Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Verb Tense Diagrams - HS22
Uploaded by
Natali OpanasiukOriginal Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Verb Tense Diagrams - HS22
Uploaded by
Natali OpanasiukCopyright:
Available Formats
nw University of Applied Sciences
Northwestern Switzerland
English Grammar
Tenses
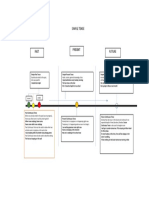
Verb tenses in English include the idea of:
Time Past, present, future
Aspect Simple, continuous (progressive), perfect
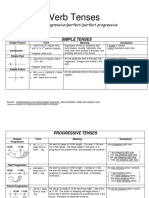
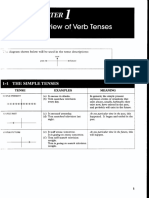
THE SIMPLE TENSES
TENSE EXAMPLES MEANING
PRESENT SIMPLE a) It snows in Alaska. In general, the simple present
expresses events or situations
b) Tom watches television every that exist always, usually,
1-:0;HH:
day. habitually; they exist now, have
1 existed in the past, and probably
c.) The sk.. 'I ·,s b \ ue....
will exit in the future.
I
PAST SIMPLE c) It snowed yesterday. At one particular time in the past,
this happened. It began and
d) Tom watched television last ended in the past.
� night.
I
FUTURE SIMPLE e) It will snow tomorrow. At one particular time in the future,
It is going to snow tomorrow. this will happen.
)(. f) Tom will watch television
tonight.
Tom is going to watch
television tonight.
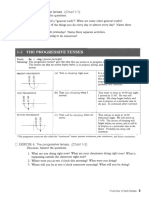
THE CONTINUOUS ( PROGRESSIVE) TENSES
Form: be + -ing (present participle)
Meaning: The continuous tenses give the idea that an activity is in progress during a particular time.
The tenses say that an activity begins before, is in progress during, and continues after
another time or action.
·+
PRESENT CONTINUOUS a) Tom is sleeping right now. It is now 11:00. Tom went to sleep
at 10:00 tonight, and he is still
0 V
asleep. His sleep began in the
past, is in progress at the present
time, and probably will continue.
PAST CONTINUOUS b) Tom was sleeping when I Tom went to sleep at 10:00 last
I
arrived. night. I arrived at 11:00. He was
still asleep. His sleep began
�I
� V before and was in progress at a
particular time in the past. It
continued after I arrived.
FUTURE CONTINUOUS c) Tom will be sleeping when we Tom will go to sleep at 10:00
I
arrive. tomorrow. We will arrive at 11:00.
The action of sleeping will begin
-!
bi'V�v'- before we arrive, and it will be in
progress at a particular time in the
future. Probably his sleep will
continue.
School of Business, UAP, Windisch; Kluser 10.09.2022
nw University of Applied Sciences
Northwestern Switzerland
English Grammar
:Tenses
THE PERFECT TENSES
Form: have + past participle
Meaning: The perfect tenses all give the idea that one thing happens before another time or event
and is linked to it in some way.
TENSE EXAMPLES MEANING
PRESENT PERFECT a) Tom has already eaten. Tom finished eating sometime
before now. The exact time is not
G=f
important.
PAST PERFECT b) Tom had already eaten when First Tom finished eating. Later
I
his friend arrived. his friend arrived. Tom's eating
was completely finished before
another time in the past.
�
I
FUTURE PERFECT e) Tom will already have eaten First Tom will finish eating. Later
when his friend arrives. his friend will arrive. Tom's eating
will be completely finished before
� another time in the future.
THE PERFECT CONTINUOUS TENSES
Form: have + been + -ing (present participle)
Meaning: The perfect continuous tenses* give the idea that one activity is in progress immediately
before, up to, until another time or event. The tenses are used to express the duration of
the first activity.
PRESENT PERFECT CONTINUOUS a) Tom has been studying for Activity in progress: studying
two hours. When? Before now, up to now.
'1
How long? For two hours
PAST PERFECT CONTINUOUS b) Tom had been studying for Activity in progress: studying
I
two hours before his friend came. When? Before another event in
the past.
How long? For two hours
bO�
I
FUTURE PERFECT CONTINUOUS c) Tom will have been studying Activity in progress: studying
for two hours by the time his friend When? Before another event in
arrives. the future.
I 0�
Q '-""'" How long? For two hours.
School of Business, UAP, Windisch; Kluser 10.09.2022
You might also like
- Tenses English Grammar PresentationDocument14 pagesTenses English Grammar PresentationMaz Gedi60% (5)
- Verb Tenses: Simple/progressive/perfect/perfect ProgressiveDocument4 pagesVerb Tenses: Simple/progressive/perfect/perfect Progressiveismail kaya100% (1)
- All Tenses NotesDocument7 pagesAll Tenses NotesKhairun Nasuha bt Mohamad TahirNo ratings yet
- 7 Perfect TensesDocument2 pages7 Perfect TensesMelanie Ayure100% (1)
- Grammar English For ScienceDocument104 pagesGrammar English For ScienceRizka Alfi100% (1)
- Overview of Verb Tenses: EXERCISE 1. Introductions and InterviewsDocument10 pagesOverview of Verb Tenses: EXERCISE 1. Introductions and InterviewsSarah AnnisaNo ratings yet
- English Verb Tenses-InfographicsDocument13 pagesEnglish Verb Tenses-InfographicsPatrícia Marcela Polidoro100% (1)
- Key Words For The English Tenses The BEST1111STARTDocument1 pageKey Words For The English Tenses The BEST1111STARTkimberlyNo ratings yet
- Playing A Ball For An HourDocument2 pagesPlaying A Ball For An HourAyu AmarciaNo ratings yet
- Understanding English Grammar 4ed Chapter 1Document12 pagesUnderstanding English Grammar 4ed Chapter 1Bobby KimNo ratings yet
- TensesDocument17 pagesTensesNaim Kharima SaraswatiNo ratings yet
- BasicTechnical English Rev.1aaaDocument68 pagesBasicTechnical English Rev.1aaabayu axselan nugrahaNo ratings yet
- Tugas Bahasa Inggris Unit 2 Verb Tense Kel 3 Kelas 2aDocument4 pagesTugas Bahasa Inggris Unit 2 Verb Tense Kel 3 Kelas 2aEsri DewiNo ratings yet
- Tenses - Simple Progresive TenseDocument21 pagesTenses - Simple Progresive TenseJuhadiNo ratings yet
- English For Physics Physics Department Universitas Negeri PadangDocument9 pagesEnglish For Physics Physics Department Universitas Negeri PadangNAURAH NAZHIFAHNo ratings yet
- EXERCISE 3. The Simple Tenses. (Chart 1-1) : Be - Ing andDocument1 pageEXERCISE 3. The Simple Tenses. (Chart 1-1) : Be - Ing andarsfNo ratings yet
- Unit 2. Verb TenseDocument15 pagesUnit 2. Verb TenseFahima tuzzahrohNo ratings yet
- English Grammar Tenses For English For MathDocument64 pagesEnglish Grammar Tenses For English For MathSyaifa AlifhiarizkiNo ratings yet
- Simple Past Simple Present Simple Future: V2 Vs Will / To Be Going To V1Document1 pageSimple Past Simple Present Simple Future: V2 Vs Will / To Be Going To V1mutlu pythonNo ratings yet
- Materi Grammar - Tenses (Autosaved)Document11 pagesMateri Grammar - Tenses (Autosaved)UtiNo ratings yet
- EF Adults - Pocket Grammar BookDocument45 pagesEF Adults - Pocket Grammar BookdhilaNo ratings yet
- Release Notes Kav2012 RuDocument4 pagesRelease Notes Kav2012 RuAurelian EusebioNo ratings yet
- Verb TensesDocument1 pageVerb TensesJiang ZahraNo ratings yet
- Expressing Ideas With VerbsDocument14 pagesExpressing Ideas With VerbsAirin RahmiNo ratings yet
- D I S U S U N: Bahasa InggrisDocument4 pagesD I S U S U N: Bahasa InggrisEsri DewiNo ratings yet
- Tenses ChartDocument1 pageTenses ChartluigiagustNo ratings yet
- Future TenseDocument6 pagesFuture TenseKareem AlhozeeliNo ratings yet
- Verb TensesDocument3 pagesVerb TensesRhea CadungoNo ratings yet
- Verbal Times: SimpleDocument7 pagesVerbal Times: Simplemaria paola ramirezNo ratings yet
- Future FormsDocument3 pagesFuture FormsAnda AdaNo ratings yet
- Unit 6: Adverb Clause A. IntroductionDocument8 pagesUnit 6: Adverb Clause A. IntroductionDenicha Eka Putri FebriantiNo ratings yet
- Verb Form in EnglishDocument2 pagesVerb Form in EnglishAnonymous eKsE5t3wNo ratings yet
- Simple TensesDocument1 pageSimple TensesarsfNo ratings yet
- Adobe Scan 20 Dic 2021Document1 pageAdobe Scan 20 Dic 2021ELENA SIMONINNo ratings yet
- Understanding English Grammar 4ed Chapter 1 PDFDocument12 pagesUnderstanding English Grammar 4ed Chapter 1 PDFWihel PaulaNo ratings yet
- English Assignment 2Document6 pagesEnglish Assignment 2Parvatham GaneshNo ratings yet
- Rangkuman InggrisDocument32 pagesRangkuman Inggristara latifahNo ratings yet
- GE 1st MeetingDocument29 pagesGE 1st MeetingintifadhahNo ratings yet
- Makalah B InggrisDocument49 pagesMakalah B InggrisMichael WidjajaNo ratings yet
- 1) Simple Tenses Simple Present TenseDocument4 pages1) Simple Tenses Simple Present TenseArturo Jiménez MNo ratings yet
- Diktan Sonra - Madan Önce Boyunca & Süresince Özel KullanimlarDocument1 pageDiktan Sonra - Madan Önce Boyunca & Süresince Özel KullanimlarAnonymous rJi74AWkNo ratings yet
- Grammar Note (Verb Tenses)Document4 pagesGrammar Note (Verb Tenses)psyhodraneNo ratings yet
- Konu Anlatımı - TENSESDocument5 pagesKonu Anlatımı - TENSESGülnihal IşıkNo ratings yet
- Compendium of English TensesDocument2 pagesCompendium of English TensesinfalliablekaranNo ratings yet
- Tenses 1. The Simple Tenses: Before, Is in Progress During, and Continuous After Another Time orDocument3 pagesTenses 1. The Simple Tenses: Before, Is in Progress During, and Continuous After Another Time orlalafadillaftrNo ratings yet
- Simple Continuous Perfect Perfect ContinuousDocument1 pageSimple Continuous Perfect Perfect ContinuousGermanNo ratings yet
- Past LaikaiDocument1 pagePast LaikaidaibitNo ratings yet
- Tense::c Diagram Shown Below Will Be Used in The Tense DescriptionsDocument1 pageTense::c Diagram Shown Below Will Be Used in The Tense DescriptionsAlex Bolivar FigueroaNo ratings yet
- English TensesDocument1 pageEnglish TensesBartłomiej SzydłowskiNo ratings yet
- ContinuousDocument9 pagesContinuousПолина ПоповаNo ratings yet
- Tenses - TableDocument2 pagesTenses - TableAnuradha MukunthanNo ratings yet
- Time Frame of Simple Tenses in EnglishDocument1 pageTime Frame of Simple Tenses in EnglishIrnaNo ratings yet
- Verbs (Tense & Aspect)Document5 pagesVerbs (Tense & Aspect)Martín AlonsoNo ratings yet
- MATERIAL FOR Nurse Students-1Document15 pagesMATERIAL FOR Nurse Students-1Lia Nadia LerebulanNo ratings yet
- Future Perfect and Future Perfect Progressive: Exercise 25 Warm-Up. (Chart 3-6)Document1 pageFuture Perfect and Future Perfect Progressive: Exercise 25 Warm-Up. (Chart 3-6)ASOOM ALGAMDIINo ratings yet
- English Tense SystemDocument11 pagesEnglish Tense SystemMuchamad Umar Chatab Nasserie100% (1)
- Hand Book SMTR 5 TK 3Document32 pagesHand Book SMTR 5 TK 3kha irunNo ratings yet
- Simplu Simplu: CONTINUU (BE) + VB-ing ContinuuDocument1 pageSimplu Simplu: CONTINUU (BE) + VB-ing ContinuuLucas HizanuNo ratings yet
- 7.1 (PDF AT Task 1) Tenses PDFDocument4 pages7.1 (PDF AT Task 1) Tenses PDFP A Wan SunarNo ratings yet
- Adverb, Adjective and Noun ClauseDocument25 pagesAdverb, Adjective and Noun ClauseRaditya FanjasmaNo ratings yet
- I'll Love YouDocument2 pagesI'll Love YouNatali OpanasiukNo ratings yet
- GiantDocument3 pagesGiantNatali OpanasiukNo ratings yet
- Celine Dion - My Heart Will Go OnDocument2 pagesCeline Dion - My Heart Will Go OnNatali OpanasiukNo ratings yet
- Fifth Harmony - Work From HomeDocument4 pagesFifth Harmony - Work From HomeNatali OpanasiukNo ratings yet
- HumanDocument4 pagesHumanNatali OpanasiukNo ratings yet
- Britney Spears - ThreeDocument6 pagesBritney Spears - ThreeNatali OpanasiukNo ratings yet
- Ed Sheeran PerfectDocument1 pageEd Sheeran PerfectIsnandar PoneNo ratings yet
- Dance MonkeyDocument4 pagesDance MonkeyNatali OpanasiukNo ratings yet
- Celine Dion - My Heart Will Go OnDocument2 pagesCeline Dion - My Heart Will Go OnNatali OpanasiukNo ratings yet
- Bruno Mars - Talking To The MoonDocument2 pagesBruno Mars - Talking To The MoonDwi DwiNo ratings yet
- Ed Sheeran PerfectDocument1 pageEd Sheeran PerfectIsnandar PoneNo ratings yet
- Bob Marley - SunshineDocument2 pagesBob Marley - SunshineNatali OpanasiukNo ratings yet
- Bieber, ED Sheeran - I Don't CareDocument4 pagesBieber, ED Sheeran - I Don't CareNatali OpanasiukNo ratings yet
- Listening Test Form 4 Semester II Task 1 Directions: in This Part of The Section You Will Listen To The Text. While TheDocument2 pagesListening Test Form 4 Semester II Task 1 Directions: in This Part of The Section You Will Listen To The Text. While TheNatali OpanasiukNo ratings yet
- Speaking Test Form 4 Semester IIDocument1 pageSpeaking Test Form 4 Semester IINatali OpanasiukNo ratings yet
- Alex Hepburn - Don't Burry MeDocument5 pagesAlex Hepburn - Don't Burry MeNatali OpanasiukNo ratings yet
- Mark and His Friends: ListeningDocument2 pagesMark and His Friends: ListeningNatali OpanasiukNo ratings yet
- Part I. ListeningDocument3 pagesPart I. ListeningNatali OpanasiukNo ratings yet
- Reading Test Form 4 Semester II Directions: Read The Texts. Look at The Statements Below The Texts, Decide, WhichDocument3 pagesReading Test Form 4 Semester II Directions: Read The Texts. Look at The Statements Below The Texts, Decide, WhichNatali OpanasiukNo ratings yet
- Simple Past, Present Perfect Simple and Presente Perfect Continuous - Keynote ProficientDocument14 pagesSimple Past, Present Perfect Simple and Presente Perfect Continuous - Keynote Proficientmarcelo meloNo ratings yet
- Media Communications: Tet EnglishDocument24 pagesMedia Communications: Tet Englishraj143007 .tNo ratings yet
- Past and Past Perfect TensesDocument7 pagesPast and Past Perfect TensesEdelmar BenosaNo ratings yet
- Auxiliary VerbDocument1 pageAuxiliary VerbHatimNo ratings yet
- Tenses CorrectedDocument1 pageTenses CorrectedAhmad JarrarNo ratings yet
- Flashcards: I Have Been Married For 5 YearsDocument8 pagesFlashcards: I Have Been Married For 5 YearsCaio DiasNo ratings yet
- DIRECT IndirectDocument8 pagesDIRECT IndirectSyafi' AhmadNo ratings yet
- Tabla Tiempos VerbalesDocument1 pageTabla Tiempos VerbalesLucía Pérez CanoNo ratings yet
- English Tenses: Group 2 Bki 2FDocument20 pagesEnglish Tenses: Group 2 Bki 2FZahra MahmudiNo ratings yet
- Passive VoiceDocument3 pagesPassive VoiceLukman Abdi WicaksonoNo ratings yet
- Iba Public School JacobabadDocument7 pagesIba Public School JacobabadGhulam Ali SoomroNo ratings yet
- English Basic LearningDocument58 pagesEnglish Basic LearningKhomisur RahmatulNo ratings yet
- (20222) ELS106 - Grammar Test 2 (Set 1)Document14 pages(20222) ELS106 - Grammar Test 2 (Set 1)Nur FadhiaNo ratings yet
- 12 Tenses With Examples in TamilDocument2 pages12 Tenses With Examples in TamilMemes tamila maree100% (2)
- Conditional SentencesDocument5 pagesConditional Sentencesamjad gul abroNo ratings yet
- TENSESDocument4 pagesTENSESJerr1 efxNo ratings yet
- Forms of Verb VocabineerDocument16 pagesForms of Verb VocabineerMalik NaeemNo ratings yet
- Activity Sheet Aspect of Verb 2q w1Document4 pagesActivity Sheet Aspect of Verb 2q w1Ning Juan100% (1)
- Guia Inglés 4to Año 2do MomDocument7 pagesGuia Inglés 4to Año 2do MomdommerNo ratings yet
- Tense Mona Rakhar Sohoj Kowsol by AxiomDocument15 pagesTense Mona Rakhar Sohoj Kowsol by AxiomAazanNo ratings yet
- Unit 1 - CONDITIONAL SENTENCE - IndonesiaDocument39 pagesUnit 1 - CONDITIONAL SENTENCE - IndonesiaMelissa LissaNo ratings yet
- English Worksheet Part2Document2 pagesEnglish Worksheet Part2Deivi GaniNo ratings yet
- Kala Dalam Bahasa Inggris Dan Bahasa Sangir (Suatu Analisis Kontrastif)Document15 pagesKala Dalam Bahasa Inggris Dan Bahasa Sangir (Suatu Analisis Kontrastif)inkanurulpadlahNo ratings yet
- 5 Pertemuan VDocument11 pages5 Pertemuan VNumpy PandasNo ratings yet
- Right Form of Verbs PDFDocument6 pagesRight Form of Verbs PDFshafait MasumNo ratings yet
- Conjugación Del Verbo WorkDocument1 pageConjugación Del Verbo Workrikan1821No ratings yet
- Tenses and Passive Sentences (Upload)Document23 pagesTenses and Passive Sentences (Upload)Hendri 1427No ratings yet
- Tabla de Tiempos Verbales MinimizadaDocument2 pagesTabla de Tiempos Verbales MinimizadaAJPNo ratings yet