Professional Documents
Culture Documents
DPP-01 Chemical Kinetics
Uploaded by
prathmfedOriginal Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
DPP-01 Chemical Kinetics
Uploaded by
prathmfedCopyright:
Available Formats
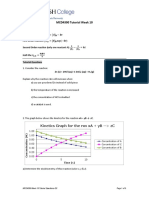
CHEMICAL KINETICS (BASICS/RATE OF REACTION/ORDER/MOLECULARITY) CODE: 2024/25-12-01
1. For gaseous reaction, the rate is expressed in Initial [A] Initial [B] Initial rate of
terms of dP/dt instead of dC/dt or dn/dt where c formation of C
is concentration and n the number of moles.
What is the relation among these expressions? 0.1M 0.1M 1.2x10-3
2. Reaction A B carried inside a container
0.1M 0.2M 1.2x10-3
concentration varies as A t=a+bt. Rate of reaction
can be expressed in terms of pressure at 0.2M 0.1M 2.4x10-3
temperature T=300K, take b=4, R=1/12 atm
mol-1K-1. a)100 atm s-1 b) 200 atm s-1 The rate law for the formation of C is
c) 300 atm s d) 400 atm s
-1 -1
a) r= k [A] [B]2 b) r= k [A]
3. Ammonia and oxygen react at high temperature c) r= k [A] [B] d) r= k [A]2 [B]
as: 4NH3 + 5O2 4NO + 6H2O.In an expt,
9. The rate constant for the reaction
the rate of formation of NO is 3.6x10-3 Ms-1.
Calculate a) rate of disappearance of ammonia 2N2O5 4NO2 + O2 is 3x10-5s-1. If the rate is
and b) rate of formation of water. 2.4x10-5 mol/L s, then the initial concentration of
4. The decomposition of NH3 on platinum surface is N2O5 is: a) 1.4 b) 1.2 c) 0.04 d) 0.8
zero order reaction. What are the rates of 10. The rate constant of a reaction is 2 x10-3 mol/L
production of N2 and H2 if sec. what is the order of the reaction.
k = 2.5 × 10–4 mol L s ?
–1 –1 a) 1 b) 1.5 c) 0 d) 2
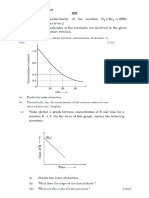
5. The decomposition of N2O5 in CCl4 at 318K has 11. For a hypothetical reaction, A B it is found that
been studied by monitoring the concentration of the rate constant is x s-1. By what factor the rate is
N2O5 in the solution. Initially the concentration of increased if the initial concentration of A is
N2O5 is 2.33 mol L–1 and after 184 minutes, it is
tripled? A) 1 b) 2 c) 3 d) 4
reduced to 2.08 mol L–1. The reaction takes place
12. For elementary reaction, xM N the rate of
according to the equation 2 N2O5 (g) → 4 NO2 (g) +
O2 (g). Calculate the average rate of this reaction disappearance of M increases by a factor of 8
in terms of hours, minutes and seconds. What is upon doubling the concentration of M. the order
the rate of production of NO2 during this period? of reaction with respect to M is:
6. I) For the reaction at 273K (gases) A) 1 b) 2 c) 3 d) 4
NO + O3 NO2 + O2. It is observed that the 13. The rate law of a rxn A + B ⇌ product is
pressure of NO falls from 700mm Hg to 500mm rate=K[A]n[B]m. on doubling the concentration of
Hg in 250s. Calculate the average rate of reaction A and halving the concentration of B, the ratio of
in atm/s. new rate to the earlier rate of reaction will be:-
a) 1.053x10-3 b) 1.053x10-4 a)n-m b)2n-m
c) 2.053x10 d) 2.053x10
-3 -4
c)1/2n+m d)m+n
II) Also, calculate the average rate of reaction in 14. The rate of reaction 3A + 2B products is given
mol/L s. by rate expression, r= k [A] [B]2. If A is taken in
a) 4.7x10-5 b) 5.9x10-5 c) 3.2x10-5 d) 9.8x10-5 excess, the order of the reaction would be
7. For a rxn, 2NO + 2H2 N2 + 2H2O the following a) 3 b) 2 c) 1 d) 5
data were obtained: 15. For the reaction R → P, the concentration of a
[NO] mol/L [H2] mol/L rate reactant changes from 0.03M to 0.02M in 25
minutes. Calculate the average rate of reaction
1. 5x10-3 2.5x10-3 3x10-5 using units of time both in minutes and seconds.
16. In a reaction, 2A → Products, the concentration
2. 15x10-3 2.5x10-3 9x10-5 of A decreases from 0.5 mol L–1 to 0.4 mol L–1 in
10 minutes. Calculate the rate during this
3. 15x10-3 10x10-3 3.6x10-4 interval?
Calculate the order of reaction and rate constant.
a) 2,2.4 b) 1,1.4 c) 3,2.4 d) 0,1.4
8. For non-stoichiometric reaction 2A + B C+D
the following data were obtained in 3 expts. All at
298K.
You might also like
- Electrochemical Processes in Biological SystemsFrom EverandElectrochemical Processes in Biological SystemsAndrzej LewenstamNo ratings yet
- Qsns On Chemical KineticsDocument1 pageQsns On Chemical KineticsprathmfedNo ratings yet
- CRE - Diagnostic Exam (USA)Document2 pagesCRE - Diagnostic Exam (USA)Kuo SarongNo ratings yet
- 08a. Chemical Kinetics SheetDocument33 pages08a. Chemical Kinetics SheetVIKRANTH KUMAR JAKKOJUNo ratings yet
- Topic 7Document6 pagesTopic 7Bert ManNo ratings yet
- Class XII Chemical KineticsDocument6 pagesClass XII Chemical KineticsvartikasinghNo ratings yet
- Chemistry File 4Document4 pagesChemistry File 4Pawan Kumar100% (1)
- MCD4390 Week 10 Tutorial QuestionsDocument5 pagesMCD4390 Week 10 Tutorial QuestionsGabbar100% (1)
- Application of Rate ReactionDocument10 pagesApplication of Rate ReactionRahmawati PutrianasariNo ratings yet
- Kinetics & Photochemistry Tutorial ProblemsDocument4 pagesKinetics & Photochemistry Tutorial ProblemsAmbuj Yadav 4-Year B.Tech. Chemical EngineeringNo ratings yet
- Practice Final CHE1112Document13 pagesPractice Final CHE1112dancer88838No ratings yet
- Practice Rate Law ProblemsDocument12 pagesPractice Rate Law ProblemsCatrina RiveraNo ratings yet
- Chemical KineticsDocument4 pagesChemical KineticssathishNo ratings yet
- Tutorial 2 StudentDocument6 pagesTutorial 2 StudentIrsyad KamilNo ratings yet
- PLTL Ch. 16 AssignmentDocument6 pagesPLTL Ch. 16 AssignmentJules BrunoNo ratings yet
- Problem Set No. 3Document1 pageProblem Set No. 3CJ GoradaNo ratings yet
- Chemical Kinetics Multiple Choice QuestionsDocument22 pagesChemical Kinetics Multiple Choice QuestionsMohamed MegahedNo ratings yet
- Tutorial-Manual CH1002Document18 pagesTutorial-Manual CH1002Gift Chulu100% (2)
- Ap ChemDocument3 pagesAp ChemEthan NguyenNo ratings yet
- Chemical KineticsDocument3 pagesChemical KineticsakritiNo ratings yet
- Kinetics Lec-1 NEET ChalisaDocument35 pagesKinetics Lec-1 NEET Chalisaashustarguy005No ratings yet
- CHEMICAL KINETICS FinalDocument6 pagesCHEMICAL KINETICS FinalBOTHRA CLASSESNo ratings yet
- DPP5 Full Chemical KineticsDocument14 pagesDPP5 Full Chemical KineticsAbhishek SinglaNo ratings yet
- Chemical Kinetics TutorialDocument2 pagesChemical Kinetics TutorialFormer TorrentNo ratings yet
- CH13 Practice ExamDocument8 pagesCH13 Practice ExamAnonymous WI0nbsNo ratings yet
- Exercises Unit4 1Document3 pagesExercises Unit4 1Mabe ArcentalesNo ratings yet
- Practice estimating to find the best answer.: Δt 5 x rate = -Δ (B) 5 x 0.0243 M/s = - Δ (B) -0.12125~ - 0.122 M/sDocument10 pagesPractice estimating to find the best answer.: Δt 5 x rate = -Δ (B) 5 x 0.0243 M/s = - Δ (B) -0.12125~ - 0.122 M/sjeffrey XiaoNo ratings yet
- CHEM311 191 Major2 SolvedDocument11 pagesCHEM311 191 Major2 SolvedhussainNo ratings yet
- Chapter 1 Reaction KineticsDocument8 pagesChapter 1 Reaction KineticsDinesh RamaNo ratings yet
- Mid_term_general_chem_II_fall_2001Document6 pagesMid_term_general_chem_II_fall_2001dr.ibrahimsalemvpNo ratings yet
- CHNG 3004 - 2019-2020 AssignmentsDocument26 pagesCHNG 3004 - 2019-2020 AssignmentsXheikhKaleem100% (1)
- 102 MSJC 13Document11 pages102 MSJC 13noelNo ratings yet
- Chm271 - Tutorial 5 - Chemical KineticsDocument6 pagesChm271 - Tutorial 5 - Chemical Kineticsfiefy zmrNo ratings yet
- CHM270 - Tutorial 3 (Chemical Kinetics)Document7 pagesCHM270 - Tutorial 3 (Chemical Kinetics)Azrie HizadNo ratings yet
- Sk0014 Physical & Iinorganic Chemistry Tutorial 4: Reaction KineticsDocument2 pagesSk0014 Physical & Iinorganic Chemistry Tutorial 4: Reaction KineticsNeil8353 GgNo ratings yet
- Chemical Kinetics-I: Part - I: Subjective QuestionsDocument34 pagesChemical Kinetics-I: Part - I: Subjective Questionshorn blowNo ratings yet
- Chapter 13 Chemical KineticsDocument10 pagesChapter 13 Chemical KineticsJacob McPhersonNo ratings yet
- Chemical Kinetics Rate Constants and Reaction OrdersDocument3 pagesChemical Kinetics Rate Constants and Reaction OrdersVANESSA JOHNS CLASS XINo ratings yet
- Kinetic NCERTDocument10 pagesKinetic NCERTSionna KatiyarNo ratings yet
- Tutorial 1 SolutionsDocument20 pagesTutorial 1 Solutionsanushka shagunNo ratings yet
- Chemical Kinetics QuestionsDocument18 pagesChemical Kinetics QuestionsAakaash C.K.No ratings yet
- JEE - Chemistry - Chemical KineticsDocument27 pagesJEE - Chemistry - Chemical Kineticsdaiwikchilukuri321No ratings yet
- College Chemistry Tutorial on Reaction RatesDocument7 pagesCollege Chemistry Tutorial on Reaction RatesbebsybiswezNo ratings yet
- Exam guide for Chemical Kinetics examDocument3 pagesExam guide for Chemical Kinetics examEzekiel MainaNo ratings yet
- Chemical KineticsDocument9 pagesChemical KineticsTrung VõNo ratings yet
- Chem 338: R K (A) K Has Units M R K (A) K Has Units M R K (PDocument7 pagesChem 338: R K (A) K Has Units M R K (A) K Has Units M R K (Pratna puspita sariNo ratings yet
- Chemistry Worksheet 2Document3 pagesChemistry Worksheet 2LemontNo ratings yet
- Deodhar Classes PDF 1Document6 pagesDeodhar Classes PDF 1Aditya MoreNo ratings yet
- Tutorial 4Document3 pagesTutorial 4aliesyaNo ratings yet
- Millennium Prize Rules 0Document2 pagesMillennium Prize Rules 0Ravi KumarNo ratings yet
- Physical Chemistry by Prince Sir: Chemical Kinetics DPP-1Document4 pagesPhysical Chemistry by Prince Sir: Chemical Kinetics DPP-1PunisherNo ratings yet
- EquationDocument9 pagesEquationHoang Uyen Vy NguyenNo ratings yet
- Revisin Test - Chemical KineticsDocument4 pagesRevisin Test - Chemical KineticsSABIQNo ratings yet
- Chemical KineticsDocument2 pagesChemical KineticsPallabi deNo ratings yet
- Exam 2 Chem 135 Blue - AnswersDocument10 pagesExam 2 Chem 135 Blue - AnswersSerena GaskellNo ratings yet
- Question On Chemical Kinetics-MA 2022Document12 pagesQuestion On Chemical Kinetics-MA 2022Sangay ChodenNo ratings yet
- Assignment 3 Chemical KineticsDocument1 pageAssignment 3 Chemical Kineticsvegamaharajfaith02No ratings yet
- CH 12 Prac Test Kinetics1Document15 pagesCH 12 Prac Test Kinetics1NolemNo ratings yet
- A Modern Course in Statistical PhysicsFrom EverandA Modern Course in Statistical PhysicsRating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (2)
- Chemical Kinetics 2020-2022Document6 pagesChemical Kinetics 2020-2022prathmfedNo ratings yet
- Organic Compounds Aldehydes Ketones Carboxylic AcidsDocument26 pagesOrganic Compounds Aldehydes Ketones Carboxylic AcidsprathmfedNo ratings yet
- QSN Bank On Coordination Compounds 2012-2022Document10 pagesQSN Bank On Coordination Compounds 2012-2022prathmfedNo ratings yet
- Cblechpl 06125Document9 pagesCblechpl 06125prathmfedNo ratings yet
- Assignment On Solid State, Solutions and KineticsDocument12 pagesAssignment On Solid State, Solutions and KineticsprathmfedNo ratings yet
- DPP 19Document1 pageDPP 19prathmfedNo ratings yet
- Assignment On Aldehydes-Ketones-Carboxylic AcidsDocument2 pagesAssignment On Aldehydes-Ketones-Carboxylic AcidsprathmfedNo ratings yet
- Assignment On Coordination CompoundsDocument8 pagesAssignment On Coordination CompoundsprathmfedNo ratings yet
- Electrochemsitry and Solid State Test CbseDocument2 pagesElectrochemsitry and Solid State Test CbseprathmfedNo ratings yet
- Assignment On Nomenclature of Aldehyde-KetonesDocument2 pagesAssignment On Nomenclature of Aldehyde-KetonesprathmfedNo ratings yet
- MCQS'S On Solutions MARKS: 50X4 200M TIME:150MIN: Y Y X X Y Y X XDocument1 pageMCQS'S On Solutions MARKS: 50X4 200M TIME:150MIN: Y Y X X Y Y X XprathmfedNo ratings yet
- Jee Mains 2018Document2 pagesJee Mains 2018prathmfedNo ratings yet
- Thermodynamics Assignment-3Document2 pagesThermodynamics Assignment-3prathmfedNo ratings yet
- DPP 17Document1 pageDPP 17Saiprasad K. MalekarNo ratings yet
- DPP 18Document1 pageDPP 18prathmfedNo ratings yet
- CHEMICAL KINETICS ORDER AND HALF-LIFEDocument1 pageCHEMICAL KINETICS ORDER AND HALF-LIFEprathmfedNo ratings yet
- Thermodynamics Assignment-3Document2 pagesThermodynamics Assignment-3prathmfedNo ratings yet
- TEST ON EQUILIBRIUM AND ACIDS AND BASES (39 CHARACTERSDocument2 pagesTEST ON EQUILIBRIUM AND ACIDS AND BASES (39 CHARACTERSprathmfedNo ratings yet
- Yet QSNS On Mole ConceptDocument2 pagesYet QSNS On Mole ConceptprathmfedNo ratings yet
- School Lesson PlanDocument17 pagesSchool Lesson PlanprathmfedNo ratings yet
- Jee Mains 2018Document2 pagesJee Mains 2018prathmfedNo ratings yet
- TEST ON EQUILIBRIUM AND ACIDS AND BASES (39 CHARACTERSDocument2 pagesTEST ON EQUILIBRIUM AND ACIDS AND BASES (39 CHARACTERSprathmfedNo ratings yet
- DPP 02Document1 pageDPP 02prathmfedNo ratings yet
- Lesson 7 EnergyDocument16 pagesLesson 7 EnergyprathmfedNo ratings yet
- Classification of PlantsDocument12 pagesClassification of Plantsprathmfed100% (1)
- Lesson 8 MirobesDocument11 pagesLesson 8 MirobesprathmfedNo ratings yet
- Lesson 2 WorkDocument15 pagesLesson 2 WorkprathmfedNo ratings yet
- School Lesson PlanDocument17 pagesSchool Lesson PlanprathmfedNo ratings yet
- Chapter 17 - Reaction RatesDocument3 pagesChapter 17 - Reaction RatescaffeinewriterNo ratings yet
- Chemical EquilibriumDocument44 pagesChemical EquilibriumAlly Hoop0% (1)
- Reaction rate can decrease with increasing temperatureDocument3 pagesReaction rate can decrease with increasing temperaturetarun_yahoo100% (1)
- سنوات قديمةDocument79 pagesسنوات قديمةahmed alseileanNo ratings yet
- Mechanism of Enzyme ActionDocument4 pagesMechanism of Enzyme ActionrohiniNo ratings yet
- Name Reaction Organic PDFDocument41 pagesName Reaction Organic PDFPummy Thakur100% (1)
- General Chemistry 2: Quarter 1 - Module 7Document16 pagesGeneral Chemistry 2: Quarter 1 - Module 7Jake Eulogio GuzmanNo ratings yet
- CHPR5501 Adv. Reaction Eng. Part 2Document26 pagesCHPR5501 Adv. Reaction Eng. Part 2Elena TodorovskaNo ratings yet
- Chapter 11 Stoichiometry PDFDocument16 pagesChapter 11 Stoichiometry PDFapi-239855791No ratings yet
- Organic Chemistry 7Th Edition Bruice Test Bank Full Chapter PDFDocument64 pagesOrganic Chemistry 7Th Edition Bruice Test Bank Full Chapter PDFjunemojarrazqmxj100% (7)
- CHEM 204 Problem Set 2 Rate Constants and KineticsDocument2 pagesCHEM 204 Problem Set 2 Rate Constants and KineticsmyriamNo ratings yet
- Tugas - 6 Senyawa AlkunaDocument3 pagesTugas - 6 Senyawa AlkunaBaiq ArinNo ratings yet
- Rates Conversions of Alcohols To Alkyl Bromide Organic Lab ReportDocument12 pagesRates Conversions of Alcohols To Alkyl Bromide Organic Lab Reportberjalankehadapan100% (1)
- Sn1 or Sn2 Guide: Determine Reaction MechanismDocument8 pagesSn1 or Sn2 Guide: Determine Reaction MechanismJayaganesh KalyanasundaramNo ratings yet
- CM134-1L Experiment 2.1Document8 pagesCM134-1L Experiment 2.1Christian JohnNo ratings yet
- Catalyst ActivityDocument14 pagesCatalyst ActivityMUHAMMAD AKRAMNo ratings yet
- ATOOCV1 7 0 Aliphatic Electrophilic SubstitutionDocument18 pagesATOOCV1 7 0 Aliphatic Electrophilic SubstitutionVel SankarNo ratings yet
- An Experimental and Modeling Study of Ammonia WithDocument12 pagesAn Experimental and Modeling Study of Ammonia WithAhmed YasiryNo ratings yet
- Enantioselective Aldol Reactions and Michael Additions Using Proline Derivatives As OrganocatalystsDocument13 pagesEnantioselective Aldol Reactions and Michael Additions Using Proline Derivatives As OrganocatalystsKhaidir WijayaNo ratings yet
- Answer Key-H.w (2) - Oxidation Reduction Reaction-G11 PDFDocument3 pagesAnswer Key-H.w (2) - Oxidation Reduction Reaction-G11 PDFbedo lucyNo ratings yet
- Catalyst DefinitionDocument17 pagesCatalyst DefinitionTRIBRATA BASKORONo ratings yet
- Organic ChemDocument113 pagesOrganic ChemTrúc Hồ0% (1)
- Chemistry Letters, 2013, Vol. 42, # 10 P. 1235 - 1237Document3 pagesChemistry Letters, 2013, Vol. 42, # 10 P. 1235 - 1237rrgodboleNo ratings yet
- Carbonyl Condensation ReactionsDocument39 pagesCarbonyl Condensation ReactionsHesstii Sii ChemmicaLissttaaNo ratings yet
- Sample Questions Rate Law (Credits To Rightful Owners)Document3 pagesSample Questions Rate Law (Credits To Rightful Owners)Li TaNo ratings yet
- Chemical KineticsDocument17 pagesChemical KineticspriyasbsNo ratings yet
- Reversible Reactions and Dynamic EquilibriumDocument5 pagesReversible Reactions and Dynamic EquilibriumFahad Hayat100% (1)
- Additional Problems Final Exam Part 2 AnswersDocument10 pagesAdditional Problems Final Exam Part 2 AnswersJohn SmithNo ratings yet
- Organic Chemistry II Reactions of Aldehydes and KetonesDocument25 pagesOrganic Chemistry II Reactions of Aldehydes and KetonesAsim Alaa Al SalehiNo ratings yet
- Chapter 8 Lecture-Energy, Enzymes, and Metabolism-MODIFIED2Document49 pagesChapter 8 Lecture-Energy, Enzymes, and Metabolism-MODIFIED2E'Lasia LarkinNo ratings yet