Professional Documents
Culture Documents
3.4 Active Transport
3.4 Active Transport
Uploaded by
zain ul AbideenOriginal Description:
Original Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
3.4 Active Transport
3.4 Active Transport
Uploaded by
zain ul AbideenCopyright:
Available Formats
3.
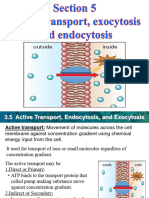
3 Active transport
Active Transport
Active transport is the movement of particles through a cell membrane from a
region of lower concentration to a region of higher concentration using
energy from respiration
The process of active transport
Importance of Active Transport:
Energy is needed because particles are being moved against a concentration
gradient, in the opposite direction from which they would naturally move (by
diffusion)
Active transport is vital process for the movement of molecules or ions across
membranes
Including:
uptake of glucose by epithelial cells in the villi of the small intestine and by
kidney tubules in the nephron
uptake of ions from soil water by root hair cells in plants
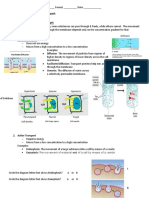
Protein Carriers:
Active transport works by using carrier proteins embedded in the cell
membrane to pick up specific molecules and take them through the cell
membrane against their concentration gradient:
1. Substance combines with carrier protein molecule in the cell membrane
2. Carrier transports substances across membrane using energy from respiration to
give them the kinetic energy needed to change shape and move the substance
through the cell membrane
3. Substance released into cell
Carrier proteins in active transport
You might also like
- Biology: a QuickStudy Laminated Reference GuideFrom EverandBiology: a QuickStudy Laminated Reference GuideRating: 3 out of 5 stars3/5 (2)
- Chapter 3 - Movement Into and Out of The Cell - Active TransportDocument12 pagesChapter 3 - Movement Into and Out of The Cell - Active TransportshammmssNo ratings yet
- Passiv TransportDocument12 pagesPassiv TransportsamskruthamanabroluNo ratings yet
- Active TransportDocument11 pagesActive TransportDARLENE JANE MAYNESNo ratings yet
- L9 Cellular TransportDocument2 pagesL9 Cellular TransportStephanie SyNo ratings yet
- Unit 3 Movement in and Out of CellsDocument2 pagesUnit 3 Movement in and Out of CellsAurora MboyaNo ratings yet
- G10 Biology Active Transport Presentation 89492Document4 pagesG10 Biology Active Transport Presentation 89492haythamkhairallaNo ratings yet
- Membrane Transport, PHR121, Human Physiology 01Document7 pagesMembrane Transport, PHR121, Human Physiology 01Aanikul IslamNo ratings yet
- 11 - Active Transport - 2020Document24 pages11 - Active Transport - 2020tireddoodleNo ratings yet
- GENBIO.1.Chapter 3 - Cellular Transport MechanismsDocument22 pagesGENBIO.1.Chapter 3 - Cellular Transport MechanismsJiro SamontañezNo ratings yet
- Cueva-Cell TransportDocument15 pagesCueva-Cell TransportCristine Jane CuevaNo ratings yet
- B1.9 Active TransportDocument2 pagesB1.9 Active TransportYevonNo ratings yet
- 1 Providing A Selectively Permeable BarDocument1 page1 Providing A Selectively Permeable Barmiqbalrana.2020No ratings yet
- Diffusion QFRDocument1 pageDiffusion QFRsyareeisyeeNo ratings yet
- Answer Key: ReinforcementDocument2 pagesAnswer Key: ReinforcementCherifa AbdallahNo ratings yet
- Duma-Ha-Bi Ctnese833006 C03S5Document3 pagesDuma-Ha-Bi Ctnese833006 C03S5Cherifa AbdallahNo ratings yet
- Unit 4 Homeostasis and Transport Review PacketDocument9 pagesUnit 4 Homeostasis and Transport Review PacketShannon ErdmanNo ratings yet
- 03 Activity 1Document2 pages03 Activity 1Precious Mae AlcayaNo ratings yet
- Membran: Kusumo Hariyadi Blok 3Document10 pagesMembran: Kusumo Hariyadi Blok 3YUFFANo ratings yet
- Cellular Transport ConceptDocument7 pagesCellular Transport ConceptRuhul Qudus NaimNo ratings yet
- Presentation 1Document20 pagesPresentation 1LUNA GamingNo ratings yet
- Sensing Extracelluar Environment - Stuti - NirabhiDocument29 pagesSensing Extracelluar Environment - Stuti - NirabhiShivam AnandNo ratings yet
- Active Vesicular TransportDocument14 pagesActive Vesicular Transportsarah abarcaNo ratings yet
- WEEK 7 TransportDocument49 pagesWEEK 7 Transportorioluna00No ratings yet
- Transport MechanismDocument2 pagesTransport MechanismLeng BunthaiNo ratings yet
- Bio NotesDocument1 pageBio NotesIshita KamraNo ratings yet
- 2 5 Transport MechanismDocument25 pages2 5 Transport Mechanismıamnıkolaı 4100% (1)
- Handout 4 Cell TransportDocument4 pagesHandout 4 Cell TransportCrissan Jejomar AbanesNo ratings yet
- Active TransportDocument2 pagesActive TransportDaniel FlorentineNo ratings yet
- Lesson 2.1 Transport Across MembranesDocument65 pagesLesson 2.1 Transport Across MembranesKaarlo OdiverNo ratings yet
- Cell 1Document48 pagesCell 1Mihai ChirniciniiNo ratings yet
- Biology (5090) Bodmas Schoolong System and Coaching Center 2.1. DiffusionDocument3 pagesBiology (5090) Bodmas Schoolong System and Coaching Center 2.1. DiffusionSamina NaurinNo ratings yet
- 4 Movement of Substances Across The Cell MembraneDocument5 pages4 Movement of Substances Across The Cell MembraneVenice LoNo ratings yet
- Movement Into and Out of CellsDocument17 pagesMovement Into and Out of CellsFaiaz AhmedNo ratings yet
- Chap-11 - Transport in Plants (27) - EDocument56 pagesChap-11 - Transport in Plants (27) - ENithin RajanNo ratings yet
- Biology Class 5Document2 pagesBiology Class 5Jon WilliamsNo ratings yet
- Membrane - FunctionDocument4 pagesMembrane - Functionphuong anhNo ratings yet
- Membrane - FunctionDocument4 pagesMembrane - Functionphuong anhNo ratings yet
- Transport Across The Cell Membrane - OdpDocument67 pagesTransport Across The Cell Membrane - OdpSilver CypressNo ratings yet
- The Big Picture: Diffusion: Movement of Particles From A Region of Higher Concentration To A Region of LowDocument5 pagesThe Big Picture: Diffusion: Movement of Particles From A Region of Higher Concentration To A Region of LowNicolas Gomez CombellasNo ratings yet
- Answer Sheet in General Biology Week 8 Cell Transport Mechanisms Activity 1: Concept MappingDocument8 pagesAnswer Sheet in General Biology Week 8 Cell Transport Mechanisms Activity 1: Concept MappingMark Joedel MendezNo ratings yet
- Transport Across Cell MembraneDocument20 pagesTransport Across Cell Membrane安 娜 胡No ratings yet
- Lesson 1 (Reviewer)Document4 pagesLesson 1 (Reviewer)Faith Angela VillasfirNo ratings yet
- Active Transport Reading Comprehension Questions FoundationDocument4 pagesActive Transport Reading Comprehension Questions FoundationlibrahimliNo ratings yet
- Cell Transport Lesson Check AnswersDocument1 pageCell Transport Lesson Check Answershanatabbal19No ratings yet
- Absorption of DrugsDocument145 pagesAbsorption of DrugsSunith KanakuntlaNo ratings yet
- Biology - Module 4Document6 pagesBiology - Module 4ASHLEY MONICA PLATANo ratings yet
- Cell ExchangesDocument28 pagesCell ExchangesBenzerari ManaNo ratings yet
- 3.5 Reinforcement: Key ConceptDocument1 page3.5 Reinforcement: Key ConceptCherifa AbdallahNo ratings yet
- Transport Mech GEN BIO 1Document16 pagesTransport Mech GEN BIO 1Quiel Tangonan Jr.No ratings yet
- San Pedro College: Senior High School DepartmentDocument54 pagesSan Pedro College: Senior High School DepartmentKrisha Diane FunaNo ratings yet
- 3.2 # Active TransportDocument2 pages3.2 # Active TransportSara Nadeem KhanNo ratings yet
- Transport MechanismDocument31 pagesTransport MechanismCecillia Evan100% (1)
- (L9) Transport Across MembranesDocument22 pages(L9) Transport Across MembranesJhon TorresNo ratings yet
- Cell Membrane and Cell TransportDocument4 pagesCell Membrane and Cell TransportAtasha MojecaNo ratings yet
- Week 2 Relationship of Body SystemsDocument1 pageWeek 2 Relationship of Body SystemsTerri LynnNo ratings yet
- Active and Passive Transport LatestDocument51 pagesActive and Passive Transport Latestxianlagajenoseamg5No ratings yet
- Types of Transport Across The Cell MembraneDocument26 pagesTypes of Transport Across The Cell MembraneAsad ShalmaniNo ratings yet
- Cellular Transport - 1Document15 pagesCellular Transport - 1Masashi NatsuNo ratings yet
- LAB SHT #2 - Cell TransportDocument3 pagesLAB SHT #2 - Cell TransportMiguel Yancy AverillaNo ratings yet