Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Worksheet 3 Polarity and Intermolecular Forces PFR
Worksheet 3 Polarity and Intermolecular Forces PFR
Uploaded by
Harkirat SinghOriginal Description:
Original Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Worksheet 3 Polarity and Intermolecular Forces PFR
Worksheet 3 Polarity and Intermolecular Forces PFR
Uploaded by
Harkirat SinghCopyright:
Available Formats
Worksheet 3 Polarity and intermolecular forces PFR
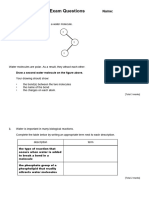
Below the main types of intermolecular forces are pictured. (fig. a-e )
a.
c.
b.
d. e.
1. What do the symbols δ - and δ + mean?
2. What is a dipole?
a. What causes permanent dipoles?
b. What is an induced dipole?
c. What is a temporary dipole?
3. Identify and explain each of the intermolecular forces pictured above.
4. Imagine you have just eaten a very hot chili pepper. You are feeling some
discomfort and one of your friends suggests that
--"you should drink milk and rinse your mouth”
Another suggests water, but a third says “rinse your mouth vegetable oil.”
Whose advice should you follow to ease your pain the fastest?
Study the molecular structure for water, vegetable oil and the components of milk then look at
capsaicin, the molecule that gives chilis heat.
You might also like
- Intermolecular Forces POGIL-1Document7 pagesIntermolecular Forces POGIL-1Crystal R.M100% (2)
- POGIL Intermolecular ForcesDocument7 pagesPOGIL Intermolecular Forcesdemyeets64No ratings yet
- Worksheet 4.6 IMFs and PropertiesDocument6 pagesWorksheet 4.6 IMFs and PropertiesJennifer Montero100% (1)
- Gen Chem 2 Q2 Module 2Document24 pagesGen Chem 2 Q2 Module 2Bernalene TasiNo ratings yet
- The ‘Mystical’ Tcm Triple Energizer: Its Elusive Location and Morphology DefinedFrom EverandThe ‘Mystical’ Tcm Triple Energizer: Its Elusive Location and Morphology DefinedNo ratings yet
- Physical Science Week 3Document18 pagesPhysical Science Week 3RAINIER DE JESUSNo ratings yet
- LAS For Physical Science Week 5-6Document4 pagesLAS For Physical Science Week 5-6Seul AsterNo ratings yet
- Alimu Teerman Rhetorical Essay - EditedDocument6 pagesAlimu Teerman Rhetorical Essay - EditedOgadaNo ratings yet
- 2021 IMF Packet WelchDocument9 pages2021 IMF Packet WelchbobNo ratings yet
- Group 5 ReportingDocument10 pagesGroup 5 ReportingJay Em Kristel MengulloNo ratings yet
- Core-Physical Science Q1 SLM - 5Document17 pagesCore-Physical Science Q1 SLM - 5Christopher Agustin Tambogon Lpt100% (1)
- Imf Online ActivityDocument2 pagesImf Online ActivityPhilip PrasadNo ratings yet
- Biomolecules Exam RevisionDocument3 pagesBiomolecules Exam RevisionCarmen CheahNo ratings yet
- Intermolecular ForcesDocument3 pagesIntermolecular ForcesJoseph renz AndayaNo ratings yet
- This Is Physical SCience Module 5, Grade 12 BezosDocument11 pagesThis Is Physical SCience Module 5, Grade 12 Bezosadrian lozanoNo ratings yet
- I. Introductory Concept: SHS-Physical Science (Intermolecular Forces)Document10 pagesI. Introductory Concept: SHS-Physical Science (Intermolecular Forces)Jane182004No ratings yet
- Chemistry Summative Study GuideDocument3 pagesChemistry Summative Study GuideJohanna Evan Cantos DolienteNo ratings yet
- SS1 Take-Home Assignments Dec, 2022-1Document11 pagesSS1 Take-Home Assignments Dec, 2022-1kenneth chinnyNo ratings yet
- Intermolecular Forces OF AttractionDocument11 pagesIntermolecular Forces OF AttractionMaria Rosabel IlaganNo ratings yet
- Water Exam Questions STUDENTDocument3 pagesWater Exam Questions STUDENTtnishtalaNo ratings yet
- Módulo Marzo 2024Document14 pagesMódulo Marzo 2024florenciamabelurNo ratings yet
- Chapter 4 Carbon and Molecular DiversityDocument3 pagesChapter 4 Carbon and Molecular DiversityZoe AposNo ratings yet
- C9apstudy GuideDocument37 pagesC9apstudy GuidejqtdNo ratings yet
- Essentials of Psychology 6th Edition Bernstein Test BankDocument17 pagesEssentials of Psychology 6th Edition Bernstein Test Bankthomasjohnsonsertzbfgqp100% (28)
- M3 Intermolecular Forces of AttractionDocument17 pagesM3 Intermolecular Forces of AttractionEvangeline AgtarapNo ratings yet
- Characteristics of ForceDocument2 pagesCharacteristics of ForceAdam PreocaninNo ratings yet
- Essentials of Psychology 6th Edition Bernstein Test Bank Full Chapter PDFDocument38 pagesEssentials of Psychology 6th Edition Bernstein Test Bank Full Chapter PDFMelissaJacksonDDSgwjp100% (12)
- Psychology Concepts and Applications 4th Edition Nevid Test BankDocument37 pagesPsychology Concepts and Applications 4th Edition Nevid Test Bankhansardsyrupedxb13y100% (28)
- Intermolecular ForcesDocument14 pagesIntermolecular ForcesJuss ChillinNo ratings yet
- Lesson PlanDocument5 pagesLesson PlanPrecious BalgunaNo ratings yet
- TD 1-Structure-Ang-2022-2023-Sans SolutionDocument2 pagesTD 1-Structure-Ang-2022-2023-Sans SolutionnarminsigaccNo ratings yet
- April Yadhi Xi.4Document2 pagesApril Yadhi Xi.4ordinarychansNo ratings yet
- BSC - 2019 - 1 - Anatomy and Physiology PDFDocument1 pageBSC - 2019 - 1 - Anatomy and Physiology PDFBasava VillanNo ratings yet
- Q3 - Intermolecular Forces of AttractionDocument19 pagesQ3 - Intermolecular Forces of Attractionynariv3No ratings yet
- ScienceDocument10 pagesScienceSaket TNo ratings yet
- Examen 1º Bachillerato C Primer Trimestre 2018-2019Document1 pageExamen 1º Bachillerato C Primer Trimestre 2018-2019David FerresNo ratings yet
- Sim Physical Science Melc q1 Week 3 l5 6Document29 pagesSim Physical Science Melc q1 Week 3 l5 6Aldrin Palma PeñaNo ratings yet
- 07 EnergeticWellness - Ebook - 23sep2014Document20 pages07 EnergeticWellness - Ebook - 23sep2014sbivekNo ratings yet
- Physical Science: San Fabian, PangasinanDocument8 pagesPhysical Science: San Fabian, Pangasinankath neeveNo ratings yet
- Para JumblesDocument50 pagesPara JumblesRICHARDSIBANDANo ratings yet
- Question Bank (Control and Coordination)Document4 pagesQuestion Bank (Control and Coordination)YASHANANDNo ratings yet
- Physical Science: Week 3: Intermolecular ForcesDocument16 pagesPhysical Science: Week 3: Intermolecular ForcesMelvin Ranera Abila100% (1)
- Genchem 2 Module 2 Q2Document24 pagesGenchem 2 Module 2 Q2Kezia LuatNo ratings yet
- A. Etiolation B. De-Etiolation C. Second Messengers: DHS AP BiologyDocument4 pagesA. Etiolation B. De-Etiolation C. Second Messengers: DHS AP BiologyAdrianna LjubiNo ratings yet
- Energy All Around Us Mind Map WorksheetDocument2 pagesEnergy All Around Us Mind Map WorksheetCociuban Miruna ElenaNo ratings yet
- SC 5 P 10 1-Forms of Energy 1Document24 pagesSC 5 P 10 1-Forms of Energy 1api-263271261No ratings yet
- Health - Ing FormDocument8 pagesHealth - Ing Formalejandraabigail.cardosoNo ratings yet
- Physical Science Q1 M3 WHLPDocument2 pagesPhysical Science Q1 M3 WHLPCiel LueNo ratings yet
- IMF and Properties of Liquids (Rina C. Moreno)Document7 pagesIMF and Properties of Liquids (Rina C. Moreno)RINA MORENONo ratings yet
- 2 IntermolecularForcesDocument7 pages2 IntermolecularForcesXyriel NalynNo ratings yet
- Machine Generated Alternative Text - Docx WordDocument1 pageMachine Generated Alternative Text - Docx WordStevenson Reinoso AbreuNo ratings yet
- Gen Chem 2 Q2 Module 2 - RemovedDocument20 pagesGen Chem 2 Q2 Module 2 - RemovedorevillojhnNo ratings yet
- Chapter 1 IntermolecularforcesliquidsandsolidsDocument101 pagesChapter 1 IntermolecularforcesliquidsandsolidsmarilyncasaulNo ratings yet
- Physical Science QTR 3 Module 3Document14 pagesPhysical Science QTR 3 Module 3Lyka Niña PasonNo ratings yet
- Physci Q1 M4Document27 pagesPhysci Q1 M4Julie Anne Portal - OdascoNo ratings yet
- Intermolecular Force Worksheet KeyDocument3 pagesIntermolecular Force Worksheet KeyBill alfonsoNo ratings yet
- PhySci Module 3 ADM EditedDocument9 pagesPhySci Module 3 ADM EditedMark Rowen De LarnaNo ratings yet
- Grade 10 June 2016Document10 pagesGrade 10 June 2016Sam AlexanderNo ratings yet
- Physical Science M3Document22 pagesPhysical Science M3Ma WiNo ratings yet