Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Untitled Presentation
Uploaded by
sswandrew.prajogo0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
8 views5 pagesTwo coils of copper wire are wrapped around a non-conducting cylinder. One coil is connected to a battery and switches it on and off, inducing a current in the other coil. When the battery is switched on, the needle moves one way, and when switched off, it moves the other way, demonstrating electromagnetic induction. Faraday's law states that a voltage is induced when a conductor cuts magnetic field lines. The induced voltage increases with the speed of motion, number of coil turns, and magnetic field strength. Lenz's law explains that the direction of induced current opposes the change that created it, conserving energy.
Original Description:
Original Title
Untitled presentation
Copyright
© © All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentTwo coils of copper wire are wrapped around a non-conducting cylinder. One coil is connected to a battery and switches it on and off, inducing a current in the other coil. When the battery is switched on, the needle moves one way, and when switched off, it moves the other way, demonstrating electromagnetic induction. Faraday's law states that a voltage is induced when a conductor cuts magnetic field lines. The induced voltage increases with the speed of motion, number of coil turns, and magnetic field strength. Lenz's law explains that the direction of induced current opposes the change that created it, conserving energy.
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
8 views5 pagesUntitled Presentation
Uploaded by
sswandrew.prajogoTwo coils of copper wire are wrapped around a non-conducting cylinder. One coil is connected to a battery and switches it on and off, inducing a current in the other coil. When the battery is switched on, the needle moves one way, and when switched off, it moves the other way, demonstrating electromagnetic induction. Faraday's law states that a voltage is induced when a conductor cuts magnetic field lines. The induced voltage increases with the speed of motion, number of coil turns, and magnetic field strength. Lenz's law explains that the direction of induced current opposes the change that created it, conserving energy.
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
You are on page 1of 5
Group 1: Gregory Troy, Arwen, Andrew
Describe an experiment to show electromagnetic
induction
Two different coils of copper wire having large numbers of turns
(say 50 and 100 turns respectively) are taken. They are now
inserted over a non-conducting cylinder roll, as shown in figure
below. The coil-1, having larger number of turns, is connected in
series with a battery and a plug key. Also, the number of turns, is
connected in series with a battery and a plug key. Also, the other
coil-2 is connected with a galvanometer as shown. The key is
initiated and the galvanometer is observed. We will observe that
the needle of the galvanometer instantly jumps to one side and
then quickly returns to zero, indicating a momentary current in
coil-2. The coil-1 is now disconnected from the battery. Now we
will observe that the needle momentarily moves, but to the
opposite side. It means that now the current flows in the opposite
direction in coil-2
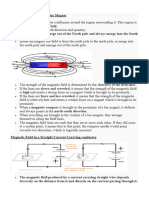
Electromagnetic Induction
Faraday’s law: a voltage is induced in a
conductor whenever it cuts or moves across
magnetic field lines, but not when it moves
along them or rests.
The induced p.d. or voltage increases with the
increase of
● The speed of motion of the magnet or coil
● The number or turns on the coil
● The strength of the magnet
Direction of induced current using Lenz’s Law or
Fleming’s right-hand rule
According to the Lenz’s law the induced current
should flow in a direction that make the coil behave
like a magnet with its top a north pole. The
downward motion of the magnet will then be
opposed since like poles repel.
Lenz’s law is an example of the principle of
conservation of energy. If the currents caused
opposite poles from those that they do make,
electrical energy would be created from nothing. As
it is, mechanical energy is provided, by whoever
moves the magnet, to overcome the forces that
arise.
For a straight wire moving at right angles to
magnetic field a more useful form of Lenz’s law is
Fleming’s right-hand rule. ( the ‘dynamo rule’)
Diagram and Sketch of Output (a.c. generator)
You might also like
- Topic 4 Electromagnetic Effects PDFDocument10 pagesTopic 4 Electromagnetic Effects PDFHakim Abbas Ali PhalasiyaNo ratings yet
- 8.3 Electromagnetic InductionDocument117 pages8.3 Electromagnetic InductionPAKK20622 CHARLENE LIONG YAN TINGNo ratings yet
- Basic Electricity Is Described in Many Ways. When AnDocument6 pagesBasic Electricity Is Described in Many Ways. When AnJasonKoylassNo ratings yet
- Magnetic Effect of Electric CurrentDocument30 pagesMagnetic Effect of Electric CurrentEllen AbrigoNo ratings yet
- Electromagnetic InductionDocument21 pagesElectromagnetic InductionEs ENo ratings yet
- Magnetic Induction and Faradays Law in General Physics 2Document43 pagesMagnetic Induction and Faradays Law in General Physics 2Heidi QuiranteNo ratings yet
- Physics NotesDocument85 pagesPhysics NotesJfoxx Samuel0% (1)
- Electromagnetic Induction: Experiment 1Document13 pagesElectromagnetic Induction: Experiment 1midhunesh41No ratings yet
- Electrical Machines Labs (No. 1 and 2)Document3 pagesElectrical Machines Labs (No. 1 and 2)Fazal AkbarNo ratings yet
- Group 3 PresentsDocument18 pagesGroup 3 PresentsShannie Longakit RacomaNo ratings yet
- Submitted By:-Name: - Mandeep Dhiman ROLL NO.: - 24 SECTION: - B4802 Course: - B.Tech (Me) - MbaDocument7 pagesSubmitted By:-Name: - Mandeep Dhiman ROLL NO.: - 24 SECTION: - B4802 Course: - B.Tech (Me) - Mbashailesh singhNo ratings yet
- Electromagnetic InductionDocument21 pagesElectromagnetic InductionParth GuptaNo ratings yet
- Basic Current TermsDocument12 pagesBasic Current TermsGhulam AbbasNo ratings yet
- Lenz's Law NotesDocument3 pagesLenz's Law Notesʀᴀᴍᴇʟᴀ ᴍᴀʜɪʟᴜᴍNo ratings yet
- Chapter 3: Electromagnetism: Magnetic Field PatternDocument29 pagesChapter 3: Electromagnetism: Magnetic Field PatternNur ArafahNo ratings yet
- Electromagnetic Induction LecturesDocument9 pagesElectromagnetic Induction LecturesDoyen DanielNo ratings yet
- Electromagnetic InductionDocument25 pagesElectromagnetic Inductionnivasan aNo ratings yet
- Magnetic Effect of A CurrentDocument6 pagesMagnetic Effect of A CurrentFaiq IrfanNo ratings yet
- LH111 - 30th Dec - ELL101 Magnetic CouplingDocument23 pagesLH111 - 30th Dec - ELL101 Magnetic CouplingDivyansh SinghNo ratings yet
- UntitledDocument23 pagesUntitledArnab DasNo ratings yet
- Case Study 5 EmiDocument12 pagesCase Study 5 EmiSANJAY RNo ratings yet
- 2 Basic ElectricityDocument5 pages2 Basic Electricityfaheem ahmedNo ratings yet
- Electromagnetic InductonDocument12 pagesElectromagnetic InductonAishwarya TripathiNo ratings yet
- CH 13Document12 pagesCH 13charanNo ratings yet
- Experiment No: 9 (A) : AIM OF THE EXPERIMENT: Demonstration of Faraday's Law ObjectivesDocument8 pagesExperiment No: 9 (A) : AIM OF THE EXPERIMENT: Demonstration of Faraday's Law ObjectivesAbhishek RajNo ratings yet
- Electrostatics - Stationary ChargesDocument39 pagesElectrostatics - Stationary ChargesmkanwarsNo ratings yet
- Electromagnetic Induction: What We Have Already LearntDocument14 pagesElectromagnetic Induction: What We Have Already LearntAnonymous pZp8uyNo ratings yet
- Electromagnetic Induction ExplainedDocument3 pagesElectromagnetic Induction ExplainedAli HamzaNo ratings yet
- Elect Roma Gneti SM: How Electric Current Produce A Magnetic FieldDocument8 pagesElect Roma Gneti SM: How Electric Current Produce A Magnetic FieldIsmail MzavaNo ratings yet
- Electromagnetic Induction (Physics) : Magnetic Flux & Faraday&apos S Law of InductionDocument15 pagesElectromagnetic Induction (Physics) : Magnetic Flux & Faraday&apos S Law of InductionistudyNo ratings yet
- 3.3 Analysing Electromagnetic InductionDocument11 pages3.3 Analysing Electromagnetic Inductionpanitiafiziksmkb100% (2)
- Faraday's Electeomagnetic Induction.Document5 pagesFaraday's Electeomagnetic Induction.Rajesh JagadeesanNo ratings yet
- Electromagnetic InductionDocument12 pagesElectromagnetic InductionPrasad MehtaNo ratings yet
- Electrical Energy GenerationDocument27 pagesElectrical Energy GenerationAlfred WunumNo ratings yet
- Relay OperationDocument26 pagesRelay Operationapi-3842326No ratings yet
- Notes Magnetic Effects of Electric CurrentDocument8 pagesNotes Magnetic Effects of Electric CurrentDr. Priyanka VashishtNo ratings yet
- Year 12 E-Note PhyDocument77 pagesYear 12 E-Note Phyjeffersonawesome28No ratings yet
- O Level EMIDocument44 pagesO Level EMIIdkNo ratings yet
- Chapter-6-Electromagnetic InductionDocument9 pagesChapter-6-Electromagnetic Inductioncharitham112No ratings yet
- Electromagnetism CSEC NotesDocument10 pagesElectromagnetism CSEC NotesCornflakes Toasted100% (1)
- Magnetic Effects of Electric Current 2018Document5 pagesMagnetic Effects of Electric Current 2018Rohit NairNo ratings yet
- Electrical & Electronic Laws & Circuits PDFDocument61 pagesElectrical & Electronic Laws & Circuits PDFclubtown paradiseNo ratings yet
- ElectromagnetismDocument10 pagesElectromagnetismrameshchinnala123No ratings yet
- Electromagnetic InductionDocument11 pagesElectromagnetic InductionblueegofxNo ratings yet
- CH 13 Magnetic Effects of Electric Current NotesDocument12 pagesCH 13 Magnetic Effects of Electric Current NotesAkshithNo ratings yet
- Electromagnetic InductionDocument4 pagesElectromagnetic InductionMonica SreeNo ratings yet
- Macalalag Lab 2Document18 pagesMacalalag Lab 2Jaloyd MacalalagNo ratings yet
- MagnetismDocument10 pagesMagnetismIvan TzNo ratings yet
- Electro 3 Finals Task PerformanceDocument23 pagesElectro 3 Finals Task PerformanceJuan Miguel TorresNo ratings yet
- Flux, Field System, Flux Level and Induced Emf of An Electrical MachineDocument18 pagesFlux, Field System, Flux Level and Induced Emf of An Electrical MachineIrish SantosNo ratings yet
- Electromgnetic InductionDocument5 pagesElectromgnetic InductionGhanshyam SinghNo ratings yet
- D.C Motor and Faradays LawDocument21 pagesD.C Motor and Faradays LawMR. KDNo ratings yet
- Phy Topic 2 F4Document12 pagesPhy Topic 2 F4Kandrossy GlassNo ratings yet
- Chapter 34: Magnetic Fields: 16 January 2022 15:58Document49 pagesChapter 34: Magnetic Fields: 16 January 2022 15:58Aazif JafriNo ratings yet
- 3.1 - Analysing The Magnetic Effect of A Current-Carrying ConductorDocument28 pages3.1 - Analysing The Magnetic Effect of A Current-Carrying ConductorsfwongNo ratings yet
- Electromagnetic InductionDocument5 pagesElectromagnetic InductionLakshmi MenonNo ratings yet
- Construction and Working Principles of Measuring InstrumentsDocument20 pagesConstruction and Working Principles of Measuring Instrumentsmarcelee wheatleNo ratings yet