Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Taxation
Uploaded by
Fiona MiralpesOriginal Description:
Original Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Taxation
Uploaded by
Fiona MiralpesCopyright:
Available Formats
lOMoARcPSD|30374161
Taxation- General Principles, Tax Remedies, Taxability of
Individuals and Corporations- Notes and Quiz
BS Accountancy (New Era University)
Scan to open on Studocu
Studocu is not sponsored or endorsed by any college or university
Downloaded by Lotivio Ma. Mica (lotiviomica@gmail.com)
lOMoARcPSD|30374161
Gener al Pr inciples of Taxation
TAXATION REVIEW
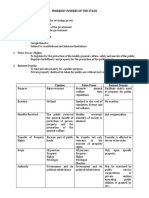
Inherent Powers of the State
- Power existing as natural or basic part of every sovereign state, without being
conferred or granted by the people or the Constitution
DISTINCTIONS AMONG THE THREE (3) INHERENT POWERS OF THE STATE
TAXATION POLICE POWER EMINENT DOMAIN
Power to enforce Power to make and Power to take private
NATURE
contributions to raise implement laws for the property for public use
gov't funds general welfare with just compensation
May be granted to
AUTHORITY
Government only Government only public service/utility
companies
PURPOSE For the support of the Promotion of general The taking of private
government through regulation property for public use
Community or a class On an individual as the
Community or a class of owner of personal
of individuals
PERSONS individuals property
Applies to all
AFFECTED Applies to all persons,
persons, property and
property and excises that
excises that may be Only particular property
may be subject thereto
subject thereto is comprehended
Property is Property is noxious or
TYPE OF Property is wholesome
wholesome and is intended for a noxious
PROPERTY devoted to public use purpose and as such
and is devoted to public
use or purpose
or purpose taken and destroyed
Contribution becomes No transfer or title. There
EFFECT part of public fund
There is a transfer of
may just be a restraint on
title or property
injurious use of property
RIGHTS
AFFECTED Property right Property right and liberty Property right
Plenary, Broader in application. Merely a power to take
SCOPE
comprehensive General power to make private. property for
supreme and implement law. public use
No direct and immediate
in form of protection benefit but only such as
BENEFITS Market value of property
and benefits received may arise from the
RECEIVED taken
from government maintenance of a healthy
economic standard of
society
AMOUNT Sufficient to cover cost of
No imposition. The
the license and the
OF No limit owner is paid equivalent
necessary expenses of
IMPOSITION to the fair value of his
police surveillance and
property.
regulation
Downloaded by Lotivio Ma. Mica (lotiviomica@gmail.com)
lOMoARcPSD|30374161
Gener al Pr inciples of Taxation
TAXATION REVIEW
PURPOSES OF TAXATION
1. Primary Purpose (also called Revenue or Fiscal Purpose)
- To raise revenues/funds to defray the necessary expenses of the
government
2. Secondary Purpose:
a. Regulatory Purpose
- employed as a devise for regulation or control (to implement the
police power of the State for the promotion of the general welfare)
by means of which certain effects or conditions envisioned by the
government may be achieved.
b. Compensatory Purposes
- Reduction of Social Inequality
- Economic Growth
- Protect local industries against unfair competition ³
protectionism
Nature and Characteristics of Taxation
1. Inherent Power - may be exercised although not expressly granted by the
constitution
2. Essentially a legislative function - only the legislative can impose taxes
3. Subject to inherent and constitutional limitations- not an absolute power
4. For public purpose
5. The strongest of all the inherent powers of the State.
6. Subject to treaty or comity
7. Generally payable in money
8. Territorial in scope
Absence of inherent
Power to tax is comprehensive, plenary, supreme &
and constitutional ³
unlimited
limitations
ÿ
<The power to tax includes the power to destroy=
-Justice Marshall
Taxes Defined
- enforced proportional contributions from persons and property, levied by
the State by virtue of its sovereignty for the support of the government and
for all its public needs.
Downloaded by Lotivio Ma. Mica (lotiviomica@gmail.com)
lOMoARcPSD|30374161
Gener al Pr inciples of Taxation
TAXATION REVIEW
ESSENTIAL CHARACTERISTICS OF TAX
a. forced charge, imposition or contribution
b. pecuniary burden payable in money, not in kind!
c. imposed for public purposes
d. imposed pursuant to a legislative authority
e. levied within the territorial and legal jurisdiction of a state
f. assessed in accordance with reasonable rule of apportionment ³ ability to
pay theory
Theory and Basis of Taxation
1. Necessity Theory
- <existence of government is a necessity=.
- power based upon necessity
- The government cannot continue to perform of serving and protecting its
people without means to pay its expenses. For this reason, the state has
the right to compel all its citizens and property within its limits to contribute
2. Lifeblood Doctrine
- Taxes are the lifeblood of the government without which it can neither
exist nor endure. Upon taxation depends the State's ability to serve the
people for whose benefits taxes are collected
MANIFESTATION OF THE LIFEBLOOD DOCTRINE/THEORY:
o No Estoppel against the Government
o Collection of taxes cannot be enjoined (stopped) by injunction
o Taxes could not be the subject of compensation or set-off
o A valid tax may result in the destruction of the taxpayer's property
o Right to select objects (subjects) of taxation
3. The Benefits-Protection Theory
- reciprocal duties of "protection and support" between the State and its
inhabitants.
- State ³ collects taxes from the subjects of taxation in order that it may
be able to perform the functions of government.
- Citizens ³ pay taxes in order to be secured in the enjoyment of the
benefits of organized society.
- This theory spawned the Doctrine of Symbiotic Relationship which
means, taxes are what we pay for a civilized society
Downloaded by Lotivio Ma. Mica (lotiviomica@gmail.com)
lOMoARcPSD|30374161
Gener al Pr inciples of Taxation
TAXATION REVIEW
Similarities among the 3 Inherent Powers
1. Inherent in the State
2. Exist independently of the constitution although the conditions for their
exercise may be prescribed by the constitution.
3. Constitutes the 3 methods by which the State interfere with private
rights and property
4. Legislative in nature and character.
5. Presuppose an equivalent compensation received, directly or indirectly, by
the persons affected.
require or imply / forced charge
Scope of the Taxing Power of the Legislative
³ power of taxation is the most absolute of all powers of
According to the government
the Supreme ÿ
Court has the broadest scope of all the powers of the
government
ÿ
in the absence of limitations, it is considered as
comprehensive, unlimited, plenary and supreme
- Comprehensive- nearly all elements/
complete
- Plenary- absolute
- Supreme -superior to all others
The matters within the competence of the legislature include the determination of
the following:
1. Subject or object (person, property and excises/privileges) to be taxed
2. Purpose of the tax as long as it is a public purpose
3. Amount or rate of the tax
4. Kind of tax
5. Apportionment of the tax (i.e., whether the tax shall be general or limited
to a particular locality or partly general and partly local)
6. Situs of taxation
7. Manner or method of collection
Downloaded by Lotivio Ma. Mica (lotiviomica@gmail.com)
lOMoARcPSD|30374161
Gener al Pr inciples of Taxation
TAXATION REVIEW
Stages/Aspects of Taxation
1. Levying or Imposition
- involves the passage of tax laws or ordinances (in case of LGU)
through the legislature
2. Assessment and Collection
- involves the act of administration and implementation of tax laws by the
executive through its administrative agencies such as the BIR and the
Bureau of Customs.
• Assessment
- determination by the executive branch (i.e., BIR, BOC, LGU) of
the correct amount of the tax
• Collection of the tax levied, which is essentially administrative in
character.
Principles of Sound Tax System (3)
A sound tax system should satisfy all the principles of taxation, such as:
• the ability to generate sufficient revenues
• fulfill the socio-economic objectives
• should not hamper the productive system of the economy
ELEMENTS OF SOUND TAX SYSTEM
1. Fiscal Adequacy
- The sources of government revenue must be sufficient to meet
government expenditures and other public needs
2. Theoretical Justice
- must be based on the taxpayer's ability to pay
- taxation must be progressive conformably with the constitutional
mandate that congress shall evolve a progressive system of taxation.
3. Administrative Feasibility
- Tax laws must be capable of convenient, just and effective
administration free from confusion and uncertainty
- should have the merits of simplicity, flexibility and diversity.
Downloaded by Lotivio Ma. Mica (lotiviomica@gmail.com)
lOMoARcPSD|30374161
Gener al Pr inciples of Taxation
TAXATION REVIEW
LIMITATIONS ON THE TAXING POWER
A. Inherent Limitations- inherent limitations proceed from the very nature of
the taxing power itself. The taxing power has very distinct and positive
limitations some of which inhere in its very nature and exist whether
declared or not declared in the written constitution.
1. Public purpose
Proceeds from tax must be used for:
a. Support of the government.
b. Some of the recognized objects of government.
c. To promote the welfare of the community (not individuals)
2. Situs of taxation or territoriality
The taxing power is limited to person and property within and subject to its
jurisdiction
PLACE OF TAXATION
a. The state where the subject be taxed has a situs may rightfully levy
& collect tax
b. The situs is necessarily in the State which has jurisdiction or which
exercises dominion over the subject in question
FACTORS TO CONSIDER IN DETERMINING SITUS OF TAXATION
a. Subject matter (person, property, activity)
b. Nature of tax
c. Citizenship
d. Residence of the taxpayer
APPLICATION SITUS TAXATION SUBJECT MATTER
SUBJECT MATTER SITUS
Persons Residence the taxpayer
Real Property Location
Tangible Personal Property Location
Intangible Personal Property Domicile of the owner
Residence, citizenship, source of
Income
income
Business Place business
Gratuitous Transfer of Residence or citizenship of the
Property transferor or location of property
Downloaded by Lotivio Ma. Mica (lotiviomica@gmail.com)
lOMoARcPSD|30374161
Gener al Pr inciples of Taxation
TAXATION REVIEW
EXC.
TAXABLE ON
Income taxation on RC & ³
Income within and outside PH
DC
Transfer Taxation on ³ Transfer of property located w/in &
Resident/Citizen
outside PH
(RC, NRC, RA)
3. International comity treaty
A State cannot tax another based on the principle of Sovereign Equality
among States (i.e., tax law passed imposing taxes on foreign
ambassadors not a valid law)
4. Non-delegability of the Taxing power (Enactment Tax Laws)
- The taxing power is purely legislative; hence power cannot be
delegated either to the executive or judicial departments.
- The limitation arises the doctrine of separation of powers among three
branches the government.
EXCEPTIONS TO THE RULE AGAINST DELEGATION:
a. Delegation to the President, subject to some limitations and
restrictions, to fix within specified limits, tariff rates and tonnage or
wharfage duties and other duties and imposts.
b. Delegation to local governments the power to create its own
sources of revenues and to levy taxes, subject to such limitations as
provided by law.
c. Delegation to administrative agencies certain aspects of the
taxing process that are not legislative such as:
▪ the power to fix value of property for purposes of taxation
pursuant to fixed rules
▪ the power to assess and collect taxes
5. Tax Exemptions of the government
a. Agencies performing governmental functions are tax-exempt
unless expressly taxed.
b. Agencies performing proprietary functions are subject to tax
unless expressly exempted
c. GOCCS performing proprietary functions are subject to tax,
however, the following are granted exemptions:
Downloaded by Lotivio Ma. Mica (lotiviomica@gmail.com)
lOMoARcPSD|30374161
Gener al Pr inciples of Taxation
TAXATION REVIEW
▪ Government Service Insurance System (GSIS)
▪ Social Security System (SSS)
▪ Philippine Health Insurance Corporation (PHIC)
▪ Local Water Districts (RA 10026)
NOTE: Philippine Charity Sweepstakes Office (PCSO) is tax-exempt prior to Jan.
1, 2018 (effectivity of TRAIN Law).
B. Constitutional Limitations on the Taxing Power
1. Observance of due process of law
2. Equal protection of law
3. Uniformity in taxation
4. Progressive scheme of taxation
5. Non-imprisonment for non-payment of poll tax
6. Non-impairment of the obligations of contracts
7. Free-worship clause
8. Exemption of charitable institutions, churches, parsonages, or convents
appurtenant thereto, mosques, and non-profit cemeteries, and all lands,
buildings and improvements actually, directly and exclusively used for
religious, charitable or educational purposes.
9. Exemption from taxes of the revenues and assets of non-profit, non-
stock educational institutions including grants, endowments, donations
or contributions for educational purposes
10. Non-appropriation of public funds or property for the benefit of any
church, sect or system of religion, etc.
11. No money shall be paid out of the Treasury 'except in pursuance of
an appropriation made by law,
12. Concurrence of a majority of ALL MEMBERS OF CONGRESS for
the passage of a law granting tax exemption
13. Non-diversification of tax collections
14. The President shall have the power to veto any particular item(s) in
an appropriation, revenue or tariff, but the veto shall not affect the
item(s) to which no objection has been made.
15. Non-impairment of the jurisdiction of the Supreme Court to review
tax cases
16. Appropriations, revenue or tariff bills shall originate exclusively in the
House of Representatives but the Senate may propose or concur with
amendments.
17. Each local government unit shall exercise the power to create its
own sources of revenue and shall have a just share in the national
taxes.
Downloaded by Lotivio Ma. Mica (lotiviomica@gmail.com)
lOMoARcPSD|30374161
Gener al Pr inciples of Taxation
TAXATION REVIEW
NATIONAL TAXES vs. LOCAL TAXES
NATIONAL LOCAL
AUTHORITY Inherent Power Delegated Power
Legislative in nature
Legislative in nature through
through enactment of tax
NATURE enactment of local ordinances by
laws by the Congress and
the local legislative branch
the Senate.
1. Levying = Congress 1. Levying = Legislative branch
PROCESS 2. Assessment/ Collection of the LGU
= BIR & BOC 2. Assessment/Collection
= Treasurer
National Internal Revenue Taxes under the administration of the BIR:
a. Income Tax
b. Estate and donor's tax
c. Value-added tax
d. Other percentage taxes
e. Excise taxes
f. Documentary stamp taxes
DOUBLE TAXATION
KINDS OF DOUBLE TAXATION
a. Direct Duplicate Taxation
- objectionable and prohibited because it violates the constitutional
provision on uniformity and equality. It means:
▪ Taxing twice;
▪ By the same taxing authority;
▪ Within the same jurisdiction or taxing district;
▪ For the same purpose;
▪ In the same year or taxing period; and
▪ Same kind or character of tax
b. Indirect Duplicate Taxation
- not legally objectionable.
- extends to all cases in which there is a burden of two or more pecuniary
imposition but imposed by different taxing authorities
Downloaded by Lotivio Ma. Mica (lotiviomica@gmail.com)
lOMoARcPSD|30374161
Gener al Pr inciples of Taxation
TAXATION REVIEW
SOURCES OF TAX LAWS
a. Constitution
b. Tax Treaties and Conventions with Foreign Countries
c. The "Tax Code" [RA No. 8424- National Internal Revenue Code, as
amended (le, RA 10963-TRAIN Law; RA 11534-CREATE Law), Tariff and
Customs Code, and portion of the Local Government Code]
d. Statutes and laws like RA 1125 (an Act Creating the Court of Tax Appeals)
and RA 7716 (E-VAT Law)
e. Presidential Decrees and Executive Orders
f. Court Decisions
g. Revenue Issuances promulgated by the Department of Finance such as
Revenue Regulations (RR) Revenue Memorandum Circulars (RMCS),
Revenue Memorandum Orders (RMOS), BIR Revenue Rulings and those
of the Bureau of Customs like Customs Memorandum Orders
h. Local Tax Ordinances
ORDER OF PRIORITY:
1 Constitution
2 Tax treaties
3 Tax Laws/statues and judicial decisions
4 Revenue issuances (revenue regulations, revenue memorandum circulars,
revenue memorandum orders, revenue rulings, etc.)
NATURE OF TAX LAWS
• civil and not penal in nature, although there are penalties provided for
their violation.
• The purpose of tax laws imposing penalties for delinquencies is to compel
the timely payment of taxes or to punish evasion or neglect of duty in
respect thereof.
CONSTRUCTION OR INTERPRETATION OF TAX LAWS IN CASE OF DOUBT
OR AMBIGUITY
a. Tax statutes are construed strictly against the government and
liberally in favor of the taxpayer. Taxes, being burdens, are not to
be presumed beyond what the statute expressly and clearly
FAVOR
declares.
{
b. Provisions granting tax exemptions are construed strictly against
the taxpayer claiming tax exemption and liberally in favor of the
government.
Downloaded by Lotivio Ma. Mica (lotiviomica@gmail.com)
lOMoARcPSD|30374161
Gener al Pr inciples of Taxation
TAXATION REVIEW
APPLICATION OF TAX LAWS
- prospective in operation because the nature and amount of the tax
could not be foreseen and understood by the taxpayer at the time the
transactions which the law seeks to tax was completed.
EXCEPTION:
While it is not favored, a statute may nevertheless operate
retroactively provided it is expressly declared or is clearly the legislative
intent. But a tax law should not be given retroactive application when
it would be harsh and oppressive.
CLASSIFICATION OF TAXES
A. According to Subject Matter:
▪ Personal, Poll or Capitation Tax
- tax of a fixed amount imposed upon individual, whether citizens or
not, residing within a specified territory without regard to their
property or the occupation in which he may be engaged (e.g. basic
community tax)
▪ Property Tax
- tax imposed on property, whether real or personal, in proportion
either to its value, or in accordance with some other reasonable
method of apportionment (e.g. real estate tax)
▪ Excise Tax
- Residual definition
- tax on the exercise of certain rights and privileges (e.g. income tax,
estate tax, donor's tax, VAT)
Downloaded by Lotivio Ma. Mica (lotiviomica@gmail.com)
lOMoARcPSD|30374161
Gener al Pr inciples of Taxation
TAXATION REVIEW
B. According to Who Bears the Burden
DIRECT TAX INDIRECT TAX
e.g. income tax, estate tax, donor's e.g. VAT and OPT
tax
Imposed on the person obliged to Payment is demanded from a
pay the same and this burden person who is allowed to transfer
cannot be shifted or passed on the burden of taxation to another
to another
Taxpayer who pays the tax is Paid by a person who is not
directly liable directly liable who may therefore
shift or pass the tax to another
person or entity
Demanded from the very person demanded in the first instance from
who, as intended, should pay the one person with the expectation
tax that he can shift the burden to
someone else, not as a tax but as
part of the purchase price
C. According to Determination of Amount
▪ Specific Tax
- fixed amount based on volume, weight or quantity of goods as
measured by tools, instruments or standards. (e.g. excise tax on
cigars and liquors)
▪ Ad Valorem Tax
- based on the value of the property subject to tax (e.g. VAT, income
tax, donor's tax and estate tax)
- Excise tax based on selling price or other specified value of goods
D. According to Purpose
▪ Fiscal/General/Revenue Tax
- levied without a specific or pre-determined purpose, (e.g.
income tax, donor's tax and estate tax)
▪ Regulatory/Special/Sumptuary Tax
- those intended to achieve some social or economic goals. (e.g.
tariff and certain duties on imports)
Downloaded by Lotivio Ma. Mica (lotiviomica@gmail.com)
lOMoARcPSD|30374161
Gener al Pr inciples of Taxation
TAXATION REVIEW
E. According to Jurisdiction/Scope or Authority
▪ National Tax-imposed by the National Government
▪ Local Tax-imposed by municipal corporations (e.g. real estate tax)
F. According to Graduation or Rate
▪ Proportional/Flat Rate Tax
- unitary or single rate, (e.g. VAT, OPT)
▪ Progressive/Graduated Tax
- as the tax base grows the tax rate increases. (e.g. income tax on
individuals, estates, trusts, estate tax, donor's tax)
▪ Regressive Tax
- the tax rate increases as the tax base decreases.
TAX DISTINGUISHED FROM OTHER CHARGES AND FEES
TAX VS. TOLL
TAX TOLL
▪ it is a demand of sovereignty ▪ it is a demand of proprietorship
▪ it is one's support for the ▪ it is a compensation for the use of
government somebody else's property
▪ it is imposed only by the ▪ it may be imposed by the
government government or private individuals
▪ it is based on governmental needs ▪ it is determined by the cost of
property or improvement thereon
TAX VS. PENALTY
TAX PENALTY
▪ it is imposed to raise revenue ▪ it is imposed to regulate conduct
▪ it is imposed only by the through punishment and
government suppression of injurious act
▪ it arises from law ▪ may be imposed by the
▪ generally, payable in money government or by private
individuals
▪ it may arise from law or contract
▪ may be paid in money or in kind
Downloaded by Lotivio Ma. Mica (lotiviomica@gmail.com)
lOMoARcPSD|30374161
Gener al Pr inciples of Taxation
TAXATION REVIEW
TAX VS. ASSESSMENT
TAX SPECIAL ASSESSMENT
▪ levied on business, interests, ▪ levied on land
transactions, rights, persons, ▪ cannot be made the personal
properties or privileges liability of the person assessed,
▪ may be made a personal liability of because it is the land that answers
the person assessed for the liability
▪ based on necessity with no hope of ▪ based wholly on benefits received
direct or immediate benefit to the ▪ it is exceptional in application for
taxpayer the recovery of cost and/or
▪ is of general application maintenance of improvement
TAX VS. LICENSE FEE
TAX LICENSE FEE
▪ tax is levied in the exercise of the ▪ license fee emanates from the
taxing power police power of the state
▪ purpose of it is to generate revenue ▪ the purpose of it is regulatory
▪ generally, amount is unlimited ▪ limited to the necessary expenses
▪ non-payment does not make the of regulation and control
business illegal ▪ imposed on the exercise of a right
or privileges
▪ non-payment makes the business
illegal.
TAX VS. DEBT TAX
TAX DEBT
▪ based on law ▪ based on contract
▪ not assignable ▪ assignable
▪ payable in money ▪ payable in kind or in money
▪ not subject to set off ▪ subject to set-off
▪ non-payment may result to ▪ No imprisonment (except when
imprisonment. debt arises from crime)
▪ bears interest only if delinquent ▪ interest depend upon the
stipulation of the parties
Downloaded by Lotivio Ma. Mica (lotiviomica@gmail.com)
lOMoARcPSD|30374161
Gener al Pr inciples of Taxation
TAXATION REVIEW
TAX VS. CUSTOMS DUTIES
TAX CUSTOM DUTIES
▪ imposed on person, property, rights ▪ Imposed on imported or exported
or transaction goods
▪ it comprehends more than the term ▪ it is also a tax
custom duties
❖ SUBSIDY
▪ Refers to a pecuniary aid directly granted by the government to an
individual or private commercial enterprise deemed beneficial to the public.
▪ NOT A TAX although tax may have to be imposed to pay it.
❖ REVENUE
▪ Refers to all the funds or income derived by the government, whether from
tax or any other source.
▪ Amount collected
❖ INTERNAL REVENUE
▪ taxes imposed by the legislature other than duties on imports and exports.
❖ TARIFF
May be used in one of three (3) senses:
1 A book of rates drawn usually in alphabetical order containing the names
of several kinds of merchandise with the corresponding duties to be paid
for the same, or
2 The duties payable on goods imported or exported; or
3 The system or principle of imposing duties on the importation (or
exportation) of goods.
*The term tariff and customs duties are used interchangeably in the Tariff and
Customs Code
Downloaded by Lotivio Ma. Mica (lotiviomica@gmail.com)
lOMoARcPSD|30374161
Gener al Pr inciples of Taxation
TAXATION REVIEW
SYSTEMS OF "INCOME" TAXATION
a. Global System
- All items of gross income, deductions are reported in one income tax
return and the applicable tax rate is applied on the tax base.
b. Schedular System
- Different types of income are subject to different sets of graduated or
flat income tax rates.
OTHER DOCTRINES/RULES IN TAXATION
❖ Equitable Recoupment
- Claim for refund which is prevented by prescription may be allowed to
be used as payment for unsettled tax liabilities if both taxes arise from
the same transaction in which overpayment is made and underpayment
is due.
❖ Set-off taxes
- taxes are not subject to set-off or legal compensation because the
government and the taxpayer are not mutual creditors and debtors of
each other.
❖ Taxpayer Suit
- This provides that a taxpayer suit can only be allowed if the act involves
a direct and illegal disbursement of public funds derived from taxation
Exemptions from Taxation
- grant of immunity, express or implied
CLASSIFICATION OF EXEMPTION
a. Express or affirmative
- these are express provisions in the Constitution, statues, treaties,
ordinances, franchises or contracts
b. Implied or exemption by omission
- this occurs when a tax is levied on certain classes of persons,
properties or transactions without mentioning other classes. Those not
mentioned are deemed exempted by omission
Downloaded by Lotivio Ma. Mica (lotiviomica@gmail.com)
lOMoARcPSD|30374161
Gener al Pr inciples of Taxation
TAXATION REVIEW
INTERPRETATION OF EXEMPTION GRANT
- strictly construed against the person or entity claiming exemption.
- One must Justify such claim by clear and positive grant.
ESCAPE FROM TAXATION
1. Evasion or Dodging
- taxpayer uses unlawful means to evade or lessen the payment tax
2. Avoidance or tax minimization
- reduction or totally escaping payment of tax through legally permissible
means of tax
3. Shifting
- Transfer of burden of tax to another without violating the law.
• Impact is the point at which tax is originally imposed.
• Incidence is the point at which the tax burden finally rests or settles
down.
THREE (3) KINDS SHIFTING
a. Forward shifting
- Follows the normal flow of distribution
- imposed on producers but passed on to consumers
b. Backward Shifting
- Common with non-essential commodities where buyers have
considerable market power and commodities with numerous
substitute products
- Tax burden is shifted back to the agents of production through
purchase transaction
c. Onward shifting
- Occurs in the distribution channel that exhibits forward or backward
shifting
4. Capitalization
- the seller is willing to lower the price of the commodity provided the
taxes will be shouldered by the buyer
Downloaded by Lotivio Ma. Mica (lotiviomica@gmail.com)
lOMoARcPSD|30374161
Gener al Pr inciples of Taxation
TAXATION REVIEW
5. Transformation
- the manufacturer absorbs the additional taxes imposed by the
government without passing it to the buyers for fear of lost of his/its
market. Instead, he/it increases quantity of production, thereby turning
their units of production at lower cost resulting to the transformation of
the tax into gain through the medium of production.
6. Exemption
- immunity, privilege or freedom from payment of a charge or burden to
which others are obliged to pay.
Downloaded by Lotivio Ma. Mica (lotiviomica@gmail.com)
lOMoARcPSD|30374161
Tax Remedies
TAXATION REVIEW NOTES
When PAN is not required:
1 When the finding for any deficiency tax is the result of mathematical error
in the computation of the tax as appearing on the face of the return;
2 When a discrepancy has been determined between the tax withheld and
the amount remitted by the withholding agent;
3 When a taxpayer who opted to claim a refund or tax credit of excess
creditable withholding tax for a taxable period was determined to have
carried over and automatically applied the same amount claimed against
the estimated tax liabilities for the taxable quarter or quarters of the
succeeding taxable year;
4 When the excise tax due on excisable articles has not been paid; or
5 When the articles locally purchased or imported by an exempt person,
such as, but not limited to, vehicles, capital equipment, machineries and
spare parts, has been sold, traded or transferred to non-exempt persons.
(Section 228, NIRC).
Under RR No. 30-02, the following can be compromised:
1 Delinquent accounts;
2 Cased under administrative protest after issuance of the FAN to the
taxpayer which are still pending in the Regional Offices, Revenue District,
Legal Service, Large Taxpayer Services (LTS), Collection Service,
Enforcement Service and other offices in the National Office;
3 Civil tax cases being disputed before the courts;
4 Collection cases filed in courts
5 Criminal violations, other than those already filed in court or those involving
criminal tax fraud.
What cannot be compromised:
1. Withholding tax cases, unless the applicant-taxpayer invokes provisions of
law that cast doubt on the taxpayer's obligation to withhold;
2. Criminal tax fraud cases confirmed by the CIR;
3. Criminal violations already filed in court;
4. Delinquent accounts with duly approved schedule of installment payments;
5. Cases where final reports of reinvestigation or reconsideration have been
issued resulting to reduction in the original assessment and the taxpayer is
agreeable to such decision by signing the required agreement form;
6. Cases which become final and executory after final judgement of a court,
where compromise is requested on the ground of doubtful validity of the
assessment; and
7. Cases which become final and executory after final judgement of a court,
where compromise is requested on the ground of doubtful validity of the
assessment.
• 25% in case of failure to:
• File the return and pay tax on time
• File the return with the proper internal revenue officer
• Pay the deficiency tax within the time prescribed
• Pay the full or part of the amount of tax shown on any return required to be
filed
Downloaded by Lotivio Ma. Mica (lotiviomica@gmail.com)
lOMoARcPSD|30374161
Tax Remedies
TAXATION REVIEW NOTES
Suspension of the running of prescriptive period:
1. For the period during with the CIR is prohibited from making the
assessment or beginning distraint or levy or a proceeding in court and for
sixty (60) days thereafter;
2. When the taxpayer requests for reinvestigation which is granted by the
Commissioner;
3. When the taxpayer cannot be located in the address given by him in the
return filed upon which a tax is being assessed or collected; UNLESS the
taxpayer informs the Commissioner of any change in address
4. When the warrant of distraint or levy is duly served upon the taxpayer, his
authorized representative, or a member of his household with sufficient
discretion, and no property could be located; and
5. When the taxpayer is out of the Philippines. (Section 223, NIRC)
6. When there is a valid waiver.
Downloaded by Lotivio Ma. Mica (lotiviomica@gmail.com)
lOMoARcPSD|30374161
Tax Remedies
REMEDIES OF TAXPAYER (before payment)
TAXATION REVIEW NOTES
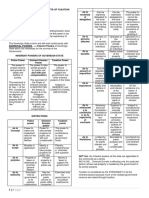
ASSESSMENT PROCESS
LOA Audit
120 days
Notice of Discrepancy
(NOD)
Discussion of Discrepancy
Taxpayer to present and explain his side on the discrepancies
Minimum of 5 days and maximum of 30 days from receipt of NOD
Preliminary Assessment
Notice (PAN)
reply within 15 days
If no reply from taxpayer or reply to PAN was found to be without merit
Final Assessment Formal Letter of
Notice (FAN) Demand (FLD)
reply within 30 days
Note whether
Request for Reinvestigation Request for Reconsideration
Submit within 30 days
without need of additional evidence
Submit new documents
within 60 days from filing request
180 days
180 days
Final Decision on Disputed Assessment (FDDA)
either by
direct denial Indirect Denial
CIR fails to act on protest within 180 days from date of
submission
30 days
30 days
Appeal to Appeal to CTA Await final decision of CIR
Court of Tax Appeals From the lapse of 180 day and appeal such to CTA
(CTA) period after receipt of decision
Downloaded by Lotivio Ma. Mica (lotiviomica@gmail.com)
lOMoARcPSD|30374161
Tax Remedies
TAXATION REVIEW NOTES
TAX REMEDIES
On the part of government - actions provided to enforce tax collection
On the part of taxpayers - avail to seek relief from undue burden, to counter
those allegations
A. ASSESSMENT PROCESS
1 Tax Audit or ● Letter of Authority (LOA)
Investigation official document that empowers a Revenue
Officer to examine and scrutinize a taxpayer’s
books in order to determine the correct internal
revenue tax liabilities
● No LOA = Null/ void assessment or
examination
● 10 days to provide necessary documents for
audit
● >10 days Letter of informal Conference
Cases not covered by LOA
1. Civil or criminal tax fraud
2. Policy cases under audit by special teams in the
National Office
Effects of issuance of LOA
● Tax return or declaration filed may be modified,
changed or modified within 3 years from the
date of filing
● Amendments are not allowed when LOA or
investigation of such has been served
LOA vs. LN (Letter Notice)
LN is not an authority to conduct an audit or
examination of the taxpayer leading up to the
issuance of assessment.
After LN, the RO should secure a LOA before
proceeding to further assessment
2 Notice of • NOD is given to a taxpayer is found to be liable
Discrepancy for deficiency tax in the course of investigation by
(NOD) the RO
• Aims to fully afford the taxpayer with fair
opportunity to present and explain his side on the
discrepancies found
• 5 days from the receipt of NOD
EXTENSION: not exceeding 30 days from receipt
of NOD
FAILURE OF TAXPAYER TO RECONCILE WILL
RESULT IN THE ISSUANCE OF DEFFICIENCY TAX
ASSESSMENT THROUGH PAN
Downloaded by Lotivio Ma. Mica (lotiviomica@gmail.com)
lOMoARcPSD|30374161
Tax Remedies
TAXATION REVIEW NOTES
3 Prelim Issued by the Regional Assessment Division,
Assessment Commissioner
Notice (PAN) • shall be in writing, otherwise void
Not required when
● Deficiency tax is the result of mathematical error
in computation
● Discrepancies between tax withheld and actual
amount has been determined by withholding
agent
● Excise tax due has not been paid
● When an article purchased by an exempt person
has been sold, traded or transferred to non-
exempt persons
The taxpayer has 15 days to contest upon receipt of
PAN
4 Final Letter of Issued when
Demand (FLD)/ ● Failed to respond to the PAN
Final ● The reply found to be w/o merit (di convincing)
Assessment
Notice (FAN) PRESCRIPTIVE PERIOD
3 years from:
a. Actual filing of return;
Return filed is NOT
or
fraudulent
b. Deadline for filing
Whichever is LATER
1. Return filed is
fraudulent 10 years from discovery
2. NO return was filed
Remedies of the taxpayer
● Protest to CIR within 30 days from the date of
receipt of FAN
○ Request for reconsideration- without need
for additional evidence
○ Request for reinvestigation - present
additional evidences within 60 days from
the date of protest
5 Final Decision DENIAL OF PROTEST
on a Disputed 1. Direct denial
Assessment 2. Indirect denial - CIR fails to act on the protest
(FDDA) within 180 days from the date of submission
Remedies of the taxpayer
1. Direct denial - file an appeal with Court of Tax
Appeal (CTA) within 30 days from the receipt
Downloaded by Lotivio Ma. Mica (lotiviomica@gmail.com)
lOMoARcPSD|30374161
Tax Remedies
TAXATION REVIEW NOTES
2. Indirect denial
a. File an appeal with CTA within 30 days
from the lapse of 180-day period
b. Await the final decision CIR and appeal
such to CTA within 30 days from the
receipt of such decision
6 Denial of Appeal Remedies of the taxpayer
by CTA Division 1. File a motion for reconsideration within 15 days
from the receipt
If denied, file an appeal with CTA en banc
within 15 days from the receipt
7 Denial of Appeal Remedies of the taxpayer
by CTA En banc 1. File a motion for reconsideration within 15days
from the receipt
a. If denied, file an appeal with Supreme Court
within 15 days from the receipt
8 Denial of Appeal Remedies of the taxpayer
by SC Division 1. File a motion for reconsideration within 15days
from the receipt
a. If denied, file an appeal with SC en banc
within 15 days from the receipt
9 Denial of Appeal Remedies of the taxpayer
by SC En banc 1. File a motion for reconsideration within 15days
from the receipt
a. If denied, the taxpayer has no more remedy
Downloaded by Lotivio Ma. Mica (lotiviomica@gmail.com)
lOMoARcPSD|30374161
Tax Remedies
TAXATION REVIEW NOTES
B. COLLECTION Allowed when the assessment is final, executory
and demandable
Exceptions as to period of Limitation of
Assessment and Collection of Tax
• (a) False & fraudulent return with intent to
evade tax or of failure to file a return- tax may
be assessed or filed without assessment, at
any time within 10 years after the discovery
provided that the fact of fraud shall be
judicially taken cognizance of in the civil or
criminal action for the collection thereof.
• Internal revenue tax as prescribed in (a) may
be collected within 5 years following the
assessment
Methods
1 Distraint- seizure of personal property,
tangible or intangible
a. Actual Distraint- personal property is
physically seized by BIR
Garnishment- distraint of bank
accounts
b. Constructive Distraint- person in
possession of personal property is
made to sign a receipt that he will
preserve the property and will not
dispose of without the express
authority of BIR
WHO CAN COMMENCE DISTRAINT
PROCEEDINGS?
Amount > 1M – CIR
Amount 1M – Revenue District
Officer
2. Levy- seizure of real properties & interest in
or rights to such property
3. Judicial Proceedings
a. Filing of civil case for collection
b. File a criminal case (Tax Evasion)
- 5 years from commission or
discovery, whichever is later
Downloaded by Lotivio Ma. Mica (lotiviomica@gmail.com)
lOMoARcPSD|30374161
Tax Remedies
TAXATION REVIEW NOTES
C. COMPROMIS Grounds
E 1. Reasonable doubt as to the validity of the claim
against the taxpayer exists
2. Final position of the taxpayer demonstrates a
clear inability to pay the assessed tax
All criminal violations may be compromised, except:
1. Those already filed in court
2. Those involving fraud
Minimum Amounts
1. Financial incapacity- minimum of 10% of the
basic assessed tax
2. Other cases- minimum of 40% of the basic
assessed tax
Instances when approval of the Board is Required
1. Basic tax > 1million
2. Settlement offered is less than the minimum
rates
D. ABATEMENT Grounds
OR 1. Tax appears to be unjustly or excessively
CANCELATIO assessed
N OF TAX 2. Administration and collection costs do not justify
LIABILITY the collection of the amount due
E. SUSPENSION Under the following situations:
OF THE 1. Taxpayer’s reinvestigation request was granted
RUNNING OF 2. Taxpayer cannot be located in the address
STATUTE OF given in the return
LIMITATIONS 3. No property of the taxpayer can be located
4. Taxpayer is out of the country
Suspension shall be for the duration of the situation
plus 60 days thereafter
F. CIVIL 1. SURCHARGE-
PENALTIES 25% in any of the following cases:
a. Failure to file any return and pay the tax due
on time
b. Filing a return with an internal revenue officer
other than those with whom the return is
required to be filed
c. Failure to pay deficiency tax within time
prescribed in the Notice of Assessment
d. Failure to pay the amount of tax due for which
no return is required to be filed
50% in any of the following cases:
a. Willful neglect to file return on time
b. Taxpayer files only after prior notice in writing
Downloaded by Lotivio Ma. Mica (lotiviomica@gmail.com)
lOMoARcPSD|30374161
Tax Remedies
TAXATION REVIEW NOTES
from the BIR
Simple neglect (25% surcharge)- files return
after deadline without notice from BIR
Evidence for false or fraudulent return
1. Substantial overstatement (>30%) of
deductions
2. Substantial under declaration (<30%) of
taxable assets, receipts & income
2. INTEREST (12% per annum)
- An increment on any unpaid amount of tax,
assessed from the date prescribed for payment
until the amount is fully paid
Kinds
1. Deficiency Interest- imposed on deficiency tax
due
-Assessed & collected from prescribed payment
date until (whichever comes first):
a. Full payment
b. Issuance of notice and demand by the
Commissioner
2. Delinquency Interest- interest imposed on the
failure of taxpayer to pay:
a. The amount tax due on any return required
to be filed
b. The amount tax due for which no return is
required
c. Deficiency tax, or any surcharge or interest
Double imposition of Interest
- In no case shall deficiency and delinquency
interest be imposed simultaneously
G. REFUND OF Requisites:
TAXES 1. Tax was erroneously or illegally collected by
BIR
2. Taxpayer should file a written claim for refund
with CIR within 2 years from the date of
payment
3. Claim with CIR= denied
File petition for refund with CTA
a. Within 30 days from receipt of denial;
AND
b. Within 2 years from the date of
payment of tax or penalty
Downloaded by Lotivio Ma. Mica (lotiviomica@gmail.com)
lOMoARcPSD|30374161
Taxability of Individuals and Cor por ations
TAXATION REVIEW
INDIVIDUALS
1 Those who are citizens of the Philippines at the time
of the adoption of the Constitution
2 Those whose fathers or mothers are citizens of the
RESIDENT Philippines
CITIZEN (RC) 3 Those born before January 17, 1973 of Filipino
mothers, who elect Philippine Citizenship upon
reaching the age of majority; and
4 Those who are naturalized in accordance with law
1 Who establishes to the satisfaction of the
Commissioner the fact of his physical presence
abroad with definite intention to reside therein
2 Works and derives income from abroad and
whose employment thereat requires him to be
physically present abroad most of the time (must
be outside PH for not less than 183 days) during
NON-RESIDENT the taxable year.
CITIZEN (NRC) 3 One who leaves the Philippines to reside abroad as
an immigrant, or for employment on a
permanent basis
4 Citizen previously considered as NRC who arrives to
reside permanently in Phil: NRC for the taxable
year which he arrives with respect to income derived
from sources abroad UNTIL the date of his arrival in
the country
1 OFW, physically present abroad as a consequence
OVERSEAS of employment
CONTRACT
WORKER 2 Salaries & wages= paid by employer abroad and
(OCW) is not borne by anyone in the Phil
Downloaded by Lotivio Ma. Mica (lotiviomica@gmail.com)
lOMoARcPSD|30374161
Taxability of Individuals and Cor por ations
TAXATION REVIEW
3 Duly registered as such with POEA with a valid
Overseas Employment Certificate (OEC)
4 Seaman who receives compensation for services
rendered abroad as a member of the complement
vessel engaged exclusively in international trade
Requirements:
a. Duly registered as such with POEA with a valid
OEC
b. With a valid Seafarer’s Identification Record
Book (SIRB) or Seaman’s Book issued by
Maritime Industry Authority (MARINA)
NOT A CITIZEN; alien with acquired residence in the PH
retains status as resident until he abandons the same and
actually departs from PH
1 An alien actually present in the Philippines who is
RESIDENT not a mere transient or sojourner
ALIEN (RA)
2 Has a definite purpose that requires an extended
stay;
PH= temporary home
3 Has no definite intention as to his stay
NONRESIDENT NON-RES & NON-CIT
ALIEN ENGAED 1 Alien engaged in trade or business in PH
IN TRADE OR 2 Alien who come to PH for an aggregate period of
BUSINESS more than 180 days
(NRA)
NONRESIDENT
ALIEN NOT
ENGAED IN Residual definition
TRADE OR
BUSINESS
Downloaded by Lotivio Ma. Mica (lotiviomica@gmail.com)
lOMoARcPSD|30374161
Taxability of Individuals and Cor por ations
TAXATION REVIEW
SITUS OF TAXABLE INCOME OF INDIVIDUALS
NATIONALITY/RESIDENCE INCOME WITHIN INCOME WITHOUT
Resident citizen ✓ ✓
Resident Alien ✓
NRC ✓
NRA ✓
TAXABILITY OF DIVIDENDS
RECEIVED BY KIND OF TAX
DC Not taxable
DIVIDENDS RFC No taxable
DECLARED BY NRFC 25%; tax sparing credit
DOMESTIC CORP Resident or Citizen 10% FWT
NRA ETB 20% FWT
NRA NETB 25% FWT
DC Ordinary income tax
DIVIDENDS Foreign Corporation Not taxable
DECLARED BY
FOREIGN CORP Resident Citizen Ordinary income tax
NRC, NRA, RA Not taxable
Downloaded by Lotivio Ma. Mica (lotiviomica@gmail.com)
lOMoARcPSD|30374161
Taxability of Individuals and Cor por ations
TAXATION REVIEW
CORPORATIONS
DEFINITION
- Artificial being created by operation of law, having the right of succession
and the powers, attributes and properties expressly authorized by law or
incidental to its existence
- Corporation shall include:
a. One Person corporation (OPC)
- corporation w/ a single stockholder provided that only a NATURAL
person, trust or an estate may form OPC
b. Partnerships, no matter how created or organized;
c. Joint stock companies
- Group of individuals, acting jointly, establish and operate
business enterprise under an artificial name, with an invested
capital divided into transferrable shares, an elected BOD and
other corporate characteristics, but operating without formal
government authority
d. Joint accounts (cuentas en participacion)
- Constituted when one interests himself in the business of another
by contributing capital and sharing P/L in proportion agreed
upon.
- Not subject to any formality; orally or in writing
- All organizations with substantially salient features of a
corporation to be taxable as a corporation
e. Associations; or
f. Insurance companies
Downloaded by Lotivio Ma. Mica (lotiviomica@gmail.com)
lOMoARcPSD|30374161
Taxability of Individuals and Cor por ations
TAXATION REVIEW
- Corporation does NOT include:
a. General Professional Partnerships (GPP)
b. Joint venture or consortium formed for the purpose of:
1. Construction projects, or
2. Engaging in coal, petroleum geothermal and other energy operations
pursuant to an operating or consortium agreement under a service
contract with the government
ELABORATION ON JOINT VENTURE OR CONSORTIUM (2)
- A commercial undertaking by 2 or more persons, differing from a
partnership in that it relates to the disposition of a single lot of goods or the
completion of a single project
- GR: Taxable as corporation
Exc. Joint ventures described in 2(a) and (b)
Additional requirements for tax exemption:
1. JV/C formed for undertaking construction projects
a. Should involve joining or pooling of resources by licensed local
contracts; licensed as general contractor by the PCAB of DTI
b. Local contractors are engaged in construction business
c. JV must likewise be duly licensed as such by PCAB of DTI
JV involving FOREIGN CONTRACTORS
a. The member foreign contractor is covered by a special license as
contractor by PCAB of DTI
b. Construction project is certified by the tendering agency (government
office) that the project is a foreign financed/ internationally-funded
project and that international bidding is allowed under Bilateral
Agreement entered into by the PH gov’t and the foreign/ international
financing institution pursuant to RA 4566 (Contractor’s License Law)
2. Engaging in petroleum, coal, geothermal and other energy operations
pursuant to an operating or consortium agreement under a service contract
with the gov’t
Downloaded by Lotivio Ma. Mica (lotiviomica@gmail.com)
lOMoARcPSD|30374161
Taxability of Individuals and Cor por ations
TAXATION REVIEW
CLASSIFICATION OF CORPORATE TAXPAYERS
1. Domestic Corporation (DC)
- Organized in the Philippines or under its law
2. Resident Foreign Corporation (RFC)
- Created or organized in a foreign country or under the laws of a foreign
country and engaged in business in the Philippines
3. Non-resident Foreign Corporation (NRFC)
- Created or organized in a foreign country or under the laws of a foreign
country and is not engaged in business in the Philippines
EXEMPT CORPORATIONS
1 Labor, agricultural or horticultural organization not organized principally for
profit;
2 Mutual savings bank not having a capital stock represented by shares, and
cooperative bank without capital stock organized and operated for mutual
purposes and without profit;
3 A beneficiary society, order or association, operating for the exclusive
benefit of the members such as a fraternal organization operating under the
lodge system, or a mutual aid association or a nonstock corporation
organized by employees providing for the payment of life, sickness accident,
or other benefits exclusively to the members of such society, order, or
association, or nonstock corporation or their dependents;
4 Cemetery company owned and operated exclusively for the benefit of its
members;
5 Nonstock corporation or association organized and operated exclusively for
religious, charitable, scientific, athletic, or cultural purposes, or for the
rehabilitation of veterans, no part of its net income or asset shall belong to
or inure to the benefit of any member, organizer, officer or any specific
person;
6 Business league, chamber of commerce, or board of trade, not organized
for profit and no part of the net income of which inures to the benefit of any
private stockholder or individual;
Downloaded by Lotivio Ma. Mica (lotiviomica@gmail.com)
lOMoARcPSD|30374161
Taxability of Individuals and Cor por ations
TAXATION REVIEW
7 Civic league or organization not organized for profit but operated exclusively
for the promotion of social welfare;
8 A non-stock and nonprofit educational institution;
9 Government educational institution;
10 Farmers' or other mutual typhoon or fire insurance company, mutual ditch
or irrigation company, mutual or cooperative telephone company, or like
organization of a purely local character, the income of which consists solely
of assessments, dues, and fees collected from members for the sole
purpose of meeting its expenses; and
11 Farmers', fruit growers', or like association organized and operated as a
sales agent for the purpose of marketing the products of its members and
turning back to them the proceeds of sales, less the necessary selling
expenses on the basis of the quantity of produce finished by them
GOVERNMENT-OWNED OR CONTROLLED CORPORATIONS
All corporations, agencies or instrumentalities owned or controlled by the
Government shall be taxable like <ordinary corporations=.
However, the following shall be exempt:
1. Government Service and Insurance System (GSIS)
2. Social Security System (SSS)
3. Home Development Mutual Fund (HDMF aka Pag-ibig)
4. Philippine Health Insurance Corporation (PHIC)
5. Local Water Districts (RA 10026)
NOTE:
• PCSO is taxable beginning Jan. 1, 2018 (TRAIN Law)
• HDMF or Pag-ibig is exempt only upon the effectivity of CREATE Law
(April 11, 2021)
Downloaded by Lotivio Ma. Mica (lotiviomica@gmail.com)
lOMoARcPSD|30374161
Taxability of Individuals and Cor por ations
TAXATION REVIEW
INCOME TAXES ON CORPORATION
TAX
TYPE SOURCES APPLICABLE TAX
BASE
Ordinary Income:
− RCIT 20% for MSME; 25% for non-MSME
Passive Income: FWT
− Interest Income: 20%;15%
Net − Royalties: 20%
DC World
Income − Dividend: Exempt
Capital Gains on sale of
• shares of stock of DC sold directly to
buyer: 15%
• sale of real property in PH classified as
capital asset: 6%
Ordinary Income
- RCIT 25%
Passive Income: FWT
Net - Interest Income: 20%;15%
RFC PH - Royalties: 20%
Income
- Dividend: Exempt
Capital Gains on sale of shares of stock of DC
sold directly to buyer
- CGT 15%
Ordinary Income
- FWT 25%
Passive Income
Gross - FWT 25%
NRFC PH
Income - FCDU: Exempt:
Capital Gains on sale of shares of stock of DC
sold directly to buyer
- CGT 15%
Downloaded by Lotivio Ma. Mica (lotiviomica@gmail.com)
lOMoARcPSD|30374161
Taxability of Individuals and Cor por ations
TAXATION REVIEW
DC with total assets 100M AND
net taxable income 5M (aka Micro
** Beg. July Small and Medium Enterprises), Reduced
1, 2020 excluding land on which the particular to 20%
business entity’s office, plant, and
equipment are situated
Type of Income Applicable Tax
DC & RFC: RCIT
Regular or ordinary income
NRFC: FWT
Passive income (Interest Income,
Royalty Income in PH, Dividend FWT
Income in PH)
Capital gains on • CGT applicable to all
• Sales of shares of stock of DC corporations (15%)
sold directly to a buyer
• Sale of real property in PH • CGT applicable only to DC
classified as capital asset (6%)
Downloaded by Lotivio Ma. Mica (lotiviomica@gmail.com)
lOMoARcPSD|30374161
TAXATION REVIEW
1. House Bill no. 123 was transmitted to the Senate and was passed accordingly.
The Bill was submitted to the President for his signature on August 1, 2021. On
September 5, 2021, the President stated on a media interview that he does not
intend to sign the bill into law that is why he is not yet acting on the bill. What is
the status of the House Bill no. 123?
a. The bill is automatically vetoed upon the lapse of 15 days
b. The bill is automatically lapsed into law after 30 days
c. The bill’s effectivity is suspended until the President signed the same.
d. The bill has become effective until the President vetoes it.
The correct answer is: The bill is automatically lapsed into law after 30 days
PRESIDENTIAL ACTION ON THE BILL
1. If the bill is approved the President, the same is assigned an RA number
and transmitted to the House where it originated
2. If the bill is vetoed, the same, together with a message citing the reason
for the veto, is transmitted to the House where the bill originated.
2. That courts cannot issue injunction against the government’s effort to collect
taxes is justified by
a. The lifeblood doctrine
b. Imprescriptibility of taxes
c. The ability to pay theory
d. The doctrine of estoppel
The correct answer is: The Lifeblood Doctrine
This <lifeblood doctrine= has been invoked to validate many of the Bureau of
Internal Revenue’s (BIR) action, including advanced collection of taxes, the no
injunction rule in taxation, taxes being a preferred credit, among others.
MANIFESTATION OF THE LIFEBLOOD DOCTRINE/THEORY:
• No Estoppel against the Government
• Collection of taxes cannot be enjoined (stopped) by injunction
• Taxes could not be the subject of compensation or set-off
• A valid tax may result in the destruction of the taxpayer's property
• Right to select objects (subjects) of taxation
Downloaded by Lotivio Ma. Mica (lotiviomica@gmail.com)
lOMoARcPSD|30374161
TAXATION REVIEW
3. The principal purpose of taxation is
a. To encourage the growth of home industries through the proper use of
tax exemptions and tax incentives
b. To implement the police power of the state
c. The reduce excessive inequalities of wealth
d. To raise revenues for governmental needs
The correct answer is: To raise revenues for governmental needs
PURPOSES OF TAXATION
1. Primary Purpose (also called Revenue or Fiscal Purpose)
- To raise revenues/funds to defray the necessary expenses of the
government
2. Secondary Purpose:
a. Regulatory Purpose
- employed as a devise for regulation or control (to implement the
police power of the State for the promotion of the general
welfare) by means of which certain effects or conditions
envisioned by the government may be achieved.
b. Compensatory Purposes
- Reduction of Social Inequality
- Economic Growth
- Protect local industries against unfair competition ³
protectionism
4. In this type of tax, non-payment is constitutionally exempted from imprisonment.
a. Income tax
b. Value-Added Tax
c. Poll tax
d. All of the above
The correct answer is: Poll Tax
Article III, Section 20 of the 1987 Constitution- No person shall be
imprisoned for debt or non-payment of a poll tax.
Downloaded by Lotivio Ma. Mica (lotiviomica@gmail.com)
lOMoARcPSD|30374161
TAXATION REVIEW
5. The aspects of taxation are
a. Legislative in character
b. Executive in character
c. Shared by the legislative and executive departments
d. Judicial in character
The correct answer is: Legislative in character
The power to tax is purely legislative in character. It is up to Congress
which will determine the subjects or objects to be taxed, purpose, the amount of
the rate and the manner and means of its collection.
6. Taxation as distinguished from police power and power of eminent domain
a. Property is taken to promote the general welfare
b. May be exercised only by the government
c. Operates upon the whole citizenry
d. There is generally no limit as to the amount that may be imposed
The correct answer is: There is generally no limit as to the amount that may be
imposed.
With regards to the amount of imposition, taxation has no limit. In police power,
the amount is ssufficient to cover cost of the license and the necessary expenses
of police surveillance and regulation while in eminent domain, there is no
imposition- the owner is paid equivalent to the fair value of his property.
7. Which of the inherent powers may be exercised even by public service
corporations and public entities?
a. Power of taxation
b. Police power
c. Power of eminent domain
d. A and C
The correct answer is: Power of eminent domain
The authority for eminent domain may be granted to public service/ utility
companies.
Downloaded by Lotivio Ma. Mica (lotiviomica@gmail.com)
lOMoARcPSD|30374161
TAXATION REVIEW
8. The power to acquire private property upon payment of just compensation for
public purpose.
a. Power of taxation
b. Police power
c. Power of eminent domain
d. Veto power
The correct answer is: Power of eminent domain
The purpose of eminent domain is to take private property for public use
wherein the owner is paid equivalent to the fair value of his property.
9. The power to regulate liberty and property to promote the general welfare.
a. Power of taxation
b. Police power
c. Power of eminent domain
d. Veto power
The correct answer is: Police power
10. The inherent powers of the government are primarily ________ in character.
a. Executive
b. Legislative
c. Judicial
d. Quasi-Judicial
The correct answer is: Legislative
Similarities among the 3 Inherent Powers
1. Inherent in the State
2. Exist independently of the constitution although the conditions for their
exercise may be prescribed by the constitution.
3. Constitutes the 3 methods by which the State interfere with private rights
and property
4. Legislative in nature and character.
5. Presuppose an equivalent compensation received, directly or indirectly,
by the persons affected.
Downloaded by Lotivio Ma. Mica (lotiviomica@gmail.com)
lOMoARcPSD|30374161
TAXATION REVIEW
11. Which of the following inherent powers of the state is inferior to
constitutional right of non-impairment of obligations of contracts?
a. Power of taxation
b. Police power
c. Power of eminent domain
d. None of the above
The correct answer is: Power of taxation
As to relationship to the non-impairment of obligations clause of the
Constitution:
1. Police power – superior to the clause
2. Power of eminent domain – inferior to the clause
3. Taxation – inferior to the clause
12. Which of the following statements is correct?
a. Income tax is an indirect tax.
b. Our National Internal Revenue Laws are criminal in nature
c. The theory of taxation states that the power of taxation is supreme,
plenary, unlimited, and comprehensive.
d. Taxation is subject to inherent and constitutional limitations.
The correct answer is: Taxation is subject to inherent and constitutional
limitations.
Choice A is incorrect because income tax is a direct tax which is
imposed directly on the liable person & cannot be shifted to another. An
undirect tax is demanded from a person who is allowed to transfer the burden
of taxation to another.
13. This is an inherent limitation on the power of taxation.
a. Rule on uniformity and equity in taxation
b. Due process of law and equal protection of the laws
c. Non-impairment of the jurisdiction of the Supreme Court in tax cases
d. Tax must be for public purpose
The correct answer is: Tax must be for public purpose.
Downloaded by Lotivio Ma. Mica (lotiviomica@gmail.com)
lOMoARcPSD|30374161
TAXATION REVIEW
14. This is a constitutional limitation on the power of taxation.
a. Tax laws must be applied within the territorial jurisdiction of the state
b. Exemption of government agencies and instrumentalities from taxation
c. No appropriation of public money for religious purposes
d. Power to tax cannot be delegated to private persons or entities
inherent
The correct answer is: No appropriation of public money for religious purposes
Choice A refers to situs of taxation or territoriality, choice B refers to tax
exemption of the government, and choice D refers to the non-delegability of the
Taxing Power (enactment of tax laws) which are all inherent limitations of
taxation.
15. The sources of revenue should be sufficient to meet the demands of public
expenditures.
a. Equality or Theoretical Justice
b. Administrative Feasibility
c. Fiscal Adequacy
d. Life Blood Doctrine
The correct answer is: Fiscal Adequacy
Principles of a Sound Tax System
1. Fiscal Adequacy
− The sources of government revenue must be sufficient to meet
government expenditures and other public needs
2. Theoretical Justice
− must be based on the taxpayer's ability to pay
− taxation must be progressive conformably with the constitutional
mandate that congress shall evolve a progressive system of taxation.
3. Administrative Feasibility
− Tax laws must be capable of convenient, just and effective
administration free from confusion and uncertainty
− should have the merits of simplicity, flexibility and diversity.
Downloaded by Lotivio Ma. Mica (lotiviomica@gmail.com)
lOMoARcPSD|30374161
TAXATION REVIEW
16. Which of the following is not an inherent limitation of taxation?
a. Territoriality
b. International Comity
c. For public purpose
d. Non-impairment of obligation and contract
The correct answer is: Non-impairment of obligation and contract
Inherent Limitations of Taxation
1. For public purpose
2. Situs of taxation/territoriality
1. International Comity or Treaty
2. 4. Non-delegability of the Taxing Power (Enactment of Tax Laws)
17. Which of the following is not a tax mechanism to minimize the impact of
double taxation?
a. Tax shifting
b. Tax levy
c. Tax capitalization
d. Tax transformation
The correct answer is: Tax Levy
Tax shifting
- Transfer of burden of tax to another without violating the law
Tax capitalization
- the seller is willing to lower the price of the commodity provided
the taxes will be shouldered by the buyer
Tax Transformation
- the manufacturer absorbs the additional taxes imposed by the
government without passing it to the buyers for fear of loss of
his/its market. Instead, he/it increases quantity of production,
thereby turning their units of production at lower cost resulting to
the transformation of the tax into gain through the medium of
production.
Downloaded by Lotivio Ma. Mica (lotiviomica@gmail.com)
lOMoARcPSD|30374161
TAXATION REVIEW
18. The tax imposed should be proportionate to the taxpayer's ability to pay.
a. Equality or Theoretical Justice
b. Administrative Feasibility
c. Fiscal Adequacy
d. Life Blood Doctrine
The correct answer is: Equality or Theoretical Justice
Principles of a Sound Tax System
1. Fiscal Adequacy
− The sources of government revenue must be sufficient to meet
government expenditures and other public needs
2. Theoretical Justice
− must be based on the taxpayer's ability to pay
− taxation must be progressive conformably with the constitutional
mandate that congress shall evolve a progressive system of taxation.
3. Administrative Feasibility
− Tax laws must be capable of convenient, just and effective
administration free from confusion and uncertainty
− should have the merits of simplicity, flexibility and diversity.
19. Withholding is:
a. A method of reducing a taxpayer’s income.
b. A method by which the government collect taxes at the time of its
deadline.
c. A method by which the government collect taxes in advance.
d. A method of increasing a taxpayer’s income.
The correct answer is: A method by which the government collect taxes in
advance
Withholding Taxes is a corporate tax obligation paid by taxpayers
engaged in trade or business activities in the Philippines. Employers
withhold from the salary of their employees every month and each amount
withheld serves as an advanced payment for the employer's Income Taxes
during the business year.
Downloaded by Lotivio Ma. Mica (lotiviomica@gmail.com)
lOMoARcPSD|30374161
TAXATION REVIEW
20. The tax laws must be capable of convenient, just and effective
administration.
a. Equality or Theoretical Justice
b. Administrative Feasibility
c. Fiscal Adequacy
d. None of the above
The correct answer is: Administrative Feasibility
Principles of a Sound Tax System
1. Fiscal Adequacy
− The sources of government revenue must be sufficient to meet
government expenditures and other public needs
2. Theoretical Justice
− must be based on the taxpayer's ability to pay
− taxation must be progressive conformably with the constitutional
mandate that congress shall evolve a progressive system of taxation.
3. Administrative Feasibility
− Tax laws must be capable of convenient, just and effective
administration free from confusion and uncertainty
− should have the merits of simplicity, flexibility and diversity.
21. When the law itself provides for non-payment of taxes; such tax escape is
known as:
a. Tax evasion
b. Tax holiday
c. Tax minimization
d. Tax avoidance
The correct answer is: Tax holiday
1. Evasion or Dodging
− taxpayer uses unlawful means to evade or lessen the payment tax
2. Avoidance or tax minimization
− reduction or totally escaping payment of tax through legally
permissible
− means of tax
Downloaded by Lotivio Ma. Mica (lotiviomica@gmail.com)
lOMoARcPSD|30374161
TAXATION REVIEW
22. The principles of a sound tax system exclude
a. Economic efficiency
b. Fiscal adequacy
c. Theoretical justice
d. Administrative feasibility
The correct answer is: Economic efficiency
Principles of a Sound Tax System
1. Fiscal Adequacy
− The sources of government revenue must be sufficient to meet
government expenditures and other public needs
2. Theoretical Justice
− must be based on the taxpayer’s ability to pay
− taxation must be progressive conformably with the constitutional
mandate that congress shall evolve a progressive system of taxation.
3. Administrative Feasibility
− Tax laws must be capable of convenient, just and effective
administration free from confusion and uncertainty
− should have the merits of simplicity, flexibility and diversity.
23. The Marshall Doctrine justifies:
a. The use of taxation as an implement of police power.
b. The imposition of taxes in progressive rates.
c. The bias of taxation for the protection of the less fortunate.
d. The power of the government to collect taxes even without the grant of
the Constitution.
The correct answer is: The use of taxation as an implement of police power
Because of the absence of inherent and constitutional limitations, the power to
tax is comprehensive, plenary, supreme & unlimited.
<The power to tax includes the power to destroy=
- Justice Marshall
Downloaded by Lotivio Ma. Mica (lotiviomica@gmail.com)
lOMoARcPSD|30374161
TAXATION REVIEW
24. Substituted filing of income tax returns is a manifestation of which principle
of a sound tax system?
a. Equality
b. Theoretical justice
c. Fiscal adequacy
d. Administrative feasibility
The correct answer is: Administrative Feasibility
25. Statement 1 – The point on which a tax is originally imposed is impact of
taxation.
Statement 2 – Police power is superior to the non-impairment clause of the
constitution
Statement 3 – As a rule, taxes are subject to set-off or compensation
Statement 4 – As rule, provisions on the validity of tax exemptions are resolved
liberally in favor of the taxpayer
Statement 1 Statement 2 Statement 3 Statement 4
a. True False False False
b. True True False True
c. True True False False
d. False False False False
The correct answer is: Correct answer is choice C.
Statement 1 is true.
Statement 2 is true because police power is broader than taxation and eminent
domain because it involves a general power to make and implement laws and
as to relationship to the non-impairment of obligations clause of the Constitution,
police power is superior to the clause while power of eminent domain and
Taxation are inferior to the clause.
Statement 3 is false because based on the other doctrines/ rules in taxation,
taxes are not subject to set-off or legal compensation because the government
and the taxpayer are not mutual creditors and debtors of each other.
Statement 4 is false provisions granting tax exemptions are construed strictly
against the taxpayer claiming tax exemption and liberally in favor of the
government.
Downloaded by Lotivio Ma. Mica (lotiviomica@gmail.com)
lOMoARcPSD|30374161
TAXATION REVIEW
26. Which of the following theory justifies taxes being a preferred credit?
a. Lifeblood Doctrine
b. Necessity Theory
c. Marshall Doctrine
d. Doctrine of Equitable Recoupment
The correct answer is: The Lifeblood Doctrine
This <lifeblood doctrine= has been invoked to validate many of the Bureau of
Internal Revenue’s (BIR) action, including advanced collection of taxes, the no
injunction rule in taxation, taxes being a preferred credit, among others.
MANIFESTATION OF THE LIFEBLOOD DOCTRINE/THEORY:
• No Estoppel against the Government
• Collection of taxes cannot be enjoined (stopped) by injunction
• Taxes could not be the subject of compensation or set-off
• A valid tax may result in the destruction of the taxpayer’s property
• Right to select objects (subjects) of taxation
27. Which of the following is not an element of direct double taxation?
a. Two taxes
b. Same subject matter
c. Same amount
d. Same year
The correct answer is: Same amount
Direct Duplicate Taxation
− objectionable and prohibited because it violates the constitutional
provision on uniformity and equality. It means:
▪ Taxing twice;
▪ By the same taxing authority;
▪ Within the same jurisdiction or taxing district;
▪ For the same purpose;
▪ In the same year or taxing period; and
▪ Same kind or character of tax
Downloaded by Lotivio Ma. Mica (lotiviomica@gmail.com)
lOMoARcPSD|30374161
TAXATION REVIEW
28. Tax evasion is
a. Also known as tax avoidance and is the illegal way of not paying taxes.
b. Also known as tax avoidance and is the legal way of not paying taxes.
c. Also known as tax dodging and is the illegal way of not paying taxes.
d. Also known as tax dodging and is the legal way of not paying taxes.
The correct answer is: Also known as tax dodging and is the illegal way of not
paying taxes.
ESCAPE FROM TAXATION
1. Evasion or Dodging
− taxpayer uses unlawful means to evade or lessen the payment tax
2. Avoidance or tax minimization
− reduction or totally escaping payment of tax through legally
permissible means of tax
3. Shifting
− Transfer of burden of tax to another without violating the law.
• Impact is the point at which tax is originally imposed.
• Incidence is the point at which the tax burden finally rests or settles
down.
4. Capitalization
− the seller is willing to lower the price of the commodity provided the
taxes will be shouldered by the buyer
5. Transformation
− the manufacturer absorbs the additional taxes imposed by the
government without passing it to the buyers for fear of loss of his/its
market. Instead, he/it increases quantity of production, thereby turning
their units of production at lower cost resulting to the transformation of
the tax into gain through the medium of production.
6. Exemption
immunity, privilege or freedom from payment of a charge or burden to which
others are obliged to pay.
Downloaded by Lotivio Ma. Mica (lotiviomica@gmail.com)
lOMoARcPSD|30374161
TAXATION REVIEW
29. It is a general pardon granted by the government for erring taxpayers to give
them a chance to reform and enable them to have a fresh start to be part of a
society with a clean slate.
a. Tax amnesty
b. Tax condonation
c. Tax exemption
d. Tax benefit
The correct answer is: Tax Amnesty
Tax Amnesty is a general pardon granted by the government for erring
taxpayers to give them a chance to reform and enable them to have a fresh start
to be part of society with a clean slate. It Is an absolute forgiveness or waiver by
the government on its right to collect and is retrospective in application.
Tax condonation also known as Tax remission- forgiveness of the tax
obligation of a certain taxpayer under certain justifiable grounds
Tax exemption also known as tax holiday- refers to the immunity, privilege
or freedom from being subject to a tax which other are subject to. Tax
exemptions may be granted by the Constitution, law or contract.
30. The House of Representative is composed of 300 district and party-list
representatives. Two hundred attended the session dated June 5, 2021. On
that particular session, House Bill no. 123 was voted upon. How many votes
are required to pass the Bill?
a. 101 votes
b. 134 votes
c. 151 votes
d. 200 votes
The correct answer is: 151 votes
At least 151 votes are required to pass the Bill as based on the rule that
majority of the members of the House.
Downloaded by Lotivio Ma. Mica (lotiviomica@gmail.com)
lOMoARcPSD|30374161
TAXATION REVIEW
31. It refers to the process of minimizing tax through means which are legal
and not prohibited by law.
a. Tax avoidance
b. Tax evasion
c. Tax dodging
d. Any of the above
The correct answer is: Tax Amnesty
ESCAPE FROM TAXATION
1. Evasion or Dodging
− taxpayer uses unlawful means to evade or lessen the payment tax
2. Avoidance or tax minimization
− reduction or totally escaping payment of tax through legally
permissible means of tax
3. Shifting
− Transfer of burden of tax to another without violating the law.
• Impact is the point at which tax is originally imposed.
• Incidence is the point at which the tax burden finally rests or settles
down.
4. Capitalization
− the seller is willing to lower the price of the commodity provided the
taxes will be shouldered by the buyer
5. Transformation
− the manufacturer absorbs the additional taxes imposed by the
government without passing it to the buyers for fear of loss of his/its
market. Instead, he/it increases quantity of production, thereby turning
their units of production at lower cost resulting to the transformation of
the tax into gain through the medium of production.
6. Exemption
- immunity, privilege or freedom from payment of a charge or burden to
which others are obliged to pay.
Downloaded by Lotivio Ma. Mica (lotiviomica@gmail.com)
lOMoARcPSD|30374161
TAXATION REVIEW
32. Which stage of taxation will the legislative department be involved with?
a. Levy
b. Assessment
c. Collection
d. Imprisonment
The correct answer is: Levy
Stages/Aspects of Taxation
1. Levying or Imposition
− involves the passage of tax laws or ordinances (in case of LGU)
through the legislature
2. Assessment and Collection
− involves the act of administration and implementation of tax laws by the
executive through its administrative agencies such as the BIR and the
Bureau of Customs.
• Assessment
− determination by the executive branch (i.e., BIR, BOC, LGU)
of the correct amount of the tax
• Collection of the tax levied, which is essentially administrative in
character.
33. Land, building and improvement actually, directly and exclusively used for
educational purposes of which educational institutions are exempted from real
property tax?
a. Nonstock nonprofit educational institutions
b. Proprietary educational institutions
c. Both a and b
d. Neither a and b
The correct answer is: Both a and b
The Constitution of the Philippines provide for tax exemptions and privileges as
follows:
<Article XIV, Section 4(3). All revenues and assets of non-stock, non-profit
educational institutions used actually, directly, and exclusively for educational
purposes shall be exempt from taxes and duties.
Downloaded by Lotivio Ma. Mica (lotiviomica@gmail.com)
lOMoARcPSD|30374161
TAXATION REVIEW
34. Statement 1: A revenue bill must originate from the House of
Representatives.
Statement 2: A bill granting tax exemption must originate from the Senate.
a. Only Statement 1 is true.
b. Only Statement 2 is true.
c. Both statements are true.
d. Both statements are false.
The correct answer is: Only Statement 1 is true.
Basis of Statement 1: Art. VI, Section 24 of 1987 Constitution
"All appropriation, revenue or tariff bills, bills authorizing increase of the public
debt, bills of local application, and private bills shall originate exclusively in the
House of Representatives, but the Senate may propose or concur with
amendments."
Basis of Statement 2: Art. VI, Section 28, par. 4 of 1987 Constitution
No law granting any tax exemption shall be passed without the concurrence of a
majority of all the members of the Congress. (Article VI, Section 28, par. 4)
35. Statement 1: In case of doubt, tax exemptions are construed liberally in favor
of the government.
Statement 2: In case of doubt, tax laws are construed liberally in favor of the
taxpayer.
a. Only Statement 1 is true.
b. Only Statement 2 is true.
c. Both statements are true.
d. Both statements are false.
The correct answer is: Both statements are true
CONSTRUCTION OR INTERPRETATION OF TAX LAWS IN CASE OF
DOUBT OR AMBIGUITY
a) Tax statutes are construed strictly against the government and liberally
in favor of the taxpayer. Taxes, being burdens, are not to be presumed
beyond what the statute expressly and clearly declares.
b) Provisions granting tax exemptions are construed strictly against the
taxpayer claiming tax exemption and liberally in favor of the government.
Downloaded by Lotivio Ma. Mica (lotiviomica@gmail.com)
lOMoARcPSD|30374161
TAXATION REVIEW
36. Statement 1: The power to impose tariffs is exercised by the President, not
by the Congress.
Statement 2: The power to tax can never be delegated to local government
units.
a. Only Statement 1 is true.
b. Only Statement 2 is true.
c. Both statements are true.
d. Both statements are false.
The correct answer is: Only Statement 1 is true.
Basis of Statement 1:
It is Congress which authorizes the President to impose tariff rates, import and
export quotas, tonnage and wharfage dues, and other duties or imposts.
Basis of Statement 2:
Non-delegability of the Taxing power (Enactment Tax Laws)
- The taxing power is purely legislative; hence power cannot be
delegated either to the executive or judicial departments.
- The limitation arises the doctrine of separation of powers among three
branches the government.
EXCEPTIONS TO THE RULE AGAINST DELEGATION:
a. Delegation to the President, subject to some limitations and
restrictions, to fix within specified limits, tariff rates and tonnage or
wharfage duties and other duties and imposts.
b. Delegation to local governments the power to create its own
sources of revenues and to levy taxes, subject to such limitations
as provided by law.
c. Delegation to administrative agencies certain aspects of the
taxing process that are not legislative such as:
▪ the power to fix value of property for purposes of taxation
pursuant to fixed rules
▪ the power to assess and collect taxes
Downloaded by Lotivio Ma. Mica (lotiviomica@gmail.com)
lOMoARcPSD|30374161
TAXATION REVIEW
37. Section 244 of the Tax Code provide that __________ shall promulgate all
needful rules and regulations for the effective enforcement of the provisions of
NIRC.
a. The Commissioner of Internal Revenue
b. The Secretary of Finance
c. The Commissioner of Internal Revenue, upon recommendation of the
Secretary of Finance
d. The Secretary of Finance, upon recommendation of the Commissioner
of Internal Revenue
The correct answer is: The Secretary of Finance, upon recommendation of the
Commissioner of Internal Revenue
Powers of the Commissioner on Internal Revenue
1. To interpret tax laws and decide tax cases;
2. To obtain information, and to summon, examine and take testimony of
persons;
3. To make assessments and prescribe additional requirements for tax
administration and enforcement;
4. To conduct inventory - taking, surveillance and to prescribe presumptive
gross sales and receipts;
5. To terminate taxable period;
6. To prescribe real property values;
7. To inquire into bank deposit accounts;
8. To accredit and register tax agents;
9. To prescribe additional procedural or documentary requirements; and
To delegate power to subordinates. (Sec. 4 to 8, NIRC)
38. What is the rationale behind the constitutionally delegated taxation power of
local government unit?
a. To promote local autonomy
b. To advocate national policy
c. To encourage separation from national government
d. To advocate federalism
The correct answer is: To promote local autonomy.
Downloaded by Lotivio Ma. Mica (lotiviomica@gmail.com)
lOMoARcPSD|30374161
TAXATION REVIEW
39. Statement 1: The CIR has the power to interpret tax laws and decide tax
cases.
Statement 2: The CIR has the power to obtain information and to
summon/examine and take testimony of persons.
a. Only Statement 1 is true.
b. Only Statement 2 is true.
c. Both statements are true.
d. Both statements are false.
The correct answer is: Both statements are true.
Republic Act No. 8424: AN ACT AMENDING THE NATIONAL INTERNAL
REVENUE CODE, AS AMENDED, AND FOR OTHER PURPOSES
Section 4. Power of the Commissioner to Interpret Tax Laws and to Decide Tax
Cases. – The power to interpret the provisions of this Code and other tax laws
shall be under the exclusive and original jurisdiction of the Commissioner,
subject to review by the Secretary of Finance.
Section 5. Power of the Commissioner to Obtain Information, and to Summon,
Examine, and Take Testimony of Persons. – In ascertaining the correctness of
any return, or in making a return when none has been made, or in determining
the liability of any person for any internal revenue tax, or in collecting any such
liability, or in evaluating tax compliance.
40. Which of the following statements is incorrect?
a. Taxes may be imposed to raise revenues or to provide disincentives to
certain activities within the state
b. The state can have the power of taxation even if the Constitution does
not expressly give it the power to tax
c. The provisions of taxation in the Philippine Constitution are grants of
power and not limitations on taxing powers
d. For the exercise of the power of taxation, the state can tax anything at
any time
The correct answer is: The provisions of taxation in the Philippine Constitution
are grants of power and not limitations on taxing powers.
Downloaded by Lotivio Ma. Mica (lotiviomica@gmail.com)
lOMoARcPSD|30374161
TAXATION REVIEW
41. What are the grounds for BIR to terminate the taxable period of taxpayer?
a. That a person is retiring from business subject to tax
b. That a person is intending to leave the Philippines or remove his
property therefrom or to hide or conceal his property
c. That a person is performing any act tending to obstruct the
proceedings for the collection of the tax for the past or current quarter
or year or to render the same totally or partly ineffective unless such
proceedings are begun immediately
d. All of the above
The correct answer is: All of the above.
NATIONAL INTERNAL REVENUE CODE OF 1997
As amended by Republic Act N0. 10963 (TRAIN), RA 11256, RA11467 and
RA 11534 (CEATE)
Section 6 (D)
(D) Authority to Terminate Taxable Period. - When it shall come to the knowledge
of the Commissioner that a taxpayer is retiring from business subject to tax, or
is intending to leave the Philippines or to remove his property therefrom or to
hide or conceal his property, or is performing any act tending to obstruct the
proceedings for the collection of the tax for the past or current quarter or year or
to render the same totally or partly ineffective unless such proceedings are
begun immediately, the Commissioner shall declare the tax period of such
taxpayer terminated at any time and shall send the taxpayer a notice of such
decision, together with a request for the immediate payment of the tax for the
period so declared terminated and the tax for the preceding year or quarter, or
such portion thereof as may be unpaid, and said taxes shall be due and payable
immediately and shall be subject to all the penalties hereafter prescribed, unless
paid within the time fixed in the demand made by the Commissioner.
42. The valuation of the CIR of real properties is called:
a. Zonal value
b. Assessed value
c. Fair market value
d. Appraised value
The correct answer is: Zonal Value
Downloaded by Lotivio Ma. Mica (lotiviomica@gmail.com)
lOMoARcPSD|30374161
TAXATION REVIEW
NATIONAL INTERNAL REVENUE CODE OF 1997
As amended by Republic Act N0. 10963 (TRAIN), RA 11256, RA11467 and
RA 11534 (CEATE)
Section 6 (E)
(E) Authority of the Commissioner to Prescribe Real Property Values. - The
Commissioner is hereby authorized to divide the Philippines into different zones
or areas and shall, upon consultation with competent appraisers both from the
private and public sectors, determine the fair market value of real properties
located in each zone or area. For purposes of computing any internal revenue
tax, the value of the property shall be, whichever is the higher of:
(1) the fair market value as determined by the Commissioner, or
(2) the fair market value as shown in the schedule of values of the Provincial
and City Assessors.
43. Which type of double taxation is expressly prohibited by the 1987
Constitution of the Republic of the Philippines?
a. Direct double taxation
b. Indirect double taxation
c. Both a and b
d. Neither a and b
The correct answer is: Neither a and b
a. Direct Duplicate Taxation
- objectionable and prohibited because it violates the constitutional
provision on uniformity and equality. It means:
▪ Taxing twice;
▪ By the same taxing authority;
▪ Within the same jurisdiction or taxing district;
▪ For the same purpose;
▪ In the same year or taxing period; and
▪ Same kind or character of tax
b. Indirect Duplicate Taxation
- not legally objectionable.
- extends to all cases in which there is a burden of two or more
pecuniary imposition but imposed by different taxing authorities
Downloaded by Lotivio Ma. Mica (lotiviomica@gmail.com)
lOMoARcPSD|30374161
TAXATION REVIEW
44. Under Article VI Section 24 of the 1987 Constitution, where shall revenue or
tariff bills originate exclusively?
a. Senate of the Philippines
b. House of Representatives
c. Office of the President
d. Department of Finance
The correct answer is: House of Representatives
SECTION 24. All appropriation, revenue or tariff bills, bills authorizing increase
of the public debt, bills of local application, and private bills shall originate
exclusively in the House of Representatives, but the Senate may propose or
concur with amendments.
45. Which is not a nature of tax?
a. Enforced proportional contribution
b. Enforced within the territorial jurisdiction of the taxing authority
c. Levied by the lawmaking body
d. Generally payable in kind
The correct answer is: Generally payable in kind
Nature and Characteristics of Taxation
1. Inherent Power - may be exercised although not expressly granted by
the constitution
2. Essentially a legislative function - only the legislative can impose taxes
3. Subject to inherent and constitutional limitations- not an absolute power
4. For public purpose
5. The strongest of all the inherent powers of the State.
6. Subject to treaty or comity
7. Generally payable in money
8. Territorial in scope
46. Which does not properly describe the scope of taxation?
a. Comprehensive
b. Supreme
c. Unlimited
d. Discretionary
Downloaded by Lotivio Ma. Mica (lotiviomica@gmail.com)
lOMoARcPSD|30374161
TAXATION REVIEW
The correct answer is: Discretionary
Scope of the Taxing Power of the Legislative
³ power of taxation is the most absolute of all powers of
According to the government
the Supreme ÿ
Court has the broadest scope of all the powers of the
government
ÿ
in the absence of limitations, it is considered as
comprehensive, unlimited, plenary and supreme
- Comprehensive- nearly all elements/
complete
- Plenary- absolute
- Supreme -superior to all others
47. What is the nature of tax laws?
a. It is penal in nature
b. It is criminal in nature
c. It is civil in nature
d. All of the above
The correct answer is: It is civil in nature.
NATURE OF TAX LAWS
• civil and not penal in nature, although there are penalties provided for
their violation.
• The purpose of tax laws imposing penalties for delinquencies is to
compel the timely payment of taxes or to punish evasion or neglect of
duty in respect thereof.
48. Which of the following is a characteristic of tax?
a. The amount to be collected is limited to the cost of regulation
b. It is considered a demand of ownership or proprietorship
c. Its efficient cause or juridical tie is contract
d. It is not subject to legal compensation
Downloaded by Lotivio Ma. Mica (lotiviomica@gmail.com)
lOMoARcPSD|30374161
TAXATION REVIEW
The correct answer is: It is not subject to legal compensation.
Choice A refers to police power, Choice B refers to toll and for Choice C,
collection of tax is not based on contract because it is INHERENT.
49. Under the 1987 Constitution, which has the power to create its own sources
of revenues and to levy, fees, and charges subject to such guidelines and
limitations as the Congress may provide?
a. Each local government unit
b. Bureau of Internal Revenue
c. Bureau of Customs
d. Department of Finance
The correct answer is: Each local government unit
The local authority has a delegated power. It is llegislative in nature through
enactment of local ordinances by the local legislative branch. The levying is done
the legislative branch of the LGU while the assessment and collection is made
by the Treasurer.
50. As a general rule, which of the following shall not be given retroactive
application?
a. Tax laws imposing business tax
b. Tax implementing rules and regulations that are remedial in nature
c. Tax circulars that are intended for internal or administrative purpose of
BIR
d. Tax memoranda that are interpretative in nature
The correct answer is: Tax laws imposing business tax.
APPLICATION OF TAX LAWS
- prospective in operation because the nature and amount of the tax
could not be foreseen and understood by the taxpayer at the time the
transactions which the law seeks to tax was completed.
EXCEPTION:
While it is not favored, a statute may nevertheless operate
retroactively provided it is expressly declared or is clearly the legislative
intent. But a tax law should not be given retroactive application
when it would be harsh and oppressive.
Downloaded by Lotivio Ma. Mica (lotiviomica@gmail.com)
You might also like
- Memorial For Respondent PDFDocument14 pagesMemorial For Respondent PDFshambhavi sinhaNo ratings yet
- CPALE REVIEWER in Principles of Income TaxationDocument9 pagesCPALE REVIEWER in Principles of Income TaxationAce LimpinNo ratings yet
- m1 Taxation Concepts PrinciplesDocument29 pagesm1 Taxation Concepts PrinciplesBryan A.No ratings yet
- Income Taxation 1Document7 pagesIncome Taxation 1Lilia Rose ClementeNo ratings yet
- Tax Part 01Document54 pagesTax Part 01Ms VampireNo ratings yet
- CON Comparative Table - Inherent Powers of State (VLE)Document1 pageCON Comparative Table - Inherent Powers of State (VLE)Emwill gem LisingNo ratings yet
- 1.0 NotesDocument10 pages1.0 NotesFranchaisen MaltoNo ratings yet
- Basis of Taxation:: Benefits-Protection TheoryDocument2 pagesBasis of Taxation:: Benefits-Protection TheoryKisha Alyana ColindresNo ratings yet
- Taxation Week 1Document13 pagesTaxation Week 1Jurian Jaan PeligroNo ratings yet
- 2019 Bar Examination Notes TaxationDocument129 pages2019 Bar Examination Notes TaxationLove-Love Jeraldine Mondia DalupinesNo ratings yet
- Consti ReviewerDocument4 pagesConsti ReviewerRiri AnredapNo ratings yet
- Inherent PowersDocument5 pagesInherent Powersfonz cabrillosNo ratings yet
- Tax 301 Income Taxation Module 1 8Document163 pagesTax 301 Income Taxation Module 1 8Rica Miña100% (2)
- Fundamental Principles: 1 Valisnotes Taxation Prof. Enrico Tabag LecturesDocument7 pagesFundamental Principles: 1 Valisnotes Taxation Prof. Enrico Tabag LecturesJaymie ValisnoNo ratings yet
- 1 Basic Principles of TaxationDocument13 pages1 Basic Principles of TaxationElsie GenovaNo ratings yet
- Taxation Police Power Eminent Domain NatureDocument4 pagesTaxation Police Power Eminent Domain NaturePeytNo ratings yet
- Chapter 1: General Principles in Taxation: Aranea, 98 Phil. 148)Document12 pagesChapter 1: General Principles in Taxation: Aranea, 98 Phil. 148)Rover RossNo ratings yet
- CLASS MATERIALS - TaxationDocument78 pagesCLASS MATERIALS - TaxationBernadette Loise VelascoNo ratings yet
- Inherent Powers of The StateDocument3 pagesInherent Powers of The StateDrake PhilNo ratings yet
- TAX GuideDocument4 pagesTAX Guidekrystel ramosNo ratings yet
- Reviewer - TaxationDocument2 pagesReviewer - TaxationjatalNo ratings yet
- TAX.2901 Basic-PrinciplesDocument11 pagesTAX.2901 Basic-PrinciplesBryan Christian MaragragNo ratings yet
- General Principles of TaxationDocument10 pagesGeneral Principles of TaxationJustineMaeMillanoNo ratings yet
- Economics and Taxation ReviewerDocument23 pagesEconomics and Taxation ReviewerTettersNo ratings yet
- Tax F1Document23 pagesTax F1Jullie anne ArigNo ratings yet
- R.A. 8424 "National Internal Revenue Code of 1997"Document3 pagesR.A. 8424 "National Internal Revenue Code of 1997"Hannah LicuananNo ratings yet
- PrinciplesDocument16 pagesPrinciplesfilnara raguroNo ratings yet
- Ch. 1 Introduction To Taxation PresentationDocument56 pagesCh. 1 Introduction To Taxation PresentationCarmen SorianoNo ratings yet
- Fundamental Powers of StateDocument1 pageFundamental Powers of Statebernardinovitto18No ratings yet
- Tax SanityDocument8 pagesTax Sanitycruisincruz.jdNo ratings yet
- Module 01 General Principles of TaxationDocument29 pagesModule 01 General Principles of TaxationKristine LuarcaNo ratings yet
- Module 01 - General Principles of TaxationDocument38 pagesModule 01 - General Principles of TaxationChel EscuetaNo ratings yet
- Income Tax PrelimDocument19 pagesIncome Tax PrelimCrasher KimNo ratings yet
- Module 1 - General Principles PDFDocument19 pagesModule 1 - General Principles PDFDarius Delacruz100% (1)
- BA223-Module 1-Lesson ProperDocument12 pagesBA223-Module 1-Lesson ProperMark Bryan ComAyaNo ratings yet
- Cpa Review: Taxation TAX - 1701. Basic Principles of Taxation Lecture Notes 1. The Inherent Powers of The State (Pet)Document26 pagesCpa Review: Taxation TAX - 1701. Basic Principles of Taxation Lecture Notes 1. The Inherent Powers of The State (Pet)Remalyn BarridaNo ratings yet
- Basic TaxationDocument13 pagesBasic TaxationMarilyn Perez OlañoNo ratings yet
- TAX.3401 General Principles in Taxation PDFDocument19 pagesTAX.3401 General Principles in Taxation PDFDestiny Lim CalambaNo ratings yet
- TAX 1801 Basic Principles - Hadji Usop, Norhanisah B PDFDocument26 pagesTAX 1801 Basic Principles - Hadji Usop, Norhanisah B PDFMohammadNo ratings yet
- Income Taxation NotesDocument45 pagesIncome Taxation NotesIlonah HizonNo ratings yet
- Chapter 1-3 (Reviewer)Document17 pagesChapter 1-3 (Reviewer)LeeshNo ratings yet
- Income TaxationDocument15 pagesIncome TaxationViky Rose EballeNo ratings yet
- Tax ReviewerDocument43 pagesTax Reviewerchowchow123No ratings yet
- Tax 301 Module 1Document39 pagesTax 301 Module 1LENLYN FALAMIGNo ratings yet
- Tax 301 INCOME TAXATION Module 1 8 PDFDocument162 pagesTax 301 INCOME TAXATION Module 1 8 PDFMaryane AngelaNo ratings yet
- Tax.3201 1 General Principles in TaxationDocument7 pagesTax.3201 1 General Principles in TaxationAether SkywardNo ratings yet
- Module-01-General Principles of TaxationDocument12 pagesModule-01-General Principles of TaxationElle LegaspiNo ratings yet
- Fundamental Principles of TaxationDocument34 pagesFundamental Principles of TaxationKaren DammogNo ratings yet
- Global Reciprocal College: Competency: Integrate The Ability of Creativity and Craftmanship Skills of The StudentDocument16 pagesGlobal Reciprocal College: Competency: Integrate The Ability of Creativity and Craftmanship Skills of The StudentRoderick RonidelNo ratings yet
- TAX 1016 Lesson ONE PDFDocument7 pagesTAX 1016 Lesson ONE PDFMonica MonicaNo ratings yet
- TXTN Module-1Document11 pagesTXTN Module-1Marian Augelio PolancoNo ratings yet
- Tax 301 - Income Taxation Module 1 Fundamentals of TaxationDocument11 pagesTax 301 - Income Taxation Module 1 Fundamentals of TaxationFallen Hieronymus100% (2)
- Income Taxation Week 2Document16 pagesIncome Taxation Week 2Hannah Rae ChingNo ratings yet
- General Principles of Taxation - DayanDocument23 pagesGeneral Principles of Taxation - Dayandanny dayanNo ratings yet
- INCOME TAXATION REVIEWER-Fundamentals of TaxationDocument7 pagesINCOME TAXATION REVIEWER-Fundamentals of TaxationEli PinesNo ratings yet
- Module 1 - Part 1Document3 pagesModule 1 - Part 1trixie maeNo ratings yet
- Principles of TaxationDocument2 pagesPrinciples of TaxationKim Nicole ReyesNo ratings yet
- Taxation NotesDocument27 pagesTaxation NotesRound RoundNo ratings yet
- Fundamental Principles and Concepts of TaxationDocument56 pagesFundamental Principles and Concepts of TaxationAnastasha GreyNo ratings yet
- Ba223: Taxation (Income Taxation) Module 1: General Principles and Concepts of Taxation - Part 1Document14 pagesBa223: Taxation (Income Taxation) Module 1: General Principles and Concepts of Taxation - Part 1Sh1njo SantosNo ratings yet
- social-studies-subject-for-high-school-executive-branchDocument30 pagessocial-studies-subject-for-high-school-executive-branchFiona MiralpesNo ratings yet
- Internal-Control-Systems_4-May-2024 (1)Document4 pagesInternal-Control-Systems_4-May-2024 (1)Fiona MiralpesNo ratings yet
- ActivityDocument3 pagesActivityFiona MiralpesNo ratings yet
- REFLECTIONDocument16 pagesREFLECTIONFiona MiralpesNo ratings yet
- ResearchDocument4 pagesResearchFiona MiralpesNo ratings yet
- Integration Course2Document61 pagesIntegration Course2Fiona MiralpesNo ratings yet
- MDL April 19Document1 pageMDL April 19Fiona MiralpesNo ratings yet
- Bsa Ii B Group 2 Music DanceDocument51 pagesBsa Ii B Group 2 Music DanceFiona MiralpesNo ratings yet
- Module 8 - ReviewerDocument8 pagesModule 8 - ReviewerFiona MiralpesNo ratings yet
- ResearchDocument5 pagesResearchFiona MiralpesNo ratings yet
- Research Questionnaire GROUP-3Document1 pageResearch Questionnaire GROUP-3Fiona MiralpesNo ratings yet
- Module 8 - THEORIESDocument5 pagesModule 8 - THEORIESFiona MiralpesNo ratings yet
- Module 8 - TheoriesDocument3 pagesModule 8 - TheoriesFiona MiralpesNo ratings yet
- Renato Dalomias: ExperienceDocument2 pagesRenato Dalomias: ExperienceFiona MiralpesNo ratings yet
- AEAIS Module 2 Overview of Transaction Processing and Enterprise Resource Planning SystemsDocument28 pagesAEAIS Module 2 Overview of Transaction Processing and Enterprise Resource Planning SystemsFiona MiralpesNo ratings yet
- ACTIVITY 10 - Ramirez, Jerrald Cliff S.Document3 pagesACTIVITY 10 - Ramirez, Jerrald Cliff S.Fiona MiralpesNo ratings yet
- Sales LawDocument191 pagesSales LawFiona MiralpesNo ratings yet
- AIS Chapter 1 17feb24 ClassDocument35 pagesAIS Chapter 1 17feb24 ClassFiona MiralpesNo ratings yet
- Black White Minimalist CV ResumeDocument1 pageBlack White Minimalist CV ResumeFiona MiralpesNo ratings yet
- Intacc Answer KeyDocument232 pagesIntacc Answer KeyFiona MiralpesNo ratings yet
- Miralpes Act2Document3 pagesMiralpes Act2Fiona MiralpesNo ratings yet
- Business LawDocument8 pagesBusiness LawFiona MiralpesNo ratings yet
- Untitled SpreadsheetDocument5 pagesUntitled SpreadsheetFiona MiralpesNo ratings yet
- Week 6 Intact 1Document6 pagesWeek 6 Intact 1Fiona MiralpesNo ratings yet
- DepartmentoDocument4 pagesDepartmentoShubhasish HaqueNo ratings yet
- Vocational Training DataDocument1 pageVocational Training DataKofi jano BokovoNo ratings yet
- PCJS Module 1 PDFDocument9 pagesPCJS Module 1 PDFPrinces joy LasalaNo ratings yet
- How To Write A Comprehensive Business PlanDocument2 pagesHow To Write A Comprehensive Business PlanODUNBAKU SAHEEDNo ratings yet
- RP Magazine July 2023 CompressedDocument60 pagesRP Magazine July 2023 CompressedMuhammad ZeeshanNo ratings yet
- The Chartered Institute of Legal Executives Unit 2 - Contract LawDocument8 pagesThe Chartered Institute of Legal Executives Unit 2 - Contract Lawantcbe100% (1)
- TAXATION 2 Chapter 4 Estate Tax Deductions From Gross EstateDocument8 pagesTAXATION 2 Chapter 4 Estate Tax Deductions From Gross EstateKim Cristian MaañoNo ratings yet
- Section 30 of HSADocument8 pagesSection 30 of HSAAditya D TanwarNo ratings yet
- Why Did The Provisional Government FailDocument2 pagesWhy Did The Provisional Government Failsanjayb1008491No ratings yet
- Module 21 Trade SecretsDocument11 pagesModule 21 Trade SecretsCarnal DesireNo ratings yet
- Data Siswa Mi Bos 20192020 JuldesDocument13 pagesData Siswa Mi Bos 20192020 JuldesAkhir Sebuah DoaNo ratings yet
- 3568c-2 Gs Pre Exp 4151 e 2024 1335784Document41 pages3568c-2 Gs Pre Exp 4151 e 2024 1335784sumitnapit2No ratings yet
- Chinas Neomarcantilism PDFDocument38 pagesChinas Neomarcantilism PDFhujjatunaNo ratings yet
- GBIT - Special Trainings RFP FinalDocument64 pagesGBIT - Special Trainings RFP FinalSardar Saad Ahmed AnsaryNo ratings yet
- Notes On Special Proceedings: de Leon, 2020 EditionDocument14 pagesNotes On Special Proceedings: de Leon, 2020 EditionNorjanisa DimaroNo ratings yet
- G.R. No. L-15315 (Merced v. Diez)Document4 pagesG.R. No. L-15315 (Merced v. Diez)VIRILITER AGITENo ratings yet
- Eviction Answer Toolkit 1.27.21Document8 pagesEviction Answer Toolkit 1.27.21Big PoohNo ratings yet
- Workplace Harassment Preventation PolicyDocument2 pagesWorkplace Harassment Preventation PolicyJohn Leo De LeusNo ratings yet
- Perjanjian Pembiayaan Pendidikan: Education Costs AgreementDocument2 pagesPerjanjian Pembiayaan Pendidikan: Education Costs AgreementFipsi EndrawanNo ratings yet
- Introduction To Conveyancing Lecture 1Document18 pagesIntroduction To Conveyancing Lecture 1Judge and Jury.No ratings yet
- Cry of Rebellion 3Document11 pagesCry of Rebellion 3ricoliwanag100% (2)
- Submitted By-:: Ravi Banwani Amlan Dutta Gaurang Kadyan Himanshu Rashee VishwaroopDocument21 pagesSubmitted By-:: Ravi Banwani Amlan Dutta Gaurang Kadyan Himanshu Rashee VishwaroopDutt_Amy_7215No ratings yet
- DLL - Tle 6 - Q2 - W8Document5 pagesDLL - Tle 6 - Q2 - W8Ma Tintin Palao GarciaNo ratings yet
- Sample Format of Certification of Legally, Peacefully and Orderly Execution of Search WarrantDocument2 pagesSample Format of Certification of Legally, Peacefully and Orderly Execution of Search WarrantEly A Zar0% (1)
- Order Denying Plaintiff Motion For Summary Judgment - Denise OatesDocument3 pagesOrder Denying Plaintiff Motion For Summary Judgment - Denise OatesMark WillensNo ratings yet
- Flaws Company Ordinance 1984Document25 pagesFlaws Company Ordinance 1984Yaman TahirNo ratings yet
- 04 Judicial Affidavit of Housemaid Dona LlamadoDocument8 pages04 Judicial Affidavit of Housemaid Dona Llamadochiiwapanda yangNo ratings yet
- Relevance of Dayanand in ModernDocument2 pagesRelevance of Dayanand in ModernVikas PrajapatiNo ratings yet
- Mr. Addams' EditingDocument15 pagesMr. Addams' EditingKim KoalaNo ratings yet