Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Fungi Classes Concised Table
Uploaded by
temp93630Original Description:
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Fungi Classes Concised Table
Uploaded by
temp93630Copyright:
Available Formats
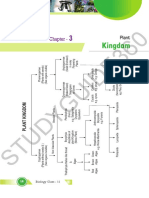
CLASS PHYCOMYCETES ASCOMYCETES BASISIOMYCETES DEUTEROMYCETES
Other Name Algal Fungi Sac Fungi Club/ Bracket Fungi Imperfect Fungi
Habitat and Aquatic, Decaying wood/ organic Saprophytic, Decomposers, Parasitic, Coprophilous Soil, on logs, tree stumps Saprophytic, Parasitic,
Habit matter, in moist, damp places Parasitic Decomposers
Obligate parasites on Plants
Mycelium Aseptate, Coenocytic Branched, Septate Branched, Septate Branched, Septate
Asexual Zoospores (motile), Conidia Absent Conidia
Reproduction Aplanospores (non-motile) But Vegetative Reproduction by
Production of Endogenously in Sporangia Exogenously on conidiophores fragmentation is common Exogenously on
spores → conidiophores
Sexual NOT KNOWN
Reproduction:
Spores → Zygospore (formed by fusion of Ascospores Basidiospores
two gametes) – Can be
isogamous, anisogamous or
oogamous
Produced on Endogenously on Asci Exogenously on Basidia
Fruiting Bodies Ascocarps (Different types) Basidiocarps
Other points Sex Organs are absent but
plasmogamy is brought by fusion
of two vegetative or somatic cells
of different strains/ genotypes.
Dikaryon Phase Absent Present Present Absent
Examples Mucor, Rhizopus (Bread Mould), Penicillium (Antibiotic Source), Yeast Mushrooms, Bracket Fungi, Alternaria,
Albugo (Mustard parasite) (Saccharomyces - Unicellular) Puffballs Colletotrichum,
Parasitic - Hypomyces, Chrysospermus Agaricus (mushroom) Trichophyton,
Coprophilous (on dung) –Sporomiella Parasitic - Rusts, Smuts Trichoderma,
Aspergillus, Claviceps , Ustilago (Smut), Puccinia Tricosporium
Neurospora (used in biochemical and genetic work) (Wheat rust fungus)
Edible (Delicacies) - Morels, Truffles
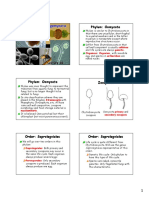
NCERT
Diagram
MUCOR ASPERGILLUS AGARICUS
You might also like
- Fungi Classes ChartDocument1 pageFungi Classes ChartManav SinghNo ratings yet
- Fungi TableDocument1 pageFungi Tablecoc-id-123 889900No ratings yet
- 3 FungiClassificationDocument33 pages3 FungiClassificationDawit GetahunNo ratings yet
- Biological Classification 2 Anatomy The RealDocument14 pagesBiological Classification 2 Anatomy The RealMukul YadavNo ratings yet
- Biological ClassificationDocument5 pagesBiological Classificationsivarigil0610No ratings yet
- Botani Tumbuhan Rendah FungiDocument16 pagesBotani Tumbuhan Rendah FungiHidayatNo ratings yet
- Fungi Kingdom Mycota / Mycetae / Fungi: Monophyletic GroupDocument15 pagesFungi Kingdom Mycota / Mycetae / Fungi: Monophyletic GroupAnonymous Xlpj86laNo ratings yet
- Lecture 04Document30 pagesLecture 04Lib PalmaresNo ratings yet
- BotanyDocument25 pagesBotanynaagin12300No ratings yet
- Fungi Lab 6Document22 pagesFungi Lab 6abualiwejdan33No ratings yet
- CLASS 11 Biological Classification Part 2 Kingdom Fungi To Lichens.Document11 pagesCLASS 11 Biological Classification Part 2 Kingdom Fungi To Lichens.Rozita PraveenNo ratings yet
- FungiDocument3 pagesFungirhodashereenNo ratings yet
- General Biology 2 (4 Quarter) : Animal and Plant ReproductionDocument23 pagesGeneral Biology 2 (4 Quarter) : Animal and Plant Reproductionamethyst grande100% (1)
- Kingdom FungiDocument2 pagesKingdom FungiAshvine BeddewelaNo ratings yet
- Microbiology - MycologyDocument7 pagesMicrobiology - Mycologytdci.franceskorineganzaNo ratings yet
- Domain Eukarya Kingdom Fungi: Systematics LaboratoryDocument10 pagesDomain Eukarya Kingdom Fungi: Systematics LaboratorySIlverNo ratings yet
- Biological ClassificationDocument4 pagesBiological ClassificationAnanya MSNo ratings yet
- Fungus PhylumDocument1 pageFungus PhylumRobert ClarkNo ratings yet
- Chapter 9: The Fungi: Presented By:Dr. Maryam MukhtarDocument12 pagesChapter 9: The Fungi: Presented By:Dr. Maryam MukhtarMaryyum UmerNo ratings yet
- Fungi NotesDocument5 pagesFungi NotesAmber PeakeNo ratings yet
- 02 Zygomycetes 2012Document10 pages02 Zygomycetes 2012Rizwan Riz QureshiNo ratings yet
- Esm MikrobiologiDocument13 pagesEsm Mikrobiologimutmainnah burhanuddinNo ratings yet
- Signs of PDiseasesDocument55 pagesSigns of PDiseasescharismae.silvelaNo ratings yet
- FUNGIDocument5 pagesFUNGIMiten AvityagrotechNo ratings yet
- Upcat Taxonomy ReviewerDocument3 pagesUpcat Taxonomy ReviewerMaeAnneMarceloTambio100% (1)
- Mycology VirologyDocument46 pagesMycology Virologychocoholic potchi100% (1)
- Class 11 Biology Notes Chapter 3 Studyguide360Document11 pagesClass 11 Biology Notes Chapter 3 Studyguide360ANo ratings yet
- Lecture02 PDFDocument8 pagesLecture02 PDFSalman GhazaliNo ratings yet
- The Five Kingdoms in Classification-Jada Knights 3cDocument3 pagesThe Five Kingdoms in Classification-Jada Knights 3cJada KnightsNo ratings yet
- FungiDocument38 pagesFungiMeong MeongNo ratings yet
- LET Reviewer Biology Majorship: Thermus Aquaticus Methanobacterium Halobacterium Ferroplasma AcidarmanusDocument34 pagesLET Reviewer Biology Majorship: Thermus Aquaticus Methanobacterium Halobacterium Ferroplasma Acidarmanusjayrald cruzadaNo ratings yet
- Mycology 1 PrelimDocument4 pagesMycology 1 PrelimKaye Angel VillonNo ratings yet
- 26 Plant Reproduction 2020Document32 pages26 Plant Reproduction 2020Prince KashyapNo ratings yet
- FungiDocument1 pageFungiapi-284522232No ratings yet
- Plant Taxonomy NotesDocument13 pagesPlant Taxonomy NotesMikaela MendozaNo ratings yet
- Biology LessonDocument33 pagesBiology LessonJojimar JulianNo ratings yet
- Fungi: Great Resources!Document5 pagesFungi: Great Resources!GUIDO ERNESTO VILLOTA CALVACHINo ratings yet
- Asexual Reproductions Bryophytes and FernsDocument16 pagesAsexual Reproductions Bryophytes and FernsGrace NicholsonNo ratings yet
- Reino FungiDocument1 pageReino FungiRuben Choquicota MaquitoNo ratings yet
- Plant KingdomDocument7 pagesPlant KingdomArthav KumarNo ratings yet
- Plant KingdomDocument13 pagesPlant Kingdomaravind kishanNo ratings yet
- LET Reviewer Biology Majorship: Thermus Aquaticus Methanobacterium Halobacterium Ferroplasma AcidarmanusDocument26 pagesLET Reviewer Biology Majorship: Thermus Aquaticus Methanobacterium Halobacterium Ferroplasma AcidarmanusLIRA MAE DE LA CRUZNo ratings yet
- LET Reviewer Biology Majorship: Thermus Aquaticus Methanobacterium Halobacterium Ferroplasma AcidarmanusDocument26 pagesLET Reviewer Biology Majorship: Thermus Aquaticus Methanobacterium Halobacterium Ferroplasma AcidarmanuslarraNo ratings yet
- Kingdom Fungi NotesDocument6 pagesKingdom Fungi Notesaini azzahraNo ratings yet
- ParawordDocument4 pagesParawordCHRISTIAN HOWARD SAGUBAYNo ratings yet
- Week 4 Medical and Public Health ParasitologyDocument36 pagesWeek 4 Medical and Public Health Parasitologylewistulio004No ratings yet
- ??reproduction in Plants and AnimalsDocument48 pages??reproduction in Plants and Animalsnadineazzahra412No ratings yet
- Plant Kingdom ChartDocument1 pagePlant Kingdom ChartTanya SiyagNo ratings yet
- 3.2. Keanekaragaman Makhluk Hidup (Fungi)Document42 pages3.2. Keanekaragaman Makhluk Hidup (Fungi)Bagus Dwi PermanaNo ratings yet
- (L+4) +chapter+02+ Biological+Classification++NEET+Questions+Menti+++ +DPP+Document48 pages(L+4) +chapter+02+ Biological+Classification++NEET+Questions+Menti+++ +DPP+AMISHA RATHISHNo ratings yet
- Carolus Linnaeus (ELS)Document4 pagesCarolus Linnaeus (ELS)Vincent Emilio L. ChanNo ratings yet
- TOPIC 4 Plant Pathogen Fungi Phylum AscomycotaDocument48 pagesTOPIC 4 Plant Pathogen Fungi Phylum AscomycotaSleeping BeautyNo ratings yet
- Adobe Scan 04 Aug 2023Document3 pagesAdobe Scan 04 Aug 2023J Nathiya ShreeNo ratings yet
- Lecture Notes 12&13 Phylum ApicomplexaDocument20 pagesLecture Notes 12&13 Phylum ApicomplexaAmirr4uddinNo ratings yet
- Kingdoms WorksheetsDocument5 pagesKingdoms WorksheetsTessNo ratings yet
- Biodiversity Part 1/2Document15 pagesBiodiversity Part 1/2Kim Say Chun / Sc.KIMNo ratings yet
- Fungi and YeastDocument15 pagesFungi and YeastNusrat TamannaNo ratings yet
- Mushroom Spotter's Deck: A Field Guide to Fungi & Their Age-Old WisdomFrom EverandMushroom Spotter's Deck: A Field Guide to Fungi & Their Age-Old WisdomNo ratings yet
- Microbiology: a QuickStudy Laminated 6-Page Reference GuideFrom EverandMicrobiology: a QuickStudy Laminated 6-Page Reference GuideNo ratings yet
- Concept Strengthening Sheet CSS 04 Based On AIATS 04 RM PhysicsDocument4 pagesConcept Strengthening Sheet CSS 04 Based On AIATS 04 RM Physicstemp93630No ratings yet
- Final Test Series For Neet-2024Document20 pagesFinal Test Series For Neet-2024temp93630No ratings yet
- THINDocument1 pageTHINtemp93630No ratings yet
- 23.reproduction in Organism New BioHackDocument7 pages23.reproduction in Organism New BioHacktemp93630No ratings yet
- Keys For The Determination of The Agaricales - Rolf SIngerDocument68 pagesKeys For The Determination of The Agaricales - Rolf SIngerMónica Rosas RiascosNo ratings yet
- The Palatability, and Potential Toxicity of Australian Weeds To GoatsDocument163 pagesThe Palatability, and Potential Toxicity of Australian Weeds To Goatsalshokairsaad513No ratings yet
- Report of Pasture Establishment 1234Document29 pagesReport of Pasture Establishment 1234FART TVNo ratings yet
- 2nd Quarter Module and Exam in SCIENCE K2Document47 pages2nd Quarter Module and Exam in SCIENCE K2Lucille AramburoNo ratings yet
- CBSE Class 7 Science - Nutrition in PlantsDocument2 pagesCBSE Class 7 Science - Nutrition in Plantssifat monga100% (1)
- Loxanthocereus Hoxeyi El Cereus en Miniatura Del Sur Del PeruDocument7 pagesLoxanthocereus Hoxeyi El Cereus en Miniatura Del Sur Del PeruJhonson Klever Vizcarra RomeroNo ratings yet
- PlantpropagationclassDocument5 pagesPlantpropagationclassapi-609686086No ratings yet
- 4 Morphology of Flowering Plants: SolutionsDocument29 pages4 Morphology of Flowering Plants: SolutionsRana GhoshNo ratings yet
- I. Underground Modifications of StemDocument7 pagesI. Underground Modifications of StemElias Libay100% (1)
- Carmona Plant Caring InstructionDocument2 pagesCarmona Plant Caring Instructiongaurav jainNo ratings yet
- Bio P2 PDFDocument264 pagesBio P2 PDFMaaz AdeelNo ratings yet
- Apiaceae (Umbelliferae) : The Carrot FamilyDocument1 pageApiaceae (Umbelliferae) : The Carrot FamilyHamid AwanNo ratings yet
- Cacao Lec. DatagonDocument73 pagesCacao Lec. DatagonVimarce CuliNo ratings yet
- 7 Science NCERT Chapter 1 PDFDocument10 pages7 Science NCERT Chapter 1 PDFDebashis MallickNo ratings yet
- Study On Identification and Isolation of Rhizopus From Decaying BreadDocument3 pagesStudy On Identification and Isolation of Rhizopus From Decaying BreadManish JhaNo ratings yet
- Introduction of Phaeophyceae (Brown Algae) :: The Important Characteristics of The Class Phaeophyceae Are Given BelowDocument12 pagesIntroduction of Phaeophyceae (Brown Algae) :: The Important Characteristics of The Class Phaeophyceae Are Given BelowArsalan AkhtarNo ratings yet
- Jurnal Metamorfosa: Journal of Biological SciencesDocument8 pagesJurnal Metamorfosa: Journal of Biological Sciencespradika audiarNo ratings yet
- BrinjalDocument31 pagesBrinjalVaibhav DafaleNo ratings yet
- Report On Field TripDocument8 pagesReport On Field TripPynskhemlang RaniNo ratings yet
- Raz Lp17 Abouttrees CLRDocument9 pagesRaz Lp17 Abouttrees CLRJanaNo ratings yet
- A LESSON PLAN in SCIENCE 6 Vertebrates and InvertebratesDocument6 pagesA LESSON PLAN in SCIENCE 6 Vertebrates and InvertebratesAbba Joy100% (1)
- Botany I (EM) BLM 2021-22Document61 pagesBotany I (EM) BLM 2021-22Tanzeela Hashmi0% (1)
- Effect of Grafting On Growth and Yield of TomatoDocument5 pagesEffect of Grafting On Growth and Yield of TomatoShailendra RajanNo ratings yet
- New Multipetalous Variety G. Ad.1 of Adenium ObesumDocument8 pagesNew Multipetalous Variety G. Ad.1 of Adenium ObesumkukkalasatishkumarNo ratings yet
- ELSC 111 2nd Quarter ExamDocument5 pagesELSC 111 2nd Quarter ExamEdelito BernalNo ratings yet
- The Turtle and The MonkeyDocument11 pagesThe Turtle and The MonkeyKaramel CaramelNo ratings yet
- Sugar PestsDocument11 pagesSugar PestsZahid AliNo ratings yet
- Plant Biotechnology (Tissue Culture)Document11 pagesPlant Biotechnology (Tissue Culture)Hewa HusenNo ratings yet
- Japanese (Bo ɰ ̃sai) : Bonsai (Document1 pageJapanese (Bo ɰ ̃sai) : Bonsai (Yan Linn AungNo ratings yet
- Flueggea Flexuosa (Poumuli) : Species Profiles For Pacific Island AgroforestryDocument13 pagesFlueggea Flexuosa (Poumuli) : Species Profiles For Pacific Island AgroforestryRalph Perez100% (1)