Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Tissues CLASS 9 CBSE
Uploaded by
Advait Abraham AbhilashOriginal Description:
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Tissues CLASS 9 CBSE
Uploaded by
Advait Abraham AbhilashCopyright:
Available Formats
Class IX Chapter 6 – Tissues Science
Question 1:
What is a tissue?
Answer:
Tissue is a group of cells that are similar in structure and are organised together to
perform a specific task.
Question 2:
What is the utility of tissues in multi-cellular organisms?
Answer:
In unicellular organisms, a single cell performs all the basic functions such as
respiration, movement, excretion, digestion, etc. But in multicellular organisms, cells
are grouped to form tissues. These tissues are specialised to carry out a particular
function at a definite place in the body. For example, the muscle cells form muscular
tissues which helps in movement, nerve cells form the nervous tissue which helps in
transmission of messages. This is known as division of labour in multicellular
organisms. It is because of this division of labour that multicellular organisms are
able to perform all functions efficiently.
Page 1 of 11
Website: www.vidhyarjan.com Email: contact@vidhyarjan.com Mobile: 9999 249717
Head Office: 1/3-H-A-2, Street # 6, East Azad Nagar, Delhi-110051
(One Km from ‘Welcome Metro Station)
Class IX Chapter 6 – Tissues Science
Question 1:
Name types of simple tissues.
Answer:
Simple permanent tissues are of three types: Parenchyma, Collenchyma, and
Sclerenchyma. Parenchyma tissue is of further two types − aerenchyma and
chlorenchyma.
Question 2:
Where is apical meristem found?
Answer:
Apical meristem is present at the growing tips of stems and roots. Their main
function is to initiate growth in new cells of seedlings, at the tip of roots, and shoots.
Question 3:
Which tissue makes up the husk of coconut?
Answer:
The husk of a coconut is made up of sclerenchyma tissue.
Question 4:
What are the constituents of phloem?
Answer:
Phloem is the food conducting tissue in plants. It is made up of four components:
(i) Sieve tubes
(ii) Companion cells
(iii) Phloem parenchyma
(iv) Phloem fibres
Page 2 of 11
Website: www.vidhyarjan.com Email: contact@vidhyarjan.com Mobile: 9999 249717
Head Office: 1/3-H-A-2, Street # 6, East Azad Nagar, Delhi-110051
(One Km from ‘Welcome Metro Station)
Class IX Chapter 6 – Tissues Science
Question 1:
Name the tissue responsible for movement in our body.
Answer:
Themuscular tissue is responsible for movement in our body.
Question 2:
What does a neuron look like?
Answer:
A neuron consists of a cell body witha nucleus and cytoplasm. It has two important
extensions known as the axon and dendrites. An axon is a long thread-like extension
of nerve cells that transmits impulses away from the cell body. Dendrites, on the
other hand, are thread-like extensions of cell body that receive nerve impulses.
Thus, the axon transmits impulses away from the cell body, whereas the dendrite
receives nerve impulses. This coordinated function helps in transmitting impulses
very quickly.
Nerve cell
Question 3:
Give three features of cardiac muscles.
Answer:
Three features of cardiac muscles are:
(i) Cardiac muscles are involuntary muscles that contract rapidly, but do not get
fatigued.
(ii) The cells of cardiac muscles are cylindrical, branched, and uninucleate.
Page 3 of 11
Website: www.vidhyarjan.com Email: contact@vidhyarjan.com Mobile: 9999 249717
Head Office: 1/3-H-A-2, Street # 6, East Azad Nagar, Delhi-110051
(One Km from ‘Welcome Metro Station)
Class IX Chapter 6 – Tissues Science
(iii) They control the contraction and relaxation of the heart.
Question 4:
What are the functions of areolar tissue?
Answer:
Functions of areolar tissue:
(i) It helps in supporting internal organs.
(ii) It helps in repairing the tissues of the skin and muscles.
Page 4 of 11
Website: www.vidhyarjan.com Email: contact@vidhyarjan.com Mobile: 9999 249717
Head Office: 1/3-H-A-2, Street # 6, East Azad Nagar, Delhi-110051
(One Km from ‘Welcome Metro Station)
Class IX Chapter 6 – Tissues Science
Question 1:
Define the term “tissue”.
Answer:
Tissue is a group of cells that are similar in structure and are organized together to
perform a specific task.
Question 2:
How many types of elements together make up the xylem tissue? Name them.
Answer:
There are four different types of cells that make up the xylem tissue. They are:
(i) Tracheids
(ii) Vessels
(iii) Xylem parenchyma
(iv) Xylem fibres
Question 3:
How are simple tissues different from complex tissues in plants?
Answer:
Simple tissue Complex tissue
These tissues consist of only one These tissues are made up of more than one
type of cells. type of cells.
The cells are more or less similar Different types of cells perform different
in structure and perform similar functions. For example, in the xylem tissue,
functions. tracheids help in water transport, whereas
parenchyma stores food.
Three types of simple tissues in Two types of complex permanent tissues in
plants are parenchyma, plants are xylem and phloem.
collenchyma, and sclerenchyma.
Question 4:
Page 5 of 11
Website: www.vidhyarjan.com Email: contact@vidhyarjan.com Mobile: 9999 249717
Head Office: 1/3-H-A-2, Street # 6, East Azad Nagar, Delhi-110051
(One Km from ‘Welcome Metro Station)
Class IX Chapter 6 – Tissues Science
Differentiate between parenchyma, collenchyma and sclerenchyma, on the basis of
their cell wall.
Answer:
Parenchyma Collenchyma Sclerenchyma
Cell walls are relatively The cell wall is irregularly The cell walls are
thin, and the cells in thickened at the corners, uniformly thickened, and
parenchyma tissues are and there is very little space there are no intercellular
loosely packed. between the cells. spaces.
The cell wall in this tissue Pectin and hemicellulose are An additional layer of the
is made up of cellulose. the major constituents of cell wall composed mainly
the cell wall. of lignin is found.
Question 5:
What are the functions of the stomata?
Answer:
Functions of the stomata:
(i) They allow the exchange of gases (CO2 and O2) with the atmosphere.
(ii) Evaporation of water from the leaf surface occurs through the stomata. Thus, the
stomata help in the process of transpiration.
Page 6 of 11
Website: www.vidhyarjan.com Email: contact@vidhyarjan.com Mobile: 9999 249717
Head Office: 1/3-H-A-2, Street # 6, East Azad Nagar, Delhi-110051
(One Km from ‘Welcome Metro Station)
Class IX Chapter 6 – Tissues Science
Question 6:
Diagrammatically show the difference between the three types of muscle fibres.
Answer:
The three types of muscle fibres are:Striated muscles, smooth muscles (unstriated
muscle fibre), and cardiac muscles.
Striated muscle fibres
Unstriated muscle fibres
Page 7 of 11
Website: www.vidhyarjan.com Email: contact@vidhyarjan.com Mobile: 9999 249717
Head Office: 1/3-H-A-2, Street # 6, East Azad Nagar, Delhi-110051
(One Km from ‘Welcome Metro Station)
Class IX Chapter 6 – Tissues Science
Cardiac muscle fibres
Question 7:
What is the specific function of the cardiac muscle?
Answer:
The specific function of the cardiac muscle is to control the contraction and relaxation
of the heart.
Question 8:
Differentiate between striated, unstriated and cardiac muscles on the basis of their
structure and site/location in the body.
Answer:
Striated muscle Unstriated muscle Cardiac muscle
On the basis of structure:
Cells are cylindrical Cells are long Cells are cylindrical
Cells are not branched Cells are not branched Cells are branched
Cells are multinucleate Cells are uninucleate Cells are uninucleate
Page 8 of 11
Website: www.vidhyarjan.com Email: contact@vidhyarjan.com Mobile: 9999 249717
Head Office: 1/3-H-A-2, Street # 6, East Azad Nagar, Delhi-110051
(One Km from ‘Welcome Metro Station)
Class IX Chapter 6 – Tissues Science
Alternate light and dark There are no bands present Faint bands are
bands are present present
Its ends are blunt Its ends are tapering Its ends are flat and
wavy
On the basis of location:
These muscles are These muscles control the These muscles
present in body parts movement of food in the control the
such as hands, legs, alimentary canal, the contraction contraction and
tongue, etc. and relaxation of blood vessels, relaxation of the
etc. heart
Question 9:
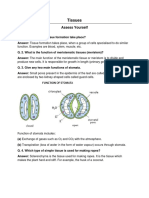
Draw a labelled diagram of a neuron.
Answer:
Structure of a neuron
Question 10:
Name the following:
(a) Tissue that forms the inner lining of our mouth.
Page 9 of 11
Website: www.vidhyarjan.com Email: contact@vidhyarjan.com Mobile: 9999 249717
Head Office: 1/3-H-A-2, Street # 6, East Azad Nagar, Delhi-110051
(One Km from ‘Welcome Metro Station)
Class IX Chapter 6 – Tissues Science
(b) Tissue that connects muscle to bone in humans.
(c) Tissue that transports food in plants.
(d) Tissue that stores fat in our body.
(e) Connective tissue with a fluid matrix.
(f) Tissue present in the brain.
Answer:
(a) Tissue that forms the inner lining of our mouth → Epithelial tissue
(b) Tissue that connects muscle to bone in humans → Dense regular connective
tissue (tendons)
(c) Tissue that transports food in plants → Phloem
(d) Tissue that stores fat in our body → Adipose tissue
(e) Connective tissue with a fluid matrix → Blood
(f) Tissue present in the brain → Nervous tissue
Question 11:
Identify the type of tissue in the following: skin, bark of tree, bone, lining of kidney
tubule, vascular bundle.
Answer:
Skin: Stratified squamous epithelial tissue
Bark of tree: Simple permanent tissue
Bone: Connective tissue
Lining of kidney tubule: Cuboidal epithelial tissue
Vascular bundle: Complex permanent tissue
Question 12:
Name the regions in which parenchyma tissue is present.
Answer:
Leaves, fruits, and flowers are the regions where the parenchyma tissue is present.
Question 13:
What is the role of epidermis in plants?
Page 10 of 11
Website: www.vidhyarjan.com Email: contact@vidhyarjan.com Mobile: 9999 249717
Head Office: 1/3-H-A-2, Street # 6, East Azad Nagar, Delhi-110051
(One Km from ‘Welcome Metro Station)
Class IX Chapter 6 – Tissues Science
Answer:
Epidermisis present on the outer surface of the entire plant body. The cells of the
epidermal tissue form a continuous layer without any intercellular space. It performs
the following important functions:
(i) It is a protective tissue of the plant body
(ii) It protects the plant against mechanical injury
(iii) It allows exchange of gases through the stomata
Question 14:
How does the cork act as a protective tissue?
Answer:
The outer protective layer or bark of a tree is known as the cork. It is made up of
dead cells. Therefore, it protects the plant against mechanical injury, temperature
extremes, etc. It also prevents the loss of water by evaporation.
Question 15:
Complete the table:
Answer:
Page 11 of 11
Website: www.vidhyarjan.com Email: contact@vidhyarjan.com Mobile: 9999 249717
Head Office: 1/3-H-A-2, Street # 6, East Azad Nagar, Delhi-110051
(One Km from ‘Welcome Metro Station)
You might also like
- PD 4 WJ SBJ UE7 XAASH4 U KZDocument11 pagesPD 4 WJ SBJ UE7 XAASH4 U KZPrincy GuptaNo ratings yet
- Chapter 6 BiologyDocument8 pagesChapter 6 BiologyMohammed mahfuzNo ratings yet
- ST - John'S School, Greater Noida West Class IX ScienceDocument4 pagesST - John'S School, Greater Noida West Class IX ScienceIndia Tech with AstitvaNo ratings yet
- Tissues Notes Class IxDocument7 pagesTissues Notes Class Ixishaan singhNo ratings yet
- Class 9 Science CH 6Document7 pagesClass 9 Science CH 6Priyanka PanwarNo ratings yet
- Aakash Institute: NCERT Solutions For Class 9 Science Chapter 6 TissuesDocument13 pagesAakash Institute: NCERT Solutions For Class 9 Science Chapter 6 TissuesNischay MahamanaNo ratings yet
- NCERT Solutions For Class 9 Science Chapter 6 - Tissues - .Document9 pagesNCERT Solutions For Class 9 Science Chapter 6 - Tissues - .AshchatNo ratings yet
- Chapter 7th TissueDocument6 pagesChapter 7th Tissuenakulvyan708No ratings yet
- Class 9TH Biology TissueDocument4 pagesClass 9TH Biology TissueChirag KashyapNo ratings yet
- Esson: Structure and Functions of Animal Tissues and Cell ModificationDocument12 pagesEsson: Structure and Functions of Animal Tissues and Cell ModificationKen Christian As a StudentNo ratings yet
- Tissue Q&ADocument6 pagesTissue Q&ASuman DasNo ratings yet
- Tissues - NotesDocument14 pagesTissues - Notesphysicsbooks.storeNo ratings yet
- Sample Paper of TissuesDocument9 pagesSample Paper of TissuesPritamprakash JhaNo ratings yet
- TissuesDocument7 pagesTissuesRohitNo ratings yet
- Animal TissuesDocument14 pagesAnimal Tissuesjitendragandhi250No ratings yet
- Important Questions For CBSE Class 9 Science Chapter 6Document16 pagesImportant Questions For CBSE Class 9 Science Chapter 6VI A 19 Aaryan JadhavNo ratings yet
- Exercise-6.1: NCERT Solution For Class 9 Science - Chapter 6 TissuesDocument9 pagesExercise-6.1: NCERT Solution For Class 9 Science - Chapter 6 TissuesShah RukhNo ratings yet
- Tissues Class 9 Extra Questions Very Short Answer TypeDocument31 pagesTissues Class 9 Extra Questions Very Short Answer TypeAyushi VermaNo ratings yet
- 9th Bio MTG Tissue QuesDocument13 pages9th Bio MTG Tissue QuesData ShareNo ratings yet
- CellDocument3 pagesCellpunitkumarNo ratings yet
- Chapter 6: "Tissues"Document5 pagesChapter 6: "Tissues"Anil TripathiNo ratings yet
- 9 Science Imp ch6 3Document8 pages9 Science Imp ch6 3deepakNo ratings yet
- TissuesDocument23 pagesTissuesAadarsh RameshNo ratings yet
- JihijiojhiDocument5 pagesJihijiojhiGaurav Kumar GoyalNo ratings yet
- TissuesDocument5 pagesTissuesDarshilNo ratings yet
- 09 Science Notes ch06 Tissues-UnlockedDocument5 pages09 Science Notes ch06 Tissues-UnlockedShekhar UpadhyayNo ratings yet
- Class 9 - CH6 TissuesDocument9 pagesClass 9 - CH6 Tissuesv.nikolikjNo ratings yet
- Chapter Science-9 CombinedDocument20 pagesChapter Science-9 CombinedAnushkaNo ratings yet
- Selina Concise Biology Class 7 ICSE Solutions For Chapter 1 - Plant and Animal TissuesDocument10 pagesSelina Concise Biology Class 7 ICSE Solutions For Chapter 1 - Plant and Animal Tissuesvedanthendre5No ratings yet
- Tissue ClassworkDocument5 pagesTissue ClassworkRajesh Kanna A亗No ratings yet
- TissuesDocument11 pagesTissuesManveethNo ratings yet
- PS Verma Biology Class 9 Chapter 3 Tissues CBSEDocument2 pagesPS Verma Biology Class 9 Chapter 3 Tissues CBSEhemac717No ratings yet
- Chapter 6 TissuesDocument7 pagesChapter 6 Tissuesh8631259No ratings yet
- Tissues Class 9Document13 pagesTissues Class 9Richa Nawani KaushikNo ratings yet
- Work Sheet 4 Classification of Tissues A28 Group1Document6 pagesWork Sheet 4 Classification of Tissues A28 Group1Japet Floyd Alipio100% (1)
- Tissues Class 9Document5 pagesTissues Class 9Arnav PatangeNo ratings yet
- Tissues: Assess YourselfDocument16 pagesTissues: Assess YourselfGamer JiNo ratings yet
- Tissue Solutions Textual Questions and Answers: Is Called A TissueDocument11 pagesTissue Solutions Textual Questions and Answers: Is Called A TissueMr Pan GamingNo ratings yet
- Tissues: PS Verma and V.K. Agarwal Biology Class 9 Page No - 165Document14 pagesTissues: PS Verma and V.K. Agarwal Biology Class 9 Page No - 165Thikshika . NNo ratings yet
- PDF 20221214 190246 0000Document11 pagesPDF 20221214 190246 0000Hiba ZiziNo ratings yet
- Ix Plant Tissues 1Document7 pagesIx Plant Tissues 1ayushiguptab0406No ratings yet
- Lakhmir Singh Solutions Class 9 Biology Chapter 3Document7 pagesLakhmir Singh Solutions Class 9 Biology Chapter 3DarshilNo ratings yet
- 9th Bio Important QuesDocument12 pages9th Bio Important QuesData ShareNo ratings yet
- Tissue Mat PDFDocument13 pagesTissue Mat PDFAyushman TripathyNo ratings yet
- Sample Paper BiologyDocument3 pagesSample Paper BiologyMini PGNo ratings yet
- Science Chapter-6-TissueDocument11 pagesScience Chapter-6-TissueJEETNo ratings yet
- Module 3Document7 pagesModule 3fiids.castroNo ratings yet
- CHAPTER-TISSUES (Class-9) Self Instructional Material S. P Model Higher Secondary School, M.A Road, Srinagar (Teacher: Burhana Rashid)Document4 pagesCHAPTER-TISSUES (Class-9) Self Instructional Material S. P Model Higher Secondary School, M.A Road, Srinagar (Teacher: Burhana Rashid)MuzafarNo ratings yet
- Tissues: 1. Ncert Intext QuestionsDocument10 pagesTissues: 1. Ncert Intext QuestionsKumar AbhishantNo ratings yet
- What Is A Tissue? Ans:: Class: 9 (Science) Tissues Chapter - 2Document21 pagesWhat Is A Tissue? Ans:: Class: 9 (Science) Tissues Chapter - 2The Silent RepentantNo ratings yet
- Ncert Notes Class 9 Science Chapter6Document5 pagesNcert Notes Class 9 Science Chapter6Mohammed AadilNo ratings yet
- Cell Types 1Document28 pagesCell Types 1IngridNo ratings yet
- Tissues NotesDocument6 pagesTissues NotesYashvi PatelNo ratings yet
- CLASS - 10th Chapter - 7 (Control and Coordination) : A Synapse or Neuromuscular JunctionDocument10 pagesCLASS - 10th Chapter - 7 (Control and Coordination) : A Synapse or Neuromuscular JunctionAnupama BharadwajNo ratings yet
- Class 9 Science CH 6 NotesDocument13 pagesClass 9 Science CH 6 NotesChetan GargNo ratings yet
- 2021 Chapter 6 Tissue Most IMP QuestionsDocument11 pages2021 Chapter 6 Tissue Most IMP QuestionsGauravNo ratings yet
- Tissues NotesDocument7 pagesTissues NotesHarshitNo ratings yet
- Selina Solutions For Class 9 Biology Chapter 3 Tissues Plant and Animal TissuesDocument12 pagesSelina Solutions For Class 9 Biology Chapter 3 Tissues Plant and Animal TissuesleenaapNo ratings yet
- Tissue 11Document5 pagesTissue 11Adnan Al-asbahiNo ratings yet
- Biology Paper 3 2019Document9 pagesBiology Paper 3 2019Tefelo QhobelaNo ratings yet
- A LEVEL Crop Science Mcqs 6049-1Document90 pagesA LEVEL Crop Science Mcqs 6049-1tapiwa nzvatu100% (3)
- BOT 121 TranspirationDocument7 pagesBOT 121 TranspirationSakshi SargarNo ratings yet
- IRRI WeedsDocument60 pagesIRRI WeedsSuperPisbol ManNo ratings yet
- Bibliografie PDFDocument9 pagesBibliografie PDFLivia AmarieiNo ratings yet
- Phylum Symmetr y Diplo/triplo ? Body Cavity In/complet e Gut? Proto or Deutero? Skeleton/mvm T Nervou S System Habita T Unique Feature?Document3 pagesPhylum Symmetr y Diplo/triplo ? Body Cavity In/complet e Gut? Proto or Deutero? Skeleton/mvm T Nervou S System Habita T Unique Feature?MichaelNo ratings yet
- 2ND Chap QuizDocument33 pages2ND Chap QuizVidyut kumarNo ratings yet
- Grade 8 Integrated Science Week 2 Lesson 1 Worksheet 2 and Answer SheetDocument4 pagesGrade 8 Integrated Science Week 2 Lesson 1 Worksheet 2 and Answer SheetBalram HaroldNo ratings yet
- 5 Biology Plant KingdomDocument4 pages5 Biology Plant KingdomHasan shaikhNo ratings yet
- Kappelle1992. Fitogeografía Costa RicaDocument18 pagesKappelle1992. Fitogeografía Costa Ricaandreita79No ratings yet
- Quiz 2Document2 pagesQuiz 2Bea Mae SangalangNo ratings yet
- Plants That Look Like WheatDocument6 pagesPlants That Look Like Wheatchristianachidimma3002No ratings yet
- The Fungi of Medical ImportanceDocument74 pagesThe Fungi of Medical ImportancenrahmaNo ratings yet
- 2023-04-11 - ALFKYSMITH - KE Garden Towers-Rev1Document12 pages2023-04-11 - ALFKYSMITH - KE Garden Towers-Rev1jonard dancalanNo ratings yet
- Diseases of Leather Leaf Fern Caused by Calonectria and Cylindrocladium SpeciesDocument7 pagesDiseases of Leather Leaf Fern Caused by Calonectria and Cylindrocladium SpeciesRicardo CachupeNo ratings yet
- Ncert Solutions For Class 11 Chemistry Chapter 1 The Living World - RemovedDocument7 pagesNcert Solutions For Class 11 Chemistry Chapter 1 The Living World - Removedraju bhaiNo ratings yet
- Naskah Seminar Ratna Pujianjani KartikasariDocument9 pagesNaskah Seminar Ratna Pujianjani KartikasarisuksmaSPNo ratings yet
- 091 51 Final Biologi t5 Dlp-6-26Document21 pages091 51 Final Biologi t5 Dlp-6-26risya mariaNo ratings yet
- AnimalsDocument4 pagesAnimalsKirstian MartinezNo ratings yet
- Biodiversity at Global, National and Local LevelsDocument10 pagesBiodiversity at Global, National and Local LevelsVansh R.100% (1)
- Jung Thomas, Manual Phytophthora MethodsDocument49 pagesJung Thomas, Manual Phytophthora MethodsCriss Guzmán100% (1)
- The Pitahaya's Arrival - Article by Edgar ValdiviaDocument5 pagesThe Pitahaya's Arrival - Article by Edgar ValdiviakxlexkNo ratings yet
- 8 Tips For Growing Better LiliesDocument6 pages8 Tips For Growing Better Liliespoint clickNo ratings yet
- Science: Quarter 2 - Module 3: Modes of Reproduction in AnimalsDocument68 pagesScience: Quarter 2 - Module 3: Modes of Reproduction in AnimalsChester Allan EduriaNo ratings yet
- 206-2000 SeedDocument14 pages206-2000 SeedyechaleNo ratings yet
- Science Q2 WK3Document62 pagesScience Q2 WK3Jolina NacpilNo ratings yet
- Flower Reproductive SystemDocument4 pagesFlower Reproductive SystemkhongbietgicaNo ratings yet
- Raw Material ConsumptionhjnnDocument2 pagesRaw Material ConsumptionhjnndvbnjfdNo ratings yet
- Glencoe Life Science2Document93 pagesGlencoe Life Science2Cosmina MariaNo ratings yet
- Bacterial Canker of Tomato: A Commercial Growers GuideDocument6 pagesBacterial Canker of Tomato: A Commercial Growers GuideBook menNo ratings yet