Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Calculation of Impact Force and Velocity of Fish On Free Fall
Uploaded by
Eloy RosilloOriginal Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Calculation of Impact Force and Velocity of Fish On Free Fall
Uploaded by
Eloy RosilloCopyright:
Available Formats
PROBLEM:
Calculate the terminal velocity and impact force of a completions tubing which fell
into KZN-6 wellbore and landed on the 7” x 4 1/2” liner crossover at 4476 m.
GIVEN:
Fluid: Brine
Weight of fluid = 1.36 sg (1360 kg/m3)
YP = 24 lbf/100ft2
PV = 33
Approximate weight of fish = 1331.6 lbs
Hole profile = Vertical
SOLUTION
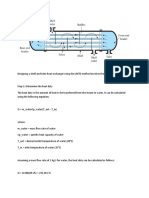
Terminal velocity of an object is given by equation 1 below
2mg
Vt = ………………………………………..……...1
ρACd
Where;
Vt = terminal velocity
m = mass of falling object
g = acceleration due to gravity
Cd = drag coefficient
ρ = density of the fluid through which the object is falling
A = project area of the object
Buoyancy effects, due to the upward force on the object by the surrounding fluid, can
be taken into account using Archimedes' principle: the mass, m has to be reduced by
the displaced fluid mass, so instead of the buoyed weight of the tubing will be used in
the calculation.
Assumptions
1. It is assumed that the flow around the tubing as it falls down the well is
turbulent i. e Reynold’s number, Re, > 4000.
2. It was not possible to determine the drag coefficient of an open-ended hollow
cylinder (to simulate the tubing) with flow stream along its longitude. The
drag co-efficient of a ring (see diagram below) is 1.2. Considering the surface
area at the bottom of the tubing as a ring and considering surface area of the
78 m long tubing, a drag co-efficient of 2.4 will used for calculations
Figure 1: Drag Co-efficient Data for Object with Re > 1000 (Courtesy: Mechanical Engineering
Handbook)
3. Friction factor of cased hole is assumed to be 0.25. This factor will be
included in equation 1 above
Calculation of Terminal Velocity
Bouyancy factor = 0.83
Buoyed weight of tubing = 0.83 * 1331.6 * 0.4536 = 501.33 kg
g = 9.81m/s2
ρ = 1360 kg/m3
Cd - 2.4
ff = friction factor = 0.25
(OD 2 − ID 2)
A = area = π ………………………………………..2
4
where
OD = outer diameter of tubing = 5.08” = 0.13 m
ID = inner diameter of tubing = 3.74” = 0.095 m
A = π (0.132 - 0.0952) / 4 = 0.0062 m2
2 * 501.33 * 9.81
Terminal Velocity, Vt =
1360 * 0.0062 * 2.4 * 0.25
= 44 m/s
Calculation of Impact Force
F = ma = mV/t………………………………………………………3
Where
m = mass
a = acceleration
v = velocity = 44 m/s
t = time
Now, V = Distance/ Time
Distance = 4476 m
therefore, time = 4476 / 44 = 101.7 s
501.33 * 44
therefore, Impact force =
101.7
= 217 N
RFERENCE
1. Kreith, F.; Berger, S. A.; et. al. “Fluid Mechanics” Mechanical Engineering
Handbook. Boca Raton: CRC Press LLC, 1999
2. http://www.engineeringtoolbox.com [Accessed on 5-Aug-09]
3. http://en.wikipedia.org [Accessed on 5-Aug-09]
4. Schlumberger well, drilling and completions bulletin board
You might also like
- Main FileDocument9 pagesMain FileSyed Munawar AliNo ratings yet
- Mathcad - Spreader Beam Design Calculations As Per DNV 5th VerDocument29 pagesMathcad - Spreader Beam Design Calculations As Per DNV 5th VerAbderraoufAffes100% (3)
- Calculations of Creep and Shrinkage Effects for an Example Bridge with Precast Concrete GirdersDocument11 pagesCalculations of Creep and Shrinkage Effects for an Example Bridge with Precast Concrete GirdersMahmood MuftiNo ratings yet
- Pipelines and Soil Mechanics 31 March 2020Document9 pagesPipelines and Soil Mechanics 31 March 2020George BabyNo ratings yet
- 2nd Power Fluid B 2011 Final With Model AnsweDocument7 pages2nd Power Fluid B 2011 Final With Model AnsweS.A. BeskalesNo ratings yet
- Upgradation and Relocation of Karakorum Highway For Basha Diamer Dam ProjectDocument14 pagesUpgradation and Relocation of Karakorum Highway For Basha Diamer Dam ProjectkuttakhaoNo ratings yet
- Design Calculation RCC Sleeper Type 6Document9 pagesDesign Calculation RCC Sleeper Type 6DrAmit Dutta100% (4)
- Ieee 80 Tiuch and Step Volt - Full CalcDocument22 pagesIeee 80 Tiuch and Step Volt - Full CalcVasu Iyer100% (1)
- Hydraulic and Structural Design of Super PassageDocument25 pagesHydraulic and Structural Design of Super PassageCPK100% (2)
- Civil FormulaDocument80 pagesCivil FormulaBharat SharmaNo ratings yet
- Rotary Drier DesignDocument29 pagesRotary Drier DesignDharamvir Singh80% (5)
- Design Project1Document19 pagesDesign Project1Syed Munawar Ali100% (1)
- Foundation design calculations for ME-EE952-S082 heat exchangerDocument11 pagesFoundation design calculations for ME-EE952-S082 heat exchangerLandon Mitchell100% (2)
- Design and Analysis of an Offshore Wind Turbine FoundationDocument33 pagesDesign and Analysis of an Offshore Wind Turbine FoundationRatnakar GadiNo ratings yet
- Where, The Temperature Ratio, Capacity Ratio, R A Value of 0.8 Is Generally Not AcceptedDocument43 pagesWhere, The Temperature Ratio, Capacity Ratio, R A Value of 0.8 Is Generally Not AcceptedAditya DeokarNo ratings yet
- Storm Water Pump StationDocument6 pagesStorm Water Pump StationНемања КараклајићNo ratings yet
- Shutter ConnectionDocument2 pagesShutter ConnectionНемања КараклајићNo ratings yet
- Design of Heat ExchangersDocument23 pagesDesign of Heat ExchangersKhalid Turki100% (2)
- Lecture 6Document9 pagesLecture 6Raj BakhtaniNo ratings yet
- Subsee Suction Pile Installation AnalysisDocument11 pagesSubsee Suction Pile Installation AnalysisKen KennyNo ratings yet
- Clarifier Tank Skert2Document20 pagesClarifier Tank Skert2ekmagisNo ratings yet
- Design of a 150 m3/hr Vertical Sludge Blanket Clarifier TankDocument15 pagesDesign of a 150 m3/hr Vertical Sludge Blanket Clarifier TankBUDAPES100% (1)
- PDA Test Report ObservationsDocument5 pagesPDA Test Report ObservationsVenkat PalliNo ratings yet
- 2marks DEM 6 Sem EEE Anna UniversityDocument18 pages2marks DEM 6 Sem EEE Anna UniversityJagadeesh MannivannanNo ratings yet
- Excel Review Center FB 17 - GeasDocument4 pagesExcel Review Center FB 17 - GeasEmanuel GabrielNo ratings yet
- EE2355 Design of Electrical Machines NotesDocument24 pagesEE2355 Design of Electrical Machines Notesmadhes14No ratings yet
- Magnetic Circuit of A D C MachineDocument14 pagesMagnetic Circuit of A D C Machineapi-319127980100% (3)
- Construction of 33kV Substation at NTPC LaraDocument5 pagesConstruction of 33kV Substation at NTPC LaraIrshad KhanNo ratings yet
- Transmission Line Design CalcDocument38 pagesTransmission Line Design CalcparmenderNo ratings yet
- T208 Bored Pile Design - XLSXDocument3 pagesT208 Bored Pile Design - XLSXerikaren85No ratings yet
- Design of Steel Truss MembersDocument6 pagesDesign of Steel Truss MembersSaim WaqarNo ratings yet
- 184 907Document40 pages184 907Ankur DubeyNo ratings yet
- EMDDocument23 pagesEMDPrakash ArumugamNo ratings yet
- Toaz - Info Main File PRDocument9 pagesToaz - Info Main File PRAbdelrahman MohamedNo ratings yet
- Design of Pile FoundationDocument16 pagesDesign of Pile FoundationJagal Udaya100% (3)
- SCOPE:: Design Input DataDocument7 pagesSCOPE:: Design Input DataEmmanuel LawrenceNo ratings yet
- Access Scaffoding DesignDocument10 pagesAccess Scaffoding DesignSyed Munawar Ali100% (5)
- Evaluate Ow and Heat Transfer in Agitated Jackets: August 2005Document4 pagesEvaluate Ow and Heat Transfer in Agitated Jackets: August 2005dania hjoujNo ratings yet
- Buoyancy Calculation Report For 10INCH PipelineDocument7 pagesBuoyancy Calculation Report For 10INCH PipelineEmmanuel LawrenceNo ratings yet
- Controllable Pitch Propeller System Using The Shaft Line EnergyDocument7 pagesControllable Pitch Propeller System Using The Shaft Line EnergyPirosca VasileNo ratings yet
- Designing a shell-and-tube heat exchangerDocument8 pagesDesigning a shell-and-tube heat exchangerLorna AhlaamiNo ratings yet
- Design of fenders and berthing energy calculationsDocument12 pagesDesign of fenders and berthing energy calculationsUygar KöprücüNo ratings yet
- Rotary Dryer DesignDocument43 pagesRotary Dryer DesignsasitharNo ratings yet
- CE Weekend Knockout Quiz With Answer Key PDFDocument19 pagesCE Weekend Knockout Quiz With Answer Key PDFppppp100% (1)
- Concrete Bridge Design (Recovered)Document82 pagesConcrete Bridge Design (Recovered)Isaac Mureithi Maina100% (1)
- Lattice Calc 1010Document19 pagesLattice Calc 1010Hari HaranNo ratings yet
- 3D Modeling of Nonlinear Wave Phenomena on Shallow Water SurfacesFrom Everand3D Modeling of Nonlinear Wave Phenomena on Shallow Water SurfacesNo ratings yet
- O level Physics Questions And Answer Practice Papers 2From EverandO level Physics Questions And Answer Practice Papers 2Rating: 5 out of 5 stars5/5 (1)
- MOS Integrated Circuit DesignFrom EverandMOS Integrated Circuit DesignE. WolfendaleNo ratings yet
- Analytical Modeling of Solute Transport in Groundwater: Using Models to Understand the Effect of Natural Processes on Contaminant Fate and TransportFrom EverandAnalytical Modeling of Solute Transport in Groundwater: Using Models to Understand the Effect of Natural Processes on Contaminant Fate and TransportNo ratings yet
- Interactions between Electromagnetic Fields and Matter: Vieweg Tracts in Pure and Applied PhysicsFrom EverandInteractions between Electromagnetic Fields and Matter: Vieweg Tracts in Pure and Applied PhysicsNo ratings yet
- Theory of Microwave Valves: International Series of Monographs on Electronics and InstrumentationFrom EverandTheory of Microwave Valves: International Series of Monographs on Electronics and InstrumentationNo ratings yet
- Electronic Devices and Circuits: The Commonwealth and International Library: Electrical Engineering Division, Volume 1From EverandElectronic Devices and Circuits: The Commonwealth and International Library: Electrical Engineering Division, Volume 1Rating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (5)
- Mechanicsssssss ExamplesDocument9 pagesMechanicsssssss ExamplesJhonrey Joey DesabilleNo ratings yet
- BDC+4013 (Final Exam)Document7 pagesBDC+4013 (Final Exam)Unefalcons UnengNo ratings yet
- 9702 p1 Waves AllDocument17 pages9702 p1 Waves AllNushanKhan100% (1)
- Cambridge IGCSE: PHYSICS 0625/43Document16 pagesCambridge IGCSE: PHYSICS 0625/43kaiNo ratings yet
- Light Formula SheetDocument1 pageLight Formula SheetManoj KulkarniNo ratings yet
- Layers - of - The - Atmosphere Final Na GrabeDocument23 pagesLayers - of - The - Atmosphere Final Na GrabeJustine PamaNo ratings yet
- Solution To p.171 of PHYSICS Bilingual For Year VIII (Yudhistira)Document1 pageSolution To p.171 of PHYSICS Bilingual For Year VIII (Yudhistira)vtendeanNo ratings yet
- Combine PDFDocument228 pagesCombine PDFSRIRAM PARASURAMANNo ratings yet
- IB PHYSICS Syllabus GuideDocument6 pagesIB PHYSICS Syllabus GuidePatrick PrakasaNo ratings yet
- Black-body Radiation Peak Wavelength vs TemperatureDocument11 pagesBlack-body Radiation Peak Wavelength vs TemperatureamanNo ratings yet
- Rectilinear Motion NotesDocument3 pagesRectilinear Motion NotesKaranbir Randhawa100% (1)
- ME 09 802 Compressible Fluid Flow APR 2013Document2 pagesME 09 802 Compressible Fluid Flow APR 2013sivanNo ratings yet
- Radio Waves - Saranya TrehanDocument9 pagesRadio Waves - Saranya TrehanJAYATINo ratings yet
- Laboratory Experiment - Thermal ConvectionDocument5 pagesLaboratory Experiment - Thermal ConvectionJ7C2No ratings yet
- The Seismic Wave Equation: Rick Aster February 15, 2011Document18 pagesThe Seismic Wave Equation: Rick Aster February 15, 2011susisoburNo ratings yet
- Dynamics and Vibrations - Notes - Free Undamped VibrationsDocument12 pagesDynamics and Vibrations - Notes - Free Undamped VibrationsNavin KumarNo ratings yet
- Compiled E105 E111Document36 pagesCompiled E105 E111MingNo ratings yet
- Flame PhotometryDocument8 pagesFlame PhotometrySai SridharNo ratings yet
- Phys Ics: GiancoliDocument21 pagesPhys Ics: GiancoliWendi Ibnu Al-FarisiNo ratings yet
- Es Chapter 13Document92 pagesEs Chapter 13api-268159571No ratings yet
- A Dual-Polarized Reconfigurable Reflectarray Antenna Based On A Symmetrically Rotated Sub-ArrayDocument7 pagesA Dual-Polarized Reconfigurable Reflectarray Antenna Based On A Symmetrically Rotated Sub-ArrayAnurag PalNo ratings yet
- Why Whips CrackDocument7 pagesWhy Whips CrackDaniel DinhNo ratings yet
- The Bouguer Beer Lambert Law Shining Lightonthe ObscureDocument20 pagesThe Bouguer Beer Lambert Law Shining Lightonthe ObscureSAMANTHA VIRGINIA TANSILNo ratings yet
- Mechanics of Machines - VibrationDocument34 pagesMechanics of Machines - VibrationGiovani Carpin100% (1)
- Observe refraction and lateral displacement through a glass slabDocument3 pagesObserve refraction and lateral displacement through a glass slabSHIBAM MANDAL100% (1)
- C18-Radioactivity and Nuclear ReactionsDocument106 pagesC18-Radioactivity and Nuclear ReactionsAbhishek UpadhyayNo ratings yet
- Coherent Sources of LightDocument5 pagesCoherent Sources of LightSamuel SujanNo ratings yet
- Laser PropertiesDocument13 pagesLaser PropertieszxcvuiopNo ratings yet
- Dedan Kimathi University of Technology exam paper electromagnetic wavesDocument3 pagesDedan Kimathi University of Technology exam paper electromagnetic wavesHenry Kabasa100% (1)
- Midterm Exam Physics General 1 Forces MotionDocument3 pagesMidterm Exam Physics General 1 Forces MotionNam Anh Nguyễn HữuNo ratings yet