Professional Documents
Culture Documents
9 Science Imp ch6 3
Uploaded by
deepakOriginal Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
9 Science Imp ch6 3
Uploaded by
deepakCopyright:
Available Formats
CBSE
Class 9 Science
Important Questions
Chapter 6
Tissues
3 Marks Questions
1. What is the utility of tissues in multi-cellular organisms?
Ans. There is a clear cut division of labour in multicellular organisms i.e. different parts of
the body of a multicellular organism perform specific functions. For example, brain controls
all other parts of body, heart pumps blood to all parts of body, kidneys remove waste
materials from body, sense organs collect information from external sources for sensory
perception etc. All these functions would never be possible without formation of tissues in
multicellular organisms.
2. Give three features of cardiac muscles.
Ans. i. Cardiac muscles are involuntary i.e. they don’t work under our will.
ii. Its cells are cylindrical, branched, striated and uninucleate.
iii. It shows rhythmic contraction and relaxation throughout the person’s life.
3. What are the functions of areolar tissue?
Ans. Areolar tissue is a kind of filler tissue found between skin and muscles, around our
blood vessels and nerve cells and also in the bone marrow. Its functions are therefore
i) To fill the space inside organs.
ii) To help in repair and maintenance of nearby tissues/organs.
iii) To support and prevent injuries to internal organs.
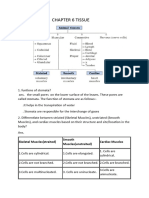
4. Diagrammatically show the difference between the three types of muscle fibres.
Ans.
Material downloaded from myCBSEguide.com. 1 / 8
5. Differentiate between striated, untreated and cardiac muscles on the basis of their
structure and site/location in the body.
Ans.
Striated muscle Untreated muscle Cardiac muscle
They show light and dark They don’t show any
They show striations on
bands (striations) when we striations on staining.
staining.
stain them. Their cells are long but
Their cells re cylindrical and
Their cells are elongated and spindle shaped and
branched.
cylindrical also unbranched. unbranched.
Cells are uninucleate.
Cells are multinucleate. Cells are uninucleate.
They are again involuntary
They are responsible to bring They are involuntary in
in their function
about voluntary movements action (walls of tubular
(contraction and relaxation
(like tongue, limbs etc) organs, blood vessels etc)
of heart)
6. Draw a labelled diagram of a neuron?
Ans.
Material downloaded from myCBSEguide.com. 2 / 8
7. Complete the table:
Ans.
8. How many types of tissues are found in animals? Name the different types.
Ans. In animal four types of tissues are found –
Material downloaded from myCBSEguide.com. 3 / 8
(a) Epithelium or Epithelial tissue (covering tissue) – It forms outer protective covering all
over the body.
(b) Connective tissue – (supporting tissue) – It binds cells of other tissues in the body and give
them rigidity and support.
(c) Muscular tissue (contractile tissue) –It helps is movement of the body by contraction and
relaxation.
(d) Nervous tissue – It receiver stimulates and transmit messages
9. Differentiate between voluntary and involuntary muscles. Give one example of each
Ans.
10. What are the major functions of blood?
Ans. Functions of blood are –
(a) Transport food materials
(b) Transports oxygen and carbon – dioxide
(c) Transports excretory products to the kidneys, from where they are eliminated
(d) Regulates temperature by distributing heat within the body
(e) WBC’S protect due body from disease and helps in wound healing
(f) Platelets help in blood clotting
11. Write about the functions of –
(a) Epidermis
(b) cork
(c) stomata.
Material downloaded from myCBSEguide.com. 4 / 8
Ans. Epidermis – its main function is protection. It forms waterproof coating, which reduces
loss of water.
Stomata – These are the small opening which helps in exchange of gases
Cork – It is protective in function. It prevents desiccation, by preventing loss of water from
the plant body. It prevents infection and mechanical injury
12. Differentiate between parenchyma and collenchyma.
Ans.
13. Mention the characteristics features of connective tissue
Ans. Characteristics of connective tissue.
a) The cells are living and are embedded in a non – living intercellular matrix
b) It is composed of cells and numerous, thick structures called fibres.
c) It binds the cells of other tissue in due body.
d) It gives rigidity and support.
14. Diagrammatically show the difference between the three types of muscels fibres
Ans.
Material downloaded from myCBSEguide.com. 5 / 8
15. How does cardiac muscle differ from both voluntary and involuntary muscles in
both structure and function?
Ans. 1) Cardiac Muscles are involuntary
2) They are composed of branching network of fibres.
3) The fibres have centrally located one or two nuclei
4) Intercalated discs are present at intervals in the fibres.
5) They function throughout the life
16. Write differences between blood and lymph.
Ans.
17. Give reasons for –
(a) intercellular spaces are absent in scleranchymatons tissues.
(b) Meristematic cells have a prominent muscles and dense cytoplaom but they lack
muscles
(c) We get crunchy and granular feeling, when we chew pear fruit.
Ans. a) Sclerenchyma has thick lignified walls. Hence, intercellular spaces are absent.
b) Meristematic cells have continuously dividing cells. Cells of meristem are not
differentiated. It continuously divides and form new cells which increase length and girth of
the plant body.
c) due to presence of stone cells or grit cells, known as sclereids
18. Why is epidermis important for the plants?
Ans. Outer protective covering of plants is called epidermis.
Material downloaded from myCBSEguide.com. 6 / 8
a) It is covered with a waterproof coating or layer called cuticle which reduces loss of water.
b) It also consist of small pores called stomata which helps in the exchange of gases
19. Describe different types of meristems.
Ans. Based on their location in the plant body, meristems are of three types.
a) Apical meristems – Occurs at the tips of roots and shoots and brings about an increase in
length of the plant
b) Lateral meristems – It occurs on the sides almost parallel to the long axis of the root, stem
and its branches. Brings about an increase in the width or girth of the organs.
c) Intercalary meristems – It occurs at the base of the internodes in monocots. It brings about
increase in the length of the internode.
20. If you are provided with three slides, each containing one types muscles fibres, how
will you identify them.
Ans. a) Striated muscles or voluntary muscles show light and dark bands under microscope
b) unstriated muscles or involuntary muscles show no light or dark bands, multinucleate.
c) Cardiac muscles fibres show light light and dark bands, fibres are interconnected with one
or two nuclei
21. If a potted plant is covered with a glass jar, water vapours appear on the wall of
glass jar. Explain why?
Ans. Plant always loose water from the surface of leaves. This process is known as
transpiration. Water reaches leaves by xylem vessels, where evaporation takes place by
stomata.
22. Identify the following tissue and mention their function.
Ans. a) Parenchyma – Food storage, they have ability to divide hence, play a role in wound
Material downloaded from myCBSEguide.com. 7 / 8
healing, regeneration and grafting
b) Collenchyma – It provides mechanical strength and elasticity
c) Sclerenchyma – It is mechanical & protective tissue.
23. Differentiate between meristmatic and permanent tissue.
Ans.
Material downloaded from myCBSEguide.com. 8 / 8
You might also like
- Aakash Institute: NCERT Solutions For Class 9 Science Chapter 6 TissuesDocument13 pagesAakash Institute: NCERT Solutions For Class 9 Science Chapter 6 TissuesNischay MahamanaNo ratings yet
- ST - John'S School, Greater Noida West Class IX ScienceDocument4 pagesST - John'S School, Greater Noida West Class IX ScienceIndia Tech with AstitvaNo ratings yet
- Tissue Mat PDFDocument13 pagesTissue Mat PDFAyushman TripathyNo ratings yet
- CHAPTER-TISSUES (Class-9) Self Instructional Material S. P Model Higher Secondary School, M.A Road, Srinagar (Teacher: Burhana Rashid)Document4 pagesCHAPTER-TISSUES (Class-9) Self Instructional Material S. P Model Higher Secondary School, M.A Road, Srinagar (Teacher: Burhana Rashid)MuzafarNo ratings yet
- NCERT Solutions For Class 9 Science Chapter 6 - Tissues - .Document9 pagesNCERT Solutions For Class 9 Science Chapter 6 - Tissues - .AshchatNo ratings yet
- Tissue Notes 9Document7 pagesTissue Notes 9Priyad MundadaNo ratings yet
- Animal TissuesDocument14 pagesAnimal Tissuesjitendragandhi250No ratings yet
- Tissue Solutions Textual Questions and Answers: Is Called A TissueDocument11 pagesTissue Solutions Textual Questions and Answers: Is Called A TissueMr Pan GamingNo ratings yet
- TissueDocument6 pagesTissuers6xhffn49No ratings yet
- Chapter 6 BiologyDocument8 pagesChapter 6 BiologyMohammed mahfuzNo ratings yet
- CH.3 PLANT AND ANIMAL TISSUES Class 9 Notes IcseDocument5 pagesCH.3 PLANT AND ANIMAL TISSUES Class 9 Notes IcseFebin GeorgeNo ratings yet
- Worksheet On TissuesDocument5 pagesWorksheet On TissuesBryan AmoresNo ratings yet
- TissuesDocument11 pagesTissuesManveethNo ratings yet
- PD 4 WJ SBJ UE7 XAASH4 U KZDocument11 pagesPD 4 WJ SBJ UE7 XAASH4 U KZPrincy GuptaNo ratings yet
- Animal TissueDocument5 pagesAnimal TissueRoopaNo ratings yet
- 9 Biology - Tissues (Animal Tissues) - Notes & Video LinkDocument9 pages9 Biology - Tissues (Animal Tissues) - Notes & Video Linksaragrover095No ratings yet
- 9th Bio MTG Tissue QuesDocument13 pages9th Bio MTG Tissue QuesData ShareNo ratings yet
- MAHANDocument9 pagesMAHANKANT JAMES D. MAHANNo ratings yet
- Chapter Science-9 CombinedDocument20 pagesChapter Science-9 CombinedAnushkaNo ratings yet
- Science Chapter-6-TissueDocument11 pagesScience Chapter-6-TissueJEETNo ratings yet
- What Is A Tissue? Ans:: Class: 9 (Science) Tissues Chapter - 2Document21 pagesWhat Is A Tissue? Ans:: Class: 9 (Science) Tissues Chapter - 2The Silent RepentantNo ratings yet
- Esson: Structure and Functions of Animal Tissues and Cell ModificationDocument12 pagesEsson: Structure and Functions of Animal Tissues and Cell ModificationKen Christian As a StudentNo ratings yet
- Class 9TH Biology TissueDocument4 pagesClass 9TH Biology TissueChirag KashyapNo ratings yet
- Chapter 6: "Tissues"Document5 pagesChapter 6: "Tissues"Anil TripathiNo ratings yet
- Work Sheet 4 Classification of Tissues A28 Group1Document6 pagesWork Sheet 4 Classification of Tissues A28 Group1Japet Floyd Alipio100% (1)
- BSRKV, Sainikpuri. Biology Notes Class 9 Ls 6 Tissues Plant TissuesDocument4 pagesBSRKV, Sainikpuri. Biology Notes Class 9 Ls 6 Tissues Plant TissuesSai Uday Shankar BommakantiNo ratings yet
- Animal Tissue PPT by KanishkaDocument20 pagesAnimal Tissue PPT by KanishkaKanishka SharmaNo ratings yet
- Tissues: Assess YourselfDocument16 pagesTissues: Assess YourselfGamer JiNo ratings yet
- Tissue ClassworkDocument5 pagesTissue ClassworkRajesh Kanna A亗No ratings yet
- Ncert Notes Class 9 Science Chapter6Document5 pagesNcert Notes Class 9 Science Chapter6Mohammed AadilNo ratings yet
- TissuesDocument23 pagesTissuesAadarsh RameshNo ratings yet
- Class 9 - CH6 TissuesDocument9 pagesClass 9 - CH6 Tissuesv.nikolikjNo ratings yet
- Animal Tissues: TissueDocument4 pagesAnimal Tissues: TissuePrasad SwaminathanNo ratings yet
- Tissues Notes Class IxDocument7 pagesTissues Notes Class Ixishaan singhNo ratings yet
- Selina Concise Biology Solutions Class 7 Chapter 1 Plant and Animal TissuesDocument12 pagesSelina Concise Biology Solutions Class 7 Chapter 1 Plant and Animal TissuesAKSHAJ AGGARWALNo ratings yet
- Answers UNIT 2 Lesson 2.2 Structures of Animal CellsDocument7 pagesAnswers UNIT 2 Lesson 2.2 Structures of Animal CellsKatznjammrNo ratings yet
- M 1 PPT-PDF XI Bio CH 7 Structural Organisation in AnimalsDocument39 pagesM 1 PPT-PDF XI Bio CH 7 Structural Organisation in Animalsamarendrar87No ratings yet
- Selina Concise Biology Class 7 ICSE Solutions For Chapter 1 - Plant and Animal TissuesDocument10 pagesSelina Concise Biology Class 7 ICSE Solutions For Chapter 1 - Plant and Animal Tissuesvedanthendre5No ratings yet
- 09 Science Notes ch06 Tissues-UnlockedDocument5 pages09 Science Notes ch06 Tissues-UnlockedShekhar UpadhyayNo ratings yet
- JihijiojhiDocument5 pagesJihijiojhiGaurav Kumar GoyalNo ratings yet
- TissuesDocument5 pagesTissuesDarshilNo ratings yet
- Chapter 3 - Tissues: Plant and Animal Tissues ExerciseDocument8 pagesChapter 3 - Tissues: Plant and Animal Tissues ExerciseArpan KaurNo ratings yet
- Assignment: Tissue Recognition /30: Part A: Epithelial TissueDocument5 pagesAssignment: Tissue Recognition /30: Part A: Epithelial Tissueapi-388753692No ratings yet
- Module 3Document7 pagesModule 3fiids.castroNo ratings yet
- TissuesDocument22 pagesTissuesmustafathegreat02No ratings yet
- Animal TissuesDocument13 pagesAnimal TissuescbseiscNo ratings yet
- Exercise-6.1: NCERT Solution For Class 9 Science - Chapter 6 TissuesDocument9 pagesExercise-6.1: NCERT Solution For Class 9 Science - Chapter 6 TissuesShah RukhNo ratings yet
- 9th TissueDocument5 pages9th TissuekniFe VisualzNo ratings yet
- Pines City Colleges Medical Laboratory Science Anatomy and Physiology Laboratory ManualDocument9 pagesPines City Colleges Medical Laboratory Science Anatomy and Physiology Laboratory ManualLynch Devin Kirtug-SalengNo ratings yet
- Sample Paper of TissuesDocument9 pagesSample Paper of TissuesPritamprakash JhaNo ratings yet
- Chapter 7th TissueDocument6 pagesChapter 7th Tissuenakulvyan708No ratings yet
- ANATOMY AND PHYSIOLOGY TISSUE NOTESpdfDocument30 pagesANATOMY AND PHYSIOLOGY TISSUE NOTESpdfYego EdwinNo ratings yet
- Body Tissues: 17. The Four Major Tissue Types Are Named in Figure 3-9. For Each TissueDocument9 pagesBody Tissues: 17. The Four Major Tissue Types Are Named in Figure 3-9. For Each TissueSireRyūjinSkylerNo ratings yet
- Chapter 5 Skletal SisitemDocument23 pagesChapter 5 Skletal SisitemAnis PuadahNo ratings yet
- Cell Types and Cell Modification: LessonDocument6 pagesCell Types and Cell Modification: Lessonjoshiah glennNo ratings yet
- Prep Bio FT 2122 Ello XidDocument17 pagesPrep Bio FT 2122 Ello XidSMAXICLouis Bintang AlexisNo ratings yet
- PDF 20221214 190246 0000Document11 pagesPDF 20221214 190246 0000Hiba ZiziNo ratings yet
- Chapter 6 TissuesDocument7 pagesChapter 6 Tissuesh8631259No ratings yet
- Chapter-8 Cell: Structure and FuctionDocument12 pagesChapter-8 Cell: Structure and FuctionTopNo ratings yet
- 9 Science Imp ch4 3Document7 pages9 Science Imp ch4 3deepakNo ratings yet
- 9 Science Imp Ch15 3Document10 pages9 Science Imp Ch15 3deepakNo ratings yet
- 9 Science Imp ch3 3Document7 pages9 Science Imp ch3 3deepakNo ratings yet
- 9 Science Imp ch5 3Document4 pages9 Science Imp ch5 3deepakNo ratings yet
- 9 Science ImportantDocument13 pages9 Science ImportantdeepakNo ratings yet
- Cristini Aeoniumof La PalmaDocument27 pagesCristini Aeoniumof La PalmaTamaraNo ratings yet
- AloeVera - Full GuideDocument20 pagesAloeVera - Full GuideSafi KhanNo ratings yet
- Agari CusDocument9 pagesAgari CusKrishna ShrimaliNo ratings yet
- Leaves:: Form and StructureDocument37 pagesLeaves:: Form and StructureJane ManalusNo ratings yet
- 15 Common Gardening Tools and Their UsesDocument28 pages15 Common Gardening Tools and Their UsesCarlos Talania100% (1)
- FlowersDocument12 pagesFlowersAMITANSHUNo ratings yet
- Forest EcologyDocument25 pagesForest Ecologyyusninda nadilliaNo ratings yet
- Bali Dan Lombok Begonia 2008dgiDocument58 pagesBali Dan Lombok Begonia 2008dgiAdhy Widya SetiawanNo ratings yet
- Ricinus CommunisDocument4 pagesRicinus CommunisWojciech RedutkoNo ratings yet
- Bisexual Rhizanthes Lowii (Beccari) Harms (Rafflesiaceae) From Borneo First Description of Flowers, Fruits and SeedsDocument13 pagesBisexual Rhizanthes Lowii (Beccari) Harms (Rafflesiaceae) From Borneo First Description of Flowers, Fruits and SeedsSari RofiqohNo ratings yet
- Science 5 - The Reproductive Parts in Plants and Their FunctionsDocument7 pagesScience 5 - The Reproductive Parts in Plants and Their FunctionsCherry Alegado PuraNo ratings yet
- Technology and Livelihood Education: AgricultureDocument19 pagesTechnology and Livelihood Education: Agriculturemaricar paracadNo ratings yet
- Teak Tree - Rishika JainDocument8 pagesTeak Tree - Rishika JainHarsimran ChadhaNo ratings yet
- Effect of IBA On Rooting and Growth of Morus Alba Shoot Cuttings Under Temperate Conditions of KashmirDocument3 pagesEffect of IBA On Rooting and Growth of Morus Alba Shoot Cuttings Under Temperate Conditions of KashmirJauhar RafeeqNo ratings yet
- PLANT MORPHOLOGY NotesDocument78 pagesPLANT MORPHOLOGY NotesAsam100% (1)
- Planting GuideDocument2 pagesPlanting Guideapi-343845661No ratings yet
- Barbula Unguiculata PDFDocument1 pageBarbula Unguiculata PDFvinca sherinNo ratings yet
- Armillaria List 2008 06 16Document18 pagesArmillaria List 2008 06 16Andrea CussighNo ratings yet
- Plant Tissues QuestionsDocument2 pagesPlant Tissues QuestionsAnri van ZylNo ratings yet
- AngiospermDocument5 pagesAngiospermAbdul BasitNo ratings yet
- Edible Barringtonia Nuts and LeavesDocument15 pagesEdible Barringtonia Nuts and Leaveschedica22No ratings yet
- Waterplantsstudy 00 ArbeuoftDocument462 pagesWaterplantsstudy 00 ArbeuoftJuditVanLondenRuizNo ratings yet
- Bio GerminationDocument6 pagesBio GerminationBea GandiniNo ratings yet
- Natural Vegetation and WildlifeDocument20 pagesNatural Vegetation and Wildlifekaltamash526No ratings yet
- 7e's Lesson PlanDocument4 pages7e's Lesson PlanRio Jane B. GahilesNo ratings yet
- Aisole Victor ReportDocument69 pagesAisole Victor ReportOlabiwonnu Temitope100% (1)
- Mangifera Indica (Mango) : DescriptionDocument10 pagesMangifera Indica (Mango) : DescriptionMelx UbaldeNo ratings yet
- RadishDocument19 pagesRadishSaiTimmaraoNo ratings yet
- Pre-Board Crop Science 2012 - With Answers-1Document7 pagesPre-Board Crop Science 2012 - With Answers-1Noel channelNo ratings yet
- Roundup Advance Liquid Concentrate 280ml-LabelDocument2 pagesRoundup Advance Liquid Concentrate 280ml-LabelPaul LesterNo ratings yet