Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Covalent Compounds Total
Uploaded by
milinlord4430 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
3 views3 pagesOriginal Title
Covalent compounds total
Copyright
© © All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
3 views3 pagesCovalent Compounds Total
Uploaded by
milinlord443Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
You are on page 1of 3
Covalent compounds
1-ﻣﺤﻤﺪ ﻣﺎ'ﺣﺪ ﻋ'ٮ*ٮﺪ
Whats !s a covalent compound
A covalent compound !s a molecule formed by covalent bonds, !n wh!ch the atoms share one or more pa!rs of valence electrons.
The D!fferent K!nds of Compounds (ڡﺔ ﻣﻦ اﻟﻤﺮﻛ'ٮﺎت.ٮﻠ2ﺤ.ٮواع اﻟﻤ.)اﻷ
Chem!cal compounds are generally grouped !nto one of two categor!es: covalent compounds and !on!c compounds.
Ion!c compounds are made up of electr!cally charged atoms or molecules as a result of ga!n!ng or los!ng electrons. Ions of oppos!te charges form !on!c
compounds, usually as a result of a metal react!ng w!th a nonmetal.
2-ٮ'ﺤﻢ ﻋ'ٮﺪﷲ. ﻋﲇ
The H!story of Covalent Compounds(ٮﺴﺎﻫﻤ*ٮﺔ2ﺎريﺦ اﻟﻤﺮﻛ'ٮﺎت اﻟ2)ٮ
Amer!can phys!cal chem!st G!lbert N. Lew!s f!rst descr!bed covalent bond!ng !n a 1916 art!cle, though he d!dn't use that term. Amer!can chem!st Irv!ng Langmu!r
f!rst used the term covalence !n reference to bond!ng !n a 1919 art!cle !n the Journal of the Amer!can Chem!cal Soc!ety.
Examples(ٮﻠﺔC)أﻣ
Water, sucrose, and DNA are examples of covalent compounds
3-ڡ*ٮﺲ 'ﺣﺎ'ٮﺮ ا'ٮراﻫ*ٮﻢ2 ﻣﺤﻤﺪ
Phys!cal and chem!cal propert!es( ڡ*ٮزيﺎﺋ*ٮﺔ واﻟﻜ*ٮﻤ*ٮﺎﺋ*ٮﺔ.ﺤﺼﺎﺋﺺ اﻟ.)اﻟ
The l!qu!d covalent compounds evaporate. Th!s means the molecules of l!qu!ds and sol!ds loses from the!r surface !nto the a!r.
These compounds have very less aff!n!ty between the!r molecules.
Var!ous covalent compounds have the!r own character!st!cally shaped molecules. The!r bonds are d!rected at pre-set angles.
4-ڡﻰ ﺻ'ٮﺎح ﺣﺴﻦ.ﻣﺼﻄ
Some compounds espec!ally med!c!nes are soluble !n water. The rest are soluble !n o!l.
Most of the covalent compounds are non-polar or have very l!ttle tendency to spl!t completely to form !ons and hence never conduct electr!c!ty.
At normal temperature and pressure, we w!ll f!nd these compounds as e!ther l!qu!ds or gases. But, there are sol!ds as well and they have h!gher molecular
we!ghts.
5- ﻫﺎرون وﻟ*ٮﺪ ﺣﺴ*ٮﺐ
Character!st!cs of CovalentCompounds (ٮﺴﺎﻫﻤ*ٮﺔ2ﺣﺼﺎﺋﺺ اﻟﻤﺮﻛ'ٮﺎت اﻟ. )
1. It d!ssolves !n water !n a molecular state.
2. They don't conduct electr!c!ty well.
3. They do not conduct heat well.
4. They have weaker bonds than !on!c bonds.
5. They are frag!le .
6. They are found !n molecular structure.
7. Polar covelent bonds soluble !n water.
8-Compared to the !on!c bond, the melt!ng and bo!l!ng po!nt !s low.
9. It occurs between nonmetal atoms.
10. Bond electrons are used jo!ntly.
6-ﻣﻮﻣﻦ ﻋﻼء اﻟﺪٮ *ﻦ ﺻﺎدق
NAMING COVALENT COMPOUNDS (ٮﺴﺎﻫﻤ*ٮﺔ2ﺴﻤ*ٮﺔ اﻟﻤﺮﻛ'ٮﺎت اﻟ2)ٮ
The chem!cal formulas for covalent compounds are referred to as molecular formulas because these compounds ex!st as separate, d!screte molecules.
Typ!cally, a molecular formula beg!ns w!th the nonmetal that !s closest to the lower left corner of the per!od!c table, except that hydrogen !s almost never wr!tten
f!rst (H2O !s the prom!nent except!on).
7-ﺣﻠﻒ. ٮﺬر.ﴣ ﻣ2ﻣﺮٮ
Then the other nonmetal symbols are l!sted. Numer!cal subscr!pts are used !f there !s more than one of a part!cular atom. For example, we have already seen
CH4, the molecular formula for methane.
To name the chem!cal formula;
1.The name of the pos!t!vely charged atom !s wr!tten.
2.Its value !s !nd!cated !n parentheses w!th the roman numeral. If !t rece!ves a s!ngle value !n atom!c compounds, there !s no need to spec!fy.
8- ڡﺎﺳﻢ2 ٮور ﻟوي.
Explanat!on Generally
Because the attract!on between molecules, wh!ch are electr!cally neutral, !s weaker than that between electr!cally charged !ons, covalent compounds generally
have much lower melt!ng and bo!l!ng po!nts than !on!c compounds.
9-ﻣﺤﻤﺪ ﺻ'ٮﺎح ﺣﺴﻦ
For example, water (molecular compound) bo!ls at 100 °C wh!le sod!um chlor!de (!on!c compound) bo!ls at 1413 °C. In fact, many covalent compounds are l!qu!ds
or gases at room temperature, and, !n the!r sol!d states, they are typ!cally much softer than !on!c sol!ds.
10-ڡﻮب ﺷﻜور2اٮ *ﻼف ٮ *ﻌ
What are covalent bonded compounds?
(ٮﺴﺎﻫﻤ*ٮﺔ؟2'ٮﻄﺔ اﻟ2ى اﻟﻤﺮﻛ'ٮﺎت اﻟﻤﺮٮe)ﻣﺎ ه
1- NON_polarڡﻄﱯ2_ﻋ*ٮﺮ.
They are covalently bonded compounds that are between nonmetal atoms of the same genus.
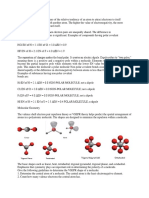
As an example, let's exam!ne the hydrogen molecule formed between two hydrogen atoms: Each hydrogen atom has 1 electron. W!th the jo!nt use of th!s
electron, a bond occurs between hydrogen atoms. The result!ng molecule !s the H2 molecule.
11- ڡﺎﻃﻤﻪ ﻋﻤﺎد.
2-POLAR ڡﻄﱯ2
A polar molecule !s a molecule !n wh!ch one end of the molecule !s sl!ghtly pos!t!ve, wh!le the other end !s sl!ghtly negat!ve.
A d!atom!c molecule that cons!sts of a polar covalent bond, such as
HF, !s a polar molecule. The two electr!cally charged reg!ons on e!ther end of the molecule are called poles, s!m!lar to a magnet hav!ng a north and a south pole.
A molecule w!th two poles !s called a d!pole . Hydrogen fluor!de !s a d!pole.
You might also like
- A-Level Chemistry Revision: Cheeky Revision ShortcutsFrom EverandA-Level Chemistry Revision: Cheeky Revision ShortcutsRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (5)
- Intermolecular ForcesDocument4 pagesIntermolecular ForcesKineticsNo ratings yet
- Class IX Chemistry Chapter 05Document10 pagesClass IX Chemistry Chapter 05Sam FisherNo ratings yet
- Bonding in Chemistry NotesDocument19 pagesBonding in Chemistry Notesteacher_555No ratings yet
- Audio Osmosis - Organic ChemistryDocument9 pagesAudio Osmosis - Organic ChemistryddNo ratings yet
- Revision 1Document69 pagesRevision 1Biology BảoNo ratings yet
- Chemical Bonding and PropertiesDocument21 pagesChemical Bonding and PropertiesRoshan Jawad ZafirNo ratings yet
- Brand Chemical BackgroundDocument8 pagesBrand Chemical Backgroundninado92No ratings yet
- Forces Between Atoms and MoleculesDocument13 pagesForces Between Atoms and MoleculesDoc_CrocNo ratings yet
- PDF Polarity of MoleculesDocument51 pagesPDF Polarity of MoleculesXandro AdrianoNo ratings yet
- Notes VSEPR (CH 6)Document21 pagesNotes VSEPR (CH 6)Nestor BalboaNo ratings yet
- Chapter 2: The Chemical Context of LifeDocument35 pagesChapter 2: The Chemical Context of LifeJustin RobenyNo ratings yet
- Lecture 1 & 2 Chemical BiologyDocument11 pagesLecture 1 & 2 Chemical BiologyParth MehraNo ratings yet
- BasicsDocument85 pagesBasicsAchilleNo ratings yet
- Dwnload Full Cell and Molecular Biology Concepts and Experiments 7th Edition Karp Solutions Manual PDFDocument36 pagesDwnload Full Cell and Molecular Biology Concepts and Experiments 7th Edition Karp Solutions Manual PDFnopalsmuggler8wa100% (8)
- Cell and Molecular Biology Concepts and Experiments 7th Edition Karp Solutions ManualDocument36 pagesCell and Molecular Biology Concepts and Experiments 7th Edition Karp Solutions Manualpoorly.germuleo6bv100% (30)
- CHEMISTRY - (With Answers)Document23 pagesCHEMISTRY - (With Answers)Arnold MutasaNo ratings yet
- Basic Chemistry ReviewDocument5 pagesBasic Chemistry ReviewArman Neil J. BudogNo ratings yet
- 2.1 The Organization of Matter: Elements and AtomsDocument6 pages2.1 The Organization of Matter: Elements and Atomsspencer_jordan_2No ratings yet
- Chemical PolarityDocument6 pagesChemical PolarityRUZCHEMISTRYNo ratings yet
- Module 1 Lecture 2Document31 pagesModule 1 Lecture 2Amirs AmjadNo ratings yet
- Notes Chemistry - ch4 - 11Document17 pagesNotes Chemistry - ch4 - 11VikramNo ratings yet
- Chemical-Bond NoteDocument9 pagesChemical-Bond NoteDixit GautamNo ratings yet
- UNIT-2 Chem Bonding-2Document13 pagesUNIT-2 Chem Bonding-2KARTIKAY LADDHANo ratings yet
- BioChemistry UNIT TESTDocument8 pagesBioChemistry UNIT TESTKezia BijuNo ratings yet
- BioChemistry UNIT TEST-2Document16 pagesBioChemistry UNIT TEST-2Kezia BijuNo ratings yet
- Chemistry Chapter 4Document6 pagesChemistry Chapter 4Simran Pamela ShahaniNo ratings yet
- Molecular Biology Lecture 4Document36 pagesMolecular Biology Lecture 4Anton IrvingNo ratings yet
- Lesson 4 - The Polarity of Molecule Based On Its StructureDocument48 pagesLesson 4 - The Polarity of Molecule Based On Its Structuretheresa balaticoNo ratings yet
- Science Notes q2Document8 pagesScience Notes q2itohtomoka017No ratings yet
- Inorganic Chemistry II Chemical Bonding and GeometryDocument29 pagesInorganic Chemistry II Chemical Bonding and GeometryAnonymous R25Vh50vnfNo ratings yet
- Polar or Nonpolar?Document28 pagesPolar or Nonpolar?Dianne CofinoNo ratings yet
- Reviewer For Physical ScienceDocument13 pagesReviewer For Physical ScienceTimothy James Tolentino BruceNo ratings yet
- 11 Chemistry-Chemical Bonding and Molecular Struture - NotesDocument23 pages11 Chemistry-Chemical Bonding and Molecular Struture - NotesSumit MahatoNo ratings yet
- Chapter 6 Shapes of Molecules and Intermolecular ForcesDocument9 pagesChapter 6 Shapes of Molecules and Intermolecular Forcesnoreen doraniNo ratings yet
- Lo5 1) Chemical BondsDocument9 pagesLo5 1) Chemical BondsabdogamreNo ratings yet
- 4.7 Intermolecular ForcesDocument5 pages4.7 Intermolecular ForcesrachpNo ratings yet
- IMFA and Chemical BondingDocument137 pagesIMFA and Chemical BondingEnna SertNo ratings yet
- Self-Check 1.1Document12 pagesSelf-Check 1.1Justine AmarantoNo ratings yet
- A. Chemical Composition of The BodyDocument15 pagesA. Chemical Composition of The BodyShumail JANNo ratings yet
- Physical Science - M3 - Polarity of MoleculesDocument15 pagesPhysical Science - M3 - Polarity of MoleculesJodi RempilloNo ratings yet
- Molecule S AND Molecul ARDocument10 pagesMolecule S AND Molecul ARken dahunanNo ratings yet
- Modules in Chemistry 2Document120 pagesModules in Chemistry 2Amanda WardNo ratings yet
- Physical Science ReportDocument35 pagesPhysical Science Reportadrian lozanoNo ratings yet
- Class 11 Chemistry Revision Notes Chemical Bonding and Molecular StructureDocument26 pagesClass 11 Chemistry Revision Notes Chemical Bonding and Molecular Structureshusa harshaNo ratings yet
- Chapter 2: Water: The Solvent For Biochemical ReactionsDocument6 pagesChapter 2: Water: The Solvent For Biochemical ReactionsMariam EidNo ratings yet
- 1-Chemistry of Life Part Two StudentDocument21 pages1-Chemistry of Life Part Two StudentteniNo ratings yet
- Lecture 1 - Basic Chemistry, Carbon, Macromolecules 2023Document48 pagesLecture 1 - Basic Chemistry, Carbon, Macromolecules 2023PPNo ratings yet
- Appendix E - Polarity WorksheetDocument3 pagesAppendix E - Polarity WorksheetshafferjfNo ratings yet
- Chemical Bonding and Molecular StructureDocument13 pagesChemical Bonding and Molecular StructureVishal MalikNo ratings yet
- Matter: Elements and Compounds MatterDocument39 pagesMatter: Elements and Compounds MattercarloNo ratings yet
- Chapter 2: Small Molecules Chemical Bonds: BIOL 112 Notes Jan 11th-Jan 13thDocument10 pagesChapter 2: Small Molecules Chemical Bonds: BIOL 112 Notes Jan 11th-Jan 13thCaroline DonovanNo ratings yet
- Chemistry in Focus A Molecular View of Our World 5Th Edition Tro Solutions Manual Full Chapter PDFDocument34 pagesChemistry in Focus A Molecular View of Our World 5Th Edition Tro Solutions Manual Full Chapter PDFjulianna.washington847100% (11)
- 3 Bio ChemistryDocument7 pages3 Bio ChemistryartichokeyNo ratings yet
- Bonding Question AnswersDocument23 pagesBonding Question Answersgyogi1989No ratings yet
- Chapter 5 Chemical BondDocument8 pagesChapter 5 Chemical Bondمسنيزواتي محمد نورNo ratings yet
- Physical-Science-Module 5 Polarity and Intermolecular Forces of AttractionDocument45 pagesPhysical-Science-Module 5 Polarity and Intermolecular Forces of AttractionJoana CastilloNo ratings yet
- CHEMISTRY - (With Answers)Document23 pagesCHEMISTRY - (With Answers)Arnold MutasaNo ratings yet
- Practice Makes Perfect in Chemistry: Chemical BondingFrom EverandPractice Makes Perfect in Chemistry: Chemical BondingRating: 5 out of 5 stars5/5 (3)
- Chemical Bonding: Chemistry DPP 3 by Garima Verma (Chemistry Faculty) - Referral Code: "Cgvmam"Document5 pagesChemical Bonding: Chemistry DPP 3 by Garima Verma (Chemistry Faculty) - Referral Code: "Cgvmam"Tanisha SubudhiNo ratings yet
- LBM EBM NotesDocument36 pagesLBM EBM NotesFRANCIS THOMASNo ratings yet
- Bioseparation Dr. Kamal E. M. Elkahlout: Mass TransferDocument56 pagesBioseparation Dr. Kamal E. M. Elkahlout: Mass TransferKemal ELkahloutNo ratings yet
- 500 MW Generator, Salient Features: SpecificationsDocument11 pages500 MW Generator, Salient Features: SpecificationsAhemadNo ratings yet
- Naming Inorganic Compounds WorksheetDocument8 pagesNaming Inorganic Compounds Worksheettalktotiffanycheng100% (1)
- 3.17 Enthalpies of Solution: Using Hess's Law To Determine Enthalpy Changes of Solution Enthalpy of SolutionDocument4 pages3.17 Enthalpies of Solution: Using Hess's Law To Determine Enthalpy Changes of Solution Enthalpy of SolutionshowhardoNo ratings yet
- Sodium and PotassiumDocument35 pagesSodium and PotassiumIrvandar NurviandyNo ratings yet
- Chemistry Syllabus New Curriculum - pdf-2Document53 pagesChemistry Syllabus New Curriculum - pdf-2donNo ratings yet
- Final Exam Review Notes PDFDocument160 pagesFinal Exam Review Notes PDFDung TranNo ratings yet
- Chemical Bonds: Resi Pratiwi, M.PDDocument35 pagesChemical Bonds: Resi Pratiwi, M.PDTeguh Wibowo UIN WalisongoNo ratings yet
- Chapter 4. Carbon and Its Compounds Class 10 Science CBSE Notes in English Medium Presence of Carbon - Bonds in Carbon - Catenation - CBSE StudyDocument21 pagesChapter 4. Carbon and Its Compounds Class 10 Science CBSE Notes in English Medium Presence of Carbon - Bonds in Carbon - Catenation - CBSE StudyAshutosh RajNo ratings yet
- SSS1 1st-Term ChemistryDocument54 pagesSSS1 1st-Term ChemistryOselumese Victor OsemeikhianNo ratings yet
- Regents Review Chemical Bonding KeyDocument7 pagesRegents Review Chemical Bonding Keycitation04No ratings yet
- Atomic StructureDocument29 pagesAtomic StructureMaureen GutierrezNo ratings yet
- Functionalized Nanoporous Graphene Membrane For Water DesalinationDocument9 pagesFunctionalized Nanoporous Graphene Membrane For Water DesalinationrafelNo ratings yet
- A Beginner's Guide To Mass Spectral InterpretationDocument240 pagesA Beginner's Guide To Mass Spectral Interpretationastroguille80% (5)
- Chemistry Reviewer PDFDocument10 pagesChemistry Reviewer PDFJom-Jom Fong Ronquillo71% (7)
- FCAT Questions: Atoms, Elements, & Molecules Module Grades 9-12 Teacher VersionDocument4 pagesFCAT Questions: Atoms, Elements, & Molecules Module Grades 9-12 Teacher VersionMae Uayan Prisco-TagaraoNo ratings yet
- ATIQ ReportDocument48 pagesATIQ ReportAdeel Aslam RajpootNo ratings yet
- (George P. Simon (Auth.) ) Ion Exchange Training ManualDocument232 pages(George P. Simon (Auth.) ) Ion Exchange Training Manualdfmorvan2100% (6)
- Summative Test Second Quarter 9Document7 pagesSummative Test Second Quarter 9Kathelyn Ruiz-SumandoNo ratings yet
- Daily Lesson PlanDocument8 pagesDaily Lesson PlanZulkifli Bin PariNo ratings yet
- Soalan Kimia Pertengahan Tahun Form 4Document11 pagesSoalan Kimia Pertengahan Tahun Form 4Ridzuan Mohd AliNo ratings yet
- A Level Chemistry Papers Nov2010 PDFDocument249 pagesA Level Chemistry Papers Nov2010 PDFByakuya BleachNo ratings yet
- Organic Acid Base Imp 2Document89 pagesOrganic Acid Base Imp 2sahil010228No ratings yet
- Lsmo 1995 PRBDocument7 pagesLsmo 1995 PRBSwayangdipta BeraNo ratings yet
- Mechanisms of Nutrient Uptake of Plant Root Cells From SoilDocument47 pagesMechanisms of Nutrient Uptake of Plant Root Cells From SoilMaha ChaudharyNo ratings yet
- A Guide For ChemistsDocument188 pagesA Guide For Chemistsneculaitarabuta100% (2)
- Cambridge Assessment International Education: Co-Ordinated Sciences 0654/41 May/June 2018Document11 pagesCambridge Assessment International Education: Co-Ordinated Sciences 0654/41 May/June 2018The MumtazNo ratings yet
- Coordination ChemistryDocument14 pagesCoordination Chemistryjangidudit115No ratings yet