Professional Documents
Culture Documents
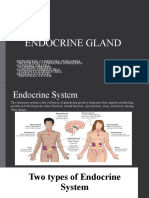
Different Glands of The Endocrine System
Uploaded by
Novie Roycell Fernandez RueloOriginal Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Different Glands of The Endocrine System
Uploaded by
Novie Roycell Fernandez RueloCopyright:
Available Formats
DIFFERENT GLANDS OF THE ENDOCRINE SYSTEM
• Hypothalamus - part of your brain that controls hormone production by
releasing different chemicals to the pituitary gland- “commander”
• Pituitary gland –gland that secretes growth hormone, prolactin,
antidiuretic hormones and others - “Master gland”
• Pineal gland - connects the endocrine system with the nervous system
produces several important hormones, including melatonin, important to
sleep/wake cycles and sexual development
• Thyroid gland – located in the front of your neck, it releases hormones
(thyroxin) that control your metabolism and govern the way your body
uses energy
-Hypothyroidism
-Cretinism-Hyperthyroidism
THYMUS GLAND -The thymus gland, lying between the lungs under the
sternum, secretes thymosins that affect production and differentiation of T
lymphocytes that are important in immunity.
Kidney- maintaining proper bodily functions and overall health.
• Parathyroid - located behind the thyroid gland, they are essential for
proper bone development
• Adrenal glands - influence the way your body uses energy
-Adrenal cortex- regulated by the pituitary hormone ACTH
(adrenocorticotrophic)
-Secretes hormones cortisol- Stress hormone produced by body to ensure
that the body gets enough fuel during emotional arousal and stress
• Pancreas - releases the hormones (insulin) your body needs to metabolize
sugar; problems with the pancreas can lead to diabetes
• Epinephrine and Norepinephrine are similar chemicals that act as both
neurotransmitters and hormones in the body. Both substances play an
important role in the body’s fight or flight response, and their release into
the bloodstream causes increases in blood pressure, heart rate, and blood
sugar levels.
• Ovaries - produce estrogen and progesterone in women, and also release egg
cells (and a small amounts of testosterone)
Estrogen- fosters female reproductive capacity, and accumulation of fatty tissue
in breast and hips
Progesterone-stimulates growth of female reproductive organ, and prepares
uterus to maintain pregnancy
• Testes - produce the hormone testosterone; in men, testosterone maintains
sperm production and bone mass.
HORMONE FUNCTIONS
Regulate the chemical composition and volume of the internal
environment (extracellular fluid).
Help regulate metabolism and energy balance.
Help regulate contraction of smooth and cardiac muscle fibers and
secretion by glands.
Help maintain homeostasis, despite disruptions, such as infection, trauma,
emotional stress, dehydration, starvation, hemorrhage, and temperature
extremes.
Regulate certain activities of the immune system.
Play a role in the smooth, sequential integration of growth and
development.
Contribute to the basic processes of reproduction, including gamete
production, fertilization, nourishment of the embryo and fetus, delivery,
and nourishment of the newborn.
The endocrine hormones help control mood, growth and development, the way our
organs work, , and reproduction. The endocrine system regulates how much of each
hormone is released.
Glucagon spurs the liver to break down glycogen
and release more glucose into the blood.
You might also like
- Balancing Hormones Naturally: A Woman's Guide to Hormonal Harmony: HealthFrom EverandBalancing Hormones Naturally: A Woman's Guide to Hormonal Harmony: HealthNo ratings yet
- Thyroid Health: The Thyroid Solution Diet ExposedFrom EverandThyroid Health: The Thyroid Solution Diet ExposedRating: 3 out of 5 stars3/5 (2)
- Identification PartDocument4 pagesIdentification PartNovie Roycell Fernandez RueloNo ratings yet
- Anfis EndokrinDocument14 pagesAnfis Endokrinyolanda merinskyNo ratings yet
- Endocrine SystemDocument22 pagesEndocrine SystemkwatsNo ratings yet
- Hormones and Young Living Essential Oils PresentationDocument30 pagesHormones and Young Living Essential Oils Presentationapi-150039816100% (9)
- Nervous System ReportDocument5 pagesNervous System ReportsharkNo ratings yet
- Endocrine System March 5 - 8, 2024Document61 pagesEndocrine System March 5 - 8, 2024Almira ZuñigaNo ratings yet
- Human PhysiologyDocument17 pagesHuman PhysiologySharanya BasakNo ratings yet
- Endocrine SystemDocument6 pagesEndocrine SystemKryztoff AlambatinNo ratings yet
- Endocrine SystemDocument11 pagesEndocrine SystemPunong Grande NHS Banga NHS Annex (R XII - South Cotabato)No ratings yet
- An Endocrine SystemDocument3 pagesAn Endocrine SystemEvbogame Iyare IbhadeNo ratings yet
- HomeostasisDocument51 pagesHomeostasisKarla HyltonNo ratings yet
- ENDOCRINE Systems Ad Its DisordersDocument21 pagesENDOCRINE Systems Ad Its DisordersAmir PermitivoNo ratings yet
- Endocrine!!!!!!!Document33 pagesEndocrine!!!!!!!Ungays ungaNo ratings yet
- Endocrine SystemDocument4 pagesEndocrine SystemKirsten GomezNo ratings yet
- Lesson 10 Endocrine SystemDocument12 pagesLesson 10 Endocrine SystemBai Donna S. AlimanNo ratings yet
- Quarter 3 Week 1 Module 1Document34 pagesQuarter 3 Week 1 Module 1Juliana Sophia BungalsoNo ratings yet
- Secretion From The Pineal GlandDocument8 pagesSecretion From The Pineal GlandVince Laurence BlancaflorNo ratings yet
- Anatomy of The Endocrine SystemDocument18 pagesAnatomy of The Endocrine SystemReign Aiken M. LaraNo ratings yet
- EndocrineDocument15 pagesEndocrineapi-200177496No ratings yet
- Anatomy & Physiology of Endocrine SystemDocument34 pagesAnatomy & Physiology of Endocrine SystemUzma Khan100% (1)
- Endocrine SystemDocument13 pagesEndocrine Systemereneovalerozo22No ratings yet
- AnaPhysio Endocrine System Borja, JayvenDocument4 pagesAnaPhysio Endocrine System Borja, JayvenJboar TbenecdiNo ratings yet
- Corticotropins and GonadotropinsDocument39 pagesCorticotropins and GonadotropinsSudhakar LakavathNo ratings yet
- Endochrine SystemDocument6 pagesEndochrine Systemskitz0frenicoNo ratings yet
- Diabetes 2nd Check Edited 5Document13 pagesDiabetes 2nd Check Edited 5Catiereign VerdeNo ratings yet
- Endocrine System LessonDocument47 pagesEndocrine System LessonMA. FRITZIE DE ASISNo ratings yet
- Lesson 4-The Endocrine SystemDocument8 pagesLesson 4-The Endocrine SystemkreativekerelleNo ratings yet
- Control of Our Bodies HomeostasisDocument20 pagesControl of Our Bodies HomeostasisJohn Philip VerastigueNo ratings yet
- Endocrine SystemDocument9 pagesEndocrine Systemkevin maheshNo ratings yet
- BT101 - Introductory Biology (Endocrine/Exocrine) DR - Navin Gupta Dept of BSBE, IIT GuwahatiDocument17 pagesBT101 - Introductory Biology (Endocrine/Exocrine) DR - Navin Gupta Dept of BSBE, IIT GuwahatirechinNo ratings yet
- Endocrine Glands and HormonesDocument6 pagesEndocrine Glands and HormoneshaileyNo ratings yet
- Anatomy and Physiology of Endocrine SystemDocument7 pagesAnatomy and Physiology of Endocrine SystemJumaimah BauloNo ratings yet
- Role of Hormones Endocrine 1Document37 pagesRole of Hormones Endocrine 1zyrle (zayrieeo)No ratings yet
- Endocrine SystemDocument14 pagesEndocrine SystemWhyL NificentNo ratings yet
- EndocrinologyDocument15 pagesEndocrinologyAbdullah EmadNo ratings yet
- Endocrine PetliukDocument3 pagesEndocrine PetliukЕкатерина ПетлюкNo ratings yet
- Animal HormonesDocument18 pagesAnimal HormonesJohn BildanNo ratings yet
- Endocrine SystemDocument48 pagesEndocrine SystemSeptember Neckohle AlunanNo ratings yet
- The Endocrine System and Glands of The HumanDocument10 pagesThe Endocrine System and Glands of The HumanKurt Ivan GonzalesNo ratings yet
- Anatomy and Physiology - Endocrine SystemDocument8 pagesAnatomy and Physiology - Endocrine Systemcn351073No ratings yet
- Demo Teaching First Law of Motion G8Document34 pagesDemo Teaching First Law of Motion G8Neil VelascoNo ratings yet
- Ms. Cynthia Bea: ProfessorDocument22 pagesMs. Cynthia Bea: ProfessorJohn Cedric Vale CruzNo ratings yet
- Endocrine SystemDocument30 pagesEndocrine SystemBrenda Domaneo BaseNo ratings yet
- University of Hassan: Government Home Science College Hassan Submitted by Swathi PattarDocument8 pagesUniversity of Hassan: Government Home Science College Hassan Submitted by Swathi Pattarmanjunathu731No ratings yet
- What Is The Difference Between Neurotransmitter and HormonesDocument17 pagesWhat Is The Difference Between Neurotransmitter and HormonesRachel Ann FranchescaNo ratings yet
- Endocrine SystemDocument41 pagesEndocrine SystemAtteya Mogote AbdullahNo ratings yet
- Endocrine System PDFDocument113 pagesEndocrine System PDFfayeleechaiyapornkulNo ratings yet
- CBSE Quick Revision Notes (Class-11 Biology) Chapter-22 Chemical Coordination and IntegrationDocument3 pagesCBSE Quick Revision Notes (Class-11 Biology) Chapter-22 Chemical Coordination and IntegrationNANDAKUMAR BABUNo ratings yet
- CBSE Quick Revision Notes (Class-11 Biology) Chapter-22 Chemical Coordination and IntegrationDocument3 pagesCBSE Quick Revision Notes (Class-11 Biology) Chapter-22 Chemical Coordination and IntegrationNANDAKUMAR BABUNo ratings yet
- Endocrine System: Anatomy and Physiology of TheDocument5 pagesEndocrine System: Anatomy and Physiology of TheRachel TiangcoNo ratings yet
- Endocrine System PresentationDocument29 pagesEndocrine System PresentationTanayNo ratings yet
- Parathyroid GlandsDocument3 pagesParathyroid GlandsRosita RamosNo ratings yet
- Endocrinesystem 180214021054Document14 pagesEndocrinesystem 180214021054levi0417No ratings yet
- Endocrine SystemDocument58 pagesEndocrine SystemBeBs jai SelasorNo ratings yet
- What Is The Endocrine System?: HormonesDocument7 pagesWhat Is The Endocrine System?: HormonesGhezyl LascoNo ratings yet
- Thyroid Diet : Thyroid Solution Diet & Natural Treatment Book For Thyroid Problems & Hypothyroidism Revealed!From EverandThyroid Diet : Thyroid Solution Diet & Natural Treatment Book For Thyroid Problems & Hypothyroidism Revealed!Rating: 1 out of 5 stars1/5 (1)
- Adrenal Fatigue: Understanding the Symptoms: How Malfunctioning Adrenal Glands Negatively Affect the BodyFrom EverandAdrenal Fatigue: Understanding the Symptoms: How Malfunctioning Adrenal Glands Negatively Affect the BodyNo ratings yet
- IntegumentaryDocument5 pagesIntegumentaryNovie Roycell Fernandez RueloNo ratings yet
- 10 Biology 1-16-07 Endocrine System Feedback SystemsDocument34 pages10 Biology 1-16-07 Endocrine System Feedback SystemsErivieNo ratings yet
- 12 - Endocrine SystemDocument20 pages12 - Endocrine SystemNovie Roycell Fernandez RueloNo ratings yet
- Endocrine System: Chemical ControlDocument36 pagesEndocrine System: Chemical ControlGary VlaicuNo ratings yet
- NSTP2 ReflectionDocument2 pagesNSTP2 ReflectionNovie Roycell Fernandez RueloNo ratings yet
- Ali Raza Forensic SupplementsDocument120 pagesAli Raza Forensic Supplementsumerq604No ratings yet
- Botany Laboratory Specimens (Bryophytes)Document40 pagesBotany Laboratory Specimens (Bryophytes)lorrainebarandonNo ratings yet
- Human Impact On The Microbiological Water Quality of The RiversDocument6 pagesHuman Impact On The Microbiological Water Quality of The Riversaddisu maruNo ratings yet
- Of Basques, Blood, and Blue PeopleDocument6 pagesOf Basques, Blood, and Blue PeopleVince MiglioreNo ratings yet
- Cassava Flour - Specification EAS 7402010Document8 pagesCassava Flour - Specification EAS 7402010Suresh PatelNo ratings yet
- ANIMILIADocument10 pagesANIMILIAAnand Teekmani AnuNo ratings yet
- Earth and Life Science (Week 4) - q2Document4 pagesEarth and Life Science (Week 4) - q2Rica ParillaNo ratings yet
- Practical Microbiology 1Document8 pagesPractical Microbiology 1Adlina TajuddinNo ratings yet
- Allegra 64R CentrifugeDocument64 pagesAllegra 64R Centrifugeluroguita-1No ratings yet
- Buffers - Principles and PracticeDocument15 pagesBuffers - Principles and PracticeLaura NogueraNo ratings yet
- LLLT in Hair GrowthDocument13 pagesLLLT in Hair GrowthCarlos SilvaNo ratings yet
- Acupuntura OcularDocument4 pagesAcupuntura OcularratamanoNo ratings yet
- LFSC Class Test GRD 10 2023Document4 pagesLFSC Class Test GRD 10 2023gugumatlanatoNo ratings yet
- Big Six PDFDocument4 pagesBig Six PDFmotibaNo ratings yet
- Science Final Revision Worksheet 1st TermDocument6 pagesScience Final Revision Worksheet 1st TermM7G Royal100% (1)
- Review of LaboratoryDocument48 pagesReview of LaboratoryIkhar RidhoNo ratings yet
- TLC DLCDocument67 pagesTLC DLCchandra shekharNo ratings yet
- General Biology 1 QTR 2 ActivitiesDocument4 pagesGeneral Biology 1 QTR 2 ActivitiesNyanko SorianoNo ratings yet
- Metabolism of XenobioticsDocument84 pagesMetabolism of XenobioticsJNo ratings yet
- Class 8 Winter Break Home-WorkDocument8 pagesClass 8 Winter Break Home-Workrani bloriaNo ratings yet
- A History of Membrane Transport and Bioenergetics PDFDocument383 pagesA History of Membrane Transport and Bioenergetics PDFEdmilson RodriguesNo ratings yet
- Ospe-Osce Microbio-Pathology SlidesDocument208 pagesOspe-Osce Microbio-Pathology Slidesdoterofthemosthigh100% (3)
- Unit Ii Biomedical Perspective in Gender and SexualityDocument46 pagesUnit Ii Biomedical Perspective in Gender and SexualityRowena Lanete ButaNo ratings yet
- Imaging Anatomy Brain and Spine Anne G Osborn Full ChapterDocument67 pagesImaging Anatomy Brain and Spine Anne G Osborn Full Chaptervicki.wilson456100% (8)
- Cerebrospinal FluidDocument3 pagesCerebrospinal FluidlecturioNo ratings yet
- CV of C.v.narasimha MurthyDocument4 pagesCV of C.v.narasimha MurthyNarasimha MurthyNo ratings yet
- Active Transport WorksheetDocument2 pagesActive Transport WorksheetLola BeeNo ratings yet
- Create A Timeline of EarthDocument2 pagesCreate A Timeline of EarthsaintEmNo ratings yet
- Vector NTI® Express SoftwareDocument184 pagesVector NTI® Express SoftwareDrgemeNo ratings yet