability - Nuclear Decay Graphing Activity InstructionsAndreaNo ratings yet
- Atoms and The Periodic TableDocument3 pagesAtoms and The Periodic TableAbdullah Sabry AzzamNo ratings yet
- Periodic Table - Dr. MahbubDocument42 pagesPeriodic Table - Dr. MahbubWREAK OFFICIALSNo ratings yet
- Atomic StructureDocument19 pagesAtomic StructureDarionNo ratings yet
- ES 67 Lesson 2Document61 pagesES 67 Lesson 2nikkihipulanNo ratings yet
- Physics of The Atom 3Document83 pagesPhysics of The Atom 3Peter-John HydeNo ratings yet
- Review of Grade 9 ChemistryDocument6 pagesReview of Grade 9 Chemistryclarisrangasajo97No ratings yet
- Rhea Margarette Mesinas LEARNING ACTIVITY SHEET Grade 8 Group Act 4Document4 pagesRhea Margarette Mesinas LEARNING ACTIVITY SHEET Grade 8 Group Act 4Gabriel Alfred PerezNo ratings yet
- Chemistry Principles and Reactions 8th Edition by Masterton Hurley ISBN 130507937X Solution ManualDocument13 pagesChemistry Principles and Reactions 8th Edition by Masterton Hurley ISBN 130507937X Solution Manualsamantha100% (26)
- Solution Manual For Chemistry Principles and Reactions 8Th Edition by Masterton Hurley Isbn 130507937X 9781305079373 Full Chapter PDFDocument32 pagesSolution Manual For Chemistry Principles and Reactions 8Th Edition by Masterton Hurley Isbn 130507937X 9781305079373 Full Chapter PDFchristopher.manteca185100% (10)
- Chap 1 - Elementary Mat Science Concepts Rev 1Document50 pagesChap 1 - Elementary Mat Science Concepts Rev 1Jay MashNo ratings yet
- Yr 12 Module 2 Electrons and OrbitalsDocument48 pagesYr 12 Module 2 Electrons and OrbitalsVikki McIntoshNo ratings yet
- Lesson Four - Half Lives and Nuclear EquationsDocument11 pagesLesson Four - Half Lives and Nuclear EquationsDeepti PatilNo ratings yet
- Ch2-Atomic Structure and Interatomic BondingDocument22 pagesCh2-Atomic Structure and Interatomic BondingSaif AlbaddawiNo ratings yet
- Ionic CompoundsDocument49 pagesIonic CompoundsShamel CurrayNo ratings yet
- 4.3 Electrolysis Molten Compounds Set 2 QPDocument4 pages4.3 Electrolysis Molten Compounds Set 2 QPAbdul RasheedNo ratings yet
- 9.4 Reaction of Metals With Water Set 1 QPDocument3 pages9.4 Reaction of Metals With Water Set 1 QPAbdul RasheedNo ratings yet
- 9.6 Reactivity Series Set 1 MsDocument6 pages9.6 Reactivity Series Set 1 MsAbdul RasheedNo ratings yet
- 4.2 IGCSE Chemistry Topic 4 Electrochemistry Electrolysis of Concentrated HCL Set 1 QP Ms PreviewDocument10 pages4.2 IGCSE Chemistry Topic 4 Electrochemistry Electrolysis of Concentrated HCL Set 1 QP Ms PreviewAbdul RasheedNo ratings yet
- 7.5 AbsorptionDocument1 page7.5 AbsorptionAbdul RasheedNo ratings yet
- Caie Igcse Ict 0417 Theory v3Document44 pagesCaie Igcse Ict 0417 Theory v3Abdul RasheedNo ratings yet
- TileDocument1 pageTileAbdul RasheedNo ratings yet
- Chemistry 1 - 11 - Q1 - M4Document14 pagesChemistry 1 - 11 - Q1 - M4Deez NutsNo ratings yet
- Dwnload Full Biology 1st Edition Marielle Hoefnagels Test Bank PDFDocument35 pagesDwnload Full Biology 1st Edition Marielle Hoefnagels Test Bank PDFhudsonlosjames100% (14)
- CHEM 1413 Homework Solutions Textbook HomeworkDocument5 pagesCHEM 1413 Homework Solutions Textbook Homeworksupernerd4everNo ratings yet
- Chemistry Form 6 Sem 1 01Document44 pagesChemistry Form 6 Sem 1 01Stephanie Tan0% (1)
- Solution Manual For General Organic and Biological Chemistry 2Nd Edition by Janice Gorzynski Smith Isbn 0073402788 9780073402789 Full Chapter PDFDocument36 pagesSolution Manual For General Organic and Biological Chemistry 2Nd Edition by Janice Gorzynski Smith Isbn 0073402788 9780073402789 Full Chapter PDFsteven.biggs159100% (10)
- Waja Chemistry The Structure of The AtomDocument8 pagesWaja Chemistry The Structure of The AtomChewfun KhooNo ratings yet
- Atomic Structure: Atomic Number Number of Mass Number Number ofDocument1 pageAtomic Structure: Atomic Number Number of Mass Number Number ofCindy LawNo ratings yet
- Chemistry 9Document153 pagesChemistry 9Naveed Ahmed ButtNo ratings yet
- 0620 17Document12 pages0620 17Haider AliNo ratings yet
- QZ 1Document5 pagesQZ 1Walid EbaiedNo ratings yet
- Chemistry IGCSE NotesDocument64 pagesChemistry IGCSE NotesMahmoud Ashraf50% (2)
- Chapter 2 Solution PDFDocument51 pagesChapter 2 Solution PDFGaurav MeenaNo ratings yet
- C3 Atomic Structure 4Document86 pagesC3 Atomic Structure 4Cassandra mwangiNo ratings yet
- To Understand The Structure of Atom-Game:: Worksheets/Atomic Structure Worksheet-PKT - PDF Atom - en - HTMLDocument18 pagesTo Understand The Structure of Atom-Game:: Worksheets/Atomic Structure Worksheet-PKT - PDF Atom - en - HTMLSaumya ThakkerNo ratings yet
- Chemistry PDFDocument217 pagesChemistry PDFRavi SinghNo ratings yet
- Dwnload Full Foundations of Materials Science and Engineering 5th Edition Smith Solutions Manual PDFDocument36 pagesDwnload Full Foundations of Materials Science and Engineering 5th Edition Smith Solutions Manual PDFroxaneblyefx100% (11)
- Isotopes - PPT 10 3 20220Document29 pagesIsotopes - PPT 10 3 20220CJNo ratings yet
- Atomic and Nuclear PhysicsDocument172 pagesAtomic and Nuclear PhysicsArjun Saraf100% (1)
- Name Father Name: Mobile No.: Important InstructionsDocument12 pagesName Father Name: Mobile No.: Important InstructionsRavinderNo ratings yet
- Chang Problems Chapter 2Document10 pagesChang Problems Chapter 2ChaNo ratings yet
- Chemistry Notes L.mwanawenyuDocument960 pagesChemistry Notes L.mwanawenyuKudakwashe Jena100% (1)
- Student - Element BuilderDocument5 pagesStudent - Element BuilderChimamanda NWERRIH100% (1)
- Gen Chem 1 Q1 M4Document9 pagesGen Chem 1 Q1 M4Joselito UbaldoNo ratings yet
- Unit - 4 Atomic Structure - 7th STDDocument29 pagesUnit - 4 Atomic Structure - 7th STDthangamuthu baskarNo ratings yet
- Mod 2 BA PhysicsDocument412 pagesMod 2 BA PhysicsBenitoKameloNo ratings yet
- IGCSE Chemistry Principles of ChemistryDocument7 pagesIGCSE Chemistry Principles of Chemistrydanielmahsa100% (1)
- Solution Manual For Chemistry 11th Edition by Chang ISBN 007766695X 9780077666958Document36 pagesSolution Manual For Chemistry 11th Edition by Chang ISBN 007766695X 9780077666958henryarmstrongypajbizoqe100% (23)
- Lesson PlanDocument9 pagesLesson PlanMarandacan, Irah A.No ratings yet
- Activity Sheets For Chem With NamesDocument7 pagesActivity Sheets For Chem With NamesJoan PenanoNo ratings yet
- Daily Practice Problems (DPB: SAT) Unit: Inside The Atom !!!Document6 pagesDaily Practice Problems (DPB: SAT) Unit: Inside The Atom !!!Mihica KhareNo ratings yet