Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Session 2: Equilibrium of Force System
Session 2: Equilibrium of Force System
Uploaded by
Rhodoralyn Ilagan BalhagOriginal Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Session 2: Equilibrium of Force System
Session 2: Equilibrium of Force System
Uploaded by
Rhodoralyn Ilagan BalhagCopyright:
Available Formats
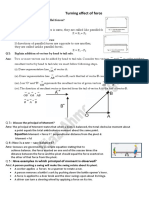
SESSION 2 : EQUILIBRIUM OF FORCE SYSTEM
Conditions of Static Equilibrium of Concurrent Forces
The body is said to be in equilibrium if the resultant of all forces acting on it is zero. There are two major
types of static equilibrium, namely, translational equilibrium and rotational equilibrium. The sum of all forces in the x-direction or horizontal is zero.
The sum of all forces in the y-direction or vertical is zero.
Important Points for Equilibrium Forces
1. Two forces are in equilibrium if they are equal and oppositely directed.
2. Three coplanar forces in equilibrium are concurrent.
3. Three or more concurrent forces in equilibrium form a close polygon when connected in
head-to-tail manner.
Conditions for Equilibrium of Parallel Forces
The sum of all the forces is zero.
The sum of moment at any point O is zero.
Equilibrium of Non-Concurrent Force System
There are three equilibrium conditions that can be used for non-concurrent, non-parallel force system.
The sum of all forces in the x-direction or horizontal is zero.
The sum of all forces in the y-direction or vertical is zero.
The sum of moment at any point O is zero.
ENGR. BRENZ EDUARD C. ILAGAN
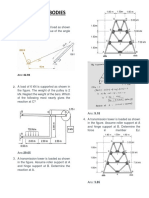
Situation 1: The figure shows that the archer aiming to release the arrow. As the archer pulls Situation 4: Three cylindrical cylinders having identical dimensions and weighing 500N are
the cord with his right arm, he applies a 540N force with his left arm. shown in the figure. Assume all contact surfaces are smooth.
1. What is the resulting tension in the upper cord? 556N
2. Calculate the tension in the lower cord? 517N 3. Which of the following most nearly gives the reaction at A? 288.68N
4. Which of the following most nearly gives the reaction at B? 750N
5. Which of the following most nearly gives the reaction at C? 144.34N
Situation 2: Determine the required length of cord AC in Fig. so that the 8-kg lamp can be
suspended in the position shown. The undeformed length of spring AB is l’AB = 0.4 m, and the spring has
a stiffness of kAB = 300 N/m. 1.32m
Situation 5: The crane shown in the figure carries the load W. The crane is hinged at B and is
supported by the cable AC. For this problem use W = 20kN
1. Which of the following most nearly gives the tension in the cable? 22.63kN
2. Which of the following most nearly gives the reaction at B? 39.4kN
3. If the cable AC could carry up to 50kN, which of the following gives the largest W? 44.19kN
Situation 3: Determine the maximum mass of the lamp that the cord system can support so that
no single cord develops a tension exceeding 400 N. 20.4kg
ENGR. BRENZ EDUARD C. ILAGAN
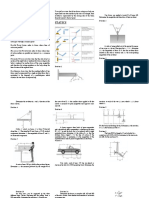
Situation 6: A cylindrical drum 2m in radius and weighing 1,200N is held by a rigid bar AB as
shown. One end of the bar (Point A) is hinged and the other end (Point B) is supported by a flexible
cable BC. Neglect friction on all contact surfaces. “Unless you try to do something beyond what you have already mastered,
4. Which of the following most nearly gives the force between the drum and the bar? 2400N
you will never grow.”
5. Which of the following most nearly gives the tension in the cable? 1804N
6. Which of the following most nearly gives the reaction at A? 645.75N
Situation 7: The machine part of negligible weight is supported by a pin at A and a roller at C.
Determine the magnitudes of the forces acting on the part at A and C. 84.12kN, 86.4kN
ENGR. BRENZ EDUARD C. ILAGAN
You might also like
- Equilibrium of Force SystemsDocument14 pagesEquilibrium of Force SystemsRocel Marie Lopez100% (1)
- Resultant of ForcesDocument117 pagesResultant of ForcesKunal kumarNo ratings yet
- Engineering Mechanics I To III Units PDFDocument143 pagesEngineering Mechanics I To III Units PDFAnil KumarNo ratings yet
- Engg Mechanics - Statics-1Document26 pagesEngg Mechanics - Statics-1Marcelo AbreraNo ratings yet
- SRB DRBDocument44 pagesSRB DRBAcads AccountNo ratings yet
- Technical Manual: For Air-Conditioning Heating System Liebherr Excavator B-LineDocument24 pagesTechnical Manual: For Air-Conditioning Heating System Liebherr Excavator B-LineRiza DSNo ratings yet
- Siemens Building Technologies: HVAC ProductsDocument299 pagesSiemens Building Technologies: HVAC Productscamus1125No ratings yet
- Mayas Online Mechanics Review ClassDocument23 pagesMayas Online Mechanics Review ClassVon Andrei MedinaNo ratings yet
- The Complete Programme For High Pressure TechnologyDocument28 pagesThe Complete Programme For High Pressure TechnologyRafael Espinosa100% (1)
- Jenbacher Type 6 Fs en Metric 2016Document2 pagesJenbacher Type 6 Fs en Metric 2016laiquz zamanNo ratings yet
- Design and Fabrication of 90 Degree Welding ClampDocument29 pagesDesign and Fabrication of 90 Degree Welding ClampAfsal Mohamed Kani 004100% (2)
- An Analysis of Lift and Drag Forces of NACA Airfoils Using PythonDocument9 pagesAn Analysis of Lift and Drag Forces of NACA Airfoils Using PythonInternational Journal of Application or Innovation in Engineering & ManagementNo ratings yet
- PART 6 Steering SystemDocument7 pagesPART 6 Steering SystemBoumediene CHIKHAOUINo ratings yet
- ME1222 - 4. Equilibrium of Rigid BodiesDocument23 pagesME1222 - 4. Equilibrium of Rigid Bodies40-eng-0003No ratings yet
- Equilibrium in 2DDocument36 pagesEquilibrium in 2DTuhafeni HailekaNo ratings yet
- Chap. 4 - Equilibrium of Rigid BodiesDocument12 pagesChap. 4 - Equilibrium of Rigid Bodies22je0766No ratings yet
- Mechanics Lab 2Document4 pagesMechanics Lab 2yogendra kumarNo ratings yet
- ElectricityDocument18 pagesElectricitySam LoveNo ratings yet
- Condition For The Equilibrium of A ParticleDocument15 pagesCondition For The Equilibrium of A ParticleErikNo ratings yet
- SRB Session1 RofsDocument4 pagesSRB Session1 RofsFullo Flores MarviloneNo ratings yet
- Session 1: Resultant of Force System: CouplesDocument4 pagesSession 1: Resultant of Force System: CouplesRhodoralyn Ilagan BalhagNo ratings yet
- Equilibrium of Colanar Non Concurrent Force System: 0, 0 - No TranslationDocument5 pagesEquilibrium of Colanar Non Concurrent Force System: 0, 0 - No TranslationSubhajyoti DasNo ratings yet
- Chapter 10momentsDocument16 pagesChapter 10momentsKarla HyltonNo ratings yet
- Unit 3: Engineering MechanicsDocument2 pagesUnit 3: Engineering MechanicsAjit MoreNo ratings yet
- Statics of Rigid Bodies: Chapter 3: Equilibrium of A ParticleDocument23 pagesStatics of Rigid Bodies: Chapter 3: Equilibrium of A ParticleRyan Philip CatapangNo ratings yet
- Equilibrium of A Particle PDFDocument16 pagesEquilibrium of A Particle PDFCristopher GonzagaNo ratings yet
- Q 1: Define Like and Unlike Parallel Forces?: A B OA AB OB AB B OB OA AB R A BDocument3 pagesQ 1: Define Like and Unlike Parallel Forces?: A B OA AB OB AB B OB OA AB R A BRiaz Hussain LaghariNo ratings yet
- EquilibriumDocument56 pagesEquilibriumJithin SreeshanNo ratings yet
- Appraisal Mechanics 1Document4 pagesAppraisal Mechanics 1Sameen ShawNo ratings yet
- SoRB - M1 23 24Document2 pagesSoRB - M1 23 24Joel MiradorNo ratings yet
- Lecture 5Document28 pagesLecture 5Lobbe JoshuaNo ratings yet
- This Study Resource Was: Nce 520 Integration Course 2 Statics of Rigid BodiesDocument2 pagesThis Study Resource Was: Nce 520 Integration Course 2 Statics of Rigid BodiesAndrea Sochayseng SolijonNo ratings yet
- Class 11 Physics Notes Chapter 4 Studyguide360Document27 pagesClass 11 Physics Notes Chapter 4 Studyguide360ryzengfx6No ratings yet
- Md. Musfiqur Rahman Milton: Lecturer, CSE BaiustDocument15 pagesMd. Musfiqur Rahman Milton: Lecturer, CSE Baiustadiba adibNo ratings yet
- Stat211 Resultant of Concurrent Force SystemDocument3 pagesStat211 Resultant of Concurrent Force Systemabandiola3819qcNo ratings yet
- Equilibrium of Force SystemDocument129 pagesEquilibrium of Force SystemSaptarshiDuttaNo ratings yet
- EM MOD2-Ktunotes - inDocument18 pagesEM MOD2-Ktunotes - inIndra Pratap SengarNo ratings yet
- Lecture 6 - Statics PDFDocument18 pagesLecture 6 - Statics PDFHabyarimana ProjecteNo ratings yet
- Mechanics 1Document2 pagesMechanics 1Eunice FiecasNo ratings yet
- FME - CH04 - Equilibrium of Rigid BodiesDocument32 pagesFME - CH04 - Equilibrium of Rigid BodiesBUTEX YENo ratings yet
- CE Board Nov 2022 Engineering Mechanics Set 1Document3 pagesCE Board Nov 2022 Engineering Mechanics Set 1Meverlyn RoqueroNo ratings yet
- Note 9 Equilibrium - Particle (Coplanar Force Systems)Document18 pagesNote 9 Equilibrium - Particle (Coplanar Force Systems)Hawstuff De HareishnathNo ratings yet
- Positive Work Negative Work: Work, Energy and PowerDocument38 pagesPositive Work Negative Work: Work, Energy and Powerpraveen.aicpNo ratings yet
- Lecture 2 StaticsDocument41 pagesLecture 2 StaticsMaro IdehNo ratings yet
- Equilibrium of Rigid BodiesDocument8 pagesEquilibrium of Rigid BodiesmicaelahsdNo ratings yet
- Ri PsadDocument25 pagesRi PsadarjiiicryptNo ratings yet
- Equilivrium of A Rigid BodyDocument66 pagesEquilivrium of A Rigid Bodyhasanyaliniz647No ratings yet
- ME 1204: Engineering Statics: Dr. Faraz JunejoDocument52 pagesME 1204: Engineering Statics: Dr. Faraz JunejoJean Zyrelle AuronNo ratings yet
- Tutorial 1 - 2 - 3 - 4Document6 pagesTutorial 1 - 2 - 3 - 4Danny MalobaNo ratings yet
- 3-1 Equilibrium of Concurrent Forces-Condition For EquilibriumDocument19 pages3-1 Equilibrium of Concurrent Forces-Condition For Equilibriumwajju007No ratings yet
- What Force and Torque Are Working With The Roberval BalanceDocument4 pagesWhat Force and Torque Are Working With The Roberval BalanceJorge HernÁn Hoyos VÉlezNo ratings yet
- CH-6 Work, Energy and PowerDocument31 pagesCH-6 Work, Energy and PowerSurendra singhNo ratings yet
- Lecture 5 (Chapter 3)Document20 pagesLecture 5 (Chapter 3)Adam SurtiNo ratings yet
- Sptopics Design Module1Document6 pagesSptopics Design Module1Christian Felix MapilesNo ratings yet
- Coplanar Equilibrium Analysis No Soln Single and Composite BodiesDocument41 pagesCoplanar Equilibrium Analysis No Soln Single and Composite BodiesFay831No ratings yet
- Equilibrium of ForcesDocument5 pagesEquilibrium of ForcesJohn joiNo ratings yet
- Part II - Charge DistributionsDocument7 pagesPart II - Charge Distributionsmito714b2002No ratings yet
- Statics ModuleDocument6 pagesStatics ModuleNafa HashimNo ratings yet
- Chapter 4 0. 4 - Equilibrium of Rigid Bodies PDFDocument24 pagesChapter 4 0. 4 - Equilibrium of Rigid Bodies PDFecercNo ratings yet
- IE C1 Statics of Rigid Bodies Part 3 Equilibrium of A ParticleDocument8 pagesIE C1 Statics of Rigid Bodies Part 3 Equilibrium of A ParticleBernadeth MontardeNo ratings yet
- Equilibrium of Rigid Bodies: Lacanilao Johnley F. AE-207Document6 pagesEquilibrium of Rigid Bodies: Lacanilao Johnley F. AE-207Jeremy ValerioNo ratings yet
- Equilibrium of A ParticleDocument37 pagesEquilibrium of A ParticleJohn CalabiaNo ratings yet
- Lesson 4-Topic 1 - Equilibrium of A ParticleDocument37 pagesLesson 4-Topic 1 - Equilibrium of A ParticleNicholas Bonn SingNo ratings yet
- Chapter 5 Laws of Motion Notes Manoj SirDocument15 pagesChapter 5 Laws of Motion Notes Manoj SirSTUDY WITH MADHAVNo ratings yet
- Source: "Sears and Zemansky's University Physics With: Fig. 1. The Work Done On A Baseball Moving inDocument8 pagesSource: "Sears and Zemansky's University Physics With: Fig. 1. The Work Done On A Baseball Moving inMaria Diane DizonNo ratings yet
- 2.equilibrium of Force SystemsDocument130 pages2.equilibrium of Force SystemsdeevNo ratings yet
- SRB Session1 RofsDocument4 pagesSRB Session1 RofsFullo Flores MarviloneNo ratings yet
- IctionDocument7 pagesIctionFullo Flores MarviloneNo ratings yet
- Lesson 1Document1 pageLesson 1Fullo Flores MarviloneNo ratings yet
- Business Plan TechnoDocument2 pagesBusiness Plan TechnoFullo Flores MarviloneNo ratings yet
- Elective Summary For IntroductionDocument3 pagesElective Summary For IntroductionFullo Flores MarviloneNo ratings yet
- Activity 7 Analysis of Variance: Single Factor ANOVADocument2 pagesActivity 7 Analysis of Variance: Single Factor ANOVAFullo Flores MarviloneNo ratings yet
- Example #8: A Copper Ingot Has A Mass of 2.94 Lb. If The Copper Is Drawn Into WireDocument2 pagesExample #8: A Copper Ingot Has A Mass of 2.94 Lb. If The Copper Is Drawn Into WireFullo Flores MarviloneNo ratings yet
- Exercise 2.1 RizalDocument3 pagesExercise 2.1 RizalFullo Flores MarviloneNo ratings yet
- Ubcv 2Document5 pagesUbcv 2Fullo Flores MarviloneNo ratings yet
- Exercise 2.2 RizalDocument2 pagesExercise 2.2 RizalFullo Flores Marvilone100% (1)
- Assembly Removal and Installation: G58 Manual TransmissionDocument9 pagesAssembly Removal and Installation: G58 Manual TransmissionPannie Ng100% (1)
- Home Assignment I: Electric Drives (Ee413N) SESSION 2017-18Document1 pageHome Assignment I: Electric Drives (Ee413N) SESSION 2017-18PRASHANT SINGHNo ratings yet
- HW4 W2016sasaSADocument4 pagesHW4 W2016sasaSAWOw WongNo ratings yet
- Joint Speed-Torque Characteristics of Electric Motors and Mechanical LoadDocument23 pagesJoint Speed-Torque Characteristics of Electric Motors and Mechanical LoadWeehao SiowNo ratings yet
- Blackmer Parts List: Pump Models: Lgld2E, Lgl2E, Lgld3F, Lgl3FDocument2 pagesBlackmer Parts List: Pump Models: Lgld2E, Lgl2E, Lgld3F, Lgl3FRAUL ARMANDO PALOMO CAMPOSNo ratings yet
- Synchronous Machine Testing With All-Test InstrumentationDocument8 pagesSynchronous Machine Testing With All-Test Instrumentationfriend120873No ratings yet
- Oman LPG Gas SuppliersDocument4 pagesOman LPG Gas SuppliersimranNo ratings yet
- Variable Valve Timing Lab ReportDocument14 pagesVariable Valve Timing Lab ReportSyed Imtinan AhmedNo ratings yet
- Heat Pump Experiment: Real Time COP Measurement MEE 443Document12 pagesHeat Pump Experiment: Real Time COP Measurement MEE 443Nova AprilNo ratings yet
- Daily Report: Pt. PJB Ubjom PLTMG ArunDocument2 pagesDaily Report: Pt. PJB Ubjom PLTMG ArunLamboux LumbantoruanNo ratings yet
- Application of Fluid Machinery: Piping Design and Pump SelectionDocument16 pagesApplication of Fluid Machinery: Piping Design and Pump SelectionLeslie CatindigNo ratings yet
- Be MT 4 Sem Fluid Mechanics and Machines p1 18mt42 2020Document2 pagesBe MT 4 Sem Fluid Mechanics and Machines p1 18mt42 2020Onsoti NyaberaNo ratings yet
- KW (Stage Iiia) KW (Stage Iv) : Telescopic Crawler CraneDocument20 pagesKW (Stage Iiia) KW (Stage Iv) : Telescopic Crawler CraneulilkhanNo ratings yet
- Assignment Gaseous State JH Sir-2621Document38 pagesAssignment Gaseous State JH Sir-2621Noob Iplay100% (1)
- Westergard MethodDocument2 pagesWestergard MethodErickSimonNo ratings yet
- Welding Defects: Ganesan V Assistant Manager-TSD D&H Secheron Electrodes PVT - LTDDocument49 pagesWelding Defects: Ganesan V Assistant Manager-TSD D&H Secheron Electrodes PVT - LTDPrakash RajNo ratings yet
- 2017-Experimental and Numerical Investigations Into Seismic Performance of Timber-Steel Hybrid Structure With Supplemental DampersDocument12 pages2017-Experimental and Numerical Investigations Into Seismic Performance of Timber-Steel Hybrid Structure With Supplemental DampersGuillaumeHNONo ratings yet
- Handling Systems ALUMINIUMDocument35 pagesHandling Systems ALUMINIUMAbhinav KumarNo ratings yet
- MACHINESDocument61 pagesMACHINESogenrwot albertNo ratings yet
- Knock Down Fittings PDFDocument4 pagesKnock Down Fittings PDFIwan SetiawanNo ratings yet
- AD353-132 r1Document9 pagesAD353-132 r1Hrishikesh RokadeNo ratings yet
- Learning Activity Sheet in General Physics 1 Lesson 11: Periodic MotionDocument9 pagesLearning Activity Sheet in General Physics 1 Lesson 11: Periodic MotionSenica Caydil Jay D.No ratings yet