Professional Documents
Culture Documents
TheEarthAsASphere F3 Loibanguti (2022)
Uploaded by
Alexander MugetaOriginal Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
TheEarthAsASphere F3 Loibanguti (2022)
Uploaded by
Alexander MugetaCopyright:
Available Formats
THE EARTH AS A
SPHERE
Tanzania syllabus
Author: Baraka Loibanguti
For more contact me:
Email: barakaloibanguti@gmail.com
Mobile: +255621842525
Loibanguti, (Baraka) 0621842525 Page 1 of 8
BARAKA LOIBANGUTI
TEL: +255621842525
E-mail: barakaloibanguti@gmail.com
Loibanguti, (Baraka) 0621842525 Page 2 of 8
THE EARTH AS A SPHERE
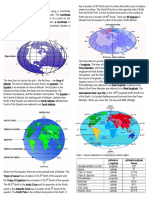
The Earth: This is one of the planets in our solar LONGITUDES:
system. This is a planet we live on (up to now 2021) These are imaginary lines drawn on the surface of the
earth running from north pole to the south pole
The sphere: Is a solid object (3 dimensional) with
round the earth, and they are measured in degrees
round surface which is equidistant from the fixed
West and East of the prime meridian called
point called Center.
GREENWICH MERIDIAN.
The name Greenwich meridian is given to this longitude because
it passes through the Greenwich City in England
The earth
LATITUDES: These are imaginary lines drawn on
the surface of the earth running from East to west
around the earth and they are measured in
degrees North and South of the equator.
The latitude which divides the earth into two
equal hemispheres is called the EQUATOR.
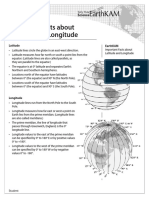
Facts about longitudes
They are also called meridians
Run in a north-south direction
Measured in degrees East or west of the
prime meridian
Crosses the equator at 90o
They are all equal in length
They are all great circle
The central angle may be from the parallel of latitudes
or longitudes
If the central angle is from latitudes, it will lie on the
same meridian. The rules like
• SSS – Same Sign Subtract and
Facts about Latitudes
• DSA – Different Sign Add
They are all parallel, never meet
applied
Run in an east-west direction
Cross the prime meridian at 90o
Get shorter toward the poles, with the only
Equator the longest (great circle)
Loibanguti, (Baraka) 0621842525 Page 3 of 8
Importance studying latitudes and longitudes
When used together, longitude and latitude define a specific
location through geographical coordinates. These
coordinates are what the Global Position System (GPS) uses Example 1
to provide an accurate locational relay.
Used in Time and dates: International Date Line: Calculate the central angle subtended by the
The International Date Line (IDL) is on the opposite side of the
following points on the earth surface.
earth to the Prime Meridian, located at 180 degrees.
Together, the Prime Meridian and IDL divide the earth into
A(30oN, 60oW) and B(70oN, 60oW)
two halves: the Western and Eastern Hemispheres. Working;
The IDL is the point at which the change of day takes place. Note that, these points lie on the same meridian
When you travel from east to west across the IDL, you gain a 60oW, so they lie on the great circle.
day. Likewise, when you travel from east to west you lose a
The central angle = ϴ = 70o – 30o = 40o. The rule here
day. Example: Australians travelling to the USA often arrive at
their destination before their departure time, because is SSS, because A is 30o North and B is 70o North too.
they've gained a day. When they go back to Australia So, the SSS is used to get the central angle
however, they lose a day. IDL goes zig-zag in order to avoid
the confusion of having different dates in the same country.
Used in navigation: No roads in the oceans or seas. The
navigators use Longitudes and latitudes to now their current
position and their destination. The compass and the GPS Example 2
devices work together to guide them to the destination. Same
applies to airplanes.
Calculate the size of the central angle subtended by
the following points on the earth surface
Points on the surface of the earth C(50oN, 45oE) and D(35oS, 45oE)
When using longitudes and latitudes to show the place Working;
on the earth surface it is always the latitude first and Note that, these points lie on the same meridian,
then longitude. The latitudes end with North (N) or 45oE, so, they lie on the great circle.
South (S) while longitudes end with West (W) or East (E). The central angle = ϴ = 50o + 35o = 85o. The DSA rule
Example: Arusha Tanzania is at (3.4oS, 36.7oE) applies here because C is on latitude 50o North while
Central angle D is on latitude 35o South. These are different sides,
A central angle is subtended on the great circle and the rule is DSA.
(meridian or longitude) if the latitude degree changes
while the longitude degree is the same.
Points like P(X1oN/S, YoE/W) and Q(X2oN/S, YoE/W) is on
the great circle.
DISTANCE ALONG THE GREAT CIRCLE
Central angle is an angle made at the center of the The distance can be in km or nm. The great circles
earth. distance are all meridian including the equator.
Let the circle to the left be the
A
meridian around the world.
We are interested with the
distance along this median
ϴ
which is the circumference of
the circle.
The full circle has 360o while
B the subtended arc has ϴ
degree.
• Let the length AB be D
• The circumference be C
Loibanguti, (Baraka) 0621842525 Page 4 of 8
(b) Dnm = 60 θ
By similarities concept;
Dnm = 60 63 = 3780 nm
C D Cθ
= thus D =
360 θ 360 Example 6
C = 2 πR
A ship sails 5000km due North from (42oN, 50oW). Find it is
2 πRθ new position for the journey.
D= Simplifying,
360 Workings
πRθ xo N
Dkm = km (i)
180
42oN
Dnm = 60 θ nm (ii)
ϴ
Example 50OW
3
Calculate the distance in kilometers from these two
towns A(40oN, 70oW) and B(25oS, 70oW)
Working
ϴ = xo – 42o
Central angle = ϴ = 40o + 25o = 65o
π 6370(x − 42)
πRθ 5000 = km
D= 180
180
45 = x – 42
3.14 6370 65
D= X = 87o
180
The new position of the ship is (87oN, 50oW)
Distance = 7222.9 km
Example 4 Example 7
Find distance between two towns located on latitude
Find the distance along a circle of longitude
40oN and 60oS both lies on the median 103oW
between A(28oN, 30oE) and B(12oS, 30oE) in both
Working km and nm
πRθ In km
Dkm = km
180 πRθ
3.14 6370 100 Dkm = , and ϴ = 28o + 12o = 40o
Dkm = = 11112.1 180
180 3.14 6370 40
The distance between the towns is 11112.1 km Dkm = = 4447.1km
180
In nm
Example 5 Dnm = 60 θ
Dnm = 60 40 = 2400 nm
Find the distance in both km and nm between the
following places
Morogoro (7oS, 38oE) and Moscow (56oN, 38oE)
In Km
πRθ
Dkm = km
180
π 6370 63
Dkm = km = 7004.2km
180
Loibanguti, (Baraka) 0621842525 Page 5 of 8
Example 8 Example 9
Find the length of the equator around the earth in Find the length of the latitude 75oS in km.
Km and in Nm. Working
Working L = 2πRcos β
Distance of the equator is the circumference of L = 2 × 3.14 × 6370 cos (75o) = 10359 km
the circle with R = 6370km
In km Example 10
Dkm = 2 πR , Thus,
Find the length of latitude 53oN in nm
Dkm = 2 3.14 6370 = 40023.89km
Working
In nm Dnm= 60×360o × cosβ
Dnm = 60 θ Dnm = 60 × 360o × cos (53o) = 13000nm
Dnm = 60 × 360o = 21600nm OR using conversion 1.852 km = 1 nm
DISTANCE ALONG THE SMALL CIRCLE D
Dnm = km nm
The distance along the small circle is all distances 1.852
involving latitudes excluding the equator. The 2 3.14 6370 cos (53)
Dnm = = 13000 nm
distance along the latitudes is what we refer as the 1.852
small circle distance.
DISTANCE ALONG TWO POINTS ON PARALLEL OF
r LATITUDE
A β B
The distance in km is given by
R πRθcosβ
C D Dkm =
180
β R The distance in nm is given by
Dnm = 60 θcos(β)
In both cases ϴ is the degree change in longitude while
β is the degree of the latitude in concern.
Example 11
Suppose, we want to find the length of the latitude Find the distance in both km and nm from the following
ϴ North. (see the figure above) points A(80oN, 30oE) and B(80oN, 35oW)
AB is parallel to CD while CD and CB are both radii Working
of the earth, therefore, angle ABC = angle BCD. Let For this case,
AB be r (radius of the latitude), using cosine
ϴ = 30o + 35o = 65o
formula
β = 80o (degree of latitude)
Adjacent
cos =
Hypotenuse
π 6370 65 cos(80)
r Dkm = = 1255 km
cos = r = Rcos 180
R
and
The length of the latitude is the perimeter of the
circle around the earth with radius r.
Thus, the length of any latitude is given by D nm = 60 65 cos(80) = 677 nm
L = 2 πr 2 πRcos
Loibanguti, (Baraka) 0621842525 Page 6 of 8
Example 12
71.8o = 19o +
Find the distance along a circle of latitude between = 71.8 − 19 = 52.8
M(30oN, 48oW) and N(30oN, 79oW) in both km and nm The position of a ship is (40oN, 52oE)
Working
This is the distance along the small circle MISCELLANEOUS EXAMPLES
ϴ = 79o – 48o =31o and β = 30o
πRθcosβ Example 15
Dkm =
180
π 6370 31 cos 30 An airbus started a journey at Tropic of Cancer 100oE to
Dkm =
180 Tropic of Capricorn while maintaining the longitudes. If
Dkm = 2985 km the journey started at 10:15 pm on Tuesday at the speed
Dnm = 60 θcosβ , thus Dnm = 60 31 cos 30 of 792 knots. When and at what time will it reach the
Dnm = 1611 nm destiny?
Working
T. Cancer (23.5oN, 100oE) and T. Capricorn (23.5oS, 100oE)
Example 13
Dnm = 60ϴ
Points A and B both lies on the same latitude 36oS of the ϴ = 23.5o + 23.5o = 47o
equator. The longitude of A is 40oW. If the distance Dnm = 60 × 47o = 2820 nm
from A to B is 194.2 nautical miles, find the degree of Distance
Speed =
longitude of B correct to nearest whole number. Time
Working 2820 2820
792 = thus T = = 3.56
Dnm = 60 θcosβ T 792
It took 3 hours, 33 minutes and 36 second to reach the
Given β = 36o while ϴ = ?
destination.
194.2 = 60 × ϴ x cos(36o)
The airbus will reach the destination at 1:33:36 on the
ϴ = 4o
next day, Wednesday.
But ϴ = 40o ± where is the degree of longitude of
B
Question: Repeat example 15 above if the airbus started
• Let assume B is in the west of A
at Antarctic circle to the Arctic circle on longitude 33oW.
= − 40 thus = 4 + 40 = 44 the degree of
longitude of B is 44o Example 16
• Again, let assume B to be in the east of A, thus
Three towns X, Y and Z are on the same latitude, 31oN with
= 40 − 4 = 36
town Y lie East of X while West of Z. If Y is on prime
The longitude of B may be 44oW and 36oW
meridian and the distance between XY is 7200nm while
the distance between XZ is 11400nm. Find the positions
Example 14
of X, Y and Z.
Working
A ship starts its journey at (40oN, 19oW) and sails due
Distance XY = 7200nm
East 3300 nm. Find the location of its new place.
The longitude of Y = 0o
Working
7200 = 60(x – 0)
Dnm = 60ϴcosβ
The longitude of X is 120o. The position of X is (31oN,
3300 = 60×ϴ×cos40o
120oW). The position of Y is given (31oN, 0o)
3300
θ= = 71.8o The distance YZ = XZ – XY = 11400 – 7200 = 4200 nm
60 cos (40)
4200 = 60(y – 0) Thus Y = 70oE
But ϴ = 19o + The position of Z is (31oN, 70oE)
Loibanguti, (Baraka) 0621842525 Page 7 of 8
OTHER MATHEMATICS TOPIC NOTES AVAILABLE
FOR O-LEVEL
1) All form 1 Mathematics + ICT topics
2) All form 2 mathematics + ICT topics
3) All form 3 mathematics + ICT topics
4) All form 4 mathematics + ICT topics
5) All additional mathematics topics
FOR A-LEVEL
1) All form 5 advance mathematics topics
2) All form 5 BAM topics
3) All form 6 advance mathematics topics
4) All form 6 BAM topics
PHYSICS NOTES AVAILABLE
FOR O-LEVEL
1) Physics form 1 full notes
2) Physics form 2 full notes
3) Physics form 3 full notes
4) Physics form 4 full notes
PHYSICS + ICT FOR A-LEVEL
*Preparation in progress until January 2022
Author: Baraka Loibanguti
For more contact me:
Email: barakaloibanguti@gmail.com
Mobile: +255714872887
Twitter: @bloibanguti
Loibanguti, (Baraka) 0621842525 Page 8 of 8
You might also like
- The Earth As A Sphere - 025327Document8 pagesThe Earth As A Sphere - 025327Baraka LoibangutiNo ratings yet
- Unit 1 The Earth: StructureDocument8 pagesUnit 1 The Earth: StructureJoseph JeganNo ratings yet
- GlobeDocument8 pagesGlobenidhiNo ratings yet
- Class 9 Geography Module 02Document12 pagesClass 9 Geography Module 02sanjaikumarmishra24No ratings yet
- GLOBEDocument19 pagesGLOBEAditya SiddharthNo ratings yet
- Chapter3 PDFDocument9 pagesChapter3 PDFAdithyan GowthamNo ratings yet
- Std9-Geog-latitude and Longitude (2013)Document8 pagesStd9-Geog-latitude and Longitude (2013)LuciaNo ratings yet
- Globe Latitudes and LongitudesLPsDocument7 pagesGlobe Latitudes and LongitudesLPsbountybackyardNo ratings yet
- Locating Places on a MapDocument5 pagesLocating Places on a MapAnonymous TqDbex8eNo ratings yet
- Latitude & Longitude: Geography 2nd Grade for Kids | Children's Earth Sciences Books EditionFrom EverandLatitude & Longitude: Geography 2nd Grade for Kids | Children's Earth Sciences Books EditionNo ratings yet
- General Navigation HandbookDocument59 pagesGeneral Navigation HandbookManas Batra100% (2)
- Chart WorkDocument485 pagesChart WorkMika Marielle TrincheraNo ratings yet
- Latitudes and Longitudes PDFDocument8 pagesLatitudes and Longitudes PDFvivan874164No ratings yet
- Latitudes and Longitudes: Geography UPSCDocument9 pagesLatitudes and Longitudes: Geography UPSCSoumen DharNo ratings yet
- Latitudes and Longitudes - The GlobeDocument9 pagesLatitudes and Longitudes - The GlobeAshish SoniNo ratings yet
- Locating Places On The Earth AnswersDocument2 pagesLocating Places On The Earth AnswersAnita MenezesNo ratings yet
- EarthKAM GeoUnderstandingMaps PDFDocument4 pagesEarthKAM GeoUnderstandingMaps PDFKalyana AyyaswamyNo ratings yet
- Understanding Maps of EarthDocument4 pagesUnderstanding Maps of EarthKalyana AyyaswamyNo ratings yet
- Emerson Radcliff Espiloy - Hyperdocs-LP1 - LOCATING PLACESDocument16 pagesEmerson Radcliff Espiloy - Hyperdocs-LP1 - LOCATING PLACESEmerson Radcliff EspiloyNo ratings yet
- CBSE Class 6 Geography Notes Chapter 2 - Globe Latitudes and LongitudesDocument3 pagesCBSE Class 6 Geography Notes Chapter 2 - Globe Latitudes and Longitudesdhivya sankarNo ratings yet
- Latitudes and LongitudesDocument13 pagesLatitudes and LongitudesLovekiran KaurNo ratings yet
- Ographic Grid-Latitudes & Longitudes PDFDocument36 pagesOgraphic Grid-Latitudes & Longitudes PDFAadya Singh100% (1)
- Latitude and Longitude For DemoDocument45 pagesLatitude and Longitude For DemoCATHLEENNo ratings yet
- Earth Geometry.Document69 pagesEarth Geometry.Kennedy Mwenya75% (4)
- Social Note (2) For Grade 7Document3 pagesSocial Note (2) For Grade 7Melkamu YigzawNo ratings yet
- Lesson 3 - Unit 1 - Latitude CirclesDocument16 pagesLesson 3 - Unit 1 - Latitude Circlestherealyou61No ratings yet
- Coordinate System ExplainedDocument8 pagesCoordinate System ExplainedMelanie Tagudin TrinidadNo ratings yet
- Solar Geometry Lecture Notes OriginalDocument78 pagesSolar Geometry Lecture Notes Originalangel2010gvNo ratings yet
- Afriyalni Syafril 21045073 Tugas Abi Ke 5Document6 pagesAfriyalni Syafril 21045073 Tugas Abi Ke 5Suci MardatillahNo ratings yet
- Basics of World GeographyDocument19 pagesBasics of World GeographyAbdulBasheerAhamadBaigNo ratings yet
- CH-2 Globe - Latitudes and LongitudesDocument3 pagesCH-2 Globe - Latitudes and LongitudesPriya ChughNo ratings yet
- Navigation Chapter-1: Direction, Latitude and LongitudeDocument76 pagesNavigation Chapter-1: Direction, Latitude and LongitudeAnusher Ansari100% (1)
- Introduction to plan and conduct a passage and determine positionDocument3 pagesIntroduction to plan and conduct a passage and determine positionShashikaNo ratings yet
- The Earth:: 1. A Prime Meridian Is A Meridian (A Line of Longitude) in A Geographical CoordinateDocument3 pagesThe Earth:: 1. A Prime Meridian Is A Meridian (A Line of Longitude) in A Geographical CoordinateKarl KiwisNo ratings yet
- M1 Latitude and Longitude NOTES With Activity (3)Document2 pagesM1 Latitude and Longitude NOTES With Activity (3)kobekob33No ratings yet
- NAVIGATING POSITION, DIRECTION AND DISTANCEDocument3 pagesNAVIGATING POSITION, DIRECTION AND DISTANCEOli Colmenares100% (1)
- Geography Class 6th NcertDocument21 pagesGeography Class 6th NcertPrachi ChoudharyNo ratings yet
- World Geography Sumit Sir EnglishDocument63 pagesWorld Geography Sumit Sir EnglishRavindra Rajput100% (1)
- World Geography - Time & Climate Zones - Latitude, Longitude, Tropics, Meridian and More | Geography for Kids | 5th Grade Social StudiesFrom EverandWorld Geography - Time & Climate Zones - Latitude, Longitude, Tropics, Meridian and More | Geography for Kids | 5th Grade Social StudiesRating: 5 out of 5 stars5/5 (2)
- CH - 2 Logitudes and LatitudesDocument7 pagesCH - 2 Logitudes and LatitudesHarsh SharmaNo ratings yet
- Terrestrial Navigation: BSC Sem I Unit 1 - EarthDocument23 pagesTerrestrial Navigation: BSC Sem I Unit 1 - EarthUtpal KantNo ratings yet
- GENERAL NAVIGATION 3m PDFDocument12 pagesGENERAL NAVIGATION 3m PDFfarryNo ratings yet
- Locating Places on EarthDocument23 pagesLocating Places on Earthellaine.garciaNo ratings yet
- Coordinate System Coordinate SystemDocument32 pagesCoordinate System Coordinate SystemBenedicto IluminNo ratings yet
- Lse 3069 - Location of Places On The EarthDocument19 pagesLse 3069 - Location of Places On The Earthmark shikaazeNo ratings yet
- ClimatologyDocument137 pagesClimatologyMukesh kumar singh BoraNo ratings yet
- WKS CLASS 5 S.S.T CH 2 Parallels and Meridians 2.1Document2 pagesWKS CLASS 5 S.S.T CH 2 Parallels and Meridians 2.1shanayaNo ratings yet
- Solar System and Solar Electricity: Subject Code: EC 38106Document94 pagesSolar System and Solar Electricity: Subject Code: EC 38106Raj TalrejaNo ratings yet
- T G 1664284633 Significance of Longitude and Latitude Activity Sheets Ver 2Document6 pagesT G 1664284633 Significance of Longitude and Latitude Activity Sheets Ver 2rosinaNo ratings yet
- Globe Latitudes and Longitudes Class 6 Notes ExplainedDocument1 pageGlobe Latitudes and Longitudes Class 6 Notes ExplainedKalai Selvi MohanNo ratings yet
- Latitude and LongitudeDocument25 pagesLatitude and Longitudeshalini singhNo ratings yet
- EarthKAM GeoLatLongDocument1 pageEarthKAM GeoLatLongSeanNo ratings yet
- What are longitudes and latitudesDocument2 pagesWhat are longitudes and latitudesClaudene GellaNo ratings yet
- CH - 2 Geography Back Questions AnswersDocument3 pagesCH - 2 Geography Back Questions Answersvijaylaxmi10041992No ratings yet
- Globe Latitudes and Longitudes1Document8 pagesGlobe Latitudes and Longitudes1varun2992No ratings yet
- Latitudes and Longitudes Classwork Geog Cls 5Document4 pagesLatitudes and Longitudes Classwork Geog Cls 5Lubna Shahzada roll:51No ratings yet
- Locating Places on a MapDocument7 pagesLocating Places on a MapJuliet Galletes100% (1)
- ViewpointsDocument4 pagesViewpointsMg BhoneNo ratings yet
- 4 Map ProjectionsDocument38 pages4 Map ProjectionsAlex KuhudzaiNo ratings yet
- Supply Chain Vision in Pharma IndustryDocument20 pagesSupply Chain Vision in Pharma Industryixion11100% (1)
- Australian F1 SUBMACHINE GUNDocument4 pagesAustralian F1 SUBMACHINE GUNCaprikorn100% (4)
- Determination of Equilibrium Constant (KeqDocument0 pagesDetermination of Equilibrium Constant (KeqPablo BernalNo ratings yet
- Fault Codes: Brake (DSC/DXC (Dynamic Stability Control) - Bosch 8.0 - Tyre Pressure Monitoring)Document5 pagesFault Codes: Brake (DSC/DXC (Dynamic Stability Control) - Bosch 8.0 - Tyre Pressure Monitoring)zacarias NiquiceNo ratings yet
- Chana Masala Powder RecipeDocument215 pagesChana Masala Powder RecipeTIRUPUR OFFICENo ratings yet
- Hepatitis - Seminary WorkDocument15 pagesHepatitis - Seminary WorkDraganaNo ratings yet
- Blake - MCQ - 25 ChaptersDocument160 pagesBlake - MCQ - 25 ChaptersAthena LouisseNo ratings yet
- Fine ArtsDocument12 pagesFine Artsatul prajapatiNo ratings yet
- Deltopectoral Approach to the ShoulderDocument28 pagesDeltopectoral Approach to the ShoulderChrysi TsiouriNo ratings yet
- Al KynesDocument12 pagesAl KynesjolanpascualNo ratings yet
- LIST of Tools-BartenderDocument5 pagesLIST of Tools-BartenderLegal DepartmentNo ratings yet
- Using Coffee Grounds as FertilizerDocument18 pagesUsing Coffee Grounds as FertilizerKyle BARRIOSNo ratings yet
- Fmea PC ProcessDocument2 pagesFmea PC Processsudeep_singh1No ratings yet
- Liugong 938l Wheel Loader Parts ManualDocument20 pagesLiugong 938l Wheel Loader Parts Manualviolet100% (56)
- Manifest Guide Ebook PDFDocument4 pagesManifest Guide Ebook PDFAnonymous dqCHWEADzNo ratings yet
- The Macadamia Industry in MalawiDocument77 pagesThe Macadamia Industry in Malawiwarlord_ckNo ratings yet
- The Concept of Representation in Psychology: January 1995Document11 pagesThe Concept of Representation in Psychology: January 1995laith AtekNo ratings yet
- BrinjalDocument2 pagesBrinjalGajananNo ratings yet
- Ujian Akhir Semester Gasal Dinas Pendidikan Kabupaten Sukabumi SMP Negeri 1 Cireunghas TAHUN PELAJARAN 2017/ 2018Document3 pagesUjian Akhir Semester Gasal Dinas Pendidikan Kabupaten Sukabumi SMP Negeri 1 Cireunghas TAHUN PELAJARAN 2017/ 2018DodiSaputraNo ratings yet
- Printing MachineDocument2 pagesPrinting MachinephamdoanketNo ratings yet
- Leptospirosis National Guidelines - Sri LankaDocument56 pagesLeptospirosis National Guidelines - Sri LankaBrainy-Paykiesaurus LuminirexNo ratings yet
- Joe Rozencwajg InterviewDocument17 pagesJoe Rozencwajg InterviewGold SunriseNo ratings yet
- Introduction To Well Completion: (Part - IV)Document36 pagesIntroduction To Well Completion: (Part - IV)Mohamed MahmoudNo ratings yet
- Cambridge English Pre A1 Starters Classroom Activities PDFDocument16 pagesCambridge English Pre A1 Starters Classroom Activities PDFFrank Guevara100% (2)
- What Are The Different Types of PollutionDocument9 pagesWhat Are The Different Types of PollutionPatricia DurandNo ratings yet
- Site Mobilisation ManagementDocument12 pagesSite Mobilisation ManagementmizaNo ratings yet
- VIVI Ref Part 2 PDFDocument111 pagesVIVI Ref Part 2 PDFAaron OliverNo ratings yet
- Unit 1 Purva Swadhyaya QuestionsDocument4 pagesUnit 1 Purva Swadhyaya QuestionsSurrender to Krishna AlwaysNo ratings yet
- DR Vatsal Patel AhmedabadDocument30 pagesDR Vatsal Patel AhmedabadSayali PhansekarNo ratings yet
- Indian MaDocument1 pageIndian MaAnass LyamaniNo ratings yet