0% found this document useful (0 votes)
54 views16 pagesShort Concrete Column Design Guide
This document provides guidance on designing short concrete columns. It includes:
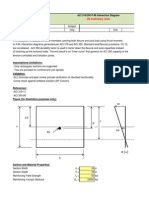
1) An overview of the input data, analysis, and design requirements for short concrete columns.
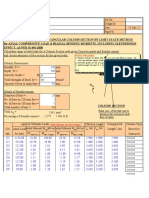
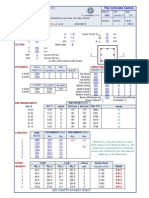
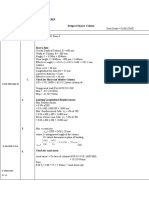
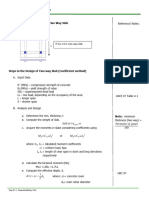
2) Steps for calculating factored axial and moment loads, selecting rebar size and layout, and checking design strength.
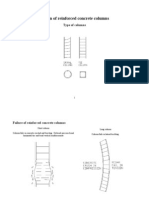
3) Requirements for column transverse reinforcement including ties and spirals.
4) Procedures for checking beam-column joint shear strength.
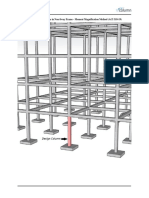
5) Instructions for using supporting software to determine gravity and seismic column loads from structural analysis models.
Uploaded by
Christoper Dela CruzCopyright
© © All Rights Reserved
We take content rights seriously. If you suspect this is your content, claim it here.
Available Formats
Download as DOCX, PDF, TXT or read online on Scribd
0% found this document useful (0 votes)
54 views16 pagesShort Concrete Column Design Guide
This document provides guidance on designing short concrete columns. It includes:
1) An overview of the input data, analysis, and design requirements for short concrete columns.
2) Steps for calculating factored axial and moment loads, selecting rebar size and layout, and checking design strength.
3) Requirements for column transverse reinforcement including ties and spirals.
4) Procedures for checking beam-column joint shear strength.
5) Instructions for using supporting software to determine gravity and seismic column loads from structural analysis models.
Uploaded by
Christoper Dela CruzCopyright
© © All Rights Reserved
We take content rights seriously. If you suspect this is your content, claim it here.
Available Formats
Download as DOCX, PDF, TXT or read online on Scribd