Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Describe The OSI Model
Uploaded by
groy47320 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
6 views1 pageOriginal Title
Describe the OSI model
Copyright
© © All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
6 views1 pageDescribe The OSI Model
Uploaded by
groy4732Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
You are on page 1of 1
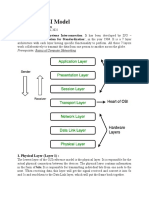
Describe the OSI model?
Transport Layer: Functions of transport layer:
There are seven OSI layer. Each layer has two different function.A List seven layer are given below. a>Segmentation and Reassembly: This layer accepts the message from session and the breaks them down into
smaller units.Each of the segment produced has a header associated with it.The transport layer at the
Physical layer: Functions of physical layers
destination layer reassemble the message.
a>line configuration:It defines the way how two or More devices can be connected physically.
b>Service Point Addressing: To deliver the message to the correct process the transport layer includes a type of
b>Data Transmission: It defines the transmission mode wheather It is simplex, half duplex or full duplex mode
addressing called service point addressing thus by specifying this process the transport layer makes sure that
between the two connected device.
the message is delivered to the correct process.
c> Topology: It defines the way how networks devices are arranged
Advantages: Ensure reliable and orderly data transfer between end to end connections.
d>Signal : It determines the type of signal is used to transmitting the infromation.
Support connection oriented(TCP) and connectionless(UDP) protocol.
Advantages: Transmits raw binary data over the physical medium.
It provides a standarized medium for tansmitting bits and signal
Session Layer: Functions of Session Layer :
a> Session Establishment and Maintenance: This layer allows two processes to establish use and terminate a
Data link Layer: Functions of data link layer: connection.
a>Framing: Framing is a function of data link layer.It provides way for a sender to transmit the sets of bits that b>Synchronisation: This layer allow to add checkpoints that are considered synchronisation points in the data
are meaningful to the reciver. This can b accomplished by attaching special bit patterns to the begining and end These synchronisation point help to identify the error so that the data is re-synchrized properly and ends of the
of the frame. messages are not cut prematurely and less is avoided.
b>Error control: The data link provides the mechanism of error control in which it detect and retransmit the c>Dialogue Controller: The session layer allows two systems to start communication and recovery of data in
damage or lost frames. case of faliures.
c>flow control: The data rate must be constant on both side else the data may got corrupted thus with flow Advantages: Manages the dialogues or session between different applications.
control coordinates the amount of data can be sent to before receiving an acknowledgment. supports checkpointing and recovery of data incase of faliures
d>Access Control: When a single communication channel is shared by multiple device the MAC sublayer of the
data link layers helps to determine which device has come over the channel at a given time.
Presentation Layer: The functions of presentation layer:
e>Physical Addressing. After executing frames the data link layer add physical address (mac address) of the
a>Translation: The process in two system exchange theinformation in the form of character, string,nunbers and
sender and for receiver to the begining and end of the frame.
so on.Different computers use different encoding methods;the presentation layer handles the interoperability
Advantages: Provides error free transmission over the data frames between node.
between the different encoding methods.
Performs framing error deletion and correction and flow control.
b>Encryption: Data encryption translates the data into another form or code.The encrypted data is known as
cliphertent and the decrypted data is known as the plain text.
Network Layer: Functions of network layer: c>Compress: Reduces the number of bits that are need to be transmitted on the network.
a>Internetworking: An internetworking is the main responsibility of the network layer.It provides a logical Advantages: Handles data representation and encryption for secure connection.
connection between different devices. Deals with data syntax,formal conversation and encryption/decryption.
b>Routing: Routing is the major component of network layer and it determine the best optimal path out of the
multiple paths from source to destination.
Application Layer: Functions of application layer:
Advantages: Enables the creation and management of logical paths.
a>File transfer access management: An application allows a user to access the files in a remote computer , to
Performs routing and forwarding of packets accross multiple network.
retrieve the files from a computer and to manage the files in a remote computer.
b>Mail service: An application provides the facilit for email forwarding and storage.
c>Directory service: The application layer provides distributed data source and is used to provide that global
information about various object.
Advantages: Provides a user interface for accessing network services.
Supports various applications such as email ,web browsing and file transfer.
You might also like
- 01 Networking ConceptsDocument39 pages01 Networking Concepts四月的奥德赛No ratings yet
- Cloud NetworkingDocument26 pagesCloud NetworkingHeliosNo ratings yet
- NetworkDocument39 pagesNetworkLarisa BalanNo ratings yet
- Local Area Network (LAN)Document3 pagesLocal Area Network (LAN)Akshay VNo ratings yet
- Q1. Layered ArchitectureDocument3 pagesQ1. Layered ArchitecturejlalithaNo ratings yet
- Abhi 2Document8 pagesAbhi 2task heistNo ratings yet
- OSI Model: Functions of Physical LayerDocument13 pagesOSI Model: Functions of Physical LayerMuhammad FayazNo ratings yet
- Chapter 2Document10 pagesChapter 2Aklilu AbrhaNo ratings yet
- OSI MODEL AssDocument16 pagesOSI MODEL AssMatovu HerbertNo ratings yet
- ISO-OSI ModelDocument34 pagesISO-OSI ModelPrathibaaNo ratings yet
- Network and System UNIT 2 NotesDocument24 pagesNetwork and System UNIT 2 Notespinkyjaiswal7890No ratings yet
- Computer Network 1Document17 pagesComputer Network 1Surendra Singh ChauhanNo ratings yet
- Layers of OSI ModelDocument5 pagesLayers of OSI Modelcivike100% (1)
- Data and Computer Communications: Protocol Architecture, TCP/IP, and Internet - Based ApplicationsDocument52 pagesData and Computer Communications: Protocol Architecture, TCP/IP, and Internet - Based ApplicationsTech HaseebNo ratings yet
- Local Area Networks Metropolitan Area Networks Wide Area Networks Intranet InternetDocument17 pagesLocal Area Networks Metropolitan Area Networks Wide Area Networks Intranet InternetJayaMadhavNo ratings yet
- 2 Layered ArchitectureDocument16 pages2 Layered ArchitectureRahul AryanNo ratings yet
- Session 5 - LAYER 2 SECURITIESDocument15 pagesSession 5 - LAYER 2 SECURITIESmunyakatimNo ratings yet
- Chapter Two - 1Document64 pagesChapter Two - 1Aklilu AyeleNo ratings yet
- Unit 2Document58 pagesUnit 2Yuvraj Singh 2》No ratings yet
- OSI Reference ModelDocument14 pagesOSI Reference ModelAnandNo ratings yet
- Vinodkumar Computer NetworksDocument143 pagesVinodkumar Computer Networksharibabu madaNo ratings yet
- Net 101 Module2 - FinalDocument14 pagesNet 101 Module2 - FinalMichael AntecristoNo ratings yet
- Networking LYQ 17 BCADocument14 pagesNetworking LYQ 17 BCAyourtraderguyNo ratings yet
- Network Models: Data Networks Dr. S. A. MoizDocument41 pagesNetwork Models: Data Networks Dr. S. A. MoizSuper SpecialNo ratings yet
- Lecture 2 - 7-Layers of OSIDocument29 pagesLecture 2 - 7-Layers of OSISheeraz Nafees UddinNo ratings yet
- CN - Roll No 123Document6 pagesCN - Roll No 123fatimaiftikhar720No ratings yet
- Job Interview Presentation TemplateDocument13 pagesJob Interview Presentation Templatemwilliams733No ratings yet
- OSI ModelDocument11 pagesOSI ModelAdi AcharyaNo ratings yet
- What Is OSI ModelDocument18 pagesWhat Is OSI Modelsoulxd1910No ratings yet
- Opolot Moses Networking NotesDocument137 pagesOpolot Moses Networking Notescalvin amecuNo ratings yet
- Layers of OSI ModelDocument7 pagesLayers of OSI Modelkndnew guadeNo ratings yet
- OSI Model - Layers and Its FunctionsDocument8 pagesOSI Model - Layers and Its FunctionsAnil Kumar BagNo ratings yet
- CN Unit 1 CompleteDocument79 pagesCN Unit 1 CompleteAbhiram SayaniNo ratings yet
- What Is OSI Model 17.01.2024Document7 pagesWhat Is OSI Model 17.01.2024aloishp36No ratings yet
- Define Computer NetworkDocument22 pagesDefine Computer Networkbhuvi2312No ratings yet
- OSI Model Layer FunctionsDocument4 pagesOSI Model Layer FunctionsJasbindar SinghNo ratings yet
- Nivel de Enlace de Datos ExposicionDocument10 pagesNivel de Enlace de Datos ExposicionFidel Eduardo MVNo ratings yet
- Osi Seven Layers Model Explained With ExamplesDocument11 pagesOsi Seven Layers Model Explained With ExamplesbarkatwaganNo ratings yet
- DCCN NotesDocument27 pagesDCCN NotesFaisal FirdousNo ratings yet
- UNIT2 Mobile ComputingDocument31 pagesUNIT2 Mobile ComputingNandan PoaptNo ratings yet
- Unit-3 Tcp/Ip Model & Osi Model: Prof - Balip A.S. M.sci Computer Science Computer NetworkDocument30 pagesUnit-3 Tcp/Ip Model & Osi Model: Prof - Balip A.S. M.sci Computer Science Computer Networkkiran sonavaneNo ratings yet
- The ISO - OSI ModelDocument16 pagesThe ISO - OSI Modelprince keshriNo ratings yet
- 2 - 16 MarksDocument20 pages2 - 16 MarksanjanbsNo ratings yet
- Koml Projectt EditDocument16 pagesKoml Projectt EditkomalNo ratings yet
- Lecture 3Document30 pagesLecture 3Muhammad NadeemNo ratings yet
- Computer Network NotesDocument129 pagesComputer Network NotesDivya VijayakumarNo ratings yet
- Mizan SuggestionsDocument19 pagesMizan Suggestionsnikhil raiNo ratings yet
- Network ModelsDocument7 pagesNetwork Modelsselajas355No ratings yet
- Seven Layers of OSI Reference ModelDocument4 pagesSeven Layers of OSI Reference ModelpervezkanjuNo ratings yet
- CN KCS-603 Important Questions SolvedDocument162 pagesCN KCS-603 Important Questions SolvedVikas RajpootNo ratings yet
- The Reference Model Part 1Document9 pagesThe Reference Model Part 1roysayanccp05No ratings yet
- CN Notes by MohanDocument17 pagesCN Notes by MohanMohan Raj KNo ratings yet
- Quiz 2 - 7th Questions Only - PDF 22222222Document2 pagesQuiz 2 - 7th Questions Only - PDF 22222222عمر اسامه محمد نصر ٢٠١٠٧٨٤٨No ratings yet
- Computer Networks: by Damera Venkatesh Assistant ProfessorDocument22 pagesComputer Networks: by Damera Venkatesh Assistant ProfessorTAMMISETTY VIJAY KUMARNo ratings yet
- Unit2 CNDocument8 pagesUnit2 CNmnatsu0432No ratings yet
- Week 2Document16 pagesWeek 2MUBEEN LIAQATNo ratings yet
- Osi ModelDocument19 pagesOsi ModelPranav SaiNo ratings yet
- PS3024GSDocument8 pagesPS3024GSiyank85No ratings yet
- LTRDCN 2223Document90 pagesLTRDCN 2223delplayNo ratings yet
- 20EC503 Data Communication Networks Unit 3Document107 pages20EC503 Data Communication Networks Unit 3Ms. Meenakshi G M MCA. Associate ProfessorNo ratings yet
- Security Configuration Guide, Cisco IOS XE Gibraltar 16.12.x (Catalyst 9500 Switches)Document756 pagesSecurity Configuration Guide, Cisco IOS XE Gibraltar 16.12.x (Catalyst 9500 Switches)LenynquirogaNo ratings yet
- ACI Remote Leaf Fabric Discovery v1.0 PDFDocument24 pagesACI Remote Leaf Fabric Discovery v1.0 PDFdelplayNo ratings yet
- Iec Lin PPTDocument20 pagesIec Lin PPTtarakram2809No ratings yet
- FlexconnectDocument42 pagesFlexconnectakarki77No ratings yet
- Quanta G7H R1ADocument106 pagesQuanta G7H R1AskyloveasdfNo ratings yet
- Unifi Glich Ort ConfigurationDocument3 pagesUnifi Glich Ort ConfigurationAlex NeukomNo ratings yet
- ISM - Lab - DA1Document23 pagesISM - Lab - DA1VardhanNo ratings yet
- FL Switch 2000Document124 pagesFL Switch 2000marcosNo ratings yet
- 05 VLAN Principles and Configuration - 1609743790342 - Copy - 101828Document33 pages05 VLAN Principles and Configuration - 1609743790342 - Copy - 101828Richard MazindeNo ratings yet
- 548 16sccca8-16scccs6-16sccit6 2020051603545429Document16 pages548 16sccca8-16scccs6-16sccit6 2020051603545429kolle arunkumarNo ratings yet
- EC3401 NETWORKS AND SECURITY SyllabusDocument2 pagesEC3401 NETWORKS AND SECURITY SyllabuspoornimaNo ratings yet
- Ddos Attack HandbookDocument25 pagesDdos Attack Handbookjyoshna yenamalaNo ratings yet
- I2 CCommunication Protocol SpecificationsDocument3 pagesI2 CCommunication Protocol Specificationshiro1610tomNo ratings yet
- 16.1.2 Lab - Configure Route Redistribution Between EIGRP and OSPF - ILMDocument32 pages16.1.2 Lab - Configure Route Redistribution Between EIGRP and OSPF - ILMAndrei Petru PârvNo ratings yet
- CNVT 1810 581 F 21 T and RDocument13 pagesCNVT 1810 581 F 21 T and Rወዲ ተስፋይ ገብረዮሱስNo ratings yet
- HTTPS LtemDocument20 pagesHTTPS LtemAlex BaranciraNo ratings yet
- Chapter - 2 - v8.1 Part 2Document59 pagesChapter - 2 - v8.1 Part 2MDPNNo ratings yet
- Rtdi 365 UkDocument2 pagesRtdi 365 UkAntonio Fernandez GonzalezNo ratings yet
- Option N Ethernet Ip 4189340801 UkDocument155 pagesOption N Ethernet Ip 4189340801 UkshashirajNo ratings yet
- Computer Networks Lesson Plan Materials Computer Networks Lesson Plan MaterialsDocument6 pagesComputer Networks Lesson Plan Materials Computer Networks Lesson Plan MaterialsAldrin Canicula CompetenteNo ratings yet
- OSI Model PosterDocument1 pageOSI Model PosterDragoș AndreiNo ratings yet
- ProductSheet MDM3315121212Document2 pagesProductSheet MDM3315121212alexggggNo ratings yet
- Cambium Networks Data Sheet Cnmatrix TX2000 SeriesDocument10 pagesCambium Networks Data Sheet Cnmatrix TX2000 Seriesrf.waveguideNo ratings yet
- Chapter 8: Single-Area Ospf: CCNA Routing and Switching Scaling Networks v6.0Document67 pagesChapter 8: Single-Area Ospf: CCNA Routing and Switching Scaling Networks v6.0raman68No ratings yet
- CN - Unit3.2Document53 pagesCN - Unit3.2Nishant BHARDWAJNo ratings yet
- HTTP WWW - Caledoncontrols.co - Uk Datash HMS 1003Document3 pagesHTTP WWW - Caledoncontrols.co - Uk Datash HMS 1003Bob YahyaNo ratings yet
- Data Communications and Networking With TCP Ip Protocol Suite 6Th Edition Behrouz A Forouzan Full ChapterDocument67 pagesData Communications and Networking With TCP Ip Protocol Suite 6Th Edition Behrouz A Forouzan Full Chapterlinda.owens263100% (5)