Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Electro 2
Uploaded by
tanmaymondalchemistry0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
4 views4 pagesOriginal Title
electro2
Copyright
© © All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
4 views4 pagesElectro 2
Uploaded by
tanmaymondalchemistryCopyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
You are on page 1of 4
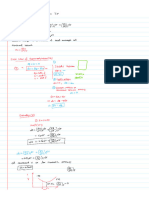
1. At 25 °C, acid dissociation constant of HCN is 4.9 × 10–10 M.
Calculate the degree of
dissociation of HCN, if its concentrations are (i) 0.1 M and (ii) 0.01 M.
2. Calculate at 25 °C the pH of a solution of (a) 0.01 M HCl and (b) 10–7 M HCl.
3. A solution is 0.1 M in Cl–, 0.1 M in Br– and 0.1 M in I–. Solid AgNO3 is gradually added to this solution. Assuming
that the addition of AgNO3 does not change the volume,
answer the following:
(a) What concentration of Ag+ ions will be required to start precipitation of each of the three ions?
(b) Which ion will precipitate first?
(c) What will be the concentration of this ion when the second ion starts precipitating?
(d) What will be the concentration of both the ions when the third ion starts
precipitating? Given:
Ks(AgCl) = 1.7 × 10–10 M2;
Ks(AgBr) = 5.0 × 10–13 M2
and Ks(AgI) = 8.5 × 10–17 M2
4. What is the pH of 0.015 M solution of ammonium chloride if K ºb for ammonia
is 1.8 × 10–5? (b) How much change in pH takes place if this solution is diluted
hundred times? Ans. (a) 5.54 (b) 6.54)
5. What is the ph of a buffer solution, prepared by adding 50ml 1m acetic acid and 25ml sodium acetate?
(K ºa = 1.8 × 10–5).
6. In a saturated solution of calcium phosphate, the concentration of PO4 3– ion is
3.3 × 10–7 M. Calculate the Kº s of Ca3(PO4)2. (Ans. 1.321 × 10–3
You might also like
- Buffer KSP ProbDocument4 pagesBuffer KSP ProbFitria Rahma DewiNo ratings yet
- Chemistry CPP Cat-3Document18 pagesChemistry CPP Cat-3faraazahmed70058No ratings yet
- Ionic Equilibrium CPP-1Document2 pagesIonic Equilibrium CPP-1phuliaikshuNo ratings yet
- Ionic Equilibrium ProblemsDocument2 pagesIonic Equilibrium ProblemsNinad Puranik0% (1)
- Part - I: Subjective QuestionsDocument11 pagesPart - I: Subjective Questionspankaj agarwalNo ratings yet
- Ionic Equilibrium: (Physical Chemistry)Document22 pagesIonic Equilibrium: (Physical Chemistry)keshavNo ratings yet
- Ionic Equilibrium: (Physical Chemistry)Document8 pagesIonic Equilibrium: (Physical Chemistry)MAHI POPLINo ratings yet
- KSP AssignmentDocument3 pagesKSP AssignmentFahri HusainiNo ratings yet
- AuChem10142C QuizDocument8 pagesAuChem10142C QuizantarescraneNo ratings yet
- Ionic Equilibrium: Chapter Practice ProblemsDocument2 pagesIonic Equilibrium: Chapter Practice ProblemsObama binladenNo ratings yet
- Contoh Soal Kelarutan Dan Hasil Kali KelarutanDocument2 pagesContoh Soal Kelarutan Dan Hasil Kali KelarutanMitha Rosyda AttaqianaNo ratings yet
- AP Chem CH 15 Practice QuizDocument8 pagesAP Chem CH 15 Practice QuizHussain MerchantNo ratings yet
- Tutorial 9 Acid Base - TaggedDocument14 pagesTutorial 9 Acid Base - TaggedNg Cheuk HeiNo ratings yet
- Unit 8 1630427312380Document41 pagesUnit 8 1630427312380l082haripriyakotariNo ratings yet
- Review For Ana ChemDocument5 pagesReview For Ana ChemRyle ArbonNo ratings yet
- 2019dec-03 - Ionic Equilibrium - PracticeSheetDocument2 pages2019dec-03 - Ionic Equilibrium - PracticeSheetRSLNo ratings yet
- Quiz-Ionic Equilibrium-Vd - SNDDocument4 pagesQuiz-Ionic Equilibrium-Vd - SNDObama binladenNo ratings yet
- Ionic Equilibrium Sheet-1 12.11.2021Document5 pagesIonic Equilibrium Sheet-1 12.11.2021sreevaishnava01No ratings yet
- KSP SolutibiltyDocument21 pagesKSP SolutibiltyBandita DattaNo ratings yet
- Unit 9. Sol Ubility Equilibria Solubility Equil Ibrium: Chem 301 LectureDocument4 pagesUnit 9. Sol Ubility Equilibria Solubility Equil Ibrium: Chem 301 LectureChelsea RubioNo ratings yet
- Chemistry EquilibriumDocument31 pagesChemistry EquilibriumAbhinavNo ratings yet
- Chemistry 1CDocument6 pagesChemistry 1CKaiJie HanNo ratings yet
- 6382 Topper 21 129 510 2 7289 Ionic Equilibrium Up201612091703 1481283226 2703Document28 pages6382 Topper 21 129 510 2 7289 Ionic Equilibrium Up201612091703 1481283226 2703NILABH NANDANNo ratings yet
- CHEM 1412. Chapter 17. Acid-Base Equilibria - Homework - Ky PDFDocument20 pagesCHEM 1412. Chapter 17. Acid-Base Equilibria - Homework - Ky PDFDi Vlad PeÑa PrietoNo ratings yet
- Equilibrium - 9.4Document3 pagesEquilibrium - 9.4Zulkaif IrshadNo ratings yet
- KSP Solutibilty Practice ProblemsDocument22 pagesKSP Solutibilty Practice ProblemsRohan BhatiaNo ratings yet
- Chapter 14Document8 pagesChapter 14dr.ibrahimsalemvpNo ratings yet
- Chem Solubility SgizzDocument4 pagesChem Solubility Sgizzkagabejan_emo29No ratings yet
- (NS) XII EM One Word Vol - IIDocument15 pages(NS) XII EM One Word Vol - IIAnishaNo ratings yet
- Ionic Equ PDFDocument25 pagesIonic Equ PDFggk2013No ratings yet
- Class Room ProblemsDocument1 pageClass Room ProblemsRishabh AgarwalNo ratings yet
- CP4001 - 0910-S2 - Practice Questions For CA02Document2 pagesCP4001 - 0910-S2 - Practice Questions For CA02cslim37100% (1)
- Chapter 16 HWDocument11 pagesChapter 16 HWsarah_choi_21No ratings yet
- Chemical & Ionic Equilibirum (ADV) QueDocument8 pagesChemical & Ionic Equilibirum (ADV) QueParth SonawaneNo ratings yet
- Ionic Equlibrium QuestionsDocument19 pagesIonic Equlibrium Questionskishangopi123No ratings yet
- Ionic+Equilibrium VEDANTUDocument295 pagesIonic+Equilibrium VEDANTUKing GokulNo ratings yet
- Day-3 - In-Class Assignment - : Phase-1Document4 pagesDay-3 - In-Class Assignment - : Phase-1Arnab DasNo ratings yet
- Chem 4Document3 pagesChem 4Lovey ChandiNo ratings yet
- Tutorial 3Document5 pagesTutorial 3Emily SwanNo ratings yet
- KSP Question A LevelDocument1 pageKSP Question A LevelIlwandy KosasihNo ratings yet
- SECTION-I (Multiple Choice Questions)Document5 pagesSECTION-I (Multiple Choice Questions)Sachin DedhiaNo ratings yet
- Exam 2 W17Document7 pagesExam 2 W17Êsrää TähäNo ratings yet
- 2nd Term Test 1Document7 pages2nd Term Test 1bhattaraisurya54No ratings yet
- FinalExam Sample Problems - 081711Document4 pagesFinalExam Sample Problems - 081711aNo ratings yet
- JEE Main Important Questions With Solutions 2023Document18 pagesJEE Main Important Questions With Solutions 2023vaibhavsatishpattanashettiNo ratings yet
- Ionic Equilibrium 520Document19 pagesIonic Equilibrium 520sarbajit mazumdarNo ratings yet
- Jee 2014 Booklet3 HWT Ionic EquilibriumDocument10 pagesJee 2014 Booklet3 HWT Ionic EquilibriumvarunkohliinNo ratings yet
- Ie +ceDocument2 pagesIe +ceVishnu kantNo ratings yet
- Physical Chemistry OBJECTIVEDocument188 pagesPhysical Chemistry OBJECTIVEGadde Gopala Krishna100% (2)
- Chem 112 - Chapter 16 Acid Base Equilibria and Solubility Equilibria WorksheetDocument3 pagesChem 112 - Chapter 16 Acid Base Equilibria and Solubility Equilibria WorksheetBuse KılıçNo ratings yet
- Buffer QuestionsDocument4 pagesBuffer Questionsactive learning educationNo ratings yet
- Ionic EquilibriumDocument10 pagesIonic EquilibriumPranav MaheshwariNo ratings yet
- Ionic QuestionsDocument4 pagesIonic QuestionsSubharna ChauhanNo ratings yet
- Ionic Eq ExDocument49 pagesIonic Eq ExMausamNo ratings yet
- Ionic EquilibriumDocument2 pagesIonic EquilibriumVidhuPandey100% (1)
- Exam 3 2010 SummerDocument10 pagesExam 3 2010 SummernsorsokNo ratings yet
- BIO1103PE1Document6 pagesBIO1103PE1bambi leeNo ratings yet
- Ionic Equilibrium-03-Objective and Subjective Assignments and Answer SheetDocument16 pagesIonic Equilibrium-03-Objective and Subjective Assignments and Answer SheetRaju SinghNo ratings yet
- Problem Set (Acids and Bases Buffers and Titrations.)Document8 pagesProblem Set (Acids and Bases Buffers and Titrations.)Nate JamesNo ratings yet
- ExpenceDocument4 pagesExpencetanmaymondalchemistryNo ratings yet
- Thermo 2Document4 pagesThermo 2tanmaymondalchemistryNo ratings yet
- Details For DL Notificaiton No 17 2023 dt30122023 240125 191439Document46 pagesDetails For DL Notificaiton No 17 2023 dt30122023 240125 191439hara vardhan reddy naruNo ratings yet
- Details For DL Notificaiton No 17 2023 dt30122023 240125 191439Document46 pagesDetails For DL Notificaiton No 17 2023 dt30122023 240125 191439hara vardhan reddy naruNo ratings yet