Professional Documents
Culture Documents
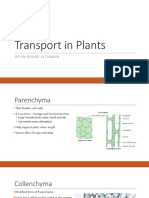
Functions of Parenchyma Cells
Functions of Parenchyma Cells
Uploaded by
renlie jane pedronan0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
7 views1 pageParenchyma cells form the ground tissue of plants and perform many important functions. They act as storage tissues by storing starches, water, fats, and oils. Parenchyma cells also aid in transport by transferring nutrients and chemicals throughout the plant and helping with radial water and mineral movement. Additionally, they perform photosynthesis when containing chloroplasts, facilitate gas exchange, provide protection, regeneration and wound healing, and grant mechanical strength and buoyancy to plants.
Original Description:
Original Title
Functions of Parenchyma cells
Copyright
© © All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
DOCX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentParenchyma cells form the ground tissue of plants and perform many important functions. They act as storage tissues by storing starches, water, fats, and oils. Parenchyma cells also aid in transport by transferring nutrients and chemicals throughout the plant and helping with radial water and mineral movement. Additionally, they perform photosynthesis when containing chloroplasts, facilitate gas exchange, provide protection, regeneration and wound healing, and grant mechanical strength and buoyancy to plants.
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as DOCX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
7 views1 pageFunctions of Parenchyma Cells
Functions of Parenchyma Cells
Uploaded by
renlie jane pedronanParenchyma cells form the ground tissue of plants and perform many important functions. They act as storage tissues by storing starches, water, fats, and oils. Parenchyma cells also aid in transport by transferring nutrients and chemicals throughout the plant and helping with radial water and mineral movement. Additionally, they perform photosynthesis when containing chloroplasts, facilitate gas exchange, provide protection, regeneration and wound healing, and grant mechanical strength and buoyancy to plants.
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as DOCX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
You are on page 1of 1
Functions of Parenchyma cells
Parenchyma cells form the ground tissue of plants. Parenchyma tissues perform various
important functions:
Storage: Parenchyma cells have large intercellular space which is ideal for storage
High amount of starch is present in the tubers of potato and cassava
These can store water, fats, oil droplets, and ergastic substances
Store water and act as a water reservoir
Transport: Parenchyma cells transport nutrients and other chemicals
Transfer cells have outgrowth for increasing absorption surface
The xylem parenchyma helps in radial transportation of water and minerals
Some cells transport light from the surface to underground cells
Photosynthesis: Chlorenchyma present in the mesophyll and the other green parts of the
plant, have chloroplasts and perform photosynthesis
Gas Exchange: Aerenchyma cells help in the gas exchange
Protection: In gymnosperms, the parenchymatous cell have spiny projections that help in
the protection from predators
Totipotent: Parenchyma cells have an ability to transform to the other types of cells and act
as a precursor for other types of cells
Buoyancy: Aerenchyma present in aquatic plants have air sacs that help in floating
Cuticle present on epidermis helps in reducing transpiration in water stress condition
Thick-walled parenchyma cells provide mechanical strength to the plant
Healing and regeneration: Parenchyma cells that retain their ability to divide even on
maturity help in regeneration and wound healing. Tyloses present in the xylem parenchyma
help in preventing damage to vascular tissues in the condition of drought.
You might also like
- Simple Tissue and Complex TissueDocument4 pagesSimple Tissue and Complex TissueHappy RoyNo ratings yet
- File 2Document2 pagesFile 2pitina7055No ratings yet
- Chapter 3Document16 pagesChapter 3Anis PuadahNo ratings yet
- ScriptDocument2 pagesScriptJames Carbonell Dela PeñaNo ratings yet
- File 1Document3 pagesFile 1pitina7055No ratings yet
- 7.plant TissueDocument3 pages7.plant TissueRAVINDRA PRASADNo ratings yet
- Transport in Plants: Devin Ryandi SetiawanDocument7 pagesTransport in Plants: Devin Ryandi SetiawanAqeela SyakiraNo ratings yet
- hssb2101t Ir SectionDocument4 pageshssb2101t Ir Sectionfhhgghhg hggghgNo ratings yet
- Structure and Functions of Plant TissuesDocument8 pagesStructure and Functions of Plant Tissuesdina aribahNo ratings yet
- Scince 3Document3 pagesScince 3Smriti AnguranaNo ratings yet
- Chapter 8Document11 pagesChapter 8sheisbonjing PHNo ratings yet
- Permanent TissueDocument3 pagesPermanent TissueTECH CORNERNo ratings yet
- Anatomy.. Paper ADocument6 pagesAnatomy.. Paper ASoha Ch100% (1)
- Miedy Corazon Tabang Sta. Monica High School PhilippinesDocument68 pagesMiedy Corazon Tabang Sta. Monica High School PhilippinesArman Austria100% (1)
- Plant TissuesDocument53 pagesPlant TissuesClarissa LaruanNo ratings yet
- Meristem Parenchyma Sclerenchyma 5: Figure 5: Cell Types and TissuesDocument8 pagesMeristem Parenchyma Sclerenchyma 5: Figure 5: Cell Types and Tissuessandy waskitoNo ratings yet
- GENBIO 2.2 Plant and Animal Organ Systems and Their FunctionsDocument20 pagesGENBIO 2.2 Plant and Animal Organ Systems and Their FunctionsivanhenryjordanNo ratings yet
- Gen BioDocument3 pagesGen BioAlly OcbianNo ratings yet
- PlantsDocument3 pagesPlantsAby LimNo ratings yet
- Plant TissueDocument19 pagesPlant TissueKAMESH .G100% (1)
- PlanttisDocument3 pagesPlanttislorraine_cuaNo ratings yet
- Lab 6 Drawing of A Root Dicot Under A Light Microscope.Document3 pagesLab 6 Drawing of A Root Dicot Under A Light Microscope.Michael TimsonNo ratings yet
- Definition and Overview of A Plant CellDocument19 pagesDefinition and Overview of A Plant CellRica NorcioNo ratings yet
- Cell TypesDocument3 pagesCell Typesakosi ararNo ratings yet
- Tissues System FinalDocument9 pagesTissues System FinalSoha Ch100% (1)
- Parts and Functions of PlantsDocument21 pagesParts and Functions of PlantsRaz QuipedNo ratings yet
- Types of Plant CellsDocument26 pagesTypes of Plant CellsJustin BiboNo ratings yet
- Plant Tissue: Ciar, Diaz, MedenillaDocument35 pagesPlant Tissue: Ciar, Diaz, MedenillaMich DiazNo ratings yet
- Plant Cell - WikipediaDocument33 pagesPlant Cell - WikipediaNaniNo ratings yet
- Plant PrintsDocument11 pagesPlant PrintsWARDAH SHOAIBNo ratings yet
- Plant - Tissue NotesDocument3 pagesPlant - Tissue NotesDikshit Rishi JainNo ratings yet
- Info Sheets On Plant TissuesDocument6 pagesInfo Sheets On Plant TissuesjasmineecasttNo ratings yet
- Ground TissuesDocument17 pagesGround TissuesHelen Gail EmbudoNo ratings yet
- Laboratory Activity 5 A Peep at The Simple Plant Tissue: Its Parenchyma, Collenchyma, and SclerenchymaDocument5 pagesLaboratory Activity 5 A Peep at The Simple Plant Tissue: Its Parenchyma, Collenchyma, and SclerenchymaAnnie Lourrie CasabuenaNo ratings yet
- Transport in Plants - Docx - 20240418 - 093821 - 0000Document11 pagesTransport in Plants - Docx - 20240418 - 093821 - 000088.renee.888No ratings yet
- Chapter3 Planttissues 170922155708Document55 pagesChapter3 Planttissues 170922155708proud.student2023No ratings yet
- Anatomy of Flowering PlantsDocument10 pagesAnatomy of Flowering Plantsl8627352No ratings yet
- Transport in Flowering PlantsDocument7 pagesTransport in Flowering PlantsSNG UZZINo ratings yet
- Anatomy of Flowering PlantsDocument5 pagesAnatomy of Flowering Plantschandutalawar187No ratings yet
- Botany Lec - Group Work 1Document3 pagesBotany Lec - Group Work 1TJ ArciagaNo ratings yet
- Plant Cell - WikipediaDocument32 pagesPlant Cell - WikipediaSherelyn Bernardo100% (1)
- Describe The Structure and Function of The Five Major Types of Cells Found in Plant TissueDocument3 pagesDescribe The Structure and Function of The Five Major Types of Cells Found in Plant TissueIshaHenryNo ratings yet
- Permanent TissuesDocument16 pagesPermanent TissuesRiyashika RNo ratings yet
- Bio 1 Module 3 4 PDFDocument101 pagesBio 1 Module 3 4 PDFJoyvy KidoNo ratings yet
- Ix Biology 6 1, PPTDocument35 pagesIx Biology 6 1, PPTShruti TiwariNo ratings yet
- Topic III - CS20Document79 pagesTopic III - CS20Jhunell JuanNo ratings yet
- General Biology ReviewerDocument4 pagesGeneral Biology ReviewerAlly OcbianNo ratings yet
- Definition of Plant TissueDocument3 pagesDefinition of Plant TissueCrash Zerocool67% (3)
- Bio 101 Lecture 5Document127 pagesBio 101 Lecture 5Lance CarandangNo ratings yet
- Notes of CH Tissues Class 9Document20 pagesNotes of CH Tissues Class 9PrabhaNo ratings yet
- A Group of Closely Associated Cells That Perform Related Functions and Are Similar in StructureDocument25 pagesA Group of Closely Associated Cells That Perform Related Functions and Are Similar in StructureMichael Pradhan100% (2)
- TissuesDocument6 pagesTissuesRahul SinghNo ratings yet
- CropSci101 Module 3Document11 pagesCropSci101 Module 3Jetro Neil GapasinNo ratings yet
- Lakhmir Singh Solutions Class 9 Biology Chapter 3Document7 pagesLakhmir Singh Solutions Class 9 Biology Chapter 3DarshilNo ratings yet
- Botany Notes 101Document7 pagesBotany Notes 101Ma. Lilian Jem MonteroNo ratings yet
- Epidermis: - Cuticle - Trichomes - Stomata - Buiiiform Ceiis (In Grasses)Document8 pagesEpidermis: - Cuticle - Trichomes - Stomata - Buiiiform Ceiis (In Grasses)Rajendra AcharyaNo ratings yet
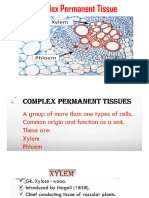
- Complex Permanent TissueDocument25 pagesComplex Permanent Tissuepragyamaharjan2No ratings yet
- Simple Permanent TissueDocument9 pagesSimple Permanent Tissueking100% (1)
- Pedronan, Renlie Jane P. - Health-Related Science LessonsDocument34 pagesPedronan, Renlie Jane P. - Health-Related Science Lessonsrenlie jane pedronanNo ratings yet
- Pedronan, Renlie Jane P. - Teaching Science Through Laboratoryinvestigationinquiry-Based Employing 7E ModelDocument17 pagesPedronan, Renlie Jane P. - Teaching Science Through Laboratoryinvestigationinquiry-Based Employing 7E Modelrenlie jane pedronanNo ratings yet
- Session 1 Session 2 Session 3 Session 4: I. ObjectivesDocument6 pagesSession 1 Session 2 Session 3 Session 4: I. Objectivesrenlie jane pedronanNo ratings yet
- Origin and Structure of The EarthDocument40 pagesOrigin and Structure of The Earthrenlie jane pedronanNo ratings yet
- w1 ElsDocument27 pagesw1 Elsrenlie jane pedronanNo ratings yet