Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Mind Map Aliesaerwan
Uploaded by
2023825896Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Mind Map Aliesaerwan
Uploaded by
2023825896Copyright:
Available Formats
Define the problem Step 1 : Define the problem or opportunity
oropportunity. (problem, characteristics of problems,
Set objectives and criteria. structured problems, unstructured problems).
MIND Generate alternatives.
Select the most feasible
Step 2 : Set objectives and criteria.
Step 3 : Generate alternatives.
MAP
alternative. Step 4 : Select the most feasible alternative.
Implement the decision. Step 5 : Implementing the decision.
Control the results. Step 6 : Control the results.
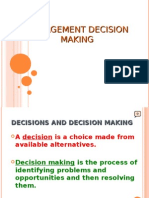
DECISION MAKING
PROCESS
6 STEPS:
Opportunity.
Objective.
Decision.
Problems.
Faces important decisions.
EXAMPLE OF
SITUATION Problem solving and decision making are crucial skills of
effective managers.
Reflexive - Reflexive decision making style. Managing is about one thing - making decision.
Reflective - Reflective decision making Some researches claim that managers typically make
DECISION INTRODUCTION TO SOLVING PROBLEMS AND about 80 decisions daily, or one every 5 or 6 minutes.
style. SPORTS MAKING DECISION Others claim that daily decisions number in the hundreds.
Consistent - Consistent decision making MAKING STYLES MANAGEMENT Bad decisions not only destroy careers, but also will
style.
destroy the companies.
THE DIFFERENCE BETWEEN
PROBLEM SOLVING AND
Problem solving : The process of taking
DECISION MAKING
corrective action to meet objectives.
Decision making : The process of
selecting a course of action that will
solve a problem (making a choice from
two or more alternatives).
DECISION - MAKING FOR DECISION MAKING TYPES OF PROBLEMS
OFFICIALS CONDITIONS AND DECISIONS
Successful Decision Certainty
A decision as a successful official (referee) depend on things. A situation in which a manager can make accurate decisions because all
Characteristics.
Be Cool outcomes are known. For managerial decisions are made under the condition
When making a decision you have to keep your cool. of certainty. Programmed Decisions.
Be Smart
Each decision has two phases : Read and Analyze the play, and then make the call.
Risk Nonprogrammed Decisions.
A situation in which the manager is able to estimate the likelihood (probability)
When To Give Penalty ?
of outcomes that result from the choice of particular alternatives. The ability to
When things happen in a split second, it can be tempting to throw a penalty flag
assign probabilities may be the result of personal experience or secondary
before you know what happened.
information.
Know How To Control
That is why officials need to work in cruise control. Uncertainty
Error ! Limited information prevents estimation of outcome probabilites for
One of the biggest errors that officials fall into is making calls too quickly. alternatives associated with the problem and may force managers to rely on
intuition and “gut feelings.”
You might also like
- Topic 4 - Decision MakingDocument28 pagesTopic 4 - Decision MakingYến NgọcNo ratings yet
- Leadership Management Decision-Making, Management and AdministrationDocument28 pagesLeadership Management Decision-Making, Management and AdministrationPat Mandawe100% (1)
- Welcom EDocument93 pagesWelcom EHồng DungNo ratings yet
- 2.Mgmt Decision MakingDocument38 pages2.Mgmt Decision MakingDevigurumurthy100% (1)
- 10.1 Strategic Decision MakingDocument22 pages10.1 Strategic Decision Makingthomastoner2204No ratings yet
- REVIEWER Engineering ManagementDocument4 pagesREVIEWER Engineering ManagementJohn Raphael JavierNo ratings yet
- Decision MakingDocument2 pagesDecision MakingJohn Alester De GuzmanNo ratings yet
- Management Science Chapter 1 - : Prepared By: Professor Irah Dianne NicolasDocument19 pagesManagement Science Chapter 1 - : Prepared By: Professor Irah Dianne NicolasAnne Maerick Jersey OteroNo ratings yet
- Management Science Prof. Irah Dianne NicolasDocument21 pagesManagement Science Prof. Irah Dianne NicolasNichole ArcletaNo ratings yet
- W3 Part 1 Problem and Decision MakingDocument12 pagesW3 Part 1 Problem and Decision MakingMelani KingsleypillaiNo ratings yet
- Management: Managers As Decision MakersDocument39 pagesManagement: Managers As Decision MakersZorez ShabkhezNo ratings yet
- Business Management - Chapter 2 - Making DecisionsDocument43 pagesBusiness Management - Chapter 2 - Making DecisionsKhondker Zarif AkhterNo ratings yet
- Hand-Out 2studDocument5 pagesHand-Out 2studJessa Eraldin OriginesNo ratings yet
- Unit 03 Decision MakingDocument28 pagesUnit 03 Decision Makingk58 Duong Thi HangNo ratings yet
- Es15 ReviwerDocument37 pagesEs15 ReviwerfjanemichelleNo ratings yet
- What To Do? and How?: Decision MakingDocument3 pagesWhat To Do? and How?: Decision MakingKhan AsifNo ratings yet
- DECISION POWER PPT 54Document24 pagesDECISION POWER PPT 54divyang natali100% (1)
- Roles Creative Thinking and Problem Solving EngDocument2 pagesRoles Creative Thinking and Problem Solving Engammaaraha47No ratings yet
- Universidad Juárez Autónoma de Tabasco División Academica de Ciencias Económicas AdministrativasDocument3 pagesUniversidad Juárez Autónoma de Tabasco División Academica de Ciencias Económicas AdministrativasEsteban MoralesNo ratings yet
- FINAL (Enregistrement Automatique)Document15 pagesFINAL (Enregistrement Automatique)Aymane Aymane RajawiNo ratings yet
- Organizational Decision Making: Tab 5 Tab 2 Tab 1 Tab 4 Tab 3 Tab 6 Tab 7Document34 pagesOrganizational Decision Making: Tab 5 Tab 2 Tab 1 Tab 4 Tab 3 Tab 6 Tab 7Hồng DungNo ratings yet
- If We're All So Busy, Why Isn't Anything Getting Done?: People & Organizational Performance PracticeDocument6 pagesIf We're All So Busy, Why Isn't Anything Getting Done?: People & Organizational Performance PracticeRahul PambharNo ratings yet
- Decision-Making May Be Defined As The Process of Defining The Problem and Identifying and ChoosingDocument5 pagesDecision-Making May Be Defined As The Process of Defining The Problem and Identifying and ChoosingThe PsychoNo ratings yet
- CH - 3Document38 pagesCH - 3TamiratNo ratings yet
- Problem Solving and Decision MakingDocument4 pagesProblem Solving and Decision MakingJohn Francis Idanan0% (1)
- Decision Making: Lingayas VidyapeethDocument14 pagesDecision Making: Lingayas VidyapeethGunjanNo ratings yet
- Decision MakingDocument25 pagesDecision MakingJulius EstrelladoNo ratings yet
- Decision Making and Problem Solving & Managing - Gashaw PDFDocument69 pagesDecision Making and Problem Solving & Managing - Gashaw PDFKokebu MekonnenNo ratings yet
- (ASC) Management Science Reviewer - Quiz #1Document24 pages(ASC) Management Science Reviewer - Quiz #1hello hayaNo ratings yet
- W5-L5 (Decision Making) Part IDocument41 pagesW5-L5 (Decision Making) Part IasadNo ratings yet
- CH 9 Decision MakingDocument24 pagesCH 9 Decision MakingTanvi AjmeraNo ratings yet
- Business & Management Mind Map - W9Document2 pagesBusiness & Management Mind Map - W9Diva Tertia AlmiraNo ratings yet
- Meet 2Document28 pagesMeet 2Alvina 4321No ratings yet
- ES 70 Module 2 - Decision MakingDocument12 pagesES 70 Module 2 - Decision MakingSteven Claude DigamonNo ratings yet
- ES 70 Module 2 - Decision MakingDocument12 pagesES 70 Module 2 - Decision MakingSteven Claude DigamonNo ratings yet
- B5301 W09 Week11Document18 pagesB5301 W09 Week11imran27pk100% (2)
- Decision Making: A Presentation OnDocument32 pagesDecision Making: A Presentation OnANDHRA PRADESH PRODUCTIVITY COUNCILNo ratings yet
- Decision Making: A Presentation OnDocument32 pagesDecision Making: A Presentation OnANDHRA PRADESH PRODUCTIVITY COUNCILNo ratings yet
- Power Management NatashaDocument15 pagesPower Management NatashaLucia Vidal morteraNo ratings yet
- Slide - Chapter 2Document23 pagesSlide - Chapter 2Nor Azlina RaisNo ratings yet
- Managierial Decision Making ProcessDocument52 pagesManagierial Decision Making Processamila1989No ratings yet
- Creative Problem Solving Approach and ProcessDocument53 pagesCreative Problem Solving Approach and ProcessShashank YadavNo ratings yet
- Decision MakingDocument25 pagesDecision MakingJulius EstrelladoNo ratings yet
- Decision - Making: An Essence To Problem SolvingDocument19 pagesDecision - Making: An Essence To Problem SolvingSubhash SoniNo ratings yet
- Decision and Problem SolvingDocument17 pagesDecision and Problem SolvingGnaneswar PiduguNo ratings yet
- Week 1 - Introduction To The Module and Creative Decision MakingDocument25 pagesWeek 1 - Introduction To The Module and Creative Decision MakingAdrianaNo ratings yet
- Chapter 5 Mice ManagementDocument26 pagesChapter 5 Mice Managementangel dacurawatNo ratings yet
- Decision MakingDocument2 pagesDecision MakingJohanna ElesterioNo ratings yet
- Rep 0 RTDocument3 pagesRep 0 RTEncylclightNo ratings yet
- Presentation 1Document23 pagesPresentation 1ankitjhaNo ratings yet
- Org - MGT 2nd MasteryDocument9 pagesOrg - MGT 2nd MasteryLettrice NovelstarNo ratings yet
- Unit 7 Decision MakingDocument3 pagesUnit 7 Decision MakingGovinda DahalNo ratings yet
- Managerial EconomicsDocument33 pagesManagerial EconomicsTherese LeyvaNo ratings yet
- PGDHRM Paper I Unit 6Document25 pagesPGDHRM Paper I Unit 6sfghNo ratings yet
- 01 What Managers Do and Leadership StylesDocument3 pages01 What Managers Do and Leadership StylesronaldthemusictechfrogNo ratings yet
- Week 04-05 - Ethical DecisionsDocument27 pagesWeek 04-05 - Ethical DecisionsLycann RolaNo ratings yet
- 3106 1638170348452 CC6052 Lecture wk04 DecisionsDocument56 pages3106 1638170348452 CC6052 Lecture wk04 DecisionsMr GamerNo ratings yet
- Decision MakingDocument3 pagesDecision MakingimadNo ratings yet
- Lecture 12 (MGT)Document20 pagesLecture 12 (MGT)M IshtiaqNo ratings yet
- Trujillo L The Relationship Between Law School and The Bar Exam 78 U.colo .L.rev - 69 2007Document27 pagesTrujillo L The Relationship Between Law School and The Bar Exam 78 U.colo .L.rev - 69 200715-0001No ratings yet
- Book ListDocument21 pagesBook ListDaniel CamposNo ratings yet
- Evolution of Computer Technology Timeline ProjectDocument2 pagesEvolution of Computer Technology Timeline Projectapi-309498815No ratings yet
- Lal Muhammad Elementary Statistics Lecture 2Document16 pagesLal Muhammad Elementary Statistics Lecture 2Muhammad BilalNo ratings yet
- Ice Task 2Document2 pagesIce Task 2nenelindelwa274No ratings yet
- Scientific AttitudesDocument24 pagesScientific AttitudesMayleen Buenavista100% (1)
- Kidzee New Brand Identy 3Document45 pagesKidzee New Brand Identy 3Indulaxmi PressNo ratings yet
- Key Functions of Op. Mgmt.-IMPDocument2 pagesKey Functions of Op. Mgmt.-IMPtapasNo ratings yet
- Study Guide (ITIL 4 Foundation) .PDF Versión 1 (27-44)Document18 pagesStudy Guide (ITIL 4 Foundation) .PDF Versión 1 (27-44)Brayhan Huaman BerruNo ratings yet
- 00 SyllabusDocument4 pages00 Syllabusrmbj94_scribdNo ratings yet
- 3G CommandsDocument22 pages3G CommandsAnup SinghNo ratings yet
- Emc Networker Module For Microsoft Applications: Installation GuideDocument80 pagesEmc Networker Module For Microsoft Applications: Installation GuideShahnawaz M KuttyNo ratings yet
- BCFN 12 Course SyllabusDocument4 pagesBCFN 12 Course Syllabusapi-237777454No ratings yet
- Facebook Addiction and Academic Anxiety Among University StudentsDocument16 pagesFacebook Addiction and Academic Anxiety Among University StudentsLawson SohNo ratings yet
- The Exodus of LanguagesDocument2 pagesThe Exodus of Languagescicak merayapNo ratings yet
- Danielle Nava: Harvard Human Rights JournalDocument1 pageDanielle Nava: Harvard Human Rights JournalfdxgfdgbfbhNo ratings yet
- Cooperative StrategiesDocument20 pagesCooperative Strategiesjamie.pantoja100% (1)
- RGSMC Learning Packet Week 1 P.E 9 UpdatedDocument4 pagesRGSMC Learning Packet Week 1 P.E 9 UpdatedAizel Nova Fermilan ArañezNo ratings yet
- Nelson Mandela University PDFDocument115 pagesNelson Mandela University PDFCarlos Chafla100% (1)
- The Five Factor Model of PersonalityDocument10 pagesThe Five Factor Model of PersonalityCristina Dobre100% (2)
- Foundations EducationDocument28 pagesFoundations EducationDennis KristineNo ratings yet
- Tori AllenDocument2 pagesTori AllengoodrajNo ratings yet
- Writers Craft LP - Day 1Document9 pagesWriters Craft LP - Day 1api-357297274No ratings yet
- The Problem and Its BackgroundDocument39 pagesThe Problem and Its BackgroundsigfridmonteNo ratings yet
- Resume Abdullah AljufayrDocument5 pagesResume Abdullah AljufayrAbdullah SalehNo ratings yet
- Discursive Strategies of - Purity of Blood - in The First New Chronicle and Good Government by Felipe Guaman Poma de AyalaDocument97 pagesDiscursive Strategies of - Purity of Blood - in The First New Chronicle and Good Government by Felipe Guaman Poma de AyalaFlorin TanasoiuNo ratings yet
- Clustering of PWUDs PUYATDocument2 pagesClustering of PWUDs PUYATJanelkris PlazaNo ratings yet
- Lars2 AnswersDocument14 pagesLars2 Answersyusuf ceribasNo ratings yet
- A Study On Educational Thought's of Aurobindo Ghosh With Relevance To Present Educational ContextDocument2 pagesA Study On Educational Thought's of Aurobindo Ghosh With Relevance To Present Educational ContextSowmya VijayNo ratings yet
- Mr. Aditya Sondhi Visiting FacultyDocument1 pageMr. Aditya Sondhi Visiting FacultyRitesh YanappaNo ratings yet