100% found this document useful (2 votes)
2K views19 pagesHow To Read Your International (IEC) Style Electrical Schematics
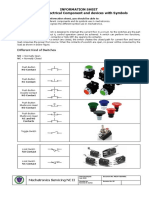
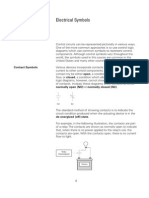
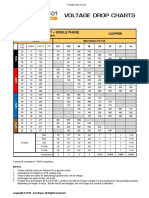
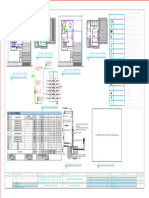
This webinar teaches the keys to reading IEC electrical schematics. It covers understanding how electricity works, the different types of drawings, symbols and abbreviations, how devices operate in circuits, title blocks, notes, and the differences between NEMA and IEC drawings. The presenter explains power and control symbols, IEC relays, contactors, motor protectors, and provides examples of IEC ladder diagrams and prints. Questions are welcomed to gain further understanding of electrical schematics.
Uploaded by
Binod KafleCopyright
© © All Rights Reserved
We take content rights seriously. If you suspect this is your content, claim it here.
Available Formats
Download as PDF, TXT or read online on Scribd
100% found this document useful (2 votes)
2K views19 pagesHow To Read Your International (IEC) Style Electrical Schematics
This webinar teaches the keys to reading IEC electrical schematics. It covers understanding how electricity works, the different types of drawings, symbols and abbreviations, how devices operate in circuits, title blocks, notes, and the differences between NEMA and IEC drawings. The presenter explains power and control symbols, IEC relays, contactors, motor protectors, and provides examples of IEC ladder diagrams and prints. Questions are welcomed to gain further understanding of electrical schematics.
Uploaded by
Binod KafleCopyright
© © All Rights Reserved
We take content rights seriously. If you suspect this is your content, claim it here.
Available Formats
Download as PDF, TXT or read online on Scribd
- Introduction
- Keys to Reading Drawings
- Understanding Electricity
- Different Types of Drawings
- Symbols and Abbreviations
- Ladder Diagrams
- IEC Components
- Conclusion