Professional Documents
Culture Documents
MQTT and OSI Model Explanation
Uploaded by
Mustaqiim Roslan0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
21 views2 pagesMQTT is a lightweight messaging protocol designed for constrained devices like IoT sensors. It uses a publish/subscribe model where devices can publish messages to a broker and subscribe to topics to receive messages. MQTT operates at the application layer of the OSI model, sitting above the transport layer which commonly uses TCP/IP to provide reliable message delivery. The OSI model is a conceptual framework that divides network communication into seven layers, with each layer providing a specific function from the physical connection between devices to the applications that access network services.
Original Description:
Copyright
© © All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
DOCX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentMQTT is a lightweight messaging protocol designed for constrained devices like IoT sensors. It uses a publish/subscribe model where devices can publish messages to a broker and subscribe to topics to receive messages. MQTT operates at the application layer of the OSI model, sitting above the transport layer which commonly uses TCP/IP to provide reliable message delivery. The OSI model is a conceptual framework that divides network communication into seven layers, with each layer providing a specific function from the physical connection between devices to the applications that access network services.
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as DOCX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
21 views2 pagesMQTT and OSI Model Explanation
Uploaded by
Mustaqiim RoslanMQTT is a lightweight messaging protocol designed for constrained devices like IoT sensors. It uses a publish/subscribe model where devices can publish messages to a broker and subscribe to topics to receive messages. MQTT operates at the application layer of the OSI model, sitting above the transport layer which commonly uses TCP/IP to provide reliable message delivery. The OSI model is a conceptual framework that divides network communication into seven layers, with each layer providing a specific function from the physical connection between devices to the applications that access network services.
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as DOCX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
You are on page 1of 2
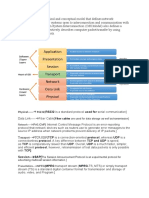
MQTT and OSI Model Explanation
MQTT and OSI Model
MQTT
MQTT stands for Message Queuing Telemetry Transport. It is a lightweight messaging
protocol designed for small sensors and mobile devices, making it ideal for Internet of
Things (IoT) applications. MQTT operates on a publish/subscribe model, which allows
devices to publish messages to a broker and subscribe to topics to receive messages.
Key Features of MQTT:
• Lightweight Messaging Protocol: Optimized for high-latency or unreliable
networks.
• Publish/Subscribe Model: Enables decoupled communication between
devices.
• Designed for IoT Devices: Ideal for constrained devices with limited bandwidth
and power.
• Quality of Service Levels: Offers three levels of message delivery guarantees:
– At most once (0): Fastest, but no guarantee of delivery.
– At least once (1): Guarantees delivery but may result in duplicate
messages.
– Exactly once (2): Guarantees delivery and ensures no duplicates, but
with higher overhead.
• Retained Messages: Allows messages to be retained by the broker for new
subscribers.
• Last Will and Testament: Enables notification to other clients in case of an
unexpected disconnection.
OSI Model
The Open Systems Interconnection (OSI) model is a conceptual framework used to
understand and standardize the functions of a telecommunication or computing system
without regard to its underlying internal structure and technology. The model is divided
into seven layers, each serving a specific function.
Layers of the OSI Model:
• Application Layer: The top layer where applications access network services,
which includes protocols like MQTT.
• Presentation Layer: Transforms data to provide a standard interface for the
Application layer.
• Session Layer: Manages sessions between applications.
• Transport Layer: Provides reliable or unreliable delivery, and performs error
correction before retransmit. Commonly, MQTT uses TCP/IP at this layer.
• Network Layer: Handles routing of the data.
• Data Link Layer: Provides node-to-node data transfer.
• Physical Layer: Concerned with the physical connection between devices.
This mind map provides a visual representation of the MQTT protocol and its place
within the OSI model, highlighting its application in IoT devices and the underlying
network layers that support it.
You might also like
- MQTT and OSI Model ExplanationDocument2 pagesMQTT and OSI Model ExplanationMustaqiim RoslanNo ratings yet
- Iot Unit 4Document53 pagesIot Unit 4SRHNo ratings yet
- Networking 2: It 219: Lesson IvDocument19 pagesNetworking 2: It 219: Lesson IvKlim Hazel Racal LumansocNo ratings yet
- MQTT (Message Queue: Telemetry Transport)Document21 pagesMQTT (Message Queue: Telemetry Transport)hpokhrelNo ratings yet
- Unit - 3 NotesDocument48 pagesUnit - 3 NotesAnish RajNo ratings yet
- Chapter - Two of Networking212Document53 pagesChapter - Two of Networking212haileNo ratings yet
- Iot Protocol: Advanced Message Queuing Protocol (AMQP)Document5 pagesIot Protocol: Advanced Message Queuing Protocol (AMQP)rujula shindeNo ratings yet
- RS232 Is A Standard Protocol Used For Serial Communication)Document3 pagesRS232 Is A Standard Protocol Used For Serial Communication)Nithya PrasathNo ratings yet
- IoT-Lecture-8 Slides Networking and Communication - IDocument27 pagesIoT-Lecture-8 Slides Networking and Communication - IARNAV JAIN100% (1)
- Data Communication & NetworkingDocument71 pagesData Communication & NetworkingShabanaNo ratings yet
- Unit 2Document121 pagesUnit 2udaykiranub20No ratings yet
- 1.definition and Characteristics of IotDocument19 pages1.definition and Characteristics of Iot18R11A0530 MUSALE AASHISHNo ratings yet
- Iot With PythonDocument68 pagesIot With PythonPriyanshuNo ratings yet
- IOT Module 1Document17 pagesIOT Module 1lekhyaNo ratings yet
- Lecture 1.1.1 and 1.1.2 - OSI Model and TCP-IP Model - DCDocument33 pagesLecture 1.1.1 and 1.1.2 - OSI Model and TCP-IP Model - DCanonymousguyinfinityNo ratings yet
- DR JWC IOTDocument43 pagesDR JWC IOTraviNo ratings yet
- Base IOTDocument99 pagesBase IOTnguyenbaviet89No ratings yet
- Internet of Things Coursefile 34 118Document85 pagesInternet of Things Coursefile 34 118SrinivasNo ratings yet
- Assignment 4Document10 pagesAssignment 4anil rajputNo ratings yet
- BSC Honours in Computer Science: Part 2 Semester 1: Kashuware Brilliant M198070 Mazonde Phyeciathy M190810Document16 pagesBSC Honours in Computer Science: Part 2 Semester 1: Kashuware Brilliant M198070 Mazonde Phyeciathy M190810Brilliant Billykash KashuwareNo ratings yet
- A Framework For Modeling and Verifying Iot Communication ProtocolsDocument21 pagesA Framework For Modeling and Verifying Iot Communication ProtocolsShivamNo ratings yet
- Chapter 2Document7 pagesChapter 2Hrituja HedauNo ratings yet
- IOTnotesDocument79 pagesIOTnotessvtNo ratings yet
- Data Communication LayersDocument22 pagesData Communication Layersendriasmit_469556062No ratings yet
- FALLSEM2019-20 CSE3009 ETH VL2019201001465 Reference Material I 12-Jul-2019 IOT LECTURE NOTES IT-2-87 2 PDFDocument86 pagesFALLSEM2019-20 CSE3009 ETH VL2019201001465 Reference Material I 12-Jul-2019 IOT LECTURE NOTES IT-2-87 2 PDFManish CherukuNo ratings yet
- UNIT 1 CNDocument16 pagesUNIT 1 CNnavya goneNo ratings yet
- C2 Dec30023Document106 pagesC2 Dec30023MUHAMMAD AFIINo ratings yet
- Lecture 03 - Network Requirements and Layered ArchitecturesDocument25 pagesLecture 03 - Network Requirements and Layered ArchitectureskijabryanNo ratings yet
- CN 1Document7 pagesCN 1T024KOUSTAV CHATTERJEENo ratings yet
- Ref ModelDocument19 pagesRef Modelkalpana.gangwarNo ratings yet
- Department of Computer Science MCADocument6 pagesDepartment of Computer Science MCAMOHAMMED ASHICKNo ratings yet
- The OSI and TCPDocument8 pagesThe OSI and TCPSreejith VaneryNo ratings yet
- Iot System Architecture Unit 1Document17 pagesIot System Architecture Unit 1lakshmiNo ratings yet
- Iot NotesDocument85 pagesIot NotesToshita SatputeNo ratings yet
- Case Study On Any One Layer of OSI ModelDocument8 pagesCase Study On Any One Layer of OSI ModelDharmesh VaishNo ratings yet
- IoT Viva SolnDocument18 pagesIoT Viva SolnRauf LalaNo ratings yet
- Osi ModelDocument5 pagesOsi ModelTaimoor ZubairNo ratings yet
- Enabling Technologies For Data Science Analytics - IoT - UNIT-I PDFDocument72 pagesEnabling Technologies For Data Science Analytics - IoT - UNIT-I PDFabid princeNo ratings yet
- OSI ModelDocument28 pagesOSI Modeltuhafenijason05No ratings yet
- Chapter 3 - Layered ModelsDocument53 pagesChapter 3 - Layered ModelsDanny KirooNo ratings yet
- Iot Unit 1 2Document45 pagesIot Unit 1 2RADHARAPU DIVYA PECNo ratings yet
- Networking Basics & OSI Reference ModelDocument79 pagesNetworking Basics & OSI Reference Modelwisedotblue100% (1)
- Network 5Document12 pagesNetwork 5Anuradha UdeshNo ratings yet
- Computer Networks-Module1Document34 pagesComputer Networks-Module1Sreedevi YashpalNo ratings yet
- On Modelling and Validation of The MQTT Iot Protocol For M2M CommunicationDocument20 pagesOn Modelling and Validation of The MQTT Iot Protocol For M2M CommunicationDươngTK VlogsNo ratings yet
- What Is MQTT ?: Kevin AshtonDocument4 pagesWhat Is MQTT ?: Kevin AshtonAbhijit PattnaikNo ratings yet
- Chapter 3 - Layered ModelsDocument52 pagesChapter 3 - Layered Modelsomika494100% (1)
- Iot Protocol and AnalyticsDocument72 pagesIot Protocol and AnalyticsToshnav KhatkeNo ratings yet
- Chapter 3 Communication On A Local NetworkDocument17 pagesChapter 3 Communication On A Local Networknathaniel manuzonNo ratings yet
- Ccna NotesDocument215 pagesCcna NotesPrasanth Jayasviji JsNo ratings yet
- Presentation Topic: Tcp/Ip Presented By: Iftakhar Hussain Roll No: 2019-BSIT-043 Department: Cs & ItDocument14 pagesPresentation Topic: Tcp/Ip Presented By: Iftakhar Hussain Roll No: 2019-BSIT-043 Department: Cs & ItIftakhar HussainNo ratings yet
- OSI and TCP-IP ModelsDocument16 pagesOSI and TCP-IP ModelsJohn OlivaNo ratings yet
- Chapter One Physical and Data Link Layer OverviewDocument68 pagesChapter One Physical and Data Link Layer Overviewabrham tesfayeNo ratings yet
- IOT Network Architecture and DesignDocument32 pagesIOT Network Architecture and DesignMegha ShreeNo ratings yet
- Module 2Document19 pagesModule 2yogeshwarkolarNo ratings yet
- Unit 5 IOTDocument40 pagesUnit 5 IOTRagul AadithyaNo ratings yet
- Chameli Devi Group of Institutions Department of Computer Science and Engineering Subject: Internet of Things (CS-801)Document10 pagesChameli Devi Group of Institutions Department of Computer Science and Engineering Subject: Internet of Things (CS-801)Sourabh porwalNo ratings yet
- Week-2 - Lesson-1 PDFDocument26 pagesWeek-2 - Lesson-1 PDFMamun Ahmed joyNo ratings yet
- Hacking Network Protocols: Unlocking the Secrets of Network Protocol AnalysisFrom EverandHacking Network Protocols: Unlocking the Secrets of Network Protocol AnalysisNo ratings yet