Professional Documents
Culture Documents
90 Ijcse 06135
Uploaded by
TamilselviOriginal Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
90 Ijcse 06135
Uploaded by
TamilselviCopyright:
Available Formats
International Journal of Computer Sciences and Engineering Open Access
Research Paper Vol.-7, Issue-3, March 2019 E-ISSN: 2347-2693
On Neighbourhood Difference Cordial Labeling of Networks
V.M.Chitra1*, D. Antony Xavior2
1
Department of Mathematics, Loyola College, Chennai 600034
2
Sriram Engineering College, Perumalpattu, 602024
Corresponding author: chithu1234@yahoo.com, Tel.: 9841218311
DOI: https://doi.org/10.26438/ijcse/v7i3.538543 | Available online at: www.ijcseonline.org
Accepted: 13/Mar/2019, Published: 31/Mar/2019
Abstract— Graph labeling is the mapping of graph elements like vertices or edges or both to set of integers under some
conditions. In a binary labeling to vertices, if we assign the edge label as the difference of the label of end vertices and if the
difference of the number of vertices with label 0 and 1 and difference of edges with label 0 and 1 is at most 1, then the labeling
is cordial labeling. If the mapping is a one to one mapping from the vertices to the labels from {1, 2, …, p}, where p is the
cardinality of the vertex set, edge label as in the cordial labeling and if the difference of the number of edges labeled with 1 and
not labeled with 1 is at most 1, then the labeling is difference cordial labeling. Neighborhood difference cordial labeling is a
variation of difference cordial labeling, if the difference of the number of edges labeled with 1 and not labeled with 1 at each
vertex is at most 1 then the labeling is neighbourhood difference cordial labeling In this paper we investigate the
neighbourhood difference cordial labeling of honey comb network, butterfly network, benes network and grid network.
Keywords— Honey comb network, butterfly network, benes network, grid and difference cordial label.
I. INTRODUCTION For , the edge is said to be a straight edge . Otherwise
Cordial labeling was established by Cahit [1] in 1987 and the edge is a cross edge. For fixed i the vertex is a
Ponraj et al [2] introduced difference cordial labeling of a vertex on level i.
graph in 2013 and discussed about the difference Definition 3: The n dimensional benes network BB (n)
cordial labeling of path, cycle, complete graph, star, consists of back to back butterfly network and it has
complete bipartite graph, bistar, wheel, fan, gear graph, web levels, vertices and edges.
graph and helm graph. In 2015 Seoud and Salman [3] Definition 4: Cartesian product of of graphs and
studied difference cordial labeling of various types of ladders is a graph with vertex set and two
and one point union of graphs. Xavier et al [5] initiated the
study of neighbourhood difference cordial labeling of graphs. vertices and in are adjacent if
In this paper we are going to discuss about neighbourhood and is adjacent to in or and is
difference cordiality of few networks. adjacent to in .
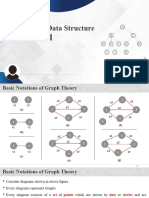
II. PRELIMINARIES Definition 5: A path is an alternating sequence of distinct
Definition 1: A honey comb network of size n is vertices and edges.
Definition 6: Let denote the path on n vertices. For
obtained from by adding a layer of hexagon
is defined as the two dimensional grid
around the boundary of , where is a
hexagon. with m rows and n columns and is denoted by . Any
Definition 2:[4] The n dimensional butterfly network, vertex in ith row and jth column is denoted by .
denoted by , has a vertex set Definition7: Difference cordial labeling: Let be a
Two vertices graph. Let be a function. For
and are linked by an edge in if and each assign the label f is called
only if and either difference cordial labeling if f is one to one and the absolute
(i). or difference of number of edges labeled with1 and edges not
(ii). x differs from y in precisely the jth bit. labeled with 1 is at most 1. Any graph with difference cordial
labeling is called difference cordial graph.
© 2019, IJCSE All Rights Reserved 538
International Journal of Computer Sciences and Engineering Vol.7(3), Mar 2019, E-ISSN: 2347-2693
Honey comb coordinate system: The coordinate system When is
honey comb network is as given below even
i=-2
i=-1
i=1
i=2 When is odd
Fig 1: Coordinate system of HC (2)
Neighbourhood difference cordial labelling:
Let be a graph where and are the vertex and
edge sets of Let be a function. For
each edge assign the label . f is called a
neighbourhood difference cordial labeling if f is one to one
map and for every vertex where
and denote the number of edges incident At
with , labeled with 1 and not labeled with 1 respectively. A
graph with neighbourhood difference cordial labeling is
called neighbourhood difference cordial graph. When is even
Theorem 1: Anyhoney comb network is
neighborhood difference cordial graph. When is odd
Proof: A honey comb network of size n has
vertices and edges.In that vertices of
degree 2 and vertices are of degree 3.
Let Case 2: When k is negative
Define
Case 1: When is positive
At ,
At
When is even
When is odd
© 2019, IJCSE All Rights Reserved 539
International Journal of Computer Sciences and Engineering Vol.7(3), Mar 2019, E-ISSN: 2347-2693
when j is even
When j is odd
At
When is even
When is odd
Case 5: When
Case 3: When ,
At
At
When is even
When is even
When is odd
When is odd
Case 4: When
© 2019, IJCSE All Rights Reserved 540
International Journal of Computer Sciences and Engineering Vol.7(3), Mar 2019, E-ISSN: 2347-2693
54 52 50
51 49 48
53
40 42 44 47
Case 6: When
39 41 43 45 46
29 31 33 35 37
28 30 32 34 38
36
17 19 21 23 25 27
18 20 22 24 26
16 14 12 10 9
15 13 11 8
At 2 4 6 7
1 3 5
At each vertex Hence
any honeycomb network is a neighborhood graph.
Theorem 2: Any grid is neighbourhood
difference cordial graph.
Let
Define
Case 1:
At , and
Case 2:
At ,
At , and
Case 3:
At , and
Case 4:
At , and
Case 5:
At
At , and
Case 6:
At
© 2019, IJCSE All Rights Reserved 541
International Journal of Computer Sciences and Engineering Vol.7(3), Mar 2019, E-ISSN: 2347-2693
Theorem 3: Anybutterfly network is neighborhood
difference cordial graph.
Proof:
At , and
The butterfly network has vertices and
Case 7: edges.
At
Let
Define
At , and .
The edge connecting the vertices and
Case 8: are straight edges and other
At edges are cross edges. By the above labeling the stright edges
are labeled with 1 and cross edges are not labeled with 1. At
each vertices , the no of stright edges and cross edges are
equal. Therefore at each vertex
At , and . Hence butterfly
network is a neighborhood differential cordial graph.
4 8 12 20 24 28 32
16
Case 9:
At ,
3 7 11 15 27
19 23 31
18 22 26
2 6 10 14
At , and 30
By the above labeling, at each vertex 1 5 9 13 17 21 25 29
Hence grid is a neighborhood
difference cordial graph.
16 17 18 19 20 Theorem 4: Any benes network is a neighbourhood
difference cordial graph.
Proof:
The n dimentional benes network has vertices
11 12 13 14 15
and edges. In level and level , vertices are
of degree 2 and in other levels, vertices are of degree 4.
6 7 8 9 10 Let
Define
Proof: The proof is similar to butterfly network.
1 4 5
2 3
© 2019, IJCSE All Rights Reserved 542
International Journal of Computer Sciences and Engineering Vol.7(3), Mar 2019, E-ISSN: 2347-2693
35 42 49 [4]. Mirka Miller, Indira Rajasingh, D.Ahima Emilet, D.AzubhaJemilet,
7 14 21 28 56
d-Lucky Labeling of graphs, Procedia Computer Science 57 (2015)
766-771.
[5]. R.Ponraj, S.Sathish Narayanan and R.Kala, Difference cordial
labeling of graphs, Global.J.Mat.Sciences: Theory and Practical,
3(2013), 192-201.
[6]. V.M.Chitra, D.Antony Xavier, D.Florence Isido, On neighbourhood
difference cordial labeling of graphs, International Journal of
Information and Computing Science, Volume 6, Issue 2, February
6 20 27 2019
13 55
41 48
34
Authors Profile
Dr. Antony Xavier pursued Bachelor
26 of Science from Government Arts
5 12 19 33 40 54
47 College, Krishnagiri in 1992 and Master
of Science from St. Xaviers College in
1994. He passed M.Phil with distinction
at Loyola College in 1995 and Ph.D from
11 25 46
4 18 32 39 53 Madras University in 2002 with a remark
of highly commended. He is working as
an Assistant professor in Depatment of Mathematics, Loyola
College, Chennai. He has 15 years of teaching experience
3 10 17 24 31 38 45 52 both in UG and in PG and 7 years for M.Phil. He has more
than 40 publications in reputed National and International
Journals. He has given invited talk both in National and
International conferences. He guided 3 students and 10
30
students are working under him for Ph.D
2 9 16 23 37 44 51
Ms.V.M.Chitra pursed her Bachelor
degree in Applied Sciences, Mater
Degree in Applied Mathematics at
Thiagarajar College of Engineering,
Madurai and M.Phil from Madurai
Kamaraj University.She has 15 years of
teaching experience in Engineering and
1 8 22 29 36 43 50 Arts and Science colleges.She has 6
15
publications in reputed National and International Journals.
She is working as an Assistant Professor in the Depatment of
Mathematics, Sriram Ebgineering College, Perumal Pattu,
From the above labeling the bene network is a neighborhood Chennai. Currently she is doing her research at The
difference cordial graph. Departmnet of Mathematics, Loyola College, Chennai
CONCLUSION
In this paper we proved that honey comb network, grid,
butterfly network and benes network are neighbourhood
difference cordial graph.
REFERENCES
[1]. I.Cahit, Cordial graph: A weaker version of graceful and
harmonious graphs, Ars Combinatorial 23(1987), 201-207
[2]. R.Ponraj, S.Sathish Narayanan and R.Kala, A note on difference
cordial graphs, Palestine Journal of mathematics, 4(1), (2015), 189-
197.
[3].M.A.Seoud ,ShakirM.Salman , On difference cordial graphs,
Mathematica Aeterna , Vol. 5, 2015, no.1, 105-124.
© 2019, IJCSE All Rights Reserved 543
You might also like
- The+Conversational+Hypnosis+Code+Digital Book PDFDocument681 pagesThe+Conversational+Hypnosis+Code+Digital Book PDFRudolfSianto100% (2)
- TractatusDocument185 pagesTractatusSattyaki BasuNo ratings yet
- Snap Fit DesignDocument4 pagesSnap Fit DesignAlex DobrescuNo ratings yet
- Ellenberger - Psychiatry From Ancient To Modern TimesDocument76 pagesEllenberger - Psychiatry From Ancient To Modern TimesSiegfriedCristoforNo ratings yet
- IBM Global Human Capital StudyDocument72 pagesIBM Global Human Capital Studypraneeth.patlola100% (9)
- Why There Has Been No Brandies Brief in India? Challenges To Socio-Legal Research in IndiaDocument2 pagesWhy There Has Been No Brandies Brief in India? Challenges To Socio-Legal Research in IndiaSubhaprad MohantyNo ratings yet
- Chap05 JOHN W. CRESWELLDocument27 pagesChap05 JOHN W. CRESWELLMuhammad Bilal100% (2)
- Lighting Fittings Performance and Design: International Series of Monographs in Electrical EngineeringFrom EverandLighting Fittings Performance and Design: International Series of Monographs in Electrical EngineeringNo ratings yet
- KSS 41 END enDocument702 pagesKSS 41 END enJavier Del Pozo Garcia100% (1)
- Experiment 8: Light As A Wave (Diffraction Grating)Document6 pagesExperiment 8: Light As A Wave (Diffraction Grating)rimagaNo ratings yet
- Radio Labeling To The Complement of Path & Cycle Related GraphsDocument10 pagesRadio Labeling To The Complement of Path & Cycle Related GraphsInternational Journal of Application or Innovation in Engineering & ManagementNo ratings yet
- First Half ScribeDocument33 pagesFirst Half ScribeSuresh KumarNo ratings yet
- Trees As Data StructuresDocument78 pagesTrees As Data Structuresbirenhirapara16No ratings yet
- A Study On Graph Theory of Path Graphs: Mr. B. Senthilkumar, M. JayafranglinDocument7 pagesA Study On Graph Theory of Path Graphs: Mr. B. Senthilkumar, M. JayafranglinRahul SharmaNo ratings yet
- 2 Disjoint Paths Problem in Oriented Mesh NetworkDocument4 pages2 Disjoint Paths Problem in Oriented Mesh NetworkiirNo ratings yet
- 5 FFD 392 D 0 BB 31Document3 pages5 FFD 392 D 0 BB 31Suresh KumarNo ratings yet
- Graph Theory ReadingDocument14 pagesGraph Theory ReadingSZNo ratings yet
- Ag02 FS05Document23 pagesAg02 FS05Sweta AkhoriNo ratings yet
- HKYASDocument20 pagesHKYASAaryan SukhadiaNo ratings yet
- 03 GraphsDocument51 pages03 GraphsIbrahim SalihNo ratings yet
- Session7 8 GraphsDocument44 pagesSession7 8 Graphsalex tylerNo ratings yet
- Graphs: Slides by Kevin Wayne. All Rights ReservedDocument44 pagesGraphs: Slides by Kevin Wayne. All Rights Reservedalex tylerNo ratings yet
- 2 GraphsDocument6 pages2 GraphsQuang NguyenNo ratings yet
- Inter-Layer Crosstalk Management in Differential Dual-StriplinesDocument6 pagesInter-Layer Crosstalk Management in Differential Dual-Striplinesggvp vasanthNo ratings yet
- MIT14 15JS18 Lec2-3Document30 pagesMIT14 15JS18 Lec2-3ehsanchahalNo ratings yet
- D Lucky Labeling of Graphs PDFDocument6 pagesD Lucky Labeling of Graphs PDFtony augustineNo ratings yet
- Section 8: Objectives:: Data Structures & AlgorithmsDocument7 pagesSection 8: Objectives:: Data Structures & AlgorithmsYT PremoneNo ratings yet
- Section 8: Objectives:: Data Structures & AlgorithmsDocument7 pagesSection 8: Objectives:: Data Structures & AlgorithmsYT PremoneNo ratings yet
- Graph TheoryDocument8 pagesGraph Theoryoliver1.shawNo ratings yet
- Part B ProblemsDocument32 pagesPart B ProblemsEmanuel Santa Cruz CasianoNo ratings yet
- T3 Graph and TreeDocument70 pagesT3 Graph and TreeCerealkillerNo ratings yet
- Graph Data StructureDocument29 pagesGraph Data StructureSuhit KulkarniNo ratings yet
- Thiagarajan 2018 J. Phys. Conf. Ser. 1000 012054Document12 pagesThiagarajan 2018 J. Phys. Conf. Ser. 1000 012054AlfiNo ratings yet
- Aboratory Anual: Searle'S ApparatusDocument5 pagesAboratory Anual: Searle'S ApparatusOmNo ratings yet
- Graphs 1Document28 pagesGraphs 1Michael Punyua Ole PeliaiNo ratings yet
- Marcatili1969 PDFDocument32 pagesMarcatili1969 PDFDevansh SrivastavaNo ratings yet
- 4ph1 1p Rms 20230302Document18 pages4ph1 1p Rms 20230302LAITH ROBERT WADIE SWAIDANNo ratings yet
- Directions: Consider The Table Below. Given Each Figure, Recall The Definition of Each Quadrilateral and Write It On The Space ProvidedDocument19 pagesDirections: Consider The Table Below. Given Each Figure, Recall The Definition of Each Quadrilateral and Write It On The Space ProvidedJaninne Villa Del ReyNo ratings yet
- Chương 3 - Các Đặc Trưng Mạng (Network Characteristics)Document7 pagesChương 3 - Các Đặc Trưng Mạng (Network Characteristics)Quốc Huy VũNo ratings yet
- Introduction To NetworksDocument60 pagesIntroduction To NetworksKarim CHERIFINo ratings yet
- Maths - Ijmcar - On The Connectivity of - Kenchappa S BetageriDocument8 pagesMaths - Ijmcar - On The Connectivity of - Kenchappa S BetageriTJPRC PublicationsNo ratings yet
- 03a GraphsDocument22 pages03a Graphsap6487No ratings yet
- Introduction To Algorithms: Design and Analysis of Algorithms 214Document42 pagesIntroduction To Algorithms: Design and Analysis of Algorithms 214Gamindu UdayangaNo ratings yet
- Beam Analysis Using The Stiffness MethodDocument20 pagesBeam Analysis Using The Stiffness MethodMirza MydulNo ratings yet
- Graph Application in Genome Circular Ideogram: Nada Afra Sabrina 13517118Document6 pagesGraph Application in Genome Circular Ideogram: Nada Afra Sabrina 13517118Afra ComNo ratings yet
- A Brief Study of Graph Data Structure: IjarcceDocument5 pagesA Brief Study of Graph Data Structure: IjarcceChowdary VinesNo ratings yet
- SeminarDocument49 pagesSeminargrma1234shNo ratings yet
- Eec 401 Basic Vlsi Design: GitamDocument52 pagesEec 401 Basic Vlsi Design: Gitamcrush on creativityNo ratings yet
- Graphs 1Document17 pagesGraphs 1KARTIKEY GARGNo ratings yet
- Isolation and Characterization of Marine Bacteria For Potential Antibacterial ActivitiesDocument4 pagesIsolation and Characterization of Marine Bacteria For Potential Antibacterial ActivitiesEditor in ChiefNo ratings yet
- Md. Kamrul Hassan: Two-Hundred Years Long Journey From Graph To Complex Network TheoryDocument47 pagesMd. Kamrul Hassan: Two-Hundred Years Long Journey From Graph To Complex Network TheoryDhusorMeghNo ratings yet
- P3 Packing Preclusion For Hexagonal Mesh Pyra-MidDocument3 pagesP3 Packing Preclusion For Hexagonal Mesh Pyra-MidiirNo ratings yet
- Biological Networks TheoryDocument77 pagesBiological Networks TheoryJessieNo ratings yet
- ReedDocument7 pagesReedKrishanu ChoudhuryNo ratings yet
- DS Unit-4Document47 pagesDS Unit-4himagiriNo ratings yet
- 4sd0 1p Rms 20230302Document18 pages4sd0 1p Rms 20230302adamgonoloNo ratings yet
- P1 EjcDocument6 pagesP1 Ejctoh tim lamNo ratings yet
- Triangular Lattice Array AntennaDocument4 pagesTriangular Lattice Array AntennaTùng Dương ThanhNo ratings yet
- 03 Some Aspects of Three-Dimensional Tonnetze (Gollin 1998)Document13 pages03 Some Aspects of Three-Dimensional Tonnetze (Gollin 1998)RobporeliNo ratings yet
- Lectures-MM323 2 XRD For StudentsDocument195 pagesLectures-MM323 2 XRD For StudentsRamiz YashNo ratings yet
- 15 Beam Analysis Using The Stiffness MethodDocument20 pages15 Beam Analysis Using The Stiffness MethodKalyani reddyNo ratings yet
- ádấdDocument24 pagesádấdThanh DinhNo ratings yet
- Edge Irregular Reflexive Labeling On Lobster GraphDocument7 pagesEdge Irregular Reflexive Labeling On Lobster GraphAry WijayaNo ratings yet
- Graphs: 3.1 Basic Definitions and ApplicationsDocument12 pagesGraphs: 3.1 Basic Definitions and Applicationsanarki417No ratings yet
- Unit3 2 TreesDocument22 pagesUnit3 2 TreesRitika LohiyaNo ratings yet
- Physics Screw Guage 2-8 - 17 Copy 2Document24 pagesPhysics Screw Guage 2-8 - 17 Copy 2PoorvaBakshiNo ratings yet
- Special Relativity Worksheet, A-Level, IB, APDocument34 pagesSpecial Relativity Worksheet, A-Level, IB, APbobNo ratings yet
- Logics and ProofsDocument12 pagesLogics and ProofsTamilselviNo ratings yet
- Lattices and Boolean AlgebraDocument11 pagesLattices and Boolean AlgebraTamilselviNo ratings yet
- Graph StructuresDocument9 pagesGraph StructuresTamilselviNo ratings yet
- Module3 Frequency FilteringDocument58 pagesModule3 Frequency FilteringTamilselviNo ratings yet
- CombinatoricsDocument9 pagesCombinatoricsTamilselviNo ratings yet
- 27-Dyanmic SurveyDocument553 pages27-Dyanmic SurveyTamilselviNo ratings yet
- PS & PQT - Unit I MCQDocument18 pagesPS & PQT - Unit I MCQTamilselviNo ratings yet
- The Web of Modularity - Arithmetic of The Coefficients of Modular Forms and $q$-Series Page 1Document20 pagesThe Web of Modularity - Arithmetic of The Coefficients of Modular Forms and $q$-Series Page 1TamilselviNo ratings yet
- Eisenstein Final 2010Document42 pagesEisenstein Final 2010TamilselviNo ratings yet
- Cordial Labeling For Different Types of Shell GraphDocument7 pagesCordial Labeling For Different Types of Shell GraphTamilselviNo ratings yet
- Explicit Formula For Divisor FunctionDocument28 pagesExplicit Formula For Divisor FunctionTamilselviNo ratings yet
- Criteria 3 by Dr. Hemant ChandakDocument39 pagesCriteria 3 by Dr. Hemant ChandakTamilselviNo ratings yet
- Ma8551 NotesDocument244 pagesMa8551 NotesTamilselviNo ratings yet
- MCQ DM For Unit 2 CombinatoricsDocument22 pagesMCQ DM For Unit 2 CombinatoricsTamilselviNo ratings yet
- Transfer - GuidelinesDocument4 pagesTransfer - GuidelinesTamilselviNo ratings yet
- Roll No.: PART-A (10 X 2 20 Marks)Document2 pagesRoll No.: PART-A (10 X 2 20 Marks)TamilselviNo ratings yet
- MA8452 QP Model Exam 2 - SNM Set ADocument2 pagesMA8452 QP Model Exam 2 - SNM Set ATamilselviNo ratings yet
- FDP Advanced LaTeX June 2022 BrochureDocument2 pagesFDP Advanced LaTeX June 2022 BrochureTamilselviNo ratings yet
- Chapter 4 EIgen Values and Eigen VectorsDocument28 pagesChapter 4 EIgen Values and Eigen VectorsTamilselviNo ratings yet
- 1 - Relations and FunctionsDocument42 pages1 - Relations and FunctionsTamilselviNo ratings yet
- NEST2017 Brochure SyllabusDocument18 pagesNEST2017 Brochure SyllabusTamilselviNo ratings yet
- Height, Depth and Level of A TreeDocument5 pagesHeight, Depth and Level of A TreeTamilselviNo ratings yet
- Central Limit TheoremDocument46 pagesCentral Limit TheoremAneesh Gopinath 2027914No ratings yet
- Calnetix BrochureDocument6 pagesCalnetix Brochuresh_saraydin3949No ratings yet
- Sans Nom 2Document320 pagesSans Nom 2khalidNo ratings yet
- Chapter 1-3Document36 pagesChapter 1-3Babyin LowNo ratings yet
- Goodrich 6e Ch03 Arrays PDFDocument12 pagesGoodrich 6e Ch03 Arrays PDFArjun SinghNo ratings yet
- Viltam User Manual enDocument13 pagesViltam User Manual enszol888No ratings yet
- CA Cooling TowerDocument19 pagesCA Cooling TowerKeshia WiseNo ratings yet
- Younified LevelupDocument9 pagesYounified LevelupMitesh NagpalNo ratings yet
- Masterfile - Archer & Bull - UG 2022 - IITMDocument9 pagesMasterfile - Archer & Bull - UG 2022 - IITMSam TyagiNo ratings yet
- Kindly Encircle The Letter of Your ChoiceDocument5 pagesKindly Encircle The Letter of Your ChoiceJheongmie ObaNo ratings yet
- The Science of Bonding From First To Sixth GenerationDocument6 pagesThe Science of Bonding From First To Sixth GenerationRolzilah RohaniNo ratings yet
- Guide SauvegardeDocument688 pagesGuide SauvegardemitrailleNo ratings yet
- Sample TestDocument2 pagesSample TestSarah Guimary PelarisNo ratings yet
- Đề 5Document4 pagesĐề 5Nga NguyenNo ratings yet
- Genetic Structuralism by Group 6Document7 pagesGenetic Structuralism by Group 6Achmad AlghifariNo ratings yet
- Evermotion Archmodels Vol 40 PDFDocument2 pagesEvermotion Archmodels Vol 40 PDFJustinNo ratings yet
- Google Calendar Integrator - v2.0Document21 pagesGoogle Calendar Integrator - v2.0Sumedh KakdeNo ratings yet
- Extemporaneous Speech in Oral CommunicationDocument3 pagesExtemporaneous Speech in Oral CommunicationStephanie BengcoNo ratings yet
- Habitat Lesson PlanDocument2 pagesHabitat Lesson Planapi-177886209No ratings yet
- Resistance To Change TQMDocument11 pagesResistance To Change TQMAlex RiveraNo ratings yet
- Sel KompetenDocument12 pagesSel KompetenEnung Warsita DahlanNo ratings yet
- Surface Tension Theory - EDocument11 pagesSurface Tension Theory - EthinkiitNo ratings yet
- Tugas Fak. Kedokteran Untad Therapy WorksheetDocument4 pagesTugas Fak. Kedokteran Untad Therapy WorksheetTha IthaNo ratings yet