Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Module Hydraulics
Uploaded by
Ho Bi0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
4 views1 pageCopyright
© © All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
4 views1 pageModule Hydraulics
Uploaded by
Ho BiCopyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
You are on page 1of 1
UNIVERSITY OF CEBU-MAIN CAMPUS
CIVIL ENGINEERING REVIEW
HYDRAULICS AND GEOTECHNICAL ENGINEERING
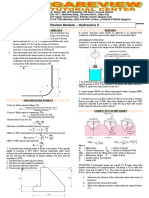
DAMS in saltwater with its base horizontal, what is the maximum height
1. A concrete dam retaining water is shown. If the Specific for stable equilibrium in the upright position?
weight of the concrete is 23.5 kN/m3 , find the factor of safety
against sliding, the factor of safety against overturning, and the 2. A regular scow, 9.5 m wide, 16 m long, and 3.6 m high has
pressure intensity on the base. Assume there is a hydrostatic a draft of 2.5 m in seawater. Its center of gravity is 2.7 m above
uplift that varies uniformly from full hydrostatic head at the heel its bottom. Determine (a) initial metacentric height; (b) If the
of the dam to zero at the toe and that the coefficient of friction scow tilts one side is just at the point of submergence,
between dam and foundation soil is 0.45. determine the righting or overturning moment.
3. A wooden barge of rectangular cross-section is 8 m wide, 4
m high, and 16 m long. It is transporting in seawater (s=1.03)
a total load of 1,550 kN including its own weight and cargo. If a
weight of 80 kN (included in the 1,500 kN) is shifted a distance
of 2.5 m to one side, it will cause the barge to go down 455 mm
in the wedge of immersion and also rise 455 mm in the
corresponding wedge of emersion. The barge floats vertically
(on an even keel) before the shifting of the weight. Compute
how far above the waterline is the center of gravity of the loaded
barge.
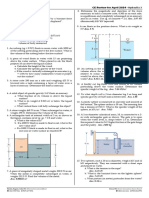
2. Water is acting on the vertical side of a trapezoidal masonry
dam, 2 m wide at the top, 15 m wide at the bottom, 20 m
high. What is the permissible height of water if the allowable
compressive stress at the toe is 3.02 kg/cm2? Assume that
there is no water pressure underneath the dam. Concrete
weighs, 2400 kg/m3. Ans: 18.76 m
STABILITY OF FLOATING BODIES
"
𝑀𝐵! = #
! $%& '
Where: M = metacenter
G = Center of Gravity
Bo = Center of Buoyancy
VD = Volume Displaced
MBo = Distance from the Metacenter to the Center of
Buoyancy
MG = Metacentric Height
𝜃 = Angle of Tilt
MBo > GBo. Stable
MBo < GBo. Unstable
MBo = GBo. Stable (Critical)
Examples:
1. A block of wood (s = 0.65) is in a shape of a rectangular
parallelepiped having a 10 cm square base. If the block floats
You might also like
- S1 FM Buyyancy T+answersDocument18 pagesS1 FM Buyyancy T+answersprabathiyaNo ratings yet
- Lecture HydraulicsDocument27 pagesLecture HydraulicsHarvey Pagaran0% (2)
- EC311: Fluid Mechanics Tutorial Sheet 01Document3 pagesEC311: Fluid Mechanics Tutorial Sheet 01chilaluNo ratings yet
- Fluid Mechanics (4th Year)Document2 pagesFluid Mechanics (4th Year)Jaypee Calamba100% (1)
- PhysicsDocument744 pagesPhysicsMark Lorens Staana100% (1)
- Program - Proposed Construction of The Earth Dam Chikuni - MonzeDocument1 pageProgram - Proposed Construction of The Earth Dam Chikuni - MonzeWoodlock Limited0% (1)
- H-Series Load Table and SpecDocument11 pagesH-Series Load Table and Specmkchanatyahoo0% (1)
- Quiz 3 - Dams and StabilityDocument5 pagesQuiz 3 - Dams and StabilityCarl Junell OcampoNo ratings yet
- Assgn 3Document2 pagesAssgn 3shishirNo ratings yet
- RM 36 - Hydraulics 2 Forces-BodiesDocument1 pageRM 36 - Hydraulics 2 Forces-BodiestheengineerNo ratings yet
- Quiz No. 3Document1 pageQuiz No. 3Janie Kyle HirangNo ratings yet
- Villavicencio - Problem Set 1 - HydraulicsDocument5 pagesVillavicencio - Problem Set 1 - HydraulicsMichaela VillavicencioNo ratings yet
- Analysis of Gravity DamsDocument10 pagesAnalysis of Gravity DamskerbyreyesmanaloNo ratings yet
- Rev5 PDFDocument16 pagesRev5 PDFErickson AbiolNo ratings yet
- σcosθ ρgd σ = surface tension in N/m θ = wetting angle, 0 for water d = diameter of tube in m ρ = density of fluidDocument1 pageσcosθ ρgd σ = surface tension in N/m θ = wetting angle, 0 for water d = diameter of tube in m ρ = density of fluidJustine Ejay MoscosaNo ratings yet
- Midterm Hge ProbsDocument2 pagesMidterm Hge ProbsIbo, Kim CaesarNo ratings yet
- 04 Buoyancy and StabilityDocument5 pages04 Buoyancy and StabilityFalconer AldNo ratings yet
- Fluid MechanicDocument4 pagesFluid MechanicteknokolikNo ratings yet
- Finals PlateDocument5 pagesFinals PlateChan SeseNo ratings yet
- Gravity Dam ForcesDocument15 pagesGravity Dam Forcesfaazizi100% (3)
- Name: - Course, Year & Section: - General Instructions: Answer The Following Questions Based On Our PreviousDocument2 pagesName: - Course, Year & Section: - General Instructions: Answer The Following Questions Based On Our PreviousCarlo CabanusNo ratings yet
- Gravity Dam Forces SummaryDocument11 pagesGravity Dam Forces SummaryMohamoud AbdulahiNo ratings yet
- Notes in HydraulicsDocument4 pagesNotes in HydraulicsMichael Angelo FernandezNo ratings yet
- Stability of Floating BodiesDocument2 pagesStability of Floating BodiesEmejoi TemblacoNo ratings yet
- Homework 1 PDFDocument4 pagesHomework 1 PDFعلي علي صالح انقعNo ratings yet
- 1981 Wave Response of A Spar Buoy With and Without A Damping PlateDocument8 pages1981 Wave Response of A Spar Buoy With and Without A Damping Plateshubham khodiyarNo ratings yet
- Stability of Floating BodiesDocument2 pagesStability of Floating Bodiescielo_cetd3670100% (1)
- Fluid Mech 3Document20 pagesFluid Mech 3Alyssa AmistosoNo ratings yet
- Hyd 3Document1 pageHyd 3Jocelyn CabarlesNo ratings yet
- 3 2 PDFDocument10 pages3 2 PDFJohn GaviolaNo ratings yet
- L2-Gravity Dam ForcesDocument49 pagesL2-Gravity Dam Forceschirag griyamNo ratings yet
- Hydraulics Review ProblemsDocument9 pagesHydraulics Review ProblemsrojethtrinidadNo ratings yet
- Today: Review Concepts From Tuesday Continuity Equation Bernoulli's Equation Applications/ExamplesDocument19 pagesToday: Review Concepts From Tuesday Continuity Equation Bernoulli's Equation Applications/ExamplesAhmed MekawyNo ratings yet
- Compilation of Solved ProblemsDocument7 pagesCompilation of Solved ProblemsyslovillanuevaNo ratings yet
- Gravity DamDocument89 pagesGravity DamartiNo ratings yet
- Tutorial Topic 3Document3 pagesTutorial Topic 3aidaNo ratings yet
- 4 Module Hydraulics Gravity Dam1Document27 pages4 Module Hydraulics Gravity Dam1Eleazar Tami-ingNo ratings yet
- Group Assignment IDocument5 pagesGroup Assignment Ilelisagetachew90No ratings yet
- Problem Set No 1Document3 pagesProblem Set No 1Fatima Therese ManaloNo ratings yet
- Hyd Ref 1Document2 pagesHyd Ref 1rando12345No ratings yet
- Buoyancy RELDocument28 pagesBuoyancy RELJOHNLEO RAMNo ratings yet
- Experiment 6Document5 pagesExperiment 6Lyka NaboaNo ratings yet
- Fresh Water: Pine LeadDocument3 pagesFresh Water: Pine LeadRobby BajamondeNo ratings yet
- Stability Analysis of Concrete Gravity Dam (An Overview) : AbstractDocument10 pagesStability Analysis of Concrete Gravity Dam (An Overview) : AbstractSri E.Maheswar Reddy Assistant ProfessorNo ratings yet
- ProblemsDocument3 pagesProblemsimPERFECTme09No ratings yet
- (01-25) Hydraulics 3Document2 pages(01-25) Hydraulics 3Ram CaniculaNo ratings yet
- Submerged BreakwaterDocument19 pagesSubmerged Breakwaterananda dwi setiawan kresfiapriliantoNo ratings yet
- PHYS 2 - Engineering Physics 2 (Week 2)Document4 pagesPHYS 2 - Engineering Physics 2 (Week 2)maang alleijaNo ratings yet
- SodapdfDocument747 pagesSodapdfMaybelyn Rivera PagkatotohanNo ratings yet
- Experimental Study On Wave in Deck Loading Under Focused Wave Conditions Tien Trung Duong Full ChapterDocument40 pagesExperimental Study On Wave in Deck Loading Under Focused Wave Conditions Tien Trung Duong Full Chaptermatthew.dunn346100% (11)
- Experimental Study On Wave in Deck Loading Under Focused Wave Conditions Tien Trung Duong Full ChapterDocument40 pagesExperimental Study On Wave in Deck Loading Under Focused Wave Conditions Tien Trung Duong Full Chapterjerry.benfield213No ratings yet
- Physics Home Package FivDocument4 pagesPhysics Home Package FivOMARY MWAKAJENo ratings yet
- Chapter 4 Dams Part2 ModifiedDocument34 pagesChapter 4 Dams Part2 ModifiedAlkheder AlyazeediNo ratings yet
- WORK POWER ENERGY-05-Subjective UnSolvedDocument7 pagesWORK POWER ENERGY-05-Subjective UnSolvedRaju SinghNo ratings yet
- Ejercicios FluidosDocument10 pagesEjercicios FluidosAle FernandezNo ratings yet
- Worksheet 3Document2 pagesWorksheet 3Yordanos MekonnenNo ratings yet
- (01-29) Hydraulics 6Document2 pages(01-29) Hydraulics 6Ram CaniculaNo ratings yet
- Fluid MechanicsDocument1 pageFluid MechanicsEj ApeloNo ratings yet
- Pressure, Resistance, and Stability of Earth American Society of Civil Engineers: Transactions, Paper No. 1174, Volume LXX, December 1910From EverandPressure, Resistance, and Stability of Earth American Society of Civil Engineers: Transactions, Paper No. 1174, Volume LXX, December 1910No ratings yet
- The Mechanics of Water-Wheels - A Guide to the Physics at Work in Water-Wheels with a Horizontal AxisFrom EverandThe Mechanics of Water-Wheels - A Guide to the Physics at Work in Water-Wheels with a Horizontal AxisNo ratings yet
- 'Case Studies'': Ar. EMMARA Abubakar Muhammad Arslan B-21878Document5 pages'Case Studies'': Ar. EMMARA Abubakar Muhammad Arslan B-21878Muhammad ArslanNo ratings yet
- Fluid Flow Thru A Bed of Particles: Che 317E Particle TechnologyDocument19 pagesFluid Flow Thru A Bed of Particles: Che 317E Particle TechnologyJulie Anne Cristales100% (1)
- Profile: LebanonDocument42 pagesProfile: LebanonMuthana JalladNo ratings yet
- Astm D 790-03Document13 pagesAstm D 790-03reniNo ratings yet
- Salient Features of Deras M.I.P. (Reservoir) : 1 LocationDocument3 pagesSalient Features of Deras M.I.P. (Reservoir) : 1 LocationAntariksha NayakNo ratings yet
- 1 Specific Energy and Critical DepthDocument21 pages1 Specific Energy and Critical DepthAbdulbasit Aba BiyaNo ratings yet
- Shape Memory Alloys: A Seminar Report ONDocument16 pagesShape Memory Alloys: A Seminar Report ONSantosh KumarNo ratings yet
- Ec 167561Document2 pagesEc 167561efac7100% (1)
- PROCEDUREFORCONDUCTINGPUMPINGTESTSDocument11 pagesPROCEDUREFORCONDUCTINGPUMPINGTESTSMubashirKhan9090No ratings yet
- We've Got You Covered: Cold To Hot Industrial InsulationDocument4 pagesWe've Got You Covered: Cold To Hot Industrial InsulationniltonNo ratings yet
- 9A01302 Strength of Materials - IDocument8 pages9A01302 Strength of Materials - IsivabharathamurthyNo ratings yet
- Briefing: Water Surface Profile Over Side Weir in A Trapezoidal ChannelDocument7 pagesBriefing: Water Surface Profile Over Side Weir in A Trapezoidal ChannelRobert MacalanaoNo ratings yet
- Karvena-Head SluiceDocument9 pagesKarvena-Head Sluicevaranasirk1No ratings yet
- Esparraguerra - 16 Divisions of ConstructionDocument7 pagesEsparraguerra - 16 Divisions of ConstructionEDRICK ESPARRAGUERRANo ratings yet
- Lect 10 Week 11 - Dam & Tunnel ConstructionDocument48 pagesLect 10 Week 11 - Dam & Tunnel ConstructionMuhammad FauzanNo ratings yet
- Astm D7913 D7913M-2020Document9 pagesAstm D7913 D7913M-2020Jan Jan100% (1)
- Component Parts of A Railway Track StructureDocument46 pagesComponent Parts of A Railway Track Structuretesfaye wondimuNo ratings yet
- NEWIRPWMDocument5 pagesNEWIRPWMDYCEC SERDNo ratings yet
- Isolated Foundation PDFDocument6 pagesIsolated Foundation PDFsoroware100% (1)
- Case Study Al Ain Juice MBR ETP3Document3 pagesCase Study Al Ain Juice MBR ETP3Rohit AdhikariNo ratings yet
- Meta and Performative ArchitectureDocument18 pagesMeta and Performative ArchitectureAllister LewisNo ratings yet
- Pressure Measurement - CHL207Document28 pagesPressure Measurement - CHL207Sakthi SNo ratings yet
- Cemfair SmoothDocument2 pagesCemfair Smoothosama mohNo ratings yet
- CEA Annual ReportDocument27 pagesCEA Annual ReportKALAIVANNAN R CVENo ratings yet
- 34 Recycling Bituminous PavementDocument4 pages34 Recycling Bituminous PavementSum BeautyNo ratings yet
- CEN-622 Advanced Foundation Engineering: By: Anumita MishraDocument31 pagesCEN-622 Advanced Foundation Engineering: By: Anumita Mishraabcd efghNo ratings yet
- Metric - A. Volume and Height Between Tubing and Hole, and Casing and HoleDocument78 pagesMetric - A. Volume and Height Between Tubing and Hole, and Casing and HoleNorfolkingNo ratings yet
- Conference HallDocument13 pagesConference HallPrerana ManjunathNo ratings yet