Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Lab #1 FEM
Uploaded by
አንዋርጀማልCopyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Lab #1 FEM
Uploaded by
አንዋርጀማልCopyright:
Available Formats
Lab #1 (Finite element modeling)
Answers will be presented in small groups on: June 12, 2021, 12:00 AM
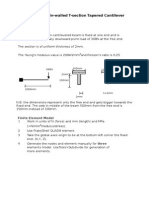
A 1m long steel box girder is loaded with a 15kNm moment as shown below. The beam
has a depth of 75mm and a width of 150mm. The material properties are E = 210GPa and
= 0.3.
wall thickness of 5mm Y
15kNm
1m 75mm
Z
X
150mm
Different types of elements are used to see the different approaches that can be taken to
model the same structure.
1. Create a table comparing the vertical deflection and maximum bending stress (σx) at
the midspan and the free end of the beam using the following modeling approaches:
(please include full screenshots of your model and results, include the whole screen of
your pc for each result). And also submit the model files (only .odb, .cae and .jnl
files) together with your answer.
- Use 2 beam elements.
- Use shell elements with an element size of 0.05m
- Use shell elements (linear and quadratic) with an element size of 0.05m
- Use solid element (linear and quadratic) with an element size of 0.05 m.
- Use solid mechanics equations (show your hand calculations)
2. In point form, discuss the differences between these results specifically addressing:
a. how the results calculated using the solid mechanics equations compare to
the FE results (explain why).
b. the differences between results using the beam, shell and solid elements in
terms of the stress results available from each element.
Hint:
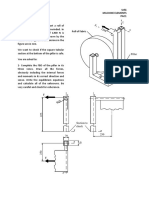
The different mesh types will require different underlying geometries.
- Beam elements require a 1D geometry to be constructed
- Shell elements require a (planar or extrusion) geometry to be constructed
- Solid element require a 3D solid geometry to be constructed
1D geometry (beam element)
Planar/extrusion geometry (shell element)
Solid geometry (solid element)
You might also like
- SAP2000 Analysis StepsDocument20 pagesSAP2000 Analysis StepsAmir RanaNo ratings yet
- Beam Tutorial 09mar2010 v1Document48 pagesBeam Tutorial 09mar2010 v1SANDRA MIKULICNo ratings yet
- Problem FormulationDocument6 pagesProblem FormulationKalev LillemetsNo ratings yet
- Reinforced Concrete Buildings: Behavior and DesignFrom EverandReinforced Concrete Buildings: Behavior and DesignRating: 5 out of 5 stars5/5 (1)
- Seminar 2 Buckling Analysis AbaqusDocument10 pagesSeminar 2 Buckling Analysis Abaqusأحمد صلاح الدينNo ratings yet
- Dynamic Damage and FragmentationFrom EverandDynamic Damage and FragmentationDavid Edward LambertNo ratings yet
- Solid 65 AnsysDocument5 pagesSolid 65 AnsysChetan B ArkasaliNo ratings yet
- Machine Design-I exam questions on shafts, springs, keys and screwsDocument3 pagesMachine Design-I exam questions on shafts, springs, keys and screwsAnup KashyapNo ratings yet
- Mesh Convergence ExercisesDocument10 pagesMesh Convergence ExercisesAbdul wahid ButtNo ratings yet
- TRN Simulation Question AnswersDocument4 pagesTRN Simulation Question AnswersCristhian Stefano Falchi PosadaNo ratings yet
- MECH4400 Assignment 2 2019Document2 pagesMECH4400 Assignment 2 2019AliMalik0% (1)
- Modelling A Cable Using Femap With NX NastranDocument2 pagesModelling A Cable Using Femap With NX NastranKumar Mintu0% (1)
- Sintering FC 0208 50Document2 pagesSintering FC 0208 50aloysiusNo ratings yet
- ENGG 410 Problem Set 2-1 - Mechanical PropertiesDocument2 pagesENGG 410 Problem Set 2-1 - Mechanical PropertiesJoana Rosette TordecillaNo ratings yet
- Tutorial 7Document16 pagesTutorial 7UdhamNo ratings yet
- Btech Me 3 Sem Mechanics of Solids Rme303 2022Document2 pagesBtech Me 3 Sem Mechanics of Solids Rme303 2022Gulshan AryaNo ratings yet
- Tutorial1-2 ElasticCantilever V4Document29 pagesTutorial1-2 ElasticCantilever V4abuumayrNo ratings yet
- 04 Trave Mista - Straus7Document12 pages04 Trave Mista - Straus7lupin2013No ratings yet
- Week 6 - Properties PDFDocument44 pagesWeek 6 - Properties PDFRichie BobbyNo ratings yet
- AbaqusDocument1 pageAbaqusaloysiusNo ratings yet
- Machine Elements MidtermDocument2 pagesMachine Elements MidtermDaniel TriasNo ratings yet
- MOM Lab Report of 19RAFIADocument9 pagesMOM Lab Report of 19RAFIARafiaNo ratings yet
- SimXpert R3.2 Modeling GuideDocument202 pagesSimXpert R3.2 Modeling Guidepaulkastle100% (2)
- Creating ETABS Default .EdbDocument4 pagesCreating ETABS Default .EdbmigemNo ratings yet
- ME 304 Finite Element Analysis Basic Types of FEA ElementsDocument7 pagesME 304 Finite Element Analysis Basic Types of FEA ElementsJoshua KarthikNo ratings yet
- 2004-Deng-Finite Element Analysis of Effects of Ball Burnishing Parameters OnDocument6 pages2004-Deng-Finite Element Analysis of Effects of Ball Burnishing Parameters OnJesus Ismael Jimenez GarciaNo ratings yet
- SOM Lab EXP1Document6 pagesSOM Lab EXP1Amisha SharonNo ratings yet
- Som Lab Exp1Document6 pagesSom Lab Exp1Amisha SharonNo ratings yet
- SJ Mepla Brief IntroductionDocument13 pagesSJ Mepla Brief IntroductiondynamicsbookNo ratings yet
- School of Mechanical Engineering Laboratory ManualDocument19 pagesSchool of Mechanical Engineering Laboratory ManualShubham TyagiNo ratings yet
- UPM Lab Task 1 (Numerical Method)Document9 pagesUPM Lab Task 1 (Numerical Method)Faizal Juan KumarNo ratings yet
- Nandha Engineering College, Erode - 52Document4 pagesNandha Engineering College, Erode - 52sakthivel balamuruganNo ratings yet
- XFEM Crack Propagation TutorialDocument19 pagesXFEM Crack Propagation TutorialVarghese MathewNo ratings yet
- Mô Phỏng Số Thầy LịchDocument104 pagesMô Phỏng Số Thầy LịchNhật AnhNo ratings yet
- Midterm ProjectDocument5 pagesMidterm ProjectአንዋርጀማልNo ratings yet
- Etabs 11Document3 pagesEtabs 11jb.dqaNo ratings yet
- Finite Element Analysis of Large Diameter Concrete Spherical Shell Domes - Hani Aziz AmeenDocument16 pagesFinite Element Analysis of Large Diameter Concrete Spherical Shell Domes - Hani Aziz AmeenHani Aziz AmeenNo ratings yet
- Chapter 06 - 1D Elements PDFDocument20 pagesChapter 06 - 1D Elements PDFdeepakNo ratings yet
- Finite Element Analysis Question PaperDocument3 pagesFinite Element Analysis Question PaperpaulsampaulNo ratings yet
- r09222502 Mechanics of SolidsDocument9 pagesr09222502 Mechanics of SolidsNida Bagoyboy NatichoNo ratings yet
- Modeling of Welded Connections in SolidWorks SimulationDocument5 pagesModeling of Welded Connections in SolidWorks SimulationCleyton L. AlvesNo ratings yet
- Assignment - 3 On CAEDocument2 pagesAssignment - 3 On CAEIsyraf FitriNo ratings yet
- Finite Element Technique: 7.1 Introduction and ScopeDocument34 pagesFinite Element Technique: 7.1 Introduction and ScopeSharon ShineNo ratings yet
- Ansys ExercisesDocument76 pagesAnsys ExercisesRuchit Solanki100% (1)
- B.Tech. Degree Examination Mechanics of Solids-IIDocument3 pagesB.Tech. Degree Examination Mechanics of Solids-IIkohli kingNo ratings yet
- Exercise 1: Bicycle Frame Study: Description of The ProblemDocument2 pagesExercise 1: Bicycle Frame Study: Description of The ProblemThiago DomingosNo ratings yet
- 2 05-BeamDocument20 pages2 05-BeamMARUFNo ratings yet
- A7 Past ExamsDocument25 pagesA7 Past ExamsWilhelm ThorleyNo ratings yet
- Ansys PZTDocument28 pagesAnsys PZTQuoc LeNo ratings yet
- MF8791-BE - IV YEAR Paste QuestionDocument8 pagesMF8791-BE - IV YEAR Paste QuestionPriyadharshan RNo ratings yet
- (EXTRACT) Ch. VIII Frame Hinge Properties - From CSI (2002) CSI Analysis Reference Manual For SAP2000, Etabs and SafeDocument12 pages(EXTRACT) Ch. VIII Frame Hinge Properties - From CSI (2002) CSI Analysis Reference Manual For SAP2000, Etabs and SafeO SNo ratings yet
- Modeling Cable in NastranDocument15 pagesModeling Cable in NastranKomarudin100% (1)
- Shear Wall Analysis - New Modelling, Same AnswersDocument3 pagesShear Wall Analysis - New Modelling, Same AnswersccapotaNo ratings yet
- Homework 2 Spring 2012Document5 pagesHomework 2 Spring 2012Muhammad HanifNo ratings yet
- Analysis of a Precast Box Beam (Super Tee) DeckDocument22 pagesAnalysis of a Precast Box Beam (Super Tee) DeckMeldi SuhatrilNo ratings yet
- Stringer Panel Method. A Discrete Model To Project Structural Reinforced Concrete ElementsDocument7 pagesStringer Panel Method. A Discrete Model To Project Structural Reinforced Concrete ElementsJose Maria GedaNo ratings yet
- Some Experiences On Numerical Modelling of Cold-Formed Steel Lapped Z-SectionsDocument8 pagesSome Experiences On Numerical Modelling of Cold-Formed Steel Lapped Z-SectionsBart HoNo ratings yet
- Is 13959 1994Document8 pagesIs 13959 1994አንዋርጀማልNo ratings yet
- Response of MDOF Structures To Ground MotionDocument53 pagesResponse of MDOF Structures To Ground Motionpuppyarav2726No ratings yet
- Protective Epoxy Coatings Guide Sherwin WilliamsDocument8 pagesProtective Epoxy Coatings Guide Sherwin WilliamsTeguh SilaNo ratings yet
- 2.1 Linear Response of MDOF To Ground ExcitationDocument56 pages2.1 Linear Response of MDOF To Ground ExcitationአንዋርጀማልNo ratings yet
- 2 Linear Analysis of Earthquake Response Spectrum Analysis June2021Document91 pages2 Linear Analysis of Earthquake Response Spectrum Analysis June2021አንዋርጀማልNo ratings yet
- Bamboo Housing Construction For Sustainable Development: in The Case of Sidama House, EthiopianDocument11 pagesBamboo Housing Construction For Sustainable Development: in The Case of Sidama House, EthiopianአንዋርጀማልNo ratings yet
- Singh 2017Document41 pagesSingh 2017puaanNo ratings yet
- Two Way Flat Plate Concrete Floor Slab Design Detailing PDFDocument64 pagesTwo Way Flat Plate Concrete Floor Slab Design Detailing PDFLe Duc ToanNo ratings yet
- Causes of Conflicts and Disputes in Construction PDocument6 pagesCauses of Conflicts and Disputes in Construction PBalaji CreatNo ratings yet
- Green Rebar EpoxyDocument1 pageGreen Rebar EpoxyአንዋርጀማልNo ratings yet
- Labour Productivity in Construction: July 2016Document6 pagesLabour Productivity in Construction: July 2016Prashanth Babu.K100% (1)
- ETAG 030: Guideline For European Technical Approval ofDocument41 pagesETAG 030: Guideline For European Technical Approval ofAli KerimzadeNo ratings yet
- ScabiesDocument9 pagesScabiesAnggi Irianti AronggearNo ratings yet
- 2015F CENG 6011 Lecture Materials Part 5Document61 pages2015F CENG 6011 Lecture Materials Part 5አንዋርጀማልNo ratings yet
- 6、盾安介绍PPT (英文完整2023版)Document49 pages6、盾安介绍PPT (英文完整2023版)አንዋርጀማልNo ratings yet
- Design and Construction Standards VolumeDocument162 pagesDesign and Construction Standards VolumeአንዋርጀማልNo ratings yet
- 7TKK000132 - Exothermic Welding Catalogue - US - DGTDocument96 pages7TKK000132 - Exothermic Welding Catalogue - US - DGTአንዋርጀማልNo ratings yet
- Assignment Submission InstructionsDocument1 pageAssignment Submission InstructionsአንዋርጀማልNo ratings yet
- ELTurki Colostate 0053N 11894Document31 pagesELTurki Colostate 0053N 11894jayant pathakNo ratings yet
- CH 2 Capital Accumulation in Economic DevelopmentDocument58 pagesCH 2 Capital Accumulation in Economic DevelopmentአንዋርጀማልNo ratings yet
- BS en 16440-2-2023Document32 pagesBS en 16440-2-2023አንዋርጀማልNo ratings yet
- ISO 1043 1 2011 PlasticsDocument11 pagesISO 1043 1 2011 PlasticsአንዋርጀማልNo ratings yet
- Design and Build New Passenger Terminal at Bahir Dar AirportDocument1 pageDesign and Build New Passenger Terminal at Bahir Dar AirportአንዋርጀማልNo ratings yet
- UntitledDocument21 pagesUntitledአንዋርጀማልNo ratings yet
- DBT DR 024 (01 04 23)Document2 pagesDBT DR 024 (01 04 23)አንዋርጀማልNo ratings yet
- Borehole log summaryDocument9 pagesBorehole log summaryአንዋርጀማልNo ratings yet
- FRC - (BS en 14889-2 - 2006) - Fibres For Concrete. Polymer Fibres. Definitions, Specifications and ConformityDocument30 pagesFRC - (BS en 14889-2 - 2006) - Fibres For Concrete. Polymer Fibres. Definitions, Specifications and ConformityE Hammam El MissiryNo ratings yet
- ABB Furse Certification To ISO 14001 (EMS 637489)Document2 pagesABB Furse Certification To ISO 14001 (EMS 637489)አንዋርጀማልNo ratings yet
- 1 Anemia PDDocument40 pages1 Anemia PDአንዋርጀማልNo ratings yet
- ABB Furse Certification To ISO 9001 (Q 06054) Feb 2024Document2 pagesABB Furse Certification To ISO 9001 (Q 06054) Feb 2024አንዋርጀማል100% (1)
- Certified Solidworks Professional Advanced Weldments Exam PreparationFrom EverandCertified Solidworks Professional Advanced Weldments Exam PreparationRating: 5 out of 5 stars5/5 (1)
- FreeCAD | Step by Step: Learn how to easily create 3D objects, assemblies, and technical drawingsFrom EverandFreeCAD | Step by Step: Learn how to easily create 3D objects, assemblies, and technical drawingsRating: 5 out of 5 stars5/5 (1)
- Certified Solidworks Professional Advanced Surface Modeling Exam PreparationFrom EverandCertified Solidworks Professional Advanced Surface Modeling Exam PreparationRating: 5 out of 5 stars5/5 (1)
- From Vision to Version - Step by step guide for crafting and aligning your product vision, strategy and roadmap: Strategy Framework for Digital Product Management RockstarsFrom EverandFrom Vision to Version - Step by step guide for crafting and aligning your product vision, strategy and roadmap: Strategy Framework for Digital Product Management RockstarsNo ratings yet
- Autodesk Fusion 360: A Power Guide for Beginners and Intermediate Users (3rd Edition)From EverandAutodesk Fusion 360: A Power Guide for Beginners and Intermediate Users (3rd Edition)Rating: 5 out of 5 stars5/5 (2)
- Mastering Autodesk Inventor 2014 and Autodesk Inventor LT 2014: Autodesk Official PressFrom EverandMastering Autodesk Inventor 2014 and Autodesk Inventor LT 2014: Autodesk Official PressRating: 5 out of 5 stars5/5 (1)
- SolidWorks 2015 Learn by doing-Part 2 (Surface Design, Mold Tools, and Weldments)From EverandSolidWorks 2015 Learn by doing-Part 2 (Surface Design, Mold Tools, and Weldments)Rating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (5)
- Autodesk Inventor | Step by Step: CAD Design and FEM Simulation with Autodesk Inventor for BeginnersFrom EverandAutodesk Inventor | Step by Step: CAD Design and FEM Simulation with Autodesk Inventor for BeginnersNo ratings yet
- Beginning AutoCAD® 2020 Exercise WorkbookFrom EverandBeginning AutoCAD® 2020 Exercise WorkbookRating: 2.5 out of 5 stars2.5/5 (3)
- Autodesk Inventor 2020: A Power Guide for Beginners and Intermediate UsersFrom EverandAutodesk Inventor 2020: A Power Guide for Beginners and Intermediate UsersNo ratings yet
- Fusion 360 | Step by Step: CAD Design, FEM Simulation & CAM for Beginners.From EverandFusion 360 | Step by Step: CAD Design, FEM Simulation & CAM for Beginners.No ratings yet
- The Geometrical Tolerancing Desk Reference: Creating and Interpreting ISO Standard Technical DrawingsFrom EverandThe Geometrical Tolerancing Desk Reference: Creating and Interpreting ISO Standard Technical DrawingsRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (10)